AtCoder Grand Contest 021 B - Holes
题目链接:
AGC021B−Holes––––––––––––––––––– A G C 021 B − H o l e s _
题目大意:
简化一下题意:给 N N 个平面上的点,现在平面上任选一点放置一个机器人。这个机器人会走到离自己距离 (此距离指欧几里得距离) 最近的点,然后停下。问机器人到每个点停下的概率是多少?
数据范围:
1≤N≤100|xi|,|yi|≤106 1 ≤ N ≤ 100 | x i | , | y i | ≤ 10 6
解题思路:
先介绍一个函数— atan2() ;atan2 (y,x) ( y , x ) 返回值表示向量 (x,y) ( x , y ) 与 x x 轴正方向的夹角度数 (单位为弧度);取值范围为 (−π,+π] ( − π , + π ] 。
先说一个比较快 (但难写) 的做法一:
先求出这 N N 个点的凸包。显然凸包里面的点是没有概率的。为什么?
如果机器人在凸包外面,显然里面的点是没有机会得;虽然机器人在凸包里的时候会有一丢丢机会,但整个平面辣么大!算出的概率相当于没有。
对于凸包上的一个点,令其与相邻两点所成的夹角为 θ θ ,那么这个点的概率就是 (π−θ)/2π ( π − θ ) / 2 π 。
如图所示,就是外面那片区域。(中间那一点点无关紧要)
这个做法就是求个凸包,总复杂度 O(NlogN) O ( N l o g N ) 。
再说一个比较慢 (但好写) 的做法二:
这个就要用到 atan2() 函数了!
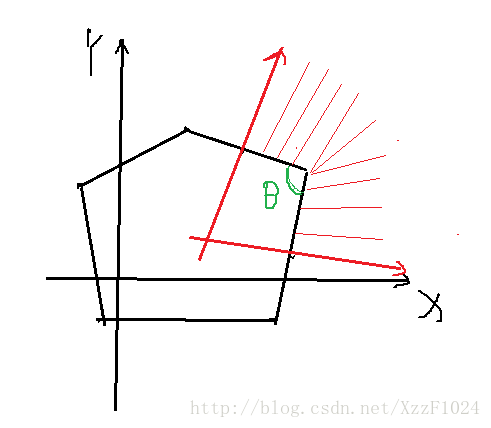
对于一个点 s s , 对该点到其余的点 atan2() 函数值进行排序。令相邻两个向量的夹角为 θ θ ,那么最后的答案 ans=max(θi−π,0)/2π(1≤i≤N) a n s = m a x ( θ i − π , 0 ) / 2 π ( 1 ≤ i ≤ N ) 。第 1 1 个向量和第 N N 个向量的夹角特判一下就好。
如图所示:

显然,在凸包里面的点,画一下就知道是莫得概率的。
总复杂度 O(N2logN) O ( N 2 l o g N )
做法一AC代码:
#include
做法二AC代码:
#include