基于SVM的cifar10分类
备注:阅读博客后的笔记,代码来自他人博客。
1. 基于线性SVM的cifar10图像分类
博客为:svm实现图片分类(python) 博客对应的代码仓库:https://github.com/452896915/cs231n_course_homework
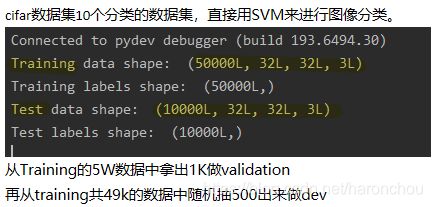
1.1 cifar10数据集的构成:http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar.html
数据集训练集有5个batch: 每个batch为10k数据。测试集有一个batch,10k数据。带有标签。分类的图像都是32×32×3。
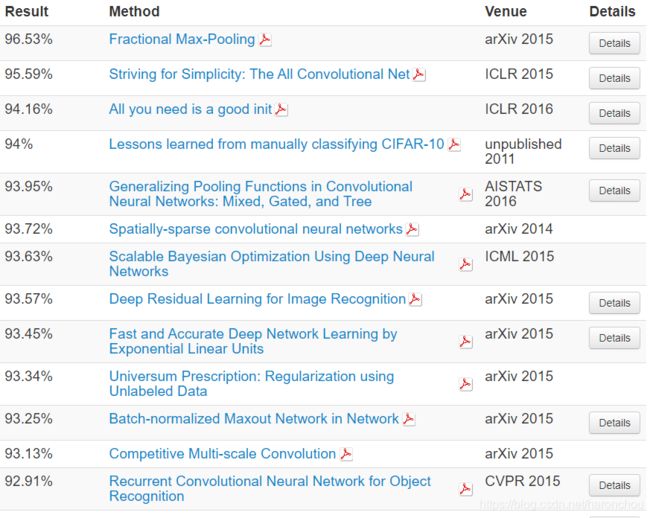
1.2 当前的result
cifar10目前的测试集准确率到了什么水平呢?
参看网站排名:http://rodrigob.github.io/are_we_there_yet/build/classification_datasets_results.html#43494641522d3130
1.3 基于线性SVM的图片分类
https://blog.csdn.net/red_stone1/article/details/80661133 更好的线性SVM的博客
博客为:svm实现图片分类(python) 博客对应的代码仓库:https://github.com/452896915/cs231n_course_homework
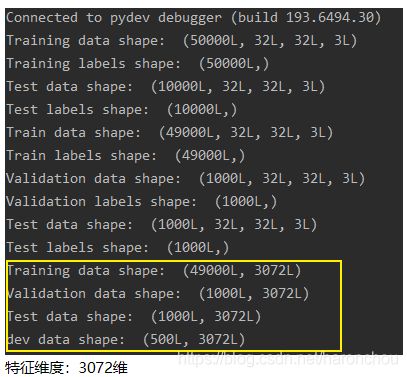
- 方法原理:将32×32×3的图像直接作为SVM的输入,输入特征就有:3072维度,每个Pixel作为一个特征。即不进行手工特征提取。
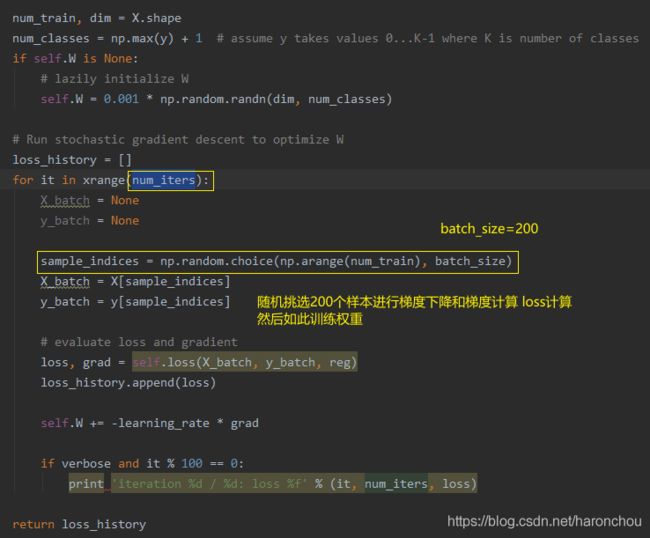
- 线性SVM分类器为博主自己写的,重点理解了Hinge Loss和gradient梯度推导,进一步理解了SVM多分类的原理。
- 小批量200的随机梯度下降。
- 数据在送入SVM之前,都减去了training的50k个样本的均值,即减去了所有样本的平均值。
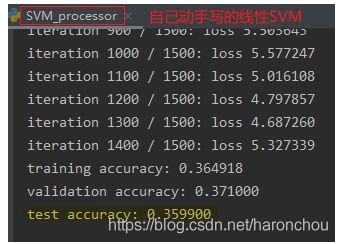
- 对于分类问题的训练误差讨论的指标都是:accuracy=0.35,准确率,而不是训练误差。
- 特征3072维,训练样本数50k,基本上不存在过拟合。同时训练误差与测试误差基本上一致,都高于human误差,所以结果是模型欠拟合。
- 可以根据样本的规模画出学习曲线,accuracy随着样本规模的变化规律!
