线程和锁总结(第一周)
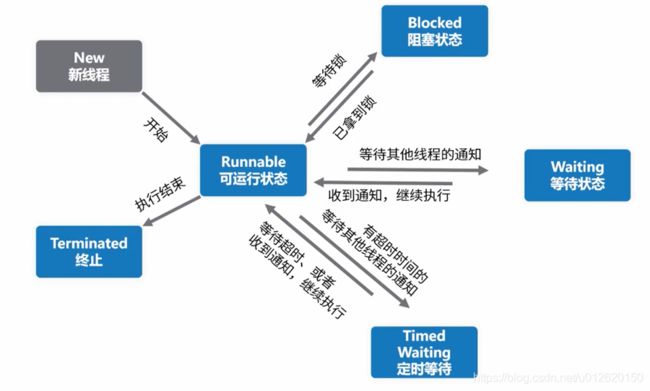
1.线程的状态:
New 、Runnable 、Blocked 、Waiting 、Timed Waiting 、Terminated
public class TestThreadState {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// thread1 执行start方法之前的状态:NEW
// thread1 执行run 方法的状态:RUNNABLE
// thread1 执行start方法之后的状态:TERMINATED
Thread thread1 = new Thread(() -> System.out.println("thread1 执行run 方法的状态:"+Thread.currentThread().getState()));
System.out.println("thread1 执行start方法之前的状态:"+thread1.getState());
thread1.start();
Thread.sleep(2000);
System.out.println("thread1 执行start方法之后的状态:"+thread1.getState());
System.out.println("======================================");
// thread2 执行start方法之前的状态:NEW
// thread2 sleep 之前的状态:RUNNABLE
// thread2 执行start方法之后的状态:TIMED_WAITING
// thread2 sleep 之后的状态:RUNNABLE
// 休眠3S后thread2的状态:TERMINATED
Thread thread2 = new Thread(() ->{
System.out.println("thread2 sleep 之前的状态:"+Thread.currentThread().getState());
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("thread2 sleep 之后的状态:"+Thread.currentThread().getState());
});
System.out.println("thread2 执行start方法之前的状态:"+thread2.getState());
thread2.start();
Thread.sleep(200);
System.out.println("thread2 执行start方法之后的状态:"+thread2.getState());
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println("休眠3S后thread2的状态:"+thread2.getState());
System.out.println("============================");
//thread3 执行start方法之前的状态:NEW
//thread3 执行start方法之后的状态:RUNNABLE
//休眠200 ms之后,thread3 的状态:BLOCKED
//thread3 调用run的状态:RUNNABLE
//休眠2000ms之后,thread3 的状态:TERMINATED
Thread thread3 = new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (TestThreadState.class){
System.out.println("thread3 调用run的状态:"+Thread.currentThread().getState());
}
});
System.out.println("thread3 执行start方法之前的状态:"+thread3.getState());
synchronized (TestThreadState.class){
thread3.start();
System.out.println("thread3 执行start方法之后的状态:"+thread3.getState());
Thread.sleep(200);
System.out.println("休眠200 ms之后,thread3 的状态:"+thread3.getState());
}
Thread.sleep(2000);
System.out.println("休眠2000ms之后,thread3 的状态:"+thread3.getState());
}
}
- 线程的中止:
2.1 stop()方法,此方法线程不安全,不推荐此用法
2.2 interrupt() 方法,会抛InterruptedException异常,执行异常之后的代码,推荐此用法
1.创建Runnable, i 和 j 自增:
public class StopRunnable implements Runnable {
int i,j;
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (StopRunnable.class){
i++;
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
j++;
}
}
public void compareValue(){
System.out.println("i 的值为 : " + i);
System.out.println("j 的值为 : " + j);
}
}
- 分别调用 stop() 和 interrupt() 方法,看执行结果:
public class TestInterrupt {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StopRunnable stopRunnable = new StopRunnable();
Thread stopThread = new Thread(stopRunnable);
stopThread.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//i 和 j 的值可能不一样,线程不安全,不推荐此用法
// stopThread.stop();
//i 和 j 的值一样,会抛InterruptedException异常,执行异常之后的代码,推荐此用法
stopThread.interrupt();
while (stopThread.isAlive()){
//死循环,等待stopThread状态为 Terminated
}
stopRunnable.compareValue();
}
}
3.线程封闭的具体实现:
ThreadLocal 和 栈封闭(局部变量)


public class TestThreadLocal {
private static String value = "";
/**
* 执行结果
* main中value 的值是:garfield
* threadLocal 中 value的值:cat
* value的值:garfield
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
value = "garfield";
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "中value 的值是:" + value);
ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<String>() {
@Override
public void set(String value) {
value = "cat";
System.out.println("threadLocal 中 value的值:" + value);
}
@Override
protected String initialValue() {
value = "tree";
System.out.println("threadLocal 中initialValue里的value的值:" + value);
return value;
}
};
threadLocal.set(value);
System.out.println("value的值:" + value);
}
}
4.线程操作的定义
write() 、read() 、lock()、unLock()、外部操作和启动停止。

