vivo2020届春季校园招聘在线编程考试 解题报告 Apare_xzc
vivo2020届春季校园招聘在线编程考试 解题报告
题目链接:牛客链接
A. 手机屏幕解锁模式
分析:
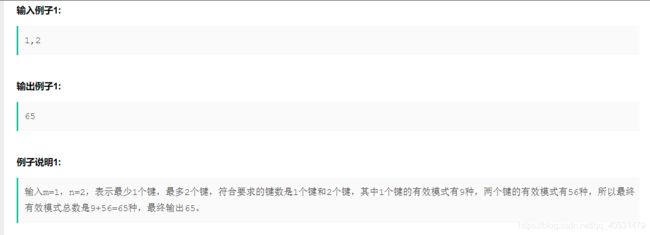
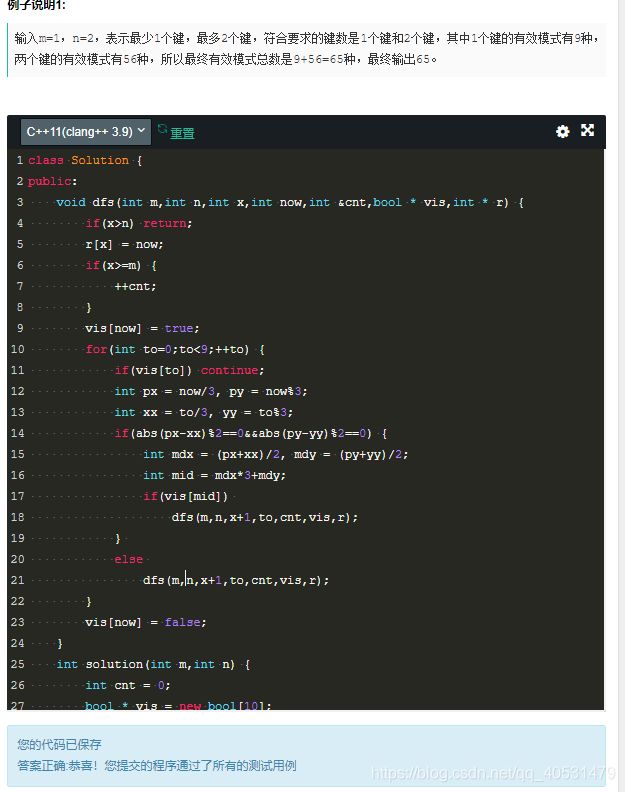
这是一个智能手机的图案锁,有3*3=9个点。现在要求所有图案中经过的点的个数再[m,n]这个范围内的方案数。一个点也算作一种方案(和一般图案锁不太一样)。
我们可以大致计算一下总共方案的个数,大概是9!这么多。当然,我们只是算了个大概,没有考虑图案的限制。这个大小远远小于10^8, 我们可以直接dfs所有方案。我们从9个点都出发一遍,每次在1-9之中都判断一次,如果还没走过,就可以考虑走到这个点。 我们一路dfs下去,如果遇到一个方案它的路径长度(经过点的个数)在[m,n]范围之内,我们就计数。如果路径长度大于n, 我们就不必往下继续搜索了。
我们需要注意一个问题,就是如果路径之中的前后两个点A, C中间那个点B还没有走过,我们就不能跨过这个点,不然A->B->C会被重复计数,因为dfs(A)的时候已经去过B了。
这题要求写在测试类里面,int solution(int m,int n)
代码:
#include
}
vis[now] = true;
for(int to=0;to<9;++to) {
if(vis[to]) continue;
int px = now/3, py = now%3;
int xx = to/3, yy = to%3;
if(abs(px-xx)%2==0&&abs(py-yy)%2==0) {
int mdx = (px+xx)/2, mdy = (py+yy)/2;
int mid = mdx*3+mdy;
if(vis[mid])
dfs(m,n,x+1,to,cnt,vis,r);
}
else
dfs(m,n,x+1,to,cnt,vis,r);
}
vis[now] = false;
}
int solution(int m,int n) {
int cnt = 0;
bool * vis = new bool[10];
int * r = new int[10];
for(int i=0;i<10;++i) vis[i] = false,r[i]=-1;
for(int i=0;i<9;++i)
dfs(m,n,1,i,cnt,vis,r);
delete []vis;
delete []r;
return cnt;
}
int main(void) {
int m,n;
while(cin>>m>>n) {
cout<<solution(m,n)<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
直接把dfs()和solution(int m,int n)两个函数复制到class Solution()作为成员函数即可。
B. 数位之积
分析:
测试类要求的函数输入的参数n和输出的答案都是int。
我们可以分析一下, 要求y的各个数位乘积等于n。我们把n分解质因数,得到n = P1^C1 * P2^C2 * P3^C3 * ... * Pk^Ck。 因为十进制整数每个数位最大为9,所以如果n存在大于9的质因数,我们便无法实现。所以,n只能包含2,3,5,7这4个质因数。
如果n==0,则y最小为10,如果1<=n<=9, 那么y最小为n+10,因为题目要求y>9。
处理完特殊的小数字后我们就可以开始讨论一般的输入。
- 如果n的质因数存在大于7的,那么n不可以被y的数位乘积表示,输出-1
- n最多只含有上述的4个质因数,那么我们就可以把n表示为:
n = 2^C2 * 3^C3 * 5^C5 * 7^C7。(C2,C3,C5,C7>=0) - 我们贪心地考虑,要使得y最小,首先要使y有最少的数位,其次在最少数位的基础上,我们要使得y的字典序最小。
- 首先,
5和7必须一个占一位,不然会超过9。我们先把2^3替换为8,3^2替换为9,这样能有效减少数位。然后3可能剩下0或1个,2可能剩下0,1,2个。如果只剩下2,优先把2^2都替换为4。如果有1个3,1个2,就替换为6。如果有2个2一个3,就替换为2,6。 - 我们处理出2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9的个数后,就可以贪心地小数在前大数在后得到答案了。
代码:
#include C. vivo智能手机产能
时间限制:C/C++ 1秒,其他语言2秒
空间限制:C/C++ 256M,其他语言512M
在vivo产线上,每位职工随着对手机加工流程认识的熟悉和经验的增加,日产量也会不断攀升。
假设第一天量产1台,接下来2天(即第二、三天)每天量产2件,接下来3天(即第四、五、六天)每天量产3件 … …
以此类推,请编程计算出第n天总共可以量产的手机数量。

分析:
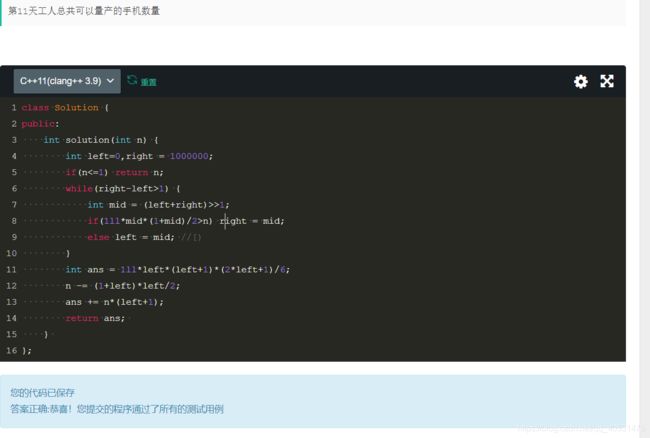
1 2 2 3 3 3 4 4 4 4 5 5 5 5 5 6 6 6 6 6 6 7 7…
二分找出最后一个连续的数字,然后求和即可。
1^2 + 2^2 + 3^2 + ...+n^2 = n*(n+1)*(2n+1)/6
代码:
#include 2020/4/10 12:33
xzc