retrofit用法详解
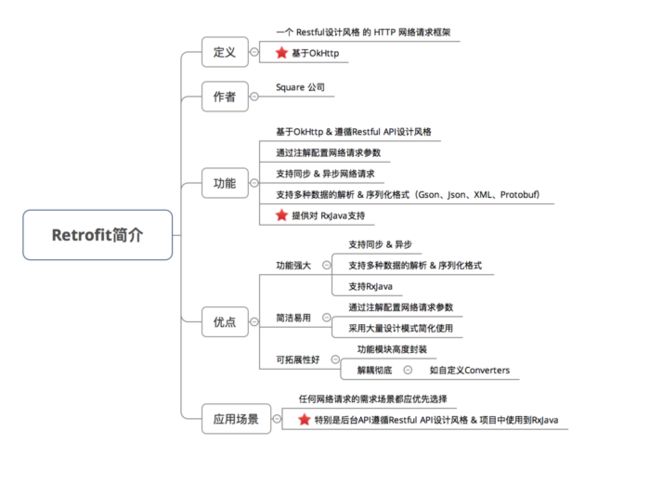
综述
retrofit是由square公司开发的。square在github上发布了很多优秀的Android开源项目。例如:otto(事件总线),leakcanary(排查内存泄露),android-times-square(日历控件),dagger(依赖注入),picasso(异步加载图片),okhttp(网络请求),retrofit(网络请求)等等。更多square上的开源项目我们可以去square的GitHub进行查看。这次就来介绍一下retrofit的一些基本用法。retrofit是REST安卓客户端请求库。使用retrofit可以进行GET,POST,PUT,DELETE等请求方式。下面就来看一下retrofit的基本用法。
retrofit用法
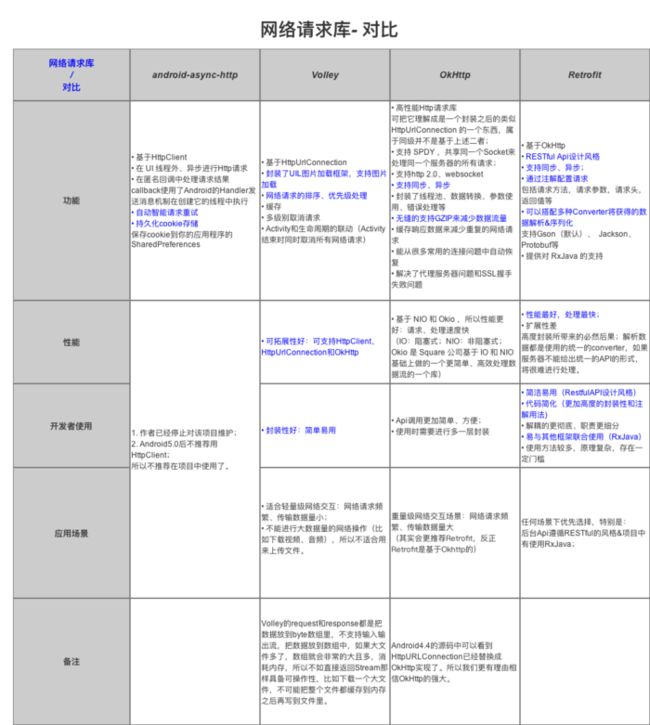
一图让你了解全部的网络请求库和他们之间的区别!
3. 使用介绍
使用 Retrofit 的步骤共有7个:
步骤1:添加Retrofit库的依赖
步骤2:创建 接收服务器返回数据 的类
步骤3:创建 用于描述网络请求 的接口
步骤4:创建 Retrofit 实例
步骤5:创建 网络请求接口实例 并 配置网络请求参数
步骤6:发送网络请求(异步 / 同步)
1,首先需要在build.gradle文件中引入需要的第三包,配置如下:
|
2创建服务器返回的数据的类
Reception.java
public class Reception {
...
