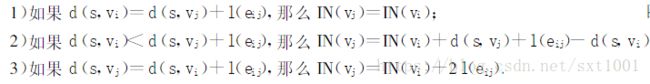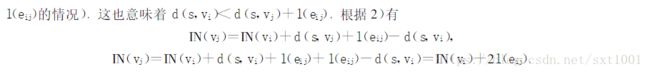一种 k-最短路 python编程
算法来自李成江的《新的k最短路算法》:
主要内容:
算法第二部分提到的定理1:
定理的证明:
算法的主要内容:
一种 k-最短路 算法python实现:
import heapq
import sys
class Graph:
def __init__(self):
self.vertices = {}
def add_vertex(self, name, edges):
self.vertices[name] = edges
def get_shortest_path(self, startpoint, endpoint):
# distances使用字典的方式保存每一个顶点到startpoint点的距离
distances = {}
# 从startpoint到某点的最优路径的前一个结点
# eg:startpoint->B->D->E,则previous[E]=D,previous[D]=B,等等
previous = {}
# 用来保存图中所有顶点的到startpoint点的距离的优先队列
# 这个距离不一定是最短距离
nodes = []
# Dikstra算法 数据初始化
for vertex in self.vertices:
if vertex == startpoint:
# 将startpoint点的距离初始化为0
distances[vertex] = 0
heapq.heappush(nodes, [0, vertex])
elif vertex in self.vertices[startpoint]:
# 把与startpoint点相连的结点距离startpoint点的距离初始化为对应的弧长/路权
distances[vertex] = self.vertices[startpoint][vertex]
heapq.heappush(nodes, [self.vertices[startpoint][vertex], vertex])
previous[vertex] = startpoint
else:
# 把与startpoint点不直接连接的结点距离startpoint的距离初始化为sys.maxsize
distances[vertex] = sys.maxsize
heapq.heappush(nodes, [sys.maxsize, vertex])
previous[vertex] = None
while nodes:
# 取出队列中最小距离的结点
smallest = heapq.heappop(nodes)[1]
if smallest == endpoint:
shortest_path = []
lenPath = distances[smallest]
temp = smallest
while temp != startpoint:
shortest_path.append(temp)
temp = previous[temp]
# 将startpoint点也加入到shortest_path中
shortest_path.append(temp)
if distances[smallest] == sys.maxsize:
# 所有点不可达
break
# 遍历与smallest相连的结点,更新其与结点的距离、前继节点
for neighbor in self.vertices[smallest]:
dis = distances[smallest] + self.vertices[smallest][neighbor]
if dis < distances[neighbor]:
distances[neighbor] = dis
# 更新与smallest相连的结点的前继节点
previous[neighbor] = smallest
for node in nodes:
if node[1] == neighbor:
# 更新与smallest相连的结点到startpoint的距离
node[0] = dis
break
heapq.heapify(nodes)
return distances, shortest_path, lenPath
def getMinDistancesIncrement(self, inputList):
inputList.sort()
lenList = [v[0] for v in inputList]
minValue = min(lenList)
minValue_index = lenList.index(minValue)
minPath = [v[1] for v in inputList][minValue_index]
return minValue, minPath, minValue_index
# def deleteCirclesWithEndpoint(self,inputList, endpoint):
# '''
# 该函数主要是删除类似于这样的例子: endpoint->...->endpoint-->...
# '''
# pathsList = [v[1] for v in inputList]
# for index, path in enumerate(pathsList):
# if len(path) > 1 and path[-1] == endpoint:
# inputList.pop(index)
# return inputList
def k_shortest_paths(self,start, finish, k = 3):
'''
:param start: 起始点
:param finish: 终点
:param k: 给出需要求的最短路数
:return: 返回K最短路和最短路长度
该算法重复计算了最短路,调用get_shortest_path()方法只是用到了起始点到其他所有点的最短距离和最短路长度
'''
distances, _, shortestPathLen = self.get_shortest_path(start, finish)
num_shortest_path = 0
paths = dict()
distancesIncrementList = [[0, finish]]
while num_shortest_path < k:
path = []
#distancesIncrementList = self.deleteCirclesWithEndpoint(distancesIncrementList,finish)
minValue, minPath, minIndex = self.getMinDistancesIncrement(distancesIncrementList)
smallest_vertex = minPath[-1]
distancesIncrementList.pop(minIndex)
if smallest_vertex == start:
path.append(minPath[::-1])
num_shortest_path += 1
# type(path) -> list,不能作为字典的key
paths[path[0]] = minValue + shortestPathLen
# 字典采用{path ; pathlen}这样的键值对,不能使用{pathlen:path}
# 因为key是唯一的,所以在此相同长度的path只能保存一个,后来的会覆盖前面的
# paths[minValue + shortestPathLen] = path
continue
for neighbor in self.vertices[smallest_vertex]:
incrementValue = minPath
increment = 0
if neighbor == finish:
# 和函数deleteCirclesWithEndpoint()作用一样
continue
if distances[smallest_vertex] == (distances[neighbor] + self.vertices[smallest_vertex][neighbor]):
increment = minValue
elif distances[smallest_vertex] < (distances[neighbor] + self.vertices[smallest_vertex][neighbor]):
increment = minValue + distances[neighbor] + self.vertices[smallest_vertex][neighbor] - distances[smallest_vertex]
elif distances[neighbor] == (distances[smallest_vertex] + self.vertices[smallest_vertex][neighbor]):
increment = minValue + 2 * self.vertices[smallest_vertex][neighbor]
distancesIncrementList.append([increment, incrementValue + neighbor])
return paths
if __name__ == '__main__':
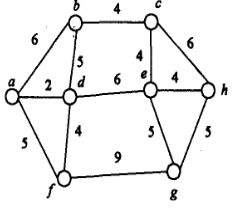
g = Graph()
g.add_vertex('a', {'b': 6, 'd': 2, 'f': 5})
g.add_vertex('b', {'a': 6, 'c': 4, 'd': 5})
g.add_vertex('c', {'b': 4, 'e': 4, 'h': 6})
g.add_vertex('d', {'a': 2, 'b': 5, 'e': 6, 'f': 4})
g.add_vertex('e', {'d': 6, 'c': 4, 'g': 5, 'h': 4})
g.add_vertex('f', {'a': 5, 'd': 4, 'g': 9})
g.add_vertex('g', {'f': 9, 'e': 5, 'h': 5})
g.add_vertex('h', {'c': 6, 'e': 4, 'g': 5})
start = 'a'
end = 'e'
k = 4
distances, shortestPath, shortestPathLen = g.get_shortest_path(start, end)
#print('{}->{}的最短路径是:{},最短路径为:{}'.format(start, end, shortestPath, shortestPathLen))
paths = g.k_shortest_paths(start, end, k)
print('\n求得的 {}-->{} 的 {}-最短路 分别是:'.format(start, end, k))
index = 1
for path, length in paths.items():
print('{}:{} 最短路长度:{}'.format(index, path, length))
index += 1
运行结果:
最后测试用例使用的无向图是:
程序还有待优化,比如从数据结构上等等。
代码如有误,欢迎评论指出