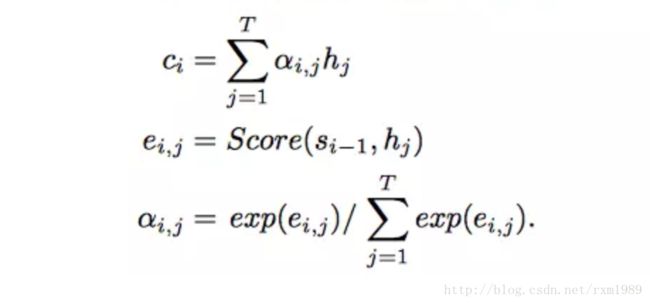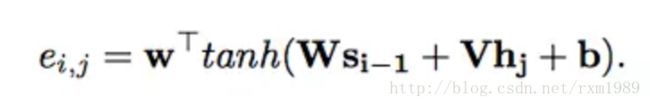基于seq2seq+attention的中文语音识别
好久没有写博客码字了
本人的中文语音识别跟小米的语音识别作者有过沟通(即参考论文1的作者),期望能够实现一个完整版的中文语音识别模型,那么这就开始啦
提纲如下:
1.数据准备
2.seq2seq介绍
3.Attention介绍
4.bilstm介绍
5.bilstm + seq2seq+Attention
1.数据准备
2.seq2seq介绍
介绍seq2seq的博客满天飞(英语好的同学可以看tensorflow的官方教程:https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/seq2seq),这里简单介绍一下,熟悉seq2seq模型的同学直接跳过
seq2seq就是把一个序列翻译成另一个序列的模型,实质就是两个rnn,一个是encoder,另一个是decoder,encoder负责将source序列编码成固定长度的表达,decoder负责将该固定长度的表达解码成target序列,刚开始是在机器翻译上使用的,其实这个模型应用非常广泛,凡是变长之间的映射关系都可以做,常见是机器翻译,语音识别,摘要提取等等;还可以把encoder和decoder拆开使用。
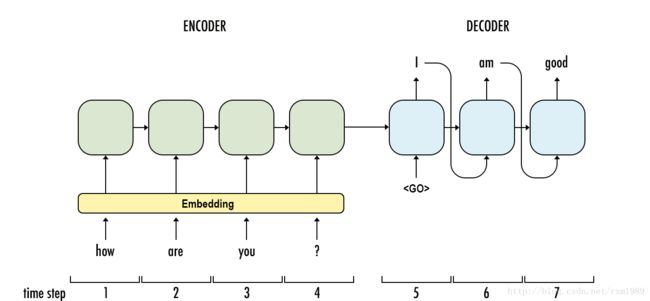
seq2seq当前比较流行的结构如下(https://arxiv.org/pdf/1409.3215.pdf)
seq2seq模型的encoder非常简单(上图中ABC对应的部分),就是rnn,可以是多层(simple-rnn,GRU,LSTM),decoder在训练和测试的时候,稍微有点不同
decoder训练的时候输入由两部分组成,一部分是encoder的last state,另一部分是target序列,如上图中的
decoder 测试的时候输入也是由两部分组成,一部分是encoder的last state,另一部分是来自于上一个时刻的输出(上一个时刻的输出作为下一个时刻的输入),直到某个时刻的输出遇到结束符
注意⚠️:decoder测试的时候需要重用 cell的参数!
