tensorflow 2.0 高阶操作 之 数据统计
4.2 tensor 数据统计
- Outline
- Norm 求范数
- Reduce_min\max\mean 求最值
- Argmax/Argmin 求最值位置
- Equal 比较
- Accuracy 求精度示例
- Unique Gather 去重与还原
Outline
- tf.norm
- tf.reduce_min/max
- tf.argmax/argmin
- tf.equal
- tf.unique
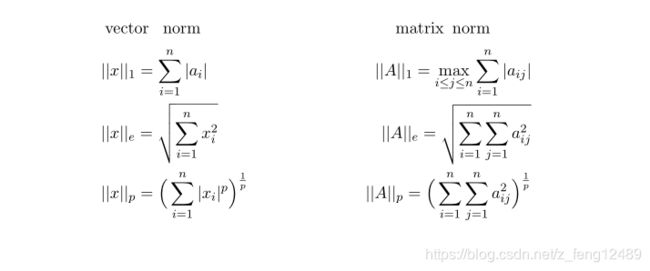
Norm 求范数
a = tf.ones([2,2])
tf.norm(a) # 统计某一维度
- ord=2, 二范数。
- axis=0, 零维度上统计统计。
b = tf.ones([4,28,28,3])
tf.norm(b).shape
tf.norm(b, ord=2, axis=0).shape # ord 2范数 # Out[4]: TensorShape([28, 28, 3])
tf.norm(b, ord=2, axis=1).shape # TensorShape([4, 28, 3])
tf.norm(b, ord=1).shape # TensorShape([])
Reduce_min\max\mean 求最值
a = tf.random.normal([4,10])
tf.reduce_min(a), tf.reduce_max(a), tf.reduce_mean(a)
# (,
# ,
# )
tf.reduce_min(a, axis=1).shape # TensorShape([4])
tf.reduce_max(a, axis=0).shape # TensorShape([10])
Argmax/Argmin 求最值位置
a = tf.random.normal([4,10])
a.shape # TensorShape([4, 10])
tf.argmax(a) # tf.argmax 的 默认axis=0
Equal 比较
a = tf.constant([2, 1, 3, 2, 5])
b = tf.range(5)
res = tf.equal(a, b) # Accuracy 求精度示例
pre = tf.constant([[0.1, 0.2, 0.7],[0.9, 0.05, 0.05]])
pre
#
# # array([[0.1 , 0.2 , 0.7 ],
# # [0.9 , 0.05, 0.05]], dtype=float32)>
pre = tf.cast(tf.argmax(pre, axis=1), dtype=tf.int32)
# Unique Gather 去重与还原
tf.unique 去除重复
tf.gather 还原
a = tf.constant([4,2,2,1,4,0])
a # ,
# )
origin_a = tf.gather(unique_tensor, idx)
#