循环神经网络实例4:处理Seq2Seq任务
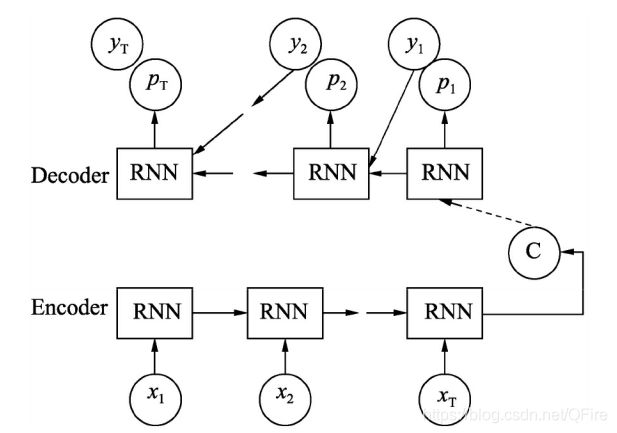
Seq2Seq任务,即从一个序列映射到另一个序列的任务。在生活中会有很多符合这样特性的例子:前面的语言模型、语音识别例子,都可以理解成一个Seq2Seq的例子,类似的应用还有机器翻译、词性标注、智能对话等。
在TensorFlow中有两套Seq2Seq的接口。一套是1.0版本之前的旧接口,tf.contrib.legacy_seq2seq;另一套为新接口,tf.contrib.seq2seq。旧接口的功能相对简单,是静态展开的网络模型。而新接口的功能更加强大,使用的是动态展开的网络模型,并提供了训练和应用两种场景的Helper类封装。从使用角度来看,旧接口同样也是比较简单。而新接口会更加灵活,需要自己组建Encoder和Decoder并通过函数把它们手动连接起来。
以旧接口为例,教程网址
tf.contrib.legacy_seq2seq.basic_rnn_seq2seq(encoder_inputs, decoder_inputs, cell, dtype=dtypes.float32, scope=None)
- encoder_inputs:一个shape为[batch_size, x_input_size]的list
- decoder_inputs:同encoder_inputs
- cell:定义的cell网络
- dtype:数据类型
- 返回值:outputs和state。outputs为[batch_size, output_size]的张量;state为[batch_size, cell.state_size];
实例:使用basic_rnn_seq2seq拟合曲线,本例使用2层的GRU循环网络,每层有12个节点。编码器和解码器中使用同样的网络结构。
通过sin和con进行叠加变形生成无规律的模拟曲线,使用Seq2Seq模型对其进行学习,拟合特征,从而达到可以预测下一时刻数据的效果。
import random
import math
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def do_generate_x_y(isTrain, batch_size, seqlen):
batch_x = []
batch_y = []
for _ in range(batch_size):
offset_rand = random.random() * 2 * math.pi
freq_rand = (random.random() - 0.5) / 1.5 * 15 + 0.5
amp_rand = random.random() + 0.1
sin_data = amp_rand * np.sin(np.linspace(
seqlen / 15.0 * freq_rand * 0.0 * math.pi + offset_rand,
seqlen / 15.0 * freq_rand * 3.0 * math.pi + offset_rand, seqlen * 2) )
offset_rand = random.random() * 2 * math.pi
freq_rand = (random.random() - 0.5) / 1.5 * 15 + 0.5
amp_rand = random.random() * 1.2
sig_data = amp_rand * np.cos(np.linspace(
seqlen / 15.0 * freq_rand * 0.0 * math.pi + offset_rand,
seqlen / 15.0 * freq_rand * 3.0 * math.pi + offset_rand, seqlen * 2)) + sin_data
batch_x.append(np.array([ sig_data[:seqlen] ]).T)
batch_y.append(np.array([ sig_data[seqlen:] ]).T)
# shape: (batch_size, seq_length, output_dim)
batch_x = np.array(batch_x).transpose((1, 0, 2))
batch_y = np.array(batch_y).transpose((1, 0, 2))
# shape: (seq_length, batch_size, output_dim)
return batch_x, batch_y
#生成15个连续序列,将con和sin随机偏移变化后的值叠加起来
def generate_data(isTrain, batch_size):
seq_length =15
if isTrain :
return do_generate_x_y(isTrain, batch_size, seq_length)
else:
return do_generate_x_y(isTrain, batch_size, seq_length*2)
sample_now, sample_f = generate_data(isTrain=True, batch_size=3)
print("training examples : ")
print(sample_now.shape)
print("(seq_length, batch_size, output_dim)")
seq_length = sample_now.shape[0]
batch_size = 10
output_dim = input_dim = sample_now.shape[-1]
hidden_dim = 12
layers_num = 2
# Optimizer
learning_rate = 0.04
nb_iters = 100
lambda_l2_reg = 0.003 # 正则化
# 构建网络
tf.reset_default_graph()
encoder_input = []
expected_output = []
decoder_input = []
for i in range(seq_length):
encoder_input.append(tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(None, input_dim)))
expected_output.append(tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(None, output_dim)))
decoder_input.append(tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(None, input_dim)))
# 层数
tcells = []
for i in range(layers_num):
tcells.append(tf.contrib.rnn.GRUCell(hidden_dim))
Mcell = tf.contrib.rnn.MultiRNNCell(tcells)
dec_outputs, dec_memory = tf.contrib.legacy_seq2seq.basic_rnn_seq2seq(encoder_input, decoder_input, Mcell)
reshaped_outputs = []
for ii in dec_outputs:
reshaped_outputs.append(tf.contrib.layers.fully_connected(ii, output_dim, activation_fn=None))
# L2 损失函数
output_loss = 0
for _y, _Y in zip(reshaped_outputs, expected_output):
output_loss += tf.reduce_mean(tf.pow(_y - _Y, 2))
# generalization capacity
reg_loss = 0
for tf_var in tf.trainable_variables():
if not ("fully_connected" in tf_var.name):