- 所以,现在基本上是欠拟合的状态。所以增大样本基本上不再有变化了。
- 需要更多的特征
- 尝试更复杂的模型
- 减小正则化
1.4 基于HOG+SVM的cifar10的图像分类
python实现HOG+SVM对CIFAR-10数据集分类
比1.3的直接将32*32*3的图像扔进SVM相比,这个先提取HOG特征,再进入SVM
- 3通道彩色图->单通道灰度图,得到灰度图的HOG
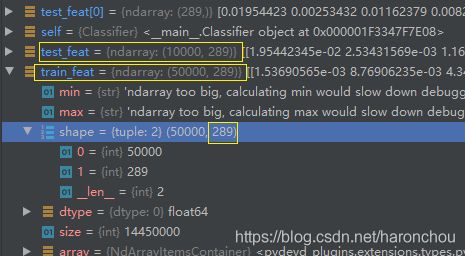
- HOG特征维度为288,最后一维为分类的标签。
- 32*32的HOG提取维度应该为36*9=324维度。
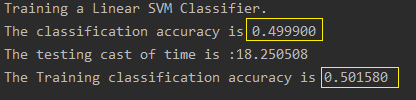
- 训练集的准确率才0.50,测试集的准确率为0.49.
- 所以泛化误差基本不存在的,模型仍然是欠拟合。需要更复杂的特征、更复杂的网络等。
(1)之前的特征为3720维度,但是是原始的pixel作为特征,可以看出仍然欠拟合,所以是特征不够好!
(2)现在的特征维度为288,但是在训练集的准确率增加到0.5,之前为0.36。更少的维度获取到更高的准确率
(3)两个模型下的泛化误差基本等于训练误差,所以仍然是模型欠拟合的问题。
- 欠拟合问题需要更复杂的模型、更好的特征表示、正则化不要太强。
(4)288维度的HOG特征相比于3720的Pixel特征,准确率却提升了14%,所以特征相当重要,但是这样的分类效率对于Human error来说,还是不够,所以需要神经网络。
稍微更改了读取数据的那一部分代码:
import os
import cv2
import math
import time
import numpy as np
import tqdm
from skimage.feature import hog
from sklearn.svm import LinearSVC
class Classifier(object):
def __init__(self, filePath):
self.filePath = filePath
def unpickle(self, file):
import pickle
with open(file, 'rb') as fo:
dict = pickle.load(fo, encoding='bytes')
return dict
def get_data(self):
TrainData = []
TestData = []
for b in range(1,6):
f = os.path.join(self.filePath, 'data_batch_%d' % (b, ))
data = self.unpickle(f)
train = np.reshape(data[b'data'], (10000, 3, 32 * 32))
labels = np.reshape(data[b'labels'], (10000, 1))
fileNames = np.reshape(data[b'filenames'], (10000, 1))
datalebels = zip(train, labels, fileNames)
TrainData.extend(datalebels)
f = os.path.join(self.filePath,'test_batch')
data = self.unpickle(f)
test = np.reshape(data[b'data'], (10000, 3, 32 * 32))
labels = np.reshape(data[b'labels'], (10000, 1))
fileNames = np.reshape(data[b'filenames'], (10000, 1))
TestData.extend(zip(test, labels, fileNames))
'''
for childDir in os.listdir(self.filePath):
if 'data_batch' in childDir:
f = os.path.join(self.filePath, childDir)
data = self.unpickle(f)
# train = np.reshape(data[str.encode('data')], (10000, 3, 32 * 32))
# If your python version do not support to use this way to transport str to bytes.
# Think another way and you can.
train = np.reshape(data[b'data'], (10000, 3, 32 * 32))
labels = np.reshape(data[b'labels'], (10000, 1))
fileNames = np.reshape(data[b'filenames'], (10000, 1))
datalebels = zip(train, labels, fileNames)
TrainData.extend(datalebels)
if childDir == "test_batch":
f = os.path.join(self.filePath, childDir)
data = self.unpickle(f)
test = np.reshape(data[b'data'], (10000, 3, 32 * 32))
labels = np.reshape(data[b'labels'], (10000, 1))
fileNames = np.reshape(data[b'filenames'], (10000, 1))
TestData.extend(zip(test, labels, fileNames))
'''
print("data read finished!")
