一篇文章吃透:为什么加载数据库驱动要用Class.forName()
1、Class.forName()和ClassLoader.loadClass()和new XX的区别
Class.forName():将类的.class文件加载到jvm中之外,还会对类进行解释,执行类中的static代码块。
ClassLoader.loadClass():只会将.class文件加载到jvm中,不会执行static中的内容,只有在newInstance才会去执行static块。
《深入理解Java虚拟机》p214讲类的加载过程:加载、验证、准备、解析和初始化。
其中
加载:主要在内存中生成class文件对应的Class对象,作为方法区这个类各种数据的访问入口。
验证:验证Class文件的字节流中的信息符合当前虚拟机的要求,并且不会危害虚拟机自身安全。
准备:为类变量分配内存并设置类变量的初始值。
解析:常量池中的符号引用替换为直接引用。
初始化:初始化阶段才开始执行类中定义的Java程序代码。
我们看Class.forName源码
@CallerSensitive
public static Class forName(String className)
throws ClassNotFoundException {
Class caller = Reflection.getCallerClass();
return forName0(className, true, ClassLoader.getClassLoader(caller), caller);
}
调用了三个参数的重载的方法
/**
* Returns the {@code Class} object associated with the class or
* interface with the given string name, using the given class loader.
* Given the fully qualified name for a class or interface (in the same
* format returned by {@code getName}) this method attempts to
* locate, load, and link the class or interface. The specified class
* loader is used to load the class or interface. If the parameter
* {@code loader} is null, the class is loaded through the bootstrap
* class loader. The class is initialized only if the
* {@code initialize} parameter is {@code true} and if it has
* not been initialized earlier.
*
* If {@code name} denotes a primitive type or void, an attempt
* will be made to locate a user-defined class in the unnamed package whose
* name is {@code name}. Therefore, this method cannot be used to
* obtain any of the {@code Class} objects representing primitive
* types or void.
*
*
If {@code name} denotes an array class, the component type of
* the array class is loaded but not initialized.
*
*
For example, in an instance method the expression:
*
*
* {@code Class.forName("Foo")}
*
*
* is equivalent to:
*
*
* {@code Class.forName("Foo", true, this.getClass().getClassLoader())}
*
*
* Note that this method throws errors related to loading, linking or
* initializing as specified in Sections 12.2, 12.3 and 12.4 of The
* Java Language Specification.
* Note that this method does not check whether the requested class
* is accessible to its caller.
*
* If the {@code loader} is {@code null}, and a security
* manager is present, and the caller's class loader is not null, then this
* method calls the security manager's {@code checkPermission} method
* with a {@code RuntimePermission("getClassLoader")} permission to
* ensure it's ok to access the bootstrap class loader.
*
* @param name fully qualified name of the desired class
* @param initialize if {@code true} the class will be initialized.
* See Section 12.4 of The Java Language Specification.
* @param loader class loader from which the class must be loaded
* @return class object representing the desired class
*
* @exception LinkageError if the linkage fails
* @exception ExceptionInInitializerError if the initialization provoked
* by this method fails
* @exception ClassNotFoundException if the class cannot be located by
* the specified class loader
*
* @see java.lang.Class#forName(String)
* @see java.lang.ClassLoader
* @since 1.2
*/
@CallerSensitive
public static Class forName(String name, boolean initialize,
ClassLoader loader)
throws ClassNotFoundException
{
Class caller = null;
SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
// Reflective call to get caller class is only needed if a security manager
// is present. Avoid the overhead of making this call otherwise.
caller = Reflection.getCallerClass();
if (sun.misc.VM.isSystemDomainLoader(loader)) {
ClassLoader ccl = ClassLoader.getClassLoader(caller);
if (!sun.misc.VM.isSystemDomainLoader(ccl)) {
sm.checkPermission(
SecurityConstants.GET_CLASSLOADER_PERMISSION);
}
}
}
return forName0(name, initialize, loader, caller);
}
提示我们第二个参数表示是否初始化,看java参考手册
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/specs/jls/se8/html/jls-12.html#jls-12.4
new可以理解粗略的理解为: 【加载class文件到jvm + 初始化static代码块】(Class.forName) +构造实例(newInstance)
/**
* Creates a new instance of the class represented by this {@code Class}
* object. The class is instantiated as if by a {@code new}
* expression with an empty argument list. The class is initialized if it
* has not already been initialized.
