Machine Learning with Scikit-Learn and Tensorflow 6.10 练习
书籍信息
Hands-On Machine Learning with Scikit-Learn and Tensorflow
出版社: O’Reilly Media, Inc, USA
平装: 566页
语种: 英语
ISBN: 1491962291
条形码: 9781491962299
商品尺寸: 18 x 2.9 x 23.3 cm
ASIN: 1491962291
系列博文为书籍中文翻译
代码以及数据下载:https://github.com/ageron/handson-ml
1、1000000个实例训练的决策树深度大约是多少(训练时没有限制)?
答:20( log21000000 )。没有限制时,样本与叶结点对应,这里假设决策树基本平衡。
2、结点的基尼不纯度通常比父结点低还是高?是通常还是总是?
答:子结点基尼不纯度通常比父结点低,但是不是总是(类别数量可能不同)。
3、当决策树过拟合时,减少max_depth是否可行?
答:可行。
4、当决策树欠拟合时,进行特征放缩(feature scaling)是否可行?
答:不可行。
5、如果1000000个实例训练决策树需要1小时,那么10000000个实例训练决策树需要多少时间?
答:11.7小时( 10log2(10m)/log2m ),决策树训练时间复杂度 O(nmlog2m) ,其中n是特征数量,m是样本数量。
6、如果训练数据包含100000个实例,那么设置presort=True是否会加速训练?
答:不会,预排序仅在小规模训练数据时可以加速训练。
7、决策树的训练
(1)使用make_moons产生训练数据(n_samples=10000, noise=0.4)。
(2)使用train_test_split划分数据为训练数据和测试数据。
(3)使用交叉验证找到最好的超参数(尝试调节max_leaf_nodes)。
(4)使用训练数据训练模型,使用测试数据进行预测,模型的准确率大约是85%-87%。
答:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
from sklearn.datasets import make_moons
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.grid_search import GridSearchCV
X, y = make_moons(n_samples=10000, noise=0.4, random_state=0)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=0)
clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state=0)
param = {"max_leaf_nodes":np.arange(5, 100, 5)}
bestrf = GridSearchCV(clf, param)
bestrf.fit(X_train, y_train)
print "best parameters : ", bestrf.best_params_
print "test accuracy : ", bestrf.score(X_test, y_test)
# output
# best parameters : {'max_leaf_nodes': 20}
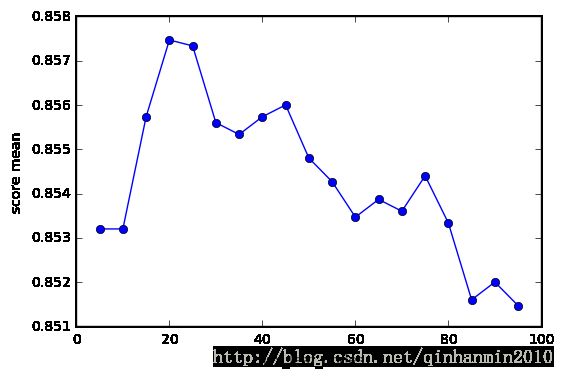
# test accuracy : 0.8648以下是调参过程可视化
def plot_clf(param, bestrf, variable):
plt.figure()
plt.plot(param[variable], map(lambda x:x[1], bestrf.grid_scores_), 'o-')
plt.xlabel(variable)
plt.ylabel("score mean")
plt.show()
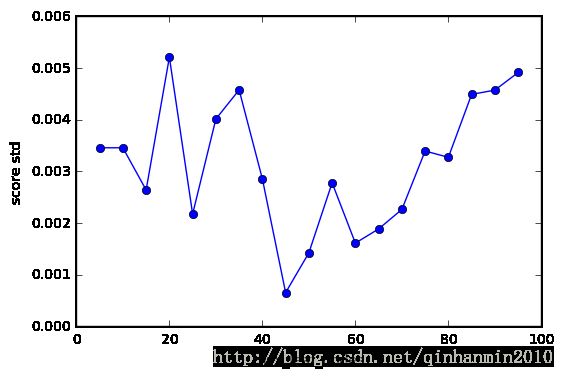
plt.figure()
plt.plot(param[variable], map(lambda x:np.std(x[2]), bestrf.grid_scores_), 'o-')
plt.xlabel(variable)
plt.ylabel("score std")
plt.show()
plot_clf(param, bestrf, "max_leaf_nodes")8、森林的训练
(1)使用上面的数据集,生成1000个子集,每个子集包含100个实例。
(2)分别对于这些子集,利用上面得到的超参数训练决策树,使用测试数据进行预测。因为训练时使用的是部分数据,所以模型的效果稍低,大约是80%。
(3)针对测试数据实例,取1000棵决策树预测结果的众数作为最后的预测结果。利用新的方法进行预测,可以发现准确率提高0.5%-1.5%,这是随机森林的基本思想。
version 1
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.datasets import make_moons
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
from scipy.stats import mode
X, y = make_moons(n_samples=10000, noise=0.4, random_state=0)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=0)
# the scores of the models
scores = []
# the predictions of the models
preds = []
for i in range(0, 1000):
ind = np.random.randint(0, len(X_train), 100)
X_train_cur = X_train[ind]
y_train_cur = y_train[ind]
clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_leaf_nodes=20, random_state=0)
clf.fit(X_train_cur, y_train_cur)
pred = clf.predict(X_test)
preds.append(pred)
score = accuracy_score(pred, y_test)
scores.append(score)
print "average accuracy of the models : ", np.mean(scores)
print "ensemble model accuracy : ", accuracy_score(mode(np.array(preds))[0][0], y_test)
# output
# average accuracy of the models : 0.7956644
# ensemble model accuracy : 0.8704version 2 (use ShuffleSplit)
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.datasets import make_moons
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.model_selection import ShuffleSplit
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
from scipy.stats import mode
X, y = make_moons(n_samples=10000, noise=0.4, random_state=0)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=0)
# the scores of the models
scores = []
# the predictions of the models
preds = []
rs = ShuffleSplit(n_splits=1000, train_size=100, random_state=0)
for train_ind, test_ind in rs.split(X_train):
X_train_cur = X_train[train_ind]
y_train_cur = y_train[train_ind]
clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_leaf_nodes=20, random_state=0)
clf.fit(X_train_cur, y_train_cur)
pred = clf.predict(X_test)
preds.append(pred)
score = accuracy_score(pred, y_test)
scores.append(score)
print "average accuracy of the models : ", np.mean(scores)
print "ensemble model accuracy : ", accuracy_score(mode(np.array(preds))[0][0], y_test)
# output
# average accuracy of the models : 0.7964496
# ensemble model accuracy : 0.8708