对于encoder 和 decoder 的理论内容也就这么多啦,下面说一下decoder部分,tensorflow是如何来实现训练和测试的不同操作的
tensorflow在decoder进行train test的时候,使用的目录下的各种tf.contrib.seq2seq目录下的各种helper方法来区分不同的输入
Helper
常用的Helper:
TrainingHelper:适用于训练的helper。InferenceHelper:适用于测试的helper。GreedyEmbeddingHelper:适用于测试中采用Greedy策略sample的helper。CustomHelper:用户自定义的helper。
以下贴出我常用的decoder train和test的函数
def decoding_layer_train(encoder_state, dec_cell, dec_embed_input,
target_sequence_length, max_summary_length,
output_layer, keep_prob):
"""
Create a decoding layer for training
:param encoder_state: Encoder State
:param dec_cell: Decoder RNN Cell
:param dec_embed_input: Decoder embedded input
:param target_sequence_length: The lengths of each sequence in the target batch
:param max_summary_length: The length of the longest sequence in the batch
:param output_layer: Function to apply the output layer
:param keep_prob: Dropout keep probability
:return: BasicDecoderOutput containing training logits and sample_id
"""
helper = tf.contrib.seq2seq.TrainingHelper(inputs = dec_embed_input, sequence_length = target_sequence_length,time_major = False)
decoder = tf.contrib.seq2seq.BasicDecoder(dec_cell, helper, encoder_state, output_layer=output_layer)
dec_outputs, dec_state,dec_sequence_length = tf.contrib.seq2seq.dynamic_decode(decoder, impute_finished=True, maximum_iterations=max_summary_length)
return dec_outputsdef decoding_layer_infer(encoder_state, dec_cell, dec_embeddings, start_of_sequence_id,
end_of_sequence_id, max_target_sequence_length,
vocab_size, output_layer, batch_size, keep_prob):
"""
Create a decoding layer for inference
:param encoder_state: Encoder state
:param dec_cell: Decoder RNN Cell
:param dec_embeddings: Decoder embeddings
:param start_of_sequence_id: GO ID
:param end_of_sequence_id: EOS Id
:param max_target_sequence_length: Maximum length of target sequences
:param vocab_size: Size of decoder/target vocabulary
:param decoding_scope: TenorFlow Variable Scope for decoding
:param output_layer: Function to apply the output layer
:param batch_size: Batch size
:param keep_prob: Dropout keep probability
:return: BasicDecoderOutput containing inference logits and sample_id
"""
# TODO: Implement Function
start_tokens = tf.tile(tf.constant([start_of_sequence_id], dtype=tf.int32), [batch_size], name='start_tokens')
helper = tf.contrib.seq2seq.GreedyEmbeddingHelper(dec_embeddings,
start_tokens, end_of_sequence_id)
decoder = tf.contrib.seq2seq.BasicDecoder(dec_cell, helper, encoder_state, output_layer=output_layer)
dec_outputs, dec_state,dec_sequence_length = tf.contrib.seq2seq.dynamic_decode(decoder,impute_finished=True,
maximum_iterations=max_target_sequence_length)
return dec_outputsdef decoding_layer(dec_input, encoder_state,
target_sequence_length, max_target_sequence_length,
rnn_size,
num_layers, target_vocab_to_int, target_vocab_size,
batch_size, keep_prob, decoding_embedding_size):
"""
Create decoding layer
:param dec_input: Decoder input
:param encoder_state: Encoder state
:param target_sequence_length: The lengths of each sequence in the target batch
:param max_target_sequence_length: Maximum length of target sequences
:param rnn_size: RNN Size
:param num_layers: Number of layers
:param target_vocab_to_int: Dictionary to go from the target words to an id
:param target_vocab_size: Size of target vocabulary
:param batch_size: The size of the batch
:param keep_prob: Dropout keep probability
:return: Tuple of (Training BasicDecoderOutput, Inference BasicDecoderOutput)
"""
