Angular 7和.NET Core 2.2——全球天气(第3部分)
目录
介绍
单元测试
.NET Core中的单元测试
创建xUnit测试项目
什么是Bddfy?
单元测试存储库通用类
NSubstitute和Shouldly
运行和调试单元测试
API控制器的单元测试
在Visual Studio 2017中运行测试
Angular 7中的单元测试
Jasmine
Karma
在Angular 7中编写单元测试规范
单元测试App组件
单元测试城市服务
设置
模拟
单元测试当前条件服务
单元测试位置服务
单元测试天气组件
总结
结论
介绍
在全球天气第1部分和全球天气第2部分中,我们逐步构建了Angular 7应用程序和.NET Core 2.2微API服务。在本文中,我们将开始研究单元测试。我将向您展示如何在xUnit 在为.NET Core使用BDDfy。另外,我将向您展示如何为Angular创建和调试单元测试。
单元测试
进行自动化测试是确保软件应用程序完成其作者打算执行的操作的好方法。软件应用程序有多种类型的测试。这些包括集成测试,Web测试,负载测试等。单元测试测试单个软件的组件和方法。单元测试应该只测试开发人员控制范围内的代码。他们不应该测试基础设施问题。基础设施问题包括数据库,文件系统和网络资源。
测试驱动开发(TDD)是指何时在要检查的代码之前编写单元测试。TDD就像在我们编写一本书之前为其创建一个大纲。它旨在帮助开发人员编写更简单、更易读、更高效的代码。
显然,全球天气文章没有关注TDD。无论如何TDD不是我们的主题。
.NET Core中的单元测试
创建xUnit测试项目
xUnit.net是一个免费的,开源的,以社区为中心的.NET Framework单元测试工具。xUnit.net是由NUnit v2的原始发明者编写的,是用于测试C#,F#,VB.NET和其他.NET语言的最新技术。xUnit.net适用于ReSharper,CodeRush,TestDriven.NET和Xamarin。
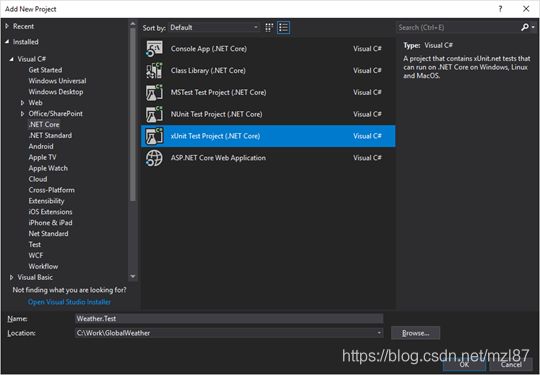
现在我向您展示如何为ASP .NET Core创建xUnit测试项目。在解决方案资源管理器中,添加新项目Weather.Test。
选择“xUnit Test Project(.NET Core)”模板并将项目命名为“ Weather.Test”。单击“ 确定 ”。Weather.Test项目在GlobalWeather解决方案下创建。
删除UnitTest1.cs。右键单击Weather.Test项目以选择“管理Nuget包 ”。
添加Micorsoft.AspNetCore,Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc,Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore,和Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection。
除了这些常见的包,我们需要添加Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.InMemory,NSubstitute,Shouldly和TestStack.BDDfy。
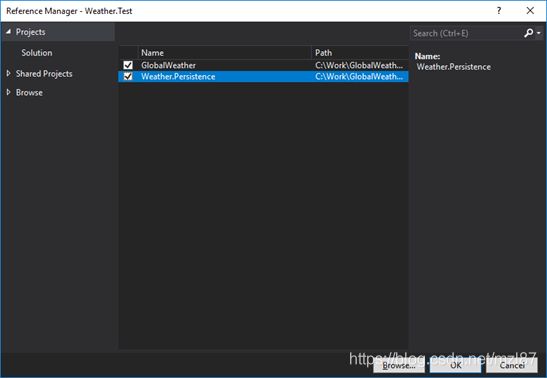
然后添加对其他两个项目的引用,GlobalWeather和Weather.Persistence。
什么是Bddfy?
BDDfy是.NET最简单的BDD框架。该名称来自于它允许您简单地将测试转换为BDD行为的事实。什么是BDD行为?
