- 前言
- CHAPTER 1
- SECTION 1.1
- SECTION 1.2
- SECTION 1.3
- SECTION 1.4
- SECTION 1.5
- SECTION 1.6
前言
本文包含了 Computer Networking A Top-Down Approach, 7th Edition 中部分回顾性习题的问题与解答,主要参考了英文第7版和中文第7版的正文内容,欢迎各位的交流与指正!
CHAPTER 1
SECTION 1.1
R1. What is the difference between a host and an end system? List several different types of end systems. Is a Web server an end system?
- 在计算机网络中,二者的含义是相同的。
- 端系统列举:手机、平板电脑、环境传感器等
- 网络服务器是端系统
R2. The word protocol is often used to describe diplomatic relations. How does Wikipedia describe diplomatic protocol?
- There are two meanings of the word "protocol". In the legal sense, it is defined as an international agreement that supplements or amends a treaty. In the diplomatic sense, the term refers to the set of rules, procedures, conventions and ceremonies that relate to relations between states. In general, protocol represents the recognized and generally accepted system of international courtesy.
- “协议”一词有两种含义。从法律意义上讲,它被定义为补充或修正条约的国际协议。在外交意义上,该术语是指与国家之间的关系有关的一组规则,程序,公约和仪式。通常,协议代表国际公认和普遍接受的礼节制度。
R3. Why are standards important for protocols?
- 无标准,则无统一的数据收发规则,那么通信实体之间将难以交换信息。
SECTION 1.2
R4. List six access technologies. Classify each one as home access, enterprise access, or wide area wireless access.
-
home access
- FTTH,光纤到户
- cable
-
enterprise access
- 以太网
- WIFI
-
wide area wireless access
- 3G/4G
- LTE
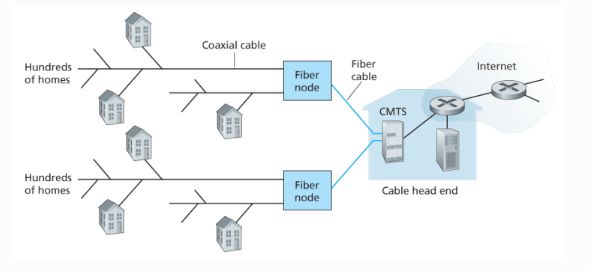
R5. Is HFC transmission rate dedicated or shared among users? Are collisions possible in a downstream HFC channel? Why or why not?
- 混合光纤同轴(Hybrid Fiber Coax, HFC)的传输率是共享的。
- 网络下行线路中会发生碰撞,因为多个家庭用户共享一个光纤节点和一条光缆。
R6. List the available residential access technologies in your city. For each type of access, provide the advertised downstream rate, upstream rate, and monthly price.
-
中国·武汉
类型 上行速率(Mbit/s) 下行速率(Mbit/s) 价格(元/年) FTTH 20 100 1000 FTTH 30 200 1200 FTTH 4 20 618 FTTH 10 50 1099 FTTH 20 100 1299
R7. What is the transmission rate of Ethernet LANs?
- 用户通常以100 Mbps或1 Gbps的速度接入太网交换机,而服务器可能具有1 Gbps甚至10 Gbps的接入速率。
R8. What are some of the physical media that Ethernet can run over?
- 双绞铜线
R9. Dial-up modems, HFC, DSL and FTTH are all used for residential access. For each of these access technologies, provide a range of transmission rates and comment on whether the transmission rate is shared or dedicated.
| access technology | upstream rate | downstream rate | shared/dedicated |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dial-up modems | 56 kbps | 56 kbps | dedicated |
| HFC | 2 Mbps | 30 Mbps | shared |
| DSL | <2.5 Mbps, typically < 1 Mbps | <24 Mbps, typically < 10 Mbps | dedicated |
| FTTH | <30 Mbps, in 2020 | <200 Mbps, in 2020 | shared |
R10. Describe the most popular wireless Internet access technologies today. Compare and contrast them.
- WiFi LANS
- 建筑内部
- 传输速率:54, 450 Mbps
- 3G/4G, LTE
- 由电信(蜂窝)运营商提供,10公里
- 传输速率:1-10 Mbps
SECTION 1.3
R11. Suppose there is exactly one packet switch between a sending host and a receiving host. The transmission rates between the sending host and the switch and between the switch and the receiving host are \(R_1\) and \(R_2\) , respectively. Assuming that the switch uses store-and-forward packet switching, what is the total end-to-end delay to send a packet of length L? (Ignore queuing, propagation delay, and processing delay.)
R12. What advantage does a circuit-switched network have over a packet-switched network? What advantages does TDM have over FDM in a circuit-switched network?
- 电路交换的延时低,连接稳定。
- TDM为时分复用,FDM为频分复用,TDM拥有更大的带宽
R13. Suppose users share a 2 Mbps link. Also suppose each user transmits continuously at 1 Mbps when transmitting, but each user transmits only 20 percent of the time. (See the discussion of statistical multiplexing in Section 1.3 .)
a. When circuit switching is used, how many users can be supported?
b. For the remainder of this problem, suppose packet switching is used. Why will there be essentially no queuing delay before the link if two or fewer users transmit at the same time? Why will there be a queuing delay if three users transmit at the same time?
c. Find the probability that a given user is transmitting.
d. Suppose now there are three users. Find the probability that at any given time, all three users are transmitting simultaneously. Find the fraction of time during which the queue grows.
-
a.
\[\frac{2 Mbps}{1 Mbps/user} = 2 \ users \] -
b.
\[traffic \ \ intensity = \frac{aL}{R} = \frac {n · 1 Mbps}{2 Mbps} = \frac{n}{2} \]当流量强度大于1,即\(n \geq 2\)时,出现排队现象,否则不会。
-
c.
\[\frac{1}{5} \] -
d.
\[p =\frac{1}{5} \times \frac{1}{5} \times \frac{1}{5} = \frac{1}{125} \]\[v = 3 Mbps \]
R14. Why will two ISPs at the same level of the hierarchy often peer with each other? How does an IXP earn money?
- 两个同级的网络服务提供商被称为对等。此时,二者间的的数据不流经上级 ISP,从而节省了这一部分数流量的费用。
- IXP 以低于上级ISP的价格提供集中的对等连接,从而得到了ISP顾客的青睐
R15. Some content providers have created their own networks. Describe Google’s network. What motivates content providers to create these networks?
- 谷歌专用网络仅承载出入谷歌服务器主机的流量。谷歌专用网络通过与较低层ISP对等(无结算)尝试“绕过”因特网的较高层,采用的方式可以是直接与它们连接,或者在IXP处与它们连接。然而,因为许多接入ISP通过第一层网络的承载仍能到达,所以谷歌网络也与第一层ISP连接,并就与它们交换的流量向这些ISP付费。
- 通过创建自己的网络,内容提供商不仅减少了向顶层ISP 支付的费用,而且对其服务最终如何交付给端用户有了更多的控制。
SECTION 1.4
R16. Consider sending a packet from a source host to a destination host over a fixed route. List the delay components in the end-to-end delay. Which of these delays are constant and which are variable?
- 处理时延
- 常量
- 排队时延
- 变量,取决于流量强度和性质
- 传输时延
- 变量,取决于包长度与传输速率
- 传播时延
- 变量,取决于物理媒介和路由器距离
R17. Visit the Transmission Versus Propagation Delay applet at the companion Web site. Among the rates, propagation delay, and packet sizes available, find a combination for which the sender finishes transmitting before the first bit of the packet reaches the receiver. Find another combination for which the first bit of the packet reaches the receiver before the sender finishes transmitting.
- 传输vs传播
- 传输快于传播:10 km, 100 Mbps, 100 Bytes
- 传播快于传输:10 km, 512 kbps, 100 Bytes
R20. Suppose end system A wants to send a large file to end system B. At a very high level, describe how end system A creates packets from the file. When one of these packets arrives to a router, what information in the packet does the router use to determine the link onto which the packet is forwarded? Why is packet switching in the Internet analogous to driving from one city to another and asking directions along the way?
- 文件首先被分割成长度一定的片段,形成报文。报文加上运输层首部信息,构成报文段。这样每次加上首部信息,依次得到网络层数据包、链路层帧。
- 网络层首部信息包含了包的目的地信息。
- 转发表和路由选择机制的作用是:解析地址并确定传输路线,故作此类比。
SECTION 1.5
R23. What are the five layers in the Internet protocol stack? What are the principal responsibilities of each of these layers?
-
应用层
- 在端系统之间使用协议交换信息
-
传输层
- 在应用程序端点之间传送应用层报文
-
网络层
- 将数据报(datagram)从一台主机移动到另一台主机
-
链路层
- 将包从一个结点(主机或路由器)移动到路径上的下一个结点
-
物理层
- 将帧中的每个比特从一个结点移动到下一个结点
R25. Which layers in the Internet protocol stack does a router process? Which layers does a link-layer switch process? Which layers does a host process?
- 路由器对应传输层
- 链路层交换机对应链路层
- 主机对应网络层
SECTION 1.6
R26. What is the difference between a virus and a worm?
- 病毒需要被用户接受且执行(比如执行邮件附件),蠕虫不需要明显的用户交互就能进入设备(比如网络)
- 个人理解:蠕虫更具有“自主性”
R27. Describe how a botnet can be created and how it can be used for a DDoS attack.
- 当病毒或蠕虫感染了一个网络的多台设备,并形成了一个被它控制的局部网络时,就得到了一个僵尸网络。
- 在分布式拒绝服务攻击中,僵尸网络利用多台主机同时发起攻击。
- 其基本原理是:单台主机的攻击容易被识破并屏蔽,但分布式攻击使得攻击源难以被甄别。
R28. Suppose Alice and Bob are sending packets to each other over a computer network. Suppose Trudy positions herself in the network so that she can capture all the packets sent by Alice and send whatever she wants to Bob; she can also capture all the packets sent by Bob and send whatever she wants to Alice. List some of the malicious things Trudy can do from this position.
- 窃真
- 获得两人互相发送的信息,窃取密码、口令、个人隐私等内容
- 造假
- 伪造成某一方给另一方发送信息,达到诈骗钱财、挑拨关系等目的