return TrainData, TestData
def get_hog_feat(self, image, stride=8, orientations=8, pixels_per_cell=(8, 8), cells_per_block=(2, 2)):
cx, cy = pixels_per_cell
bx, by = cells_per_block
sx, sy = image.shape
n_cellsx = int(np.floor(sx // cx)) # number of cells in x
n_cellsy = int(np.floor(sy // cy)) # number of cells in y
n_blocksx = (n_cellsx - bx) + 1
n_blocksy = (n_cellsy - by) + 1
gx = np.zeros((sx, sy), dtype=np.float32)
gy = np.zeros((sx, sy), dtype=np.float32)
eps = 1e-5
grad = np.zeros((sx, sy, 2), dtype=np.float32)
for i in range(1, sx-1):
for j in range(1, sy-1):
gx[i, j] = image[i, j-1] - image[i, j+1]
gy[i, j] = image[i+1, j] - image[i-1, j]
grad[i, j, 0] = np.arctan(gy[i, j] / (gx[i, j] + eps)) * 180 / math.pi
if gx[i, j] < 0:
grad[i, j, 0] += 180
grad[i, j, 0] = (grad[i, j, 0] + 360) % 360
grad[i, j, 1] = np.sqrt(gy[i, j] ** 2 + gx[i, j] ** 2)
normalised_blocks = np.zeros((n_blocksy, n_blocksx, by * bx * orientations))
for y in range(n_blocksy):
for x in range(n_blocksx):
block = grad[y*stride:y*stride+16, x*stride:x*stride+16]
hist_block = np.zeros(32, dtype=np.float32)
eps = 1e-5
for k in range(by):
for m in range(bx):
cell = block[k*8:(k+1)*8, m*8:(m+1)*8]
hist_cell = np.zeros(8, dtype=np.float32)
for i in range(cy):
for j in range(cx):
n = int(cell[i, j, 0] / 45)
hist_cell[n] += cell[i, j, 1]
hist_block[(k * bx + m) * orientations:(k * bx + m + 1) * orientations] = hist_cell[:]
normalised_blocks[y, x, :] = hist_block / np.sqrt(hist_block.sum() ** 2 + eps)
return normalised_blocks.ravel()
def get_feat(self, TrainData, TestData):
train_feat = []
test_feat = []
for data in tqdm.tqdm(TestData):
image = np.reshape(data[0].T, (32, 32, 3))
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)/255.
fd = self.get_hog_feat(gray) #你可以用我写的hog提取函数,也可以用下面skimage提供的,我的速度会慢一些
# fd = hog(gray, 9, [8, 8], [2, 2])
fd = np.concatenate((fd, data[1]))
test_feat.append(fd)
test_feat = np.array(test_feat)
np.save("test_feat.npy", test_feat)
print("Test features are extracted and saved.")
for data in tqdm.tqdm(TrainData):
image = np.reshape(data[0].T, (32, 32, 3))
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) / 255.
fd = self.get_hog_feat(gray)
# fd = hog(gray, 9, [8, 8], [2, 2])
fd = np.concatenate((fd, data[1]))
train_feat.append(fd)
train_feat = np.array(train_feat)
np.save("train_feat.npy", train_feat)
print("Train features are extracted and saved.")
return train_feat, test_feat
def classification(self, train_feat, test_feat):
t0 = time.time()
clf = LinearSVC()
print("Training a Linear SVM Classifier.")
clf.fit(train_feat[:, :-1], train_feat[:, -1])
predict_result = clf.predict(test_feat[:, :-1])
num = 0
for i in range(len(predict_result)):
if int(predict_result[i]) == int(test_feat[i, -1]):
num += 1
rate = float(num) / len(predict_result)
t1 = time.time()
print('The testing classification accuracy is %f' % rate)
print('The testing cast of time is :%f' % (t1 - t0))
predict_result2 = clf.predict(train_feat[:, :-1])
num2 = 0
for i in range(len(predict_result2)):
if int(predict_result2[i]) == int(train_feat[i, -1]):
num2 += 1
rate2 = float(num2) / len(predict_result2)
print('The Training classification accuracy is %f' % rate2)
def run(self):
if os.path.exists("train_feat.npy") and os.path.exists("test_feat.npy"):
train_feat = np.load("train_feat.npy")
test_feat = np.load("test_feat.npy")
else:
TrainData, TestData = self.get_data()
train_feat, test_feat = self.get_feat(TrainData, TestData)
self.classification(train_feat, test_feat)
if __name__ == '__main__':
#filePath = r'F:\DataSets\cifar-10-batches-py'
filePath = r'.\datasets'
cf = Classifier(filePath)
cf.run()