// 根据返回数据的格式和数据解析方式(Json、XML等)定义
// 下面会在实例进行说明
}
3创建用于描述网络的接口
- Retrofit将 Http请求 抽象成 Java接口:采用 注解 描述网络请求参数 和配置网络请求参数
- 用 动态代理 动态 将该接口的注解“翻译”成一个 Http 请求,最后再执行 Http 请求
- 注:接口中的每个方法的参数都需要使用注解标注,否则会报错
GetRequest_Interface.interface
public interface GetRequest_Interface {
@GET("openapi.do?keyfrom=Yanzhikai&key=2032414398&type=data&doctype=json&version=1.1&q=car")
Call getCall();
// @GET注解的作用:采用Get方法发送网络请求
// getCall() = 接收网络请求数据的方法
// 其中返回类型为Call<*>,*是接收数据的类(即上面定义的Translation类)
// 如果想直接获得Responsebody中的内容,可以定义网络请求返回值为Call 注解的类型
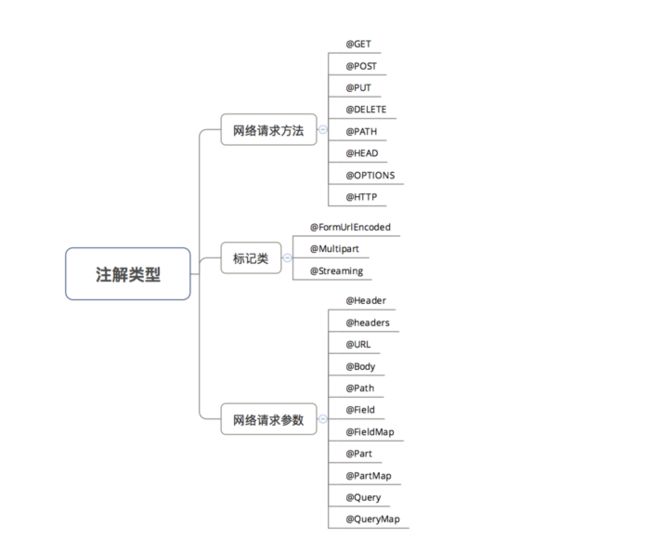
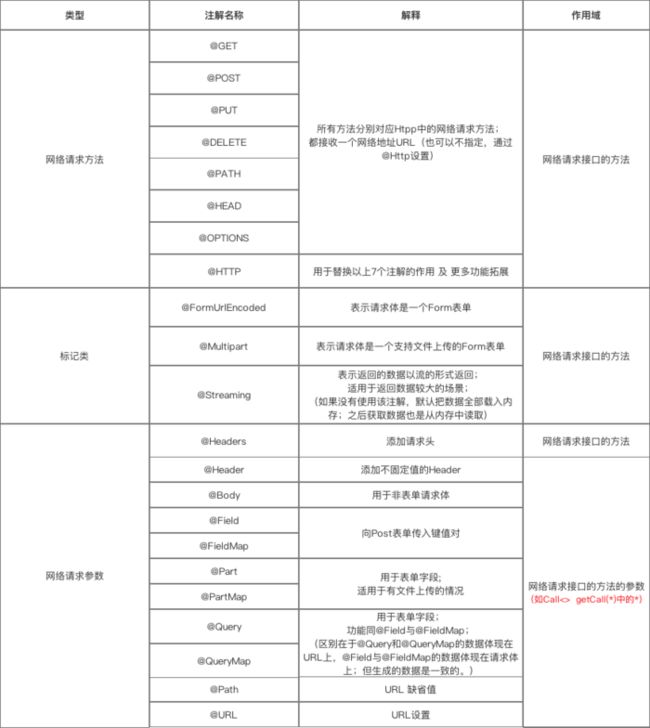
注解的说明
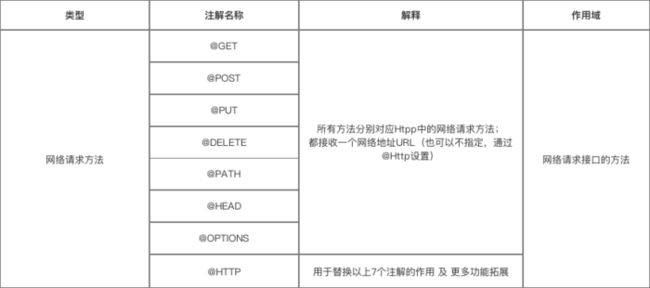
第一类:网络请求的方法
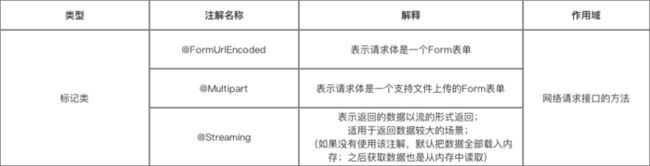
第二类:标记
标记类注解
a. @FormUrlEncoded
- 作用:表示发送form-encoded的数据
每个键值对需要用@Filed来注解键名,随后的对象需要提供值。
b. @Multipart
- 作用:表示发送form-encoded的数据(适用于 有文件 上传的场景)
每个键值对需要用@Part来注解键名,随后的对象需要提供值。
具体使用如下:
GetRequest_Interface
public interface GetRequest_Interface {
/**
*表明是一个表单格式的请求(Content-Type:application/x-www-form-urlencoded)
* Field("username") 表示将后面的 String name 中name的取值作为 username 的值
*/
@POST("/form")
@FormUrlEncoded
Call testFormUrlEncoded1(@Field("username") String name, @Field("age") int age);
/**
* {@link Part} 后面支持三种类型,{@link RequestBody}、{@link okhttp3.MultipartBody.Part} 、任意类型
* 除 {@link okhttp3.MultipartBody.Part} 以外,其它类型都必须带上表单字段({@link okhttp3.MultipartBody.Part} 中已经包含了表单字段的信息),
*/
@POST("/form")
@Multipart
Call testFileUpload1(@Part("name") RequestBody name, @Part("age") RequestBody age, @Part MultipartBody.Part file);
}
// 具体使用
GetRequest_Interface service = retrofit.create(GetRequest_Interface.class);
// @FormUrlEncoded
Call call1 = service.testFormUrlEncoded1("Carson", 24);
// @Multipart
RequestBody name = RequestBody.create(textType, "Carson");
RequestBody age = RequestBody.create(textType, "24");
MultipartBody.Part filePart = MultipartBody.Part.createFormData("file", "test.txt", file);
Call call3 = service.testFileUpload1(name, age, filePart);