简单来说,BDD行为是Given,When和Then。
Given-When-Then是一种表示测试的风格——或者正如其拥护者所说的——使用SpecificationByExample指定系统的行为。
基本思想是将场景(或测试)分解为三个部分:
在given 部分描述了在开始您在这个场景中指定的行为之前的世界状态。您可以将其视为测试的前提条件。
在when部分是你指定的行为。
最后,then部分描述了由于指定的行为而导致的更改。
单元测试存储库通用类
右键单击Weather.Test项目,添加Persistence文件夹。因为持久性测试需要模拟数据库,所以使用Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.InMemory创建MockDatabaseHelper类。
public static class MockDatabaseHelper
{
public static DbContextOptions CreateNewContextOptions(string databaseName)
{
//Create a fresh service provider, and therefore a fresh
// InMemory database instance
var serviceProvider = new ServiceCollection()
.AddEntityFrameworkInMemoryDatabase()
.BuildServiceProvider();
// Create a new options instance telling the context to use an
// InMemory database and the new service provider
var builder = new DbContextOptionsBuilder();
builder.UseInMemoryDatabase(databaseName)
.UseInternalServiceProvider(serviceProvider);
return builder.Options;
}
} 我们首先为通用存储库类创建单元测试。创建一个名为RepositoryTest.cs的新C#文件。添加以下代码:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Weather.Persistence.Config;
using Weather.Persistence.Models;
using Weather.Persistence.Repositories;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Options;
using NSubstitute;
using Serilog;
using Shouldly;
using TestStack.BDDfy;
using Xunit;
namespace Weather.Test.Persistence
{
public class RepositoryTest
{
private DbContextOptions _contextOptions;
private City _testData;
private WeatherDbContext _appContext;
private IOptions _settings;
private IDbContextFactory _dbContextFactory;
private Repository _subject;
private City _result;
public RepositoryTest()
{
_testData = new City { Id = "26216", Name = "Melbourne",
CountryId = "AU", AccessedDate = new DateTime(2018, 12, 29, 10, 1, 2) };
}
} 然后添加测试用例。该[Fact]属性表示由测试运行器运行的测试方法。
第一个测试是测试是否正确地在数据库中创建新城市。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Weather.Persistence.Config;
using Weather.Persistence.Models;
using Weather.Persistence.Repositories;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Options;
using NSubstitute;
using Serilog;
using Shouldly;
using TestStack.BDDfy;
using Xunit;
namespace Weather.Test.Persistence
{
public class RepositoryTest
{
private DbContextOptions _contextOptions;
private City _testData;
private WeatherDbContext _appContext;
private IOptions _settings;
private IDbContextFactory _dbContextFactory;
private Repository _subject;
private City _result;
public RepositoryTest()
{
_testData = new City { Id = "26216", Name = "Melbourne",
CountryId = "AU", AccessedDate = new DateTime(2018, 12, 29, 10, 1, 2) };
}
} - GivenADatabase 方法是一个在内存中创建数据库上下文的设置步骤。
- GivenTheDatabaseHasCities方法是一个在Cities表中添加city条目的设置步骤。
- WhenCreateIsCalledWithTheCityAsync方法是一个被认为是调用AddEntity方法的状态转换步骤。
- ThenItShouldReturnTheCity 方法是断言步骤。
在这个测试中,我们正在使用NSubstitute和Shouldly。
NSubstitute和Shouldly
NSubstitute是.NET模拟框架的友好替代品。
编写单元测试时,有时需要模拟被测对象(SUT)的依赖关系。到目前为止,最简单的方法是使用模拟库,它具有额外的好处,它允许您通过检查它与模拟的交互来验证SUT的行为。
NSubstitute和Moq是两个最流行的.NET模拟框架。但是,NSubstitute具有比Moq更清晰的语法,它支持开箱即用的上下文/规范样式。
Shouldly是另一个测试框架,它提高了测试代码的可读性并具有更好的测试失败消息。Shouldly的一个好处是它可以帮助提高测试代码的可读性。它以两种方式实现:
- 消除预期和实际值的歧义,以及
- 生成流畅可读的代码。
运行和调试单元测试
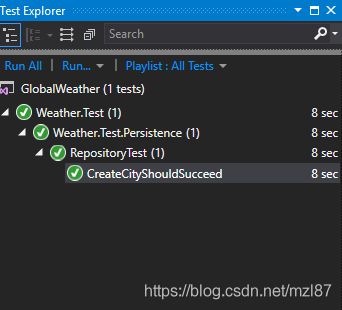
运行后,您可以在Test Explorer中看到结果。
