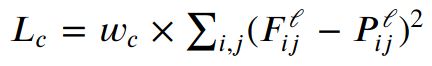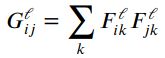基于Pytorch实现风格迁移(CS231n assignment3)
风格迁移由Gatys等与2015年提出,论文:https://www.cv-foundation.org/openaccess/content_cvpr_2016/papers/Gatys_Image_Style_Transfer_CVPR_2016_paper.pdf。本篇博客基于CS231n课程2017年Pytorch版本的作业内容,对其进行实现。
风格迁移主要目的是将一幅图的艺术风格转移到另一幅图中去。为了实现这个目的,我们首先需要使用相应的损失函数以描述在神经网络的特征空间中各图片的内容以及风格,之后对图片中的像素使用梯度下降来使图片向目标风格转变。
练习所使用的网络是SqueezeNet,这种网络容量相当于AlexNet,但是效率更高。换用其他的网络也可以达到同样的效果,一般而言,容量越大的网络风格迁移的效果会越好。
练习最终生成的图片效果将如下所示:
首先还是一些库文件、参数的初始化和辅助函数,如下:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torchvision
import torchvision.transforms as T
import PIL
import numpy as np
from scipy.misc import imread
from collections import namedtuple
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from cs231n.image_utils import SQUEEZENET_MEAN, SQUEEZENET_STD
# %matplotlib inline
def preprocess(img, size=512):
transform = T.Compose([
T.Resize(size),
T.ToTensor(),
T.Normalize(mean=SQUEEZENET_MEAN.tolist(),
std=SQUEEZENET_STD.tolist()),
T.Lambda(lambda x: x[None]),
])
return transform(img)
def deprocess(img):
transform = T.Compose([
T.Lambda(lambda x: x[0]),
T.Normalize(mean=[0, 0, 0], std=[1.0 / s for s in SQUEEZENET_STD.tolist()]),
T.Normalize(mean=[-m for m in SQUEEZENET_MEAN.tolist()], std=[1, 1, 1]),
T.Lambda(rescale),
T.ToPILImage(),
])
return transform(img)
def rescale(x):
low, high = x.min(), x.max()
x_rescaled = (x - low) / (high - low)
return x_rescaled
def rel_error(x,y):
return np.max(np.abs(x - y) / (np.maximum(1e-8, np.abs(x) + np.abs(y))))
def features_from_img(imgpath, imgsize):
img = preprocess(PIL.Image.open(imgpath), size=imgsize)
img_var = img.type(dtype)
return extract_features(img_var, cnn), img_var
# Older versions of scipy.misc.imresize yield different results
# from newer versions, so we check to make sure scipy is up to date.
def check_scipy():
import scipy
vnum = int(scipy.__version__.split('.')[1])
major_vnum = int(scipy.__version__.split('.')[0])
assert vnum >= 16 or major_vnum >= 1, "You must install SciPy >= 0.16.0 to complete this notebook."
check_scipy()
answers = dict(np.load('style-transfer-checks.npz'))
dtype = torch.FloatTensor
# Uncomment out the following line if you're on a machine with a GPU set up for PyTorch!
#dtype = torch.cuda.FloatTensor
# Load the pre-trained SqueezeNet model.
cnn = torchvision.models.squeezenet1_1(pretrained=True).features
cnn.type(dtype)
# We don't want to train the model any further, so we don't want PyTorch to waste computation
# computing gradients on parameters we're never going to update.
for param in cnn.parameters():
param.requires_grad = False
# We provide this helper code which takes an image, a model (cnn), and returns a list of
# feature maps, one per layer.
def extract_features(x, cnn):
"""
Use the CNN to extract features from the input image x.
Inputs:
- x: A PyTorch Tensor of shape (N, C, H, W) holding a minibatch of images that
will be fed to the CNN.
- cnn: A PyTorch model that we will use to extract features.
Returns:
- features: A list of feature for the input images x extracted using the cnn model.
features[i] is a PyTorch Tensor of shape (N, C_i, H_i, W_i); recall that features
from different layers of the network may have different numbers of channels (C_i) and
spatial dimensions (H_i, W_i).
"""
features = []
prev_feat = x
for i, module in enumerate(cnn._modules.values()):
next_feat = module(prev_feat)
features.append(next_feat)
prev_feat = next_feat
return features
#please disregard warnings about initialization下面我们来计算损失函数。风格迁移中的损失函数由三个部分组成:content loss + style loss + total variation loss。下面分别对这三个损失函数进行实现。
首先是content loss,简单理解就是两张图像之间的像素误差。公式如下:
这个实现起来没啥难度,但是矩阵运算的结果在测试的时候会产生一定误差,大约0.00018,但是递归方法计算的结果没有这个误差。我不是特别清楚原理:
def content_loss(content_weight, content_current, content_original):
"""
Compute the content loss for style transfer.