# embedding target sequence
dec_embeddings = tf.Variable(tf.random_uniform([target_vocab_size, decoding_embedding_size]))
dec_embed_input = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(dec_embeddings, dec_input)
# construct decoder lstm cell
dec_cell = tf.contrib.rnn.MultiRNNCell([
tf.contrib.rnn.LSTMCell(rnn_size) \
for _ in range(num_layers) ])
# create output layer to map the outputs of the decoder to the elements of our vocabulary
output_layer = layers_core.Dense(target_vocab_size,
kernel_initializer = tf.truncated_normal_initializer(mean = 0.0, stddev=0.1))
# decoder train
with tf.variable_scope("decoding") as decoding_scope:
dec_outputs_train = decoding_layer_train(encoder_state, dec_cell, dec_embed_input,
target_sequence_length, max_target_sequence_length,
output_layer, keep_prob)
# decoder inference
start_of_sequence_id = target_vocab_to_int[""]
end_of_sequence_id = target_vocab_to_int[""]
with tf.variable_scope("decoding", reuse=True) as decoding_scope:
dec_outputs_infer = decoding_layer_infer(encoder_state, dec_cell, dec_embeddings, start_of_sequence_id,
end_of_sequence_id, max_target_sequence_length,
target_vocab_size, output_layer, batch_size, keep_prob)
# rerturn
return dec_outputs_train, dec_outputs_infer 3.Attention介绍:
Attention的原理介绍,网上也是满天飞,这里简单介绍一下,熟悉Attention模型的同学直接跳过(英语好的同学依旧可以从tensorflow的官方教程找到:https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/seq2seq)
首先说一下为什么要有Attention模型
Attention模型的出现是上述的seq2seq模型存在缺陷,即无论之前的encoder的context有多长,包含多少信息量,最终都要被压缩成一个几百维的vector。这意味着context越大,decoder的输入之一的last state 会丢失越多的信息。对于机器翻译问题,意味着输入sentence长度增加后,最终decoder翻译的结果会显著变差。
Attention实质上是一种content-based addressing的机制,即从网络中某些状态集合中选取与给定状态较为相似的状态,进而做后续的信息抽取;说人话就是:首先根据Encoder和Decoder的特征计算权值,然后对Encoder的特征进行加权求和,作为Decoder的输入,其作用是将Encoder的特征以更好的方式呈献给Decoder,即:并不是所有context都对下一个状态的生成产生影响,Attention就是选择恰当的context用它生成下一个状态。
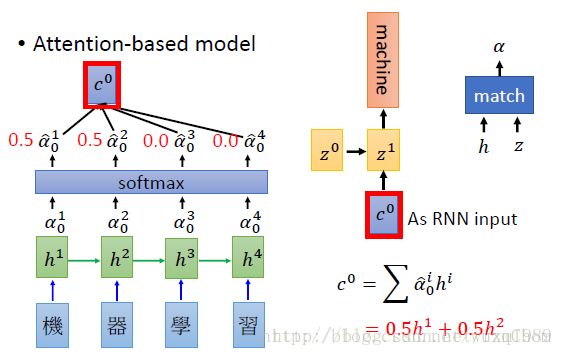
下面使用李宏毅老师经典的一页PPT来表达Attention算法的核心内容
上图已经很形象概括了Attention的处理过程,下面以公式来表达一下:
其中hj是encoder的对应输出,公式中的初始值的s0(对应图中z0) 是encoder的last state,上图的Match对应公式中的Score,这个Score计算方法有很多种,常用的是多层感知机(MLP),这就是常说的attention context,表达式如下:
实际上attention的计算过程比较简单,attention的原理部分就介绍完啦,下面看看tensorflow是如何实现attention的。tensorflow对attention在不同版本改动比较大,我们只看当前tf1.4.1版本中tensorflow是如何使用attention的
tensorflow把attention单独分出来,引入了attention_wrapper文件,定义的几种attention机制(BahdanauAttention、 LuongAttention、 BahdanauMonotonicAttention、 LuongMonotonicAttention),将attention机制封装到RNNCell上面的方法AttentionWrapper。其实很简单,就跟dropoutwrapper、outputwrapper一样,我们只需要在原本RNNCell的基础上在封装一层attention即可。
下面贴一下我常用的attention函数:
def decoder_attn(batch_size,encoder_hidden_size,attention_size,enc_seq_len,encoder_output,encoder_state,dec_cell):
attention_mechanism = tf.contrib.seq2seq.BahdanauAttention(num_units=encoder_hidden_size,
memory=encoder_output,
memory_sequence_length=enc_seq_len,
name="BahdanauAttention")
attention_cell = tf.contrib.seq2seq.AttentionWrapper(dec_cell, attention_mechanism,attention_size,
name="attention_wrapper")
init_state = attention_cell.zero_state(batch_size, tf.float32).clone(cell_state=encoder_state)
return attention_cell,init_statedef decoding_layer(dec_input, encoder_state,encoder_output,source_sequence_length,
target_sequence_length, max_target_sequence_length,
encoder_rnn_hidden_unit,
decode_rnn_hidden_unit,
attention_size,
target_vocab_to_int, target_vocab_size,
batch_size, keep_prob, decoding_embedding_size):
# embedding target sequence
dec_embeddings = tf.Variable(tf.random_uniform([target_vocab_size, decoding_embedding_size]))
dec_embed_input = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(dec_embeddings, dec_input)