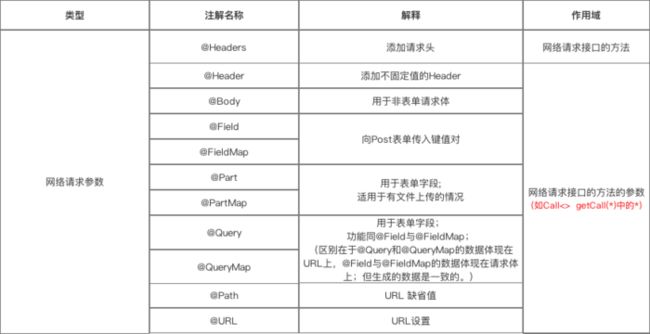
第三类:网络请求参数
网络请求参数注解
详细说明
a. @Header & @Headers
- 作用:添加请求头 &添加不固定的请求头
- 具体使用如下:
// @Header
@GET("user")
Call getUser(@Header("Authorization") String authorization)
// @Headers
@Headers("Authorization: authorization")
@GET("user")
Call getUser()
// 以上的效果是一致的。
// 区别在于使用场景和使用方式
// 1. 使用场景:@Header用于添加不固定的请求头,@Headers用于添加固定的请求头
// 2. 使用方式:@Header作用于方法的参数;@Headers作用于方法
b. @Body
- 作用:以
Post方式 传递 自定义数据类型 给服务器 - 特别注意:如果提交的是一个Map,那么作用相当于
@Field
不过Map要经过
FormBody.Builder类处理成为符合 Okhttp 格式的表单,如:
FormBody.Builder builder = new FormBody.Builder();
builder.add("key","value");
c. @Field & @FieldMap
- 作用:发送 Post请求 时提交请求的表单字段
- 具体使用:与
@FormUrlEncoded注解配合使用
public interface GetRequest_Interface {
/**
*表明是一个表单格式的请求(Content-Type:application/x-www-form-urlencoded)
* Field("username") 表示将后面的 String name 中name的取值作为 username 的值
*/
@POST("/form")
@FormUrlEncoded
Call testFormUrlEncoded1(@Field("username") String name, @Field("age") int age);
/**
* Map的key作为表单的键
*/
@POST("/form")
@FormUrlEncoded
Call testFormUrlEncoded2(@FieldMap Map map);
}
// 具体使用
// @Field
Call call1 = service.testFormUrlEncoded1("Carson", 24);
// @FieldMap
// 实现的效果与上面相同,但要传入Map
Map map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("username", "Carson");
map.put("age", 24);
Call call2 = service.testFormUrlEncoded2(map);
d. @Part & @PartMap
- 作用:发送 Post请求 时提交请求的表单字段
与@Field的区别:功能相同,但携带的参数类型更加丰富,包括数据流,所以适用于 有文件上传 的场景
- 具体使用:与
@Multipart注解配合使用
public interface GetRequest_Interface {
/**
* {@link Part} 后面支持三种类型,{@link RequestBody}、{@link okhttp3.MultipartBody.Part} 、任意类型
* 除 {@link okhttp3.MultipartBody.Part} 以外,其它类型都必须带上表单字段({@link okhttp3.MultipartBody.Part} 中已经包含了表单字段的信息),
*/
@POST("/form")
@Multipart
Call testFileUpload1(@Part("name") RequestBody name, @Part("age") RequestBody age, @Part MultipartBody.Part file);
/**
* PartMap 注解支持一个Map作为参数,支持 {@link RequestBody } 类型,
* 如果有其它的类型,会被{@link retrofit2.Converter}转换,如后面会介绍的 使用{@link com.google.gson.Gson} 的 {@link retrofit2.converter.gson.GsonRequestBodyConverter}