现在,我们添加其他测试:CreateCityShouldThrowException(),GetCityShouldSucceed(),UpdateCityShouldSucceed()和DeleteCityShouldSucceed()。
CreateCityShouldThrowException:
[Fact]
public void CreateCityShouldThrowException()
{
this.Given(x => GivenADatabase("TestDb"))
.Given(x => GivenTheDatabaseHasACity(_testData))
.When(x => WhenCreateSameIdIsCalledWithTheCityAsync(_testData))
.Then(x => ThenItShouldBeSuccessful())
.BDDfy();
}
private void GivenTheDatabaseHasACity(City city)
{
_appContext.Cities.Add(city);
_appContext.SaveChanges();
}
private async Task WhenCreateSameIdIsCalledWithTheCityAsync(City city)
{
await Assert.ThrowsAsync(async () => await _subject.AddEntity(city));
}
private void ThenItShouldBeSuccessful()
{ } GetCityShouldSucceed:
[Fact]
public void GetCityShouldSucceed()
{
this.Given(x => GivenADatabase("TestDb"))
.Given(x => GivenTheDatabaseHasACity(_testData))
.When(x => WhenGetCalledWithTheCityIdAsync(_testData.Id))
.Then(x => ThenItShouldReturnTheCity(_testData))
.BDDfy();
}
private async Task WhenGetCalledWithTheCityIdAsync(string id)
{
_result = await _subject.GetEntity(id);
return true;
} UpdateCityShouldSucceed:
[Fact]
public void UpdateCityShouldSucceed()
{
var city = new City
{
Id = _testData.Id,
Name = "Melbourne",
CountryId = "AU",
AccessedDate = new DateTime(2018, 12, 30, 10, 1, 2)
};
this.Given(x => GivenADatabase("TestDb"))
.Given(x => GivenTheDatabaseHasACity(_testData))
.When(x => WhenUpdateCalledWithTheCityAsync(city))
.Then(x => ThenItShouldReturnTheCity(city))
.BDDfy();
}
private async Task WhenUpdateCalledWithTheCityAsync(City city)
{
var entity = await _subject.GetEntity(city.Id);
entity.Name = city.Name;
entity.CountryId = city.CountryId;
entity.AccessedDate = city.AccessedDate;
_result = await _subject.UpdateEntity(entity);
return true;
} DeleteCityShouldSucceed:
[Fact]
public void DeleteCityShouldSucceed()
{
this.Given(x => GivenADatabase("TestDb"))
.Given(x => GivenTheDatabaseHasACity(_testData))
.When(x => WhenDeleteCalledWithTheCityIdAsync(_testData.Id))
.Then(x => ThenItShouldBeNoExistCity())
.BDDfy();
}
private async Task WhenDeleteCalledWithTheCityIdAsync(string id)
{
await _subject.DeleteEntity(id);
return true;
}
private void ThenItShouldBeNoExistCity()
{
_appContext.Cities.Count().ShouldBe(0);
} API控制器的单元测试
设置控制器操作的单元测试以关注控制器的行为。控制器单元测试可避免过滤器,路由和模型绑定等情况。覆盖集体响应请求的组件之间的交互的测试由集成测试处理。
在Weather.Test项目中创建“Controllers ”文件夹。添加一个名为CitiesController.cs的类,并使用以下代码替换代码:
using System;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using GlobalWeather.Controllers;
using GlobalWeather.Services;
using NSubstitute;
using Serilog;
using TestStack.BDDfy;
using Xunit;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Weather.Persistence.Models;
namespace Weather.Test.Controllers
{
public class CitiesControllerTest
{
private ICityService _service;
private CitiesController _controller;
private City _testData;
private ActionResult _result;
#region Facts
[Fact]
public void GetReturnsExpectedResult()
{
this.Given(x => GivenCitiesControllerSetup())
.And(x => GivenGeLastAccessedCityReturnsExpected())
.When(x => WhenGetCalledAsync())
.Then(x => ThenResultShouldBeOk())
.BDDfy();
}
[Fact]
public void PostCallService()
{
this.Given(x => GivenCitiesControllerSetup())
.When(x => WhenPostCalledAsync())