*
* Note that this method propagates any exception thrown by the
* nullary constructor, including a checked exception. Use of
* this method effectively bypasses the compile-time exception
* checking that would otherwise be performed by the compiler.
* The {@link
* java.lang.reflect.Constructor#newInstance(java.lang.Object...)
* Constructor.newInstance} method avoids this problem by wrapping
* any exception thrown by the constructor in a (checked) {@link
* java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException}.
*
* @return a newly allocated instance of the class represented by this
* object.
* @throws IllegalAccessException if the class or its nullary
* constructor is not accessible.
* @throws InstantiationException
* if this {@code Class} represents an abstract class,
* an interface, an array class, a primitive type, or void;
* or if the class has no nullary constructor;
* or if the instantiation fails for some other reason.
* @throws ExceptionInInitializerError if the initialization
* provoked by this method fails.
* @throws SecurityException
* If a security manager, s, is present and
* the caller's class loader is not the same as or an
* ancestor of the class loader for the current class and
* invocation of {@link SecurityManager#checkPackageAccess
* s.checkPackageAccess()} denies access to the package
* of this class.
*/
@CallerSensitive
public T newInstance()
throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException
{
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
checkMemberAccess(Member.PUBLIC, Reflection.getCallerClass(), false);
}
// NOTE: the following code may not be strictly correct under
// the current Java memory model.
// Constructor lookup
if (cachedConstructor == null) {
if (this == Class.class) {
throw new IllegalAccessException(
"Can not call newInstance() on the Class for java.lang.Class"
);
}
try {
Class[] empty = {};
final Constructor c = getConstructor0(empty, Member.DECLARED);
// Disable accessibility checks on the constructor
// since we have to do the security check here anyway
// (the stack depth is wrong for the Constructor's
// security check to work)
java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(
new java.security.PrivilegedAction() {
public Void run() {
c.setAccessible(true);
return null;
}
});
cachedConstructor = c;
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw (InstantiationException)
new InstantiationException(getName()).initCause(e);
}
}
Constructor tmpConstructor = cachedConstructor;
// Security check (same as in java.lang.reflect.Constructor)
int modifiers = tmpConstructor.getModifiers();
if (!Reflection.quickCheckMemberAccess(this, modifiers)) {
Class caller = Reflection.getCallerClass();
if (newInstanceCallerCache != caller) {
Reflection.ensureMemberAccess(caller, this, null, modifiers);
newInstanceCallerCache = caller;
}
}
// Run constructor
try {
return tmpConstructor.newInstance((Object[])null);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
Unsafe.getUnsafe().throwException(e.getTargetException());
// Not reached
return null;
}
}
其中根据newInstance是创建一个代表这个类对象的实例,如果没有初始化会触发初始化。
代码的主要逻辑是查找无参数构造方法,然后通过反射来调用构造实例。
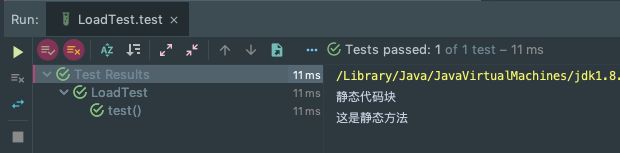
写个测试类验证一下:
/**
* 加载测试demo类
*
* @author: 明明如月 [email protected]
* @date: 2019-04-09 12:43
*/
public class LoadTestClass {
static {
System.out.println("静态代码块");
}
public LoadTestClass() {
System.out.println("构造方法");
}
public static void test() {
System.out.println("这是静态方法");
}
}测试类
/**
* 加载测试类
*
* @author: 明明如月 [email protected]
* @date: 2019-04-09 12:42
*/
public class LoadTest {
@Test
public void test(){
LoadTestClass.test();
}
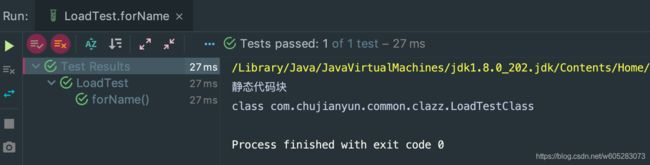
@Test
public void forName() throws ClassNotFoundException {
Class aClass = Class.forName("com.chujianyun.common.clazz.LoadTestClass");
System.out.println(aClass);
}
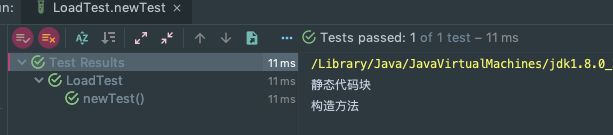
@Test
public void newTest() {
new LoadTestClass();
}
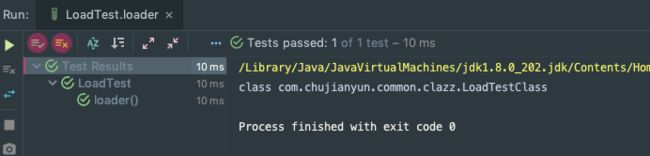
@Test
public void loader() throws ClassNotFoundException {
Class aClass = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader().loadClass("com.chujianyun.common.clazz.LoadTestClass");
System.out.println(aClass);
}
@Test
public void loaderNewInstance() throws ClassNotFoundException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {
Class aClass = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader().loadClass("com.chujianyun.common.clazz.LoadTestClass");
System.out.println(aClass);
Object result = aClass.newInstance();
System.out.println(result instanceof LoadTestClass);
}
}
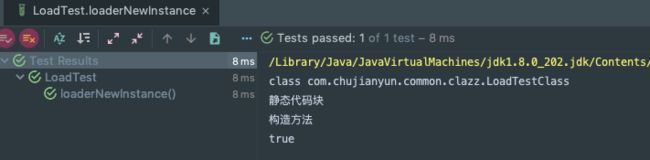
测试类分别输出:
另外可以看到调用静态方法前,会触发静态代码块的调用(也会触发类的加载)。
二、为什么加载数据库驱动要用Class.forName()?
其实JDBC4.0以后(mysql-connector-java 5.1.6之后) + java6以后,不再需要显示调用Class.forName()加载驱动了。
下面是摘录的一段话,简单明了:
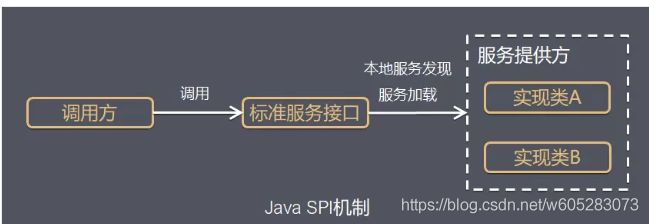
JDBC 4.0的特性
得益于Mustang中的Java SE 服务提供商机制,Java开发人员再也不必用类似Class.forName() 的代码注册JDBC驱动来明确加载JDBC。当调用DriverManager.getConnection()方法时,DriverManager类将 自动设置合适的驱动程序。该特性向后兼容,因此无需对现有的JDBC代码作任何改动。
https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/j-lo-jse65/#N100EE
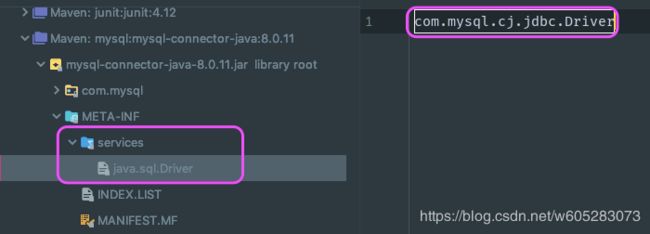
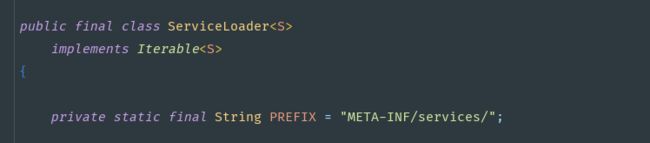
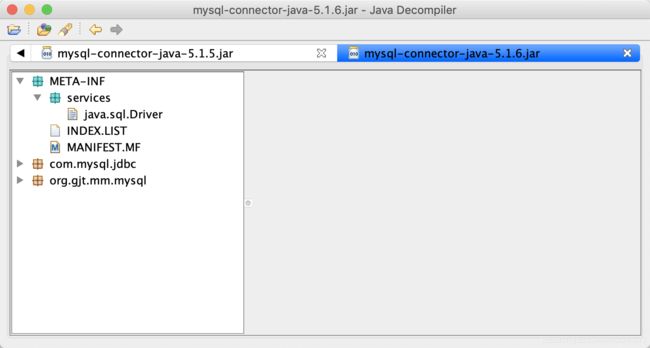
JDBC 4.0 的规范规定,所有 JDBC 4.0 的驱动 jar 文件必须包含一个
java.sql.Driver,它位于 jar 文件的 META-INF/services 目录下
接下来详细展开:
以mysql驱动 8.0.11为例,采用了SPI机制(这里不展开,详细了解可参考这篇文章:https://juejin.im/post/5af952fdf265da0b9e652de3)
Java SPI 实际上是“基于接口的编程+策略模式+配置文件”组合实现的动态加载机制。
使用时可以这么写:
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test";
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password);
package com.mysql.cj.jdbc;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class Driver extends NonRegisteringDriver implements java.sql.Driver {
public Driver() throws SQLException {
}
static {
try {
DriverManager.registerDriver(new Driver());
} catch (SQLException var1) {
throw new RuntimeException("Can't register driver!");
}
}
}
驱动的类静态代码块中,调用DriverManager的注册驱动方法new一个自己当参数传给驱动管理器。
public static synchronized void registerDriver(java.sql.Driver driver)
throws SQLException {
registerDriver(driver, null);
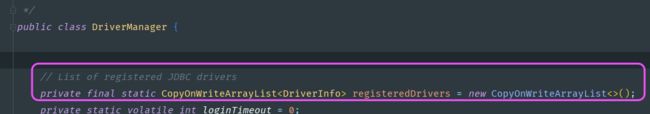
}另外最关键的是,驱动管理器的静态代码块有加载初始化驱动的方法
/**
* Load the initial JDBC drivers by checking the System property
* jdbc.properties and then use the {@code ServiceLoader} mechanism
*/
static {
loadInitialDrivers();
println("JDBC DriverManager initialized");
}
private static void loadInitialDrivers() {
String drivers;
try {
drivers = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction() {
public String run() {
return System.getProperty("jdbc.drivers");
}
});
} catch (Exception ex) {
drivers = null;
}
// If the driver is packaged as a Service Provider, load it.
// Get all the drivers through the classloader
// exposed as a java.sql.Driver.class service.
// ServiceLoader.load() replaces the sun.misc.Providers()
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction() {
public Void run() {
ServiceLoader loadedDrivers = ServiceLoader.load(Driver.class);
Iterator driversIterator = loadedDrivers.iterator();
/* Load these drivers, so that they can be instantiated.
* It may be the case that the driver class may not be there
* i.e. there may be a packaged driver with the service class
* as implementation of java.sql.Driver but the actual class
* may be missing. In that case a java.util.ServiceConfigurationError
* will be thrown at runtime by the VM trying to locate
* and load the service.