Inputs:
- content_weight: Scalar giving the weighting for the content loss.
- content_current: features of the current image; this is a PyTorch Tensor of shape
(1, C_l, H_l, W_l).
- content_target: features of the content image, Tensor with shape (1, C_l, H_l, W_l).
Returns:
- scalar content loss
"""
return ((content_current - content_original) ** 2).sum() * content_weight测试:
def content_loss_test(correct):
content_image = 'styles/tubingen.jpg'
image_size = 192
content_layer = 3
content_weight = 6e-2
c_feats, content_img_var = features_from_img(content_image, image_size)
bad_img = torch.zeros(*content_img_var.data.size()).type(dtype)
feats = extract_features(bad_img, cnn)
student_output = content_loss(content_weight, c_feats[content_layer], feats[content_layer]).cpu().data.numpy()
error = rel_error(correct, student_output)
print('Maximum error is {:.3f}'.format(error))
content_loss_test(answers['cl_out'])下一步是计算Style loss。这里我们用到的是如下描述的Gram矩阵,其能够突出图像中的特征结构:
对于单层网络所提取的特征,Style loss的计算为两个图像的在这一层特征的Gram矩阵之间距离的平方和,公式如下:
最后将对网络各层的Style loss求和,即得到整个网络的Style loss:
下面对上述公式进行实现,首先是Gram矩阵:
def gram_matrix(features, normalize=True):
"""
Compute the Gram matrix from features.
Inputs:
- features: PyTorch Tensor of shape (N, C, H, W) giving features for
a batch of N images.
- normalize: optional, whether to normalize the Gram matrix
If True, divide the Gram matrix by the number of neurons (H * W * C)
Returns:
- gram: PyTorch Tensor of shape (N, C, C) giving the
(optionally normalized) Gram matrices for the N input images.
"""
NoN = features.shape[1] * features.shape[2] * features.shape[3]
features = features.view(features.shape[0], features.shape[1], -1)
gram = features.matmul(features.permute(0, 2, 1))
if normalize == True:
gram = gram / NoN
return gram
测试:
def gram_matrix_test(correct):
style_image = 'styles/starry_night.jpg'
style_size = 192
feats, _ = features_from_img(style_image, style_size)
student_output = gram_matrix(feats[5].clone()).cpu().data.numpy()
error = rel_error(correct, student_output)
print('Maximum error is {:.3f}'.format(error))
gram_matrix_test(answers['gm_out'])然后是Style loss:
# Now put it together in the style_loss function...
def style_loss(feats, style_layers, style_targets, style_weights):
"""
Computes the style loss at a set of layers.
Inputs:
- feats: list of the features at every layer of the current image, as produced by
the extract_features function.
- style_layers: List of layer indices into feats giving the layers to include in the
style loss.
- style_targets: List of the same length as style_layers, where style_targets[i] is
a PyTorch Tensor giving the Gram matrix of the source style image computed at
layer style_layers[i].
- style_weights: List of the same length as style_layers, where style_weights[i]
is a scalar giving the weight for the style loss at layer style_layers[i].
Returns:
- style_loss: A PyTorch Tensor holding a scalar giving the style loss.
"""
# Hint: you can do this with one for loop over the style layers, and should
# not be very much code (~5 lines). You will need to use your gram_matrix function.
style_loss = 0
for ii in range(len(style_layers)):
gram = gram_matrix(feats[style_layers[ii]])
style_loss += style_weights[ii] * ((gram - style_targets[ii]) ** 2).sum()
return style_loss
测试:
def style_loss_test(correct):
content_image = 'styles/tubingen.jpg'
style_image = 'styles/starry_night.jpg'
image_size = 192
style_size = 192
style_layers = [1, 4, 6, 7]
style_weights = [300000, 1000, 15, 3]
c_feats, _ = features_from_img(content_image, image_size)
feats, _ = features_from_img(style_image, style_size)
style_targets = []
for idx in style_layers:
style_targets.append(gram_matrix(feats[idx].clone()))
student_output = style_loss(c_feats, style_layers, style_targets, style_weights).cpu().data.numpy()
error = rel_error(correct, student_output)
print('Error is {:.3f}'.format(error))
style_loss_test(answers['sl_out'])最后,我们希望生成的图像比较平滑,于是使用total variation loss来进行控制,这个其实就相当于逻辑回归里边的正则项:
实现如下:
def tv_loss(img, tv_weight):
"""
Compute total variation loss.
