手写代码实现mini_batch以及神经网络预测波士顿房价(百度飞桨paddle公开课2020/8/12)感谢百度,2333,给个礼物波,muamua
关于波士顿房价数据集的下载与安装
首先说百度的paddle真的可以解放我们双手与大脑,看看我本文中的工作量就清楚了,另外matlab都能禁,万一tf torch也给和谐了,对吧。所以多学个框架对我们也是很有好处的。同时感谢百度免费的公开课,谢谢,谢谢。
回到正文,本文采用keras.datasets中的boston数据集,导入方法如下图所示:
from keras.datasets import boston_housing
(train_x,train_y),(test_x,test_y)=boston_housing.load_data()
但是没有的伙计估计下不了,这里你可以先从网上找到波士顿数据集的文件,然后放置于:C:\Users\你家电脑用户名的名称s\datasets。然后直接运行上方代码,就可以成功运行了。
关于神经网络
神经网络的手动搭建需要用到numpy库进行矩阵运算。
同时补充最关键的数学知识
if y=np.matmul(x,w)+b
dy/dx=np.matmul(dy,w.T)
dy/dw=np.matmul(x.T,dy)
dy/db=dy
关于神经网络的原理就不多说了
关于mini_batch的实现
sklearn库里有skfold函数,挺好用的,这里手写mini_batch主要是为了玩耍。
参数有四个:输入数据集,Label,batch_size,是否正则化,是否洗牌。
def creat_bunch(Input,Label,bunch_size,random_shuffle=False,normalization=False):
if not isinstance(Input,np.ndarray):
Input=np.array(Input)
if normalization==True:
MAX=Input.max(axis=1)
MIN=Input.min(axis=1)
MEAN=Input.sum(axis=1)/Input.shape[0]
for i in range(Input.shape[1]):
Input[:,i]=(Input[:,i]-MEAN)/(MAX-MIN)
print("normalization ready")
print(" ")
if random_shuffle==True:
EVEN=1
if Input.shape[0]//2!=0:
EVEN=0
if EVEN==1:
mid=Input.shape[0]/2
for i in range(int(mid)):
index_choice=int(np.random.randint(0,mid))
index2=int(index_choice+mid-1)
Input[[index_choice,0,index2],:]
Label[[index_choice,0,index2]]
else:
mid=(Input.shape[0]+1)/2
for i in range(int(mid)-1):
index_choice=int(np.random.randint(0,mid))
index2=int(2*(mid-1)-index_choice)
Input[[index_choice,0,index2],:]
Label[[index_choice,0,index2]]
print("shuffle ready")
print(" ")
Size=len(Label)
if Size//bunch_size==0:
Bunch_num=Size/bunch_size
else:
Bunch_num=Size//bunch_size+1
Input_bunch=[]
Label_bunch=[]
print("total {0} pieces".format(Bunch_num))
for i in range(Bunch_num):
print("{0}th bunch is ready!".format(i+1))
if i!=Bunch_num-1:
Input_bunch.append(Input[i*bunch_size:(i+1)*bunch_size,:])
Label_bunch.append(Label[i*bunch_size:(i+1)*bunch_size])
else:
Input_bunch.append(Input[(i-1)*bunch_size:Input.shape[0],:])
Label_bunch.append(Label[(i-1)*bunch_size:Input.shape[0]])
print("complete!")
return Input_bunch,Label_bunch
ok,mini_batch实现了。如果直接运行我的有问题的话,可以找找缩进是否存在错误,我写的源代码是没有错的。
房价预测之一层神经网络的实现
由于该数据集不大,所以我没有minibatch处理,直接干拉。
标准化feature
def normoralization(data):
try:
MAX=data.max(axis=1)
MIN=data.min(axis=1)
MEAN=data.sum(axis=1)/data.shape[0]
for i in range(data.shape[1]):
data[:,i]=(data[:,i]-MEAN)/(MAX-MIN)
return data
except Exception as result:
print(result)
train_x=normoralization(train_x)
一层神经网络的实现without激活函数
class network:
def __init__(self,Input,Label):
self.weighten=np.random.random((Input.shape[1],1))
self.bias=np.random.random((Input.shape[0],1))
self.Input=Input
self.Label=Label
def predict(self):
self.predict_=np.matmul(self.Input,self.weighten)+self.bias
return self.predict_
def cost(self):
error=(self.predict_-self.Label.reshape(-1,1))
self.error_=error
for i in range(error.shape[0]):
error[i]=error[i]*error[i]
self.error=error
return np.sum(self.error)/self.error.shape[0]
def backward(self,leraning_rate):
for i in range(self.weighten.shape[0]):
dic=np.mean(self.error_*(-self.Input[:,i]*0.0001)*leraning_rate)
self.weighten[i]=self.weighten[i]+abs(dic)
self.bias=self.bias+abs(self.error_*0.0001)
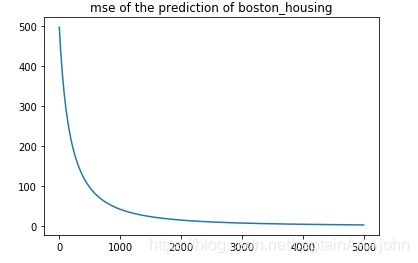
模型训练并且绘制损失函数
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
net=network(train_x,train_y)
net.predict()
loss=[]
for i in range(5000):
net.predict()
net.cost()
net.backward(0.0000000000001)
loss.append(net.cost())
plt.title("mse of the prediction of boston_housing")
plt.plot(loss)
plt.show()
最后我简单地实现了一下两层神经网络的实现,基于反向传播
两层神经元简单实现
定义各类函数
relu
class relu():
def __init__(self):
pass
def prediction(self,Input):
for i in range(Input.shape[0]):
for j in range(Input.shape[1]):
Input[i,j]=max(Input[i,j],0)
return Input
def backward(self,diff):
for i in range(diff.shape[0]):
for j in range(diff.shape[1]):
if diff[i,j]>0:
diff[i,j]=1
else:
diff[i,j]=0
return diff
matmul
class matmul():
def __init__(self):
pass
def prediction(self,x,w,b):
result=np.matmul(x,w)+b
return result
def backward(slef,diff,x,w,b):
b_diff=diff
w_diff=np.matmul(x.T,diff)
return b_diff,w_diff,np.matmul(diff,w.T)
mse(mean squared error)
class mean_squared_error:
def __init__(self):
pass
def prediction(self,y,label):
cost=(y-label.reshape(-1,1))
return cost*cost
def backward(self,diff,y,label):
return 2*(y-label.reshape(-1,1))*y
定义参数
#parameters
Epoch=20
Learning_rate=1e-20*3
初始化变量
w1=np.random.random((train_x.shape[1],5))
b1=np.random.random((train_x.shape[0],5))
w2=np.random.random((5,1))
b2=np.random.random((train_x.shape[0],1))
开始训练
mse=mean_squared_error()
matmul=matmul()
activation=relu()
接上
for j in range(100000):
#prediction
y1=matmul.prediction(train_x,w1,b1)
y2=activation.prediction(y1)
y3=matmul.prediction(y2,w2,b2)
#optimize
cost=mse.prediction(y3,train_y)
error=np.mean(cost,axis=0)
#backward
diff=mse.backward(0.00001,cost,train_y)
b2_diff,w2_diff,diff2=matmul.backward(diff,y2,w2,b2)
diff3=activation.backward(diff2)
b1_diff,w1_diff,diff4=matmul.backward(diff3,train_x,w1,b1)
b2-=b2_diff*Learning_rate
w2-=w2_diff*Learning_rate
b1-=b1_diff*Learning_rate
w1-=w1_diff*Learning_rate
print("the {0} turn's loss is {1}".format(j,error))
完成,请大佬指出不足。也请各位施舍个赞,谢谢各位。比我还要新手的新手,建议不要把时间花在这上面,一方面算法用CPP可能写的更nice一点,另一方面学下paddle吧,可以让你事半功倍。