reg_loss += tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.l2_loss(tf_var))
loss = output_loss + lambda_l2_reg * reg_loss
train_op = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(loss)
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
# 训练
def train_batch(batch_size):
X, Y = generate_data(isTrain=True, batch_size=batch_size)
feed_dict = {encoder_input[t]: X[t] for t in range(len(encoder_input))}
feed_dict.update({expected_output[t]: Y[t] for t in range(len(expected_output))})
c = np.concatenate( ([np.zeros_like(Y[0])], Y[:-1]), axis=0)
feed_dict.update({decoder_input[t]: c[t] for t in range(len(c))})
_, loss_t = sess.run([train_op, loss], feed_dict)
return loss_t
# 测试
def test_batch(batch_size):
X, Y = generate_data(isTrain=True, batch_size=batch_size)
feed_dict = {encoder_input[t]: X[t] for t in range(len(encoder_input))}
feed_dict.update({expected_output[t]: Y[t] for t in range(len(expected_output))})
c = np.concatenate( ([np.zeros_like(Y[0])], Y[:-1]), axis=0)
feed_dict.update({decoder_input[t]: c[t] for t in range(len(c))})
output_lossv, reg_lossv, loss_t = sess.run([output_loss, reg_loss, loss], feed_dict)
print("----------------")
print(output_lossv, reg_lossv)
return loss_t
# 训练运行
train_losses = []
test_losses = []
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for t in range(nb_iters + 1):
train_loss = train_batch(batch_size)
train_losses.append(train_loss)
if t % 50 == 0:
test_loss = test_batch(batch_size)
test_losses.append(test_loss)
print("Step {}/{}, train loss: {}, \tTEST loss: {}".format(t,nb_iters, train_loss, test_loss))
print("Fin. train loss: {}, \tTEST loss: {}".format(train_loss, test_loss))
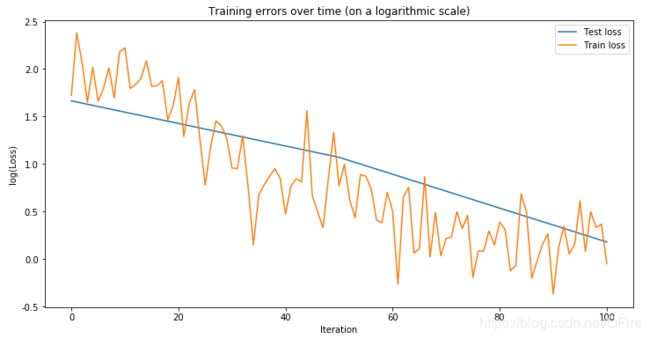
# 可视化
# Plot loss over time:
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
plt.plot(np.array(range(0, len(test_losses))) /
float(len(test_losses) - 1) * (len(train_losses) - 1),
np.log(test_losses),label="Test loss")
plt.plot(np.log(train_losses),label="Train loss")
plt.title("Training errors over time (on a logarithmic scale)")
plt.xlabel('Iteration')
plt.ylabel('log(Loss)')
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.show()
# Test
nb_predictions = 5
print("visualize {} predictions data:".format(nb_predictions))
preout =[]
X, Y = generate_data(isTrain=False, batch_size=nb_predictions)
print(np.shape(X),np.shape(Y))
for tt in range(seq_length):
feed_dict = {encoder_input[t]: X[t+tt] for t in range(seq_length)}
feed_dict.update({expected_output[t]: Y[t+tt] for t in range(len(expected_output))})
c =np.concatenate(( [np.zeros_like(Y[0])],Y[tt:seq_length+tt-1]),axis = 0) #从前15个的最后一个开始预测
feed_dict.update({decoder_input[t]: c[t] for t in range(len(c))})
outputs = np.array(sess.run([reshaped_outputs], feed_dict)[0])
preout.append(outputs[-1])
print(np.shape(preout))#将每个未知预测值收集起来准备显示出来。
preout =np.reshape(preout,[seq_length,nb_predictions,output_dim])
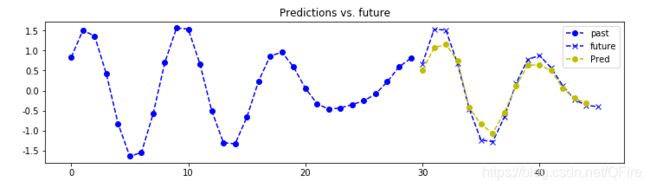
for j in range(nb_predictions):
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 3))
for k in range(output_dim):
past = X[:, j, k]
expected = Y[seq_length-1:, j, k]#对应预测值的打印
pred = preout[:, j, k]
label1 = "past" if k == 0 else "_nolegend_"
label2 = "future" if k == 0 else "_nolegend_"
label3 = "Pred" if k == 0 else "_nolegend_"
plt.plot(range(len(past)), past, "o--b", label=label1)
plt.plot(range(len(past), len(expected) + len(past)),
expected, "x--b", label=label2)
plt.plot(range(len(past), len(pred) + len(past)),
pred, "o--y", label=label3)
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.title("Predictions vs. future")
plt.show()