Inputs:
- img: PyTorch Variable of shape (1, 3, H, W) holding an input image.
- tv_weight: Scalar giving the weight w_t to use for the TV loss.
Returns:
- loss: PyTorch Variable holding a scalar giving the total variation loss
for img weighted by tv_weight.
"""
# Your implementation should be vectorized and not require any loops!
sum1 = ((img[:, :, :-1, :] - img[:, :, 1:, :]) ** 2).sum()
sum2 = ((img[:, :, :, :-1] - img[:, :, :, 1:]) ** 2).sum()
return tv_weight * (sum1 + sum2)测试:
def tv_loss_test(correct):
content_image = 'styles/tubingen.jpg'
image_size = 192
tv_weight = 2e-2
content_img = preprocess(PIL.Image.open(content_image), size=image_size)
student_output = tv_loss(content_img, tv_weight).cpu().data.numpy()
error = rel_error(correct, student_output)
print('Error is {:.3f}'.format(error))
tv_loss_test(answers['tv_out'])以上,作业部分的内容全部完成,下面是作业提供的风格迁移本体代码:
def style_transfer(content_image, style_image, image_size, style_size, content_layer, content_weight,
style_layers, style_weights, tv_weight, init_random = False):
"""
Run style transfer!
Inputs:
- content_image: filename of content image
- style_image: filename of style image
- image_size: size of smallest image dimension (used for content loss and generated image)
- style_size: size of smallest style image dimension
- content_layer: layer to use for content loss
- content_weight: weighting on content loss
- style_layers: list of layers to use for style loss
- style_weights: list of weights to use for each layer in style_layers
- tv_weight: weight of total variation regularization term
- init_random: initialize the starting image to uniform random noise
"""
# Extract features for the content image
content_img = preprocess(PIL.Image.open(content_image), size=image_size)
feats = extract_features(content_img, cnn)
content_target = feats[content_layer].clone()
# Extract features for the style image
style_img = preprocess(PIL.Image.open(style_image), size=style_size)
feats = extract_features(style_img, cnn)
style_targets = []
for idx in style_layers:
style_targets.append(gram_matrix(feats[idx].clone()))
# Initialize output image to content image or nois
if init_random:
img = torch.Tensor(content_img.size()).uniform_(0, 1).type(dtype)
else:
img = content_img.clone().type(dtype)
# We do want the gradient computed on our image!
img.requires_grad_()
# Set up optimization hyperparameters
initial_lr = 3.0
decayed_lr = 0.1
decay_lr_at = 180
# Note that we are optimizing the pixel values of the image by passing
# in the img Torch tensor, whose requires_grad flag is set to True
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam([img], lr=initial_lr)
f, axarr = plt.subplots(1,2)
axarr[0].axis('off')
axarr[1].axis('off')
axarr[0].set_title('Content Source Img.')
axarr[1].set_title('Style Source Img.')
axarr[0].imshow(deprocess(content_img.cpu()))
axarr[1].imshow(deprocess(style_img.cpu()))
plt.show()
plt.figure()
for t in range(200):
if t < 190:
img.data.clamp_(-1.5, 1.5)
optimizer.zero_grad()
feats = extract_features(img, cnn)
# Compute loss
c_loss = content_loss(content_weight, feats[content_layer], content_target)
s_loss = style_loss(feats, style_layers, style_targets, style_weights)
t_loss = tv_loss(img, tv_weight)
loss = c_loss + s_loss + t_loss
loss.backward()
# Perform gradient descents on our image values
if t == decay_lr_at:
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam([img], lr=decayed_lr)
optimizer.step()
if t % 100 == 0:
print('Iteration {}'.format(t))
plt.axis('off')
plt.imshow(deprocess(img.data.cpu()))
plt.show()
print('Iteration {}'.format(t))
plt.axis('off')
plt.imshow(deprocess(img.data.cpu()))
plt.show()最后是生成梵高风格的建筑图片:
# Starry Night + Tubingen
params3 = {
'content_image' : 'styles/tubingen.jpg',
'style_image' : 'styles/starry_night.jpg',
'image_size' : 192,
'style_size' : 192,
'content_layer' : 3,
'content_weight' : 6e-2,
'style_layers' : [1, 4, 6, 7],
'style_weights' : [300000, 1000, 15, 3],
'tv_weight' : 2e-2
}
style_transfer(**params3)生成的结果如下: