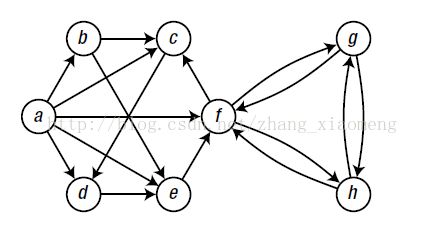
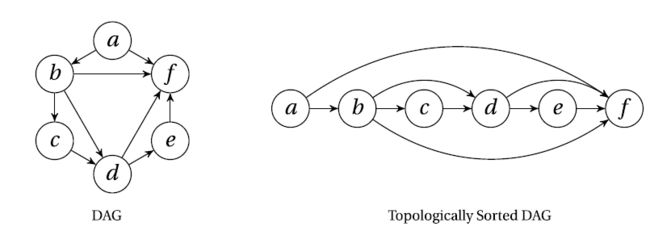
深度优先的时间戳与拓扑排序
我们为每个结点添加了时间戳,其中一种代表它被探索到的时间(探索开始时,标识为d)而另一种代表我们回溯到该节点的时间(探索完成时,标识为f)
清单5-7 带时间戳的深度优先搜索:
def dfs(G,s,d,f,S=None,t=0):
if S is None:S=set()
d[s]=t;t+=1
S.add(s)
for u in G[s]:
if u in S:continue
t=dfs(G,u,d,f,S,t)
f[s]=t;t+=1
return t
if __name__=="__main__":
from collections import defaultdict
a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i= range(9)
N = [
{b, c, d}, # a
{a, d}, # b
{a,d}, # c
{a,b,c}, # d
{g,f}, # e
{e,g}, # f
{e,f}, # g
{i}, # h
{h} #i
]
G=[{b,c,d,e,f},#a
{c,e},#b
{d},#c
{e},#d
{f},#e
{c,g,h},#f
{f,h},#g
{f,g}#h
]
d=defaultdict()
f=defaultdict()
t=dfs(G,0,d,f,S=None,t=0)
print("d:",d)
print("f:",f)
运行:
>>>
=== RESTART: D:\Program Files\Python\test\algorithms\Python算法教程\5-7-dfs.py ===
d: defaultdict(None, {0: 0, 1: 1, 2: 2, 3: 3, 4: 4, 5: 5, 6: 6, 7: 7})
f: defaultdict(None, {7: 8, 6: 9, 5: 10, 4: 11, 3: 12, 2: 13, 1: 14, 0: 15})
基于深度优先搜索的拓扑排序:
def dfs_topsort(G):
S,res=set(),[]
def recurse(u):
if u in S:return
S.add(u)
for v in G[u]:
recurse(v)
res.append(u)
for u in G:
recurse(u)
res.reverse()
return res
if __name__=="__main__":
a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i= range(9)
G={
'a':set('bf'),
'b':set('cdf'),
'c':set('d'),
'd':set('ef'),
'e':set('f'),
'f':set('')
}
res=dfs_topsort(G)
运行:
>>> res
['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f']