*
* Adding a try catch block to catch those runtime errors
* if driver not available in classpath but it's
* packaged as service and that service is there in classpath.
*/
try{
while(driversIterator.hasNext()) {
driversIterator.next();
}
} catch(Throwable t) {
// Do nothing
}
return null;
}
});
println("DriverManager.initialize: jdbc.drivers = " + drivers);
if (drivers == null || drivers.equals("")) {
return;
}
String[] driversList = drivers.split(":");
println("number of Drivers:" + driversList.length);
for (String aDriver : driversList) {
try {
println("DriverManager.Initialize: loading " + aDriver);
Class.forName(aDriver, true,
ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader());
} catch (Exception ex) {
println("DriverManager.Initialize: load failed: " + ex);
}
}
} 先查找 jdbc.drivers 属性的指,然后SPI机制查找驱动
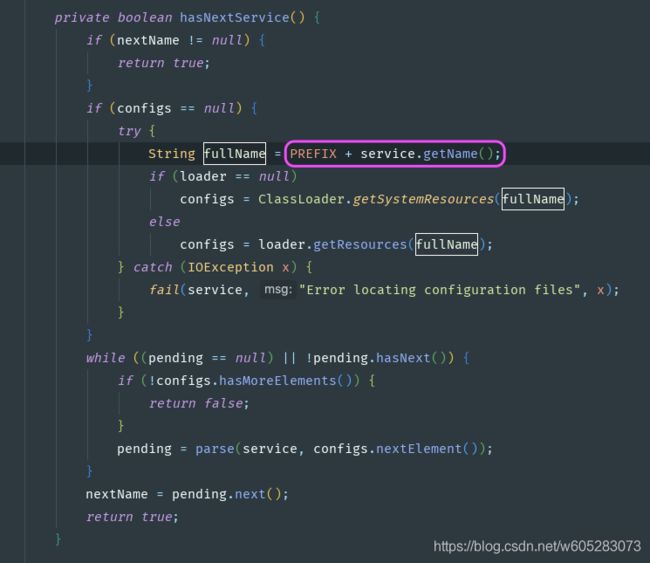
ServiceLoader loadedDrivers = ServiceLoader.load(Driver.class); 可以研究下ServiceLoader的源码
可以看到加载META-INF/services/ 文件夹下类名为文件名(这里相当于Driver.class.getName())的资源,然后将其加载到虚拟机。
注释有这么一句“Load these drivers, so that they can be instantiated.” 意思是加载SPI扫描到的驱动来触发他们的初始化。既触发他们的static代码块,既
既
/**
* Registers the given driver with the {@code DriverManager}.
* A newly-loaded driver class should call
* the method {@code registerDriver} to make itself
* known to the {@code DriverManager}. If the driver is currently
* registered, no action is taken.
*
* @param driver the new JDBC Driver that is to be registered with the
* {@code DriverManager}
* @param da the {@code DriverAction} implementation to be used when
* {@code DriverManager#deregisterDriver} is called
* @exception SQLException if a database access error occurs
* @exception NullPointerException if {@code driver} is null
* @since 1.8
*/
public static synchronized void registerDriver(java.sql.Driver driver,
DriverAction da)
throws SQLException {
/* Register the driver if it has not already been added to our list */
if(driver != null) {
registeredDrivers.addIfAbsent(new DriverInfo(driver, da));
} else {
// This is for compatibility with the original DriverManager
throw new NullPointerException();
}
println("registerDriver: " + driver);
}将自己注册到 驱动管理器的驱动列表中
然后调用驱动管理器的获取连接方法时从这里列表(registeredDrivers)中取
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password);调用 Url,用户名和密码三个参数的获取连接的方法
@CallerSensitive
public static Connection getConnection(String url,
String user, String password) throws SQLException {
java.util.Properties info = new java.util.Properties();
if (user != null) {
info.put("user", user);
}
if (password != null) {
info.put("password", password);
}
return (getConnection(url, info, Reflection.getCallerClass()));
}具体又调用如下私有方法
// Worker method called by the public getConnection() methods.
private static Connection getConnection(
String url, java.util.Properties info, Class caller) throws SQLException {
/*
* When callerCl is null, we should check the application's
* (which is invoking this class indirectly)
* classloader, so that the JDBC driver class outside rt.jar
* can be loaded from here.