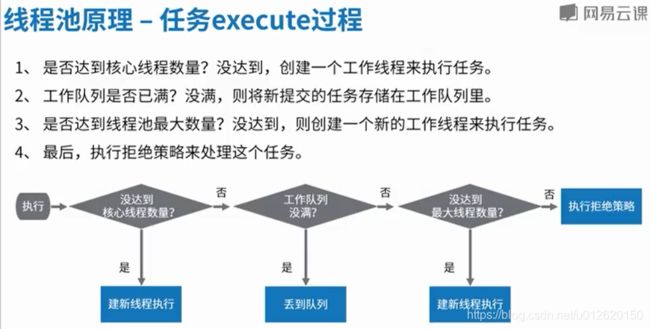
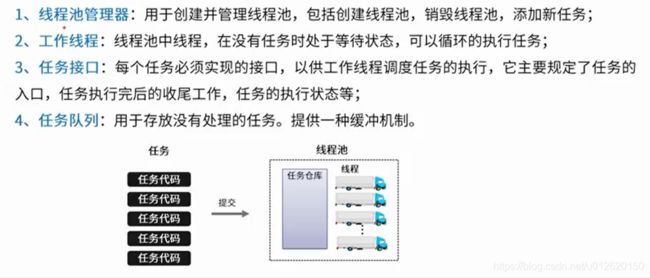
5.线程池

6.线程的唤醒
方式一:suspend() 和 resume() ,已废弃
方式二:wait() 和 notify()、notifyAll(),Thread的方法
方式三:LockSupport.park() 和LockSupport.unPark()
/**
* @author jingliyuan
* @date 2020/8/10
* 创建三个线程,交替循环从1打印到100
* 1,判断条件自增打印
* 2,通知其他线程
* 3,自己进入等待状态
*/
public class TestCount {
private static int count = 0;
private static String lock1 = "Lock1";
private static String lock2 = "Lock2";
private static String lock3 = "Lock3";
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread1 = new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (lock1){
while (count < 100){
count++;
try {
System.out.println("thread1 的count值:"+count);
synchronized (lock2){
lock2.notify();
}
lock1.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
synchronized (lock2){
lock2.notify();
}
}
});
Thread thread2 = new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (lock2){
try {
lock2.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
while (count < 100){
count++;
try {
System.out.println("thread2 的count值:"+count);
synchronized (lock3){
lock3.notify();
}
lock2.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
synchronized (lock3){
lock3.notify();
}
}
});
Thread thread3 = new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (lock3){
try {
lock3.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
while (count < 100){
count++;
try {
System.out.println("thread3 的count值:"+count);
synchronized (lock1){
lock1.notify();
}
lock3.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
synchronized (lock1){
lock1.notify();
}
}
});
// thread1.start();
// thread2.start();
// thread3.start();
testParkAndUnPark();
}
private static Thread thread1,thread2,thread3;
/**
* 创建三个线程,交替循环从1打印到100,使用park()和unpark(),不在同步代码块里不会死锁
*/
private static void testParkAndUnPark(){
thread1 = new Thread(() -> {
while (count < 100){
count++;
System.out.println("thread1 的count值:"+count);
LockSupport.unpark(thread2);
LockSupport.park();
}
LockSupport.unpark(thread2);
});
thread2 = new Thread(() -> {
LockSupport.park();
while (count < 100){
count++;
System.out.println("thread2 的count值:"+count);
LockSupport.unpark(thread3);
LockSupport.park();
}
LockSupport.unpark(thread3);
});
thread3 = new Thread(() -> {
LockSupport.park();
while (count < 100){
count++;
System.out.println("thread3 的count值:"+count);
LockSupport.unpark(thread1);
LockSupport.park();
}
LockSupport.unpark(thread1);
});
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread3.start();
}
}