* 所以{@link MultipartBody.Part} 就不适用了,所以文件只能用 @Part MultipartBody.Part
*/
@POST("/form")
@Multipart
Call testFileUpload2(@PartMap Map args, @Part MultipartBody.Part file);
@POST("/form")
@Multipart
Call testFileUpload3(@PartMap Map args);
}
// 具体使用
MediaType textType = MediaType.parse("text/plain");
RequestBody name = RequestBody.create(textType, "Carson");
RequestBody age = RequestBody.create(textType, "24");
RequestBody file = RequestBody.create(MediaType.parse("application/octet-stream"), "这里是模拟文件的内容");
// @Part
MultipartBody.Part filePart = MultipartBody.Part.createFormData("file", "test.txt", file);
Call call3 = service.testFileUpload1(name, age, filePart);
ResponseBodyPrinter.printResponseBody(call3);
// @PartMap
// 实现和上面同样的效果
Map fileUpload2Args = new HashMap<>();
fileUpload2Args.put("name", name);
fileUpload2Args.put("age", age);
//这里并不会被当成文件,因为没有文件名(包含在Content-Disposition请求头中),但上面的 filePart 有
//fileUpload2Args.put("file", file);
Call call4 = service.testFileUpload2(fileUpload2Args, filePart); //单独处理文件
ResponseBodyPrinter.printResponseBody(call4);
}
e. @Query和@QueryMap
- 作用:用于
@GET方法的查询参数(Query = Url 中 ‘?’ 后面的 key-value)
如:url = http://www.println.net/?cate=android,其中,Query = cate
- 具体使用:配置时只需要在接口方法中增加一个参数即可:
@GET("/")
Call cate(@Query("cate") String cate);
}
// 其使用方式同 @Field与@FieldMap,这里不作过多描述
f. @Path
- 作用:URL地址的缺省值
- 具体使用:
public interface GetRequest_Interface {
@GET("users/{user}/repos")
Call getBlog(@Path("user") String user );
// 访问的API是:https://api.github.com/users/{user}/repos
// 在发起请求时, {user} 会被替换为方法的第一个参数 user(被@Path注解作用)
}
g. @Url
- 作用:直接传入一个请求的 URL变量 用于URL设置
- 具体使用:
public interface GetRequest_Interface {
@GET
Call testUrlAndQuery(@Url String url, @Query("showAll") boolean showAll);
// 当有URL注解时,@GET传入的URL就可以省略
// 当GET、POST...HTTP等方法中没有设置Url时,则必须使用 {@link Url}提供
}
汇总
步骤4:创建 Retrofit 实例
Retrofit retrofit = new Retrofit.Builder()
.baseUrl("http://fanyi.youdao.com/") // 设置网络请求的Url地址
.addConverterFactory(GsonConverterFactory.create()) // 设置数据解析器
.addCallAdapterFactory(RxJavaCallAdapterFactory.create()) // 支持RxJava平台
.build();
a.关于数据解析器(Converter)
- Retrofit支持多种数据解析方式
- 使用时需要在Gradle添加依赖
| 数据解析器 | Gradle依赖 |
|---|---|
| Gson | com.squareup.retrofit2:converter-gson:2.0.2 |
| Jackson | com.squareup.retrofit2:converter-jackson:2.0.2 |
| Simple XML | com.squareup.retrofit2:converter-simplexml:2.0.2 |
| Protobuf | com.squareup.retrofit2:converter-protobuf:2.0.2 |
| Moshi | com.squareup.retrofit2:converter-moshi:2.0.2 |
| Wire | com.squareup.retrofit2:converter-wire:2.0.2 |
| Scalars | com.squareup.retrofit2:converter-scalars:2.0.2 |
b. 关于网络请求适配器(CallAdapter)
- Retrofit支持多种网络请求适配器方式:guava、Java8和rxjava
使用时如使用的是
Android默认的CallAdapter,则不需要添加网络请求适配器的依赖,否则则需要按照需求进行添加
Retrofit 提供的CallAdapter
- 使用时需要在Gradle添加依赖:
| 网络请求适配器 | Gradle依赖 |
|---|---|
| guava | com.squareup.retrofit2:adapter-guava:2.0.2 |
| Java8 | com.squareup.retrofit2:adapter-java8:2.0.2 |
| rxjava | com.squareup.retrofit2:adapter-rxjava:2.0.2 |
步骤5:创建 网络请求接口实例
// 创建 网络请求接口 的实例
GetRequest_Interface request = retrofit.create(GetRequest_Interface.class);
//对 发送请求 进行封装
Call call = request.getCall();
步骤6:发送网络请求(异步 / 同步)
封装了 数据转换、线程切换的操作
//发送网络请求(异步)
call.enqueue(new Callback() {
//请求成功时回调
@Override
public void onResponse(Call call, Response response) {
//请求处理,输出结果
response.body().show();
}
//请求失败时候的回调
@Override
public void onFailure(Call call, Throwable throwable) {
System.out.println("连接失败");
}
});
// 发送网络请求(同步)
Response response = call.execute();
步骤7:处理返回数据
通过response类的 body()对返回的数据进行处理
//发送网络请求(异步)
call.enqueue(new Callback() {
//请求成功时回调
@Override
public void onResponse(Call call, Response response) {
// 对返回数据进行处理
response.body().show();
}
//请求失败时候的回调
@Override
public void onFailure(Call call, Throwable throwable) {
System.out.println("连接失败");
}
});
// 发送网络请求(同步)
Response response = call.execute();
// 对返回数据进行处理
response.body().show();