# Todo : 这里一定不能用 MultiRNNCell,否则出错: 'Tensor' object is not iterable.
dec_cell = tf.contrib.rnn.LSTMCell(decode_rnn_hidden_unit)
# create output layer to map the outputs of the decoder to the elements of our vocabulary
output_layer = layers_core.Dense(target_vocab_size,
kernel_initializer = tf.truncated_normal_initializer(mean = 0.0, stddev=0.1))
attention_cell,init_state = decoder_attn(batch_size,encoder_rnn_hidden_unit, attention_size,
source_sequence_length, encoder_output, encoder_state, dec_cell)
# decoder train
with tf.variable_scope("decoding") as decoding_scope:
dec_outputs_train = decoding_layer_train(init_state, attention_cell, dec_embed_input,
target_sequence_length, max_target_sequence_length,
output_layer, keep_prob)
# decoder inference
start_of_sequence_id = target_vocab_to_int[""]
end_of_sequence_id = target_vocab_to_int[""]
with tf.variable_scope("decoding", reuse=True) as decoding_scope:
dec_outputs_infer = decoding_layer_infer(init_state, attention_cell, dec_embeddings,
start_of_sequence_id,
end_of_sequence_id, max_target_sequence_length,
output_layer, batch_size, keep_prob)
# rerturn
return dec_outputs_train, dec_outputs_infer 这里的decoding_layer函数要重新定义,但是修改非常小,可自行比较。
4.bilstm介绍
其实bilstm没有啥好介绍的,就是把单向的变成双向而已,可以获取完整信息,对于文本或者不要求实时的语音识别比较适用。
直接上自己常用的encoder的代码:
def encoding_layer(emb_encoder_inputs, rnn_size, encoder_num_layers, keep_prob,
source_sequence_length,encode_type = "lstm"):
# time_major=False
if encode_type == "lstm":
# construcll rnn cell
cell = tf.contrib.rnn.MultiRNNCell([
tf.contrib.rnn.LSTMCell(rnn_size) \
for _ in range(encoder_num_layers) ])
# rnn forward
cell = DropoutWrapper(cell, output_keep_prob=keep_prob)
enc_output, enc_state = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(cell, emb_encoder_inputs, sequence_length=source_sequence_length, dtype=tf.float32)
return enc_output,enc_state if encoder_num_layers <=1 else enc_state[-1]
elif encode_type == "bilstm":
cell_fw = tf.nn.rnn_cell.LSTMCell(
rnn_size,
initializer=tf.random_uniform_initializer(-0.1, 0.1, seed=123),
state_is_tuple=True)
cell_bw = tf.nn.rnn_cell.LSTMCell(
rnn_size,
initializer=tf.random_uniform_initializer(-0.1, 0.1, seed=113),
state_is_tuple=True)
encoder_f_cell = DropoutWrapper(cell_fw, output_keep_prob=keep_prob)
encoder_b_cell = DropoutWrapper(cell_bw, output_keep_prob=keep_prob)
(encoder_fw_outputs, encoder_bw_outputs), (encoder_fw_final_state, encoder_bw_final_state) = \
tf.nn.bidirectional_dynamic_rnn(
encoder_f_cell, encoder_b_cell, inputs=emb_encoder_inputs, dtype=tf.float32, sequence_length=source_sequence_length)
emb_encoder_outputs = tf.concat((encoder_fw_outputs, encoder_bw_outputs), 2)
encoder_final_state_c = tf.concat((encoder_fw_final_state.c, encoder_bw_final_state.c), 1)
encoder_final_state_h = tf.concat((encoder_fw_final_state.h, encoder_bw_final_state.h), 1)
encoder_final_state = LSTMStateTuple(
c=encoder_final_state_c,
h=encoder_final_state_h
)
return emb_encoder_outputs, encoder_final_state5.
完整代码见我的github
本文参考论文如下:
1.ATTENTION-BASED END-TO-END SPEECH RECOGNITION ON VOICE SEARCH
2.Listen, Attend and Spell
3.STATE-OF-THE-ART SPEECH RECOGNITION WITH SEQUENCE-TO-SEQUENCE MODELS
4.VERY DEEP CONVOLUTIONAL NETWORKS FOR END-TO-END SPEECH RECOGNITION