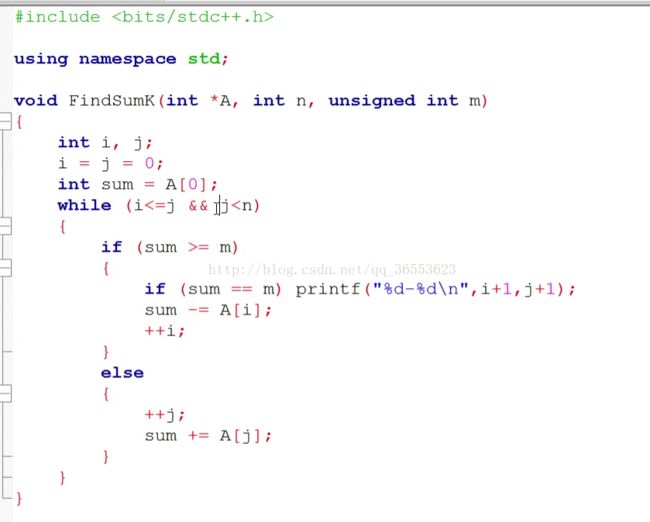
尺取法
- - 由于现在比较晚了, 贼想睡觉,所以先弄一个不完整版的 23333
例题:题目
Value_Dragon是一个有钱人。快过年了,所以他准备发红包。但是他发红包的方式很奇葩。他让n个人排成一排。每次选择1-n中的一段区间[l,r]发,给区间中的每一个人一块钱。就这样发了m次红包。发完后他想知道在[1,n]的子区间中有多少个区间满足以下要求
-
这个区间得到钱的总数不少于s
-
这个区间可以被分成两个不相交的子区间且每个子区间得到的钱的总数不小于w
(注:一个区间的子区间包括自己本身)
防坑提醒,长度为1的区间比如[1,1],是不能被拆成两个子区间的
Input
第一行是一个整数T代表数据的组数。
接下来有T组数据
每组数据开头有四个整数,分别代表n m s w
接下来m行,每行是是两个数l,r代表区间[l,r]的左右端点
其中T<=10
n<=10^6,m<=10^5
0 0<=w<=s<10^8
Output
对于每组数据输出一行,代表符合要求的区间个数
SampleInput
4 1 0 0 0 1000000 0 0 0 1000000 1 0 0 1 1000000 10 10 20 14 2 10 5 9 5 5 6 8 2 6 9 10 6 7 6 10 4 5 5 7
SampleOutput
0 499999500000 499999500000 8
暂时先给出代码,我会补充的- - 23333
#include
//#include
//#include
//using namespace __gnu_pbds;
using namespace std;
#define pi acos(-1)
#define endl '\n'
#define me(x) memset(x,0,sizeof(x));
#define foreach(it,a) for(__typeof((a).begin()) it=(a).begin();it!=(a).end();it++)
typedef long long LL;
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL LINF=0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3fLL;
const int dx[]={-1,0,1,0,-1,-1,1,1};
const int dy[]={0,1,0,-1,1,-1,1,-1};
const int maxn=1e3+5;
const int maxx=1e6+10;
const double EPS=1e-7;
const int mod=1000000007;
templateinline T min(T a,T b,T c) { return min(min(a,b),c);}
templateinline T max(T a,T b,T c) { return max(max(a,b),c);}
templateinline T min(T a,T b,T c,T d) { return min(min(a,b),min(c,d));}
templateinline T max(T a,T b,T c,T d) { return max(max(a,b),max(c,d));}
//typedef tree,rb_tree_tag,tree_order_statistics_node_update> rbtree;
/*lch[root] = build(L1,p-1,L2+1,L2+cnt);
rch[root] = build(p+1,R1,L2+cnt+1,R2);中前*/
/*lch[root] = build(L1,p-1,L2,L2+cnt-1);
rch[root] = build(p+1,R1,L2+cnt,R2-1);中后*/
long long gcd(long long a , long long b){if(b==0) return a;a%=b;return gcd(b,a);}
int n,m,s,w;
int a[maxx],sum[maxx];
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
me(a);me(sum);
scanf("%d%d%d%d",&n,&m,&s,&w);
while(m--)
{
int x,y;
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
a[x]++;a[y+1]--;
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
a[i]=a[i-1]+a[i];
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
sum[i]=sum[i-1]+a[i];
LL ans=0,l=1,r=1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
while(r=w)
r++;
while(l=s&&sum[r-1]-sum[l]>=w)
l++;
if(l=s&&sum[i]-sum[r-1]>=w&&
sum[r-1]-sum[l-1]>=w)
ans+=l;
}
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
}