*/
ClassLoader callerCL = caller != null ? caller.getClassLoader() : null;
synchronized(DriverManager.class) {
// synchronize loading of the correct classloader.
if (callerCL == null) {
callerCL = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
}
}
if(url == null) {
throw new SQLException("The url cannot be null", "08001");
}
println("DriverManager.getConnection(\"" + url + "\")");
// Walk through the loaded registeredDrivers attempting to make a connection.
// Remember the first exception that gets raised so we can reraise it.
SQLException reason = null;
for(DriverInfo aDriver : registeredDrivers) {
// If the caller does not have permission to load the driver then
// skip it.
if(isDriverAllowed(aDriver.driver, callerCL)) {
try {
println(" trying " + aDriver.driver.getClass().getName());
Connection con = aDriver.driver.connect(url, info);
if (con != null) {
// Success!
println("getConnection returning " + aDriver.driver.getClass().getName());
return (con);
}
} catch (SQLException ex) {
if (reason == null) {
reason = ex;
}
}
} else {
println(" skipping: " + aDriver.getClass().getName());
}
}
// if we got here nobody could connect.
if (reason != null) {
println("getConnection failed: " + reason);
throw reason;
}
println("getConnection: no suitable driver found for "+ url);
throw new SQLException("No suitable driver found for "+ url, "08001");
}
其中又判断调用者是否有权限加载驱动类,如果没有就忽略(利用Class.forName尝试加载,加载失败则忽略))从前往后找到第一个可以构造Connection的对象就返回。
private static boolean isDriverAllowed(Driver driver, ClassLoader classLoader) {
boolean result = false;
if(driver != null) {
Class aClass = null;
try {
aClass = Class.forName(driver.getClass().getName(), true, classLoader);
} catch (Exception ex) {
result = false;
}
result = ( aClass == driver.getClass() ) ? true : false;
}
return result;
}因此在调用
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password);这个静态函数前, DriverManager的静态代码块已经被执行,既已经通过SPI机制讲驱动注入到驱动列表中,因此无需在之前调用一次Class.forName。
由于JDBC 4.0之前并没有采用SPI机制也没有用static代码块讲自己注册到驱动管理器的驱动列表中,另外配套的Java版本好像也比较低(是为了适配jdk5),对应的驱动管理器代码和现在也不一样。因此需要手动调用Class.forName来加载class文件到jvm并初始化。
JDK6之后提供了SPI机制,另外mysql-connector-java 5.1.6之后采用了SPI方式编写驱动。
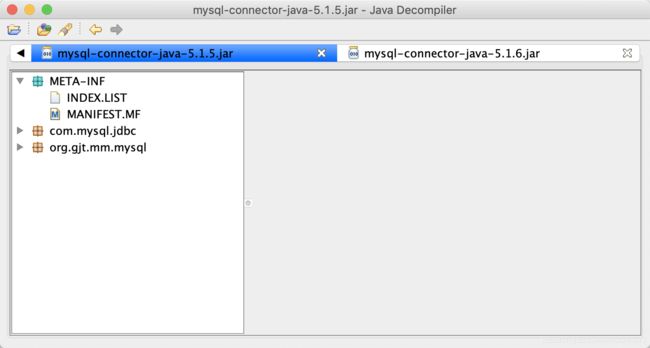
以下是5.1.5版本的结构
5.1.6版本的结构
参考文章:
https://blog.csdn.net/w369033345/article/details/54173818
https://www.cnblogs.com/gaojing/archive/2012/03/15/2413638.html
https://blog.csdn.net/fengyuzhengfan/article/details/38086743
http://www.runoob.com/w3cnote/java-class-forname.html