.Then(x => ThenItShouldCallUpdateAccessedCityInService())
.BDDfy();
}
#endregion
#region Gievns
private void GivenCitiesControllerSetup()
{
_testData = new City
{ Id = "26216", Name = "Melbourne",
CountryId = "AU", AccessedDate = DateTimeOffset.UtcNow };
_service = Substitute.For();
_controller = new CitiesController(_service, Substitute.For());
}
private void GivenGeLastAccessedCityReturnsExpected()
{
_service.GetLastAccessedCityAsync().Returns(new City());
}
#endregion
#region Whens
private async Task WhenGetCalledAsync()
{
_result = await _controller.Get();
}
private async Task WhenPostCalledAsync()
{
await _controller.Post(_testData);
}
#endregion
#region Thens
private void ThenResultShouldBeOk()
{
Assert.NotNull(_result);
Assert.IsType(_result.Value);
}
private void ThenItShouldCallUpdateAccessedCityInService()
{
_service.Received().UpdateLastAccessedCityAsync(_testData);
}
#endregion
}
} 如前所述,在控制器单元测试中,我们用替代模拟服务。然后为http get和http post编写测试。
在上面的代码中,我们使用_service.Received().UpdateLastAccessedCityAsync(_testData)。在某些情况下(特别是对于void方法),检查替代者是否已收到特定调用是有用的。可以使用Received()扩展方法检查,然后检查调用。
在Visual Studio 2017中运行测试
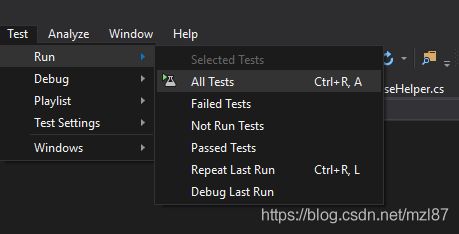
您现在可以运行测试了。将测试使用[Fact]属性标记的所有方法。从“测试”菜单项中,运行测试。
打开“测试资源管理器”窗口,注意测试结果。
Angular 7中的单元测试
在这里,我们将使用Jasmine和Karma来测试我们的Angular 7应用程序。
Jasmine
Jasmine是一个JavaScript的开源测试框架。
在开始之前,您需要了解Jasmine的基础知识。
- Describe——是具有单个测试规范集合的函数。
- test spec——它只有一个或多个测试期望。
在执行我们的测试用例之前或之后,我们需要插入一些模拟数据,或者我们需要做一些清理活动。出于这些目的,我们有:
- beforeAll——在运行测试套件中的所有规范之前调用此函数一次。
- afterAll——完成测试套件中的所有规范后将调用此函数一次。
- beforeEach——在每个测试规范之前调用此函数。
- afterEach——在每个测试规范之后调用此函数。
Karma
它只是一个测试运行者。它是一个工具,它允许我们从命令行生成浏览器并在其中运行jasmine测试。测试结果也显示在命令行中。
在Angular 7中编写单元测试规范
Angular CLI下载并安装使用Jasmine测试框架测试Angular应用程序所需的一切。
当我们使用Angular CLI命令创建组件和服务时,已经创建了默认测试规范。例如,app.component.spec.ts。
import { TestBed, async } from '@angular/core/testing';
import { RouterTestingModule } from '@angular/router/testing';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
describe('AppComponent', () => {
beforeEach(async(() => {
TestBed.configureTestingModule({
imports: [
RouterTestingModule
],
declarations: [
AppComponent
],
}).compileComponents();
}));
it('should create the app', () => {
const fixture = TestBed.createComponent(AppComponent);
const app = fixture.debugElement.componentInstance;
expect(app).toBeTruthy();
});
it(`should have as title 'WeatherClient'`, () => {
const fixture = TestBed.createComponent(AppComponent);
const app = fixture.debugElement.componentInstance;
expect(app.title).toEqual('WeatherClient');
});
it('should render title in a h1 tag', () => {
const fixture = TestBed.createComponent(AppComponent);
fixture.detectChanges();
const compiled = fixture.debugElement.nativeElement;
expect(compiled.querySelector('h1').textContent).toContain('Welcome to WeatherClient!');
});
});如果你运行ng test,karma会打开你的浏览器,你可以看到测试结果。启动PowerShell,转到GlobalWeather\GlobalWeather\WeatherClient文件夹。运行以下命令:
ng testKarma打开您的浏览器,我假设您将Chrome设置为默认浏览器。
您可以看到所有单元测试都失败了。但不要惊慌。大多数错误是由未正确导入的模块引起的。让我们让测试规格有效。首先,从app.component.spec.ts开始。
单元测试App组件
我们更改app.component.spec.ts,如下所示:
import { TestBed, async } from '@angular/core/testing';
import { RouterTestingModule } from '@angular/router/testing';
import { ReactiveFormsModule } from '@angular/forms';
import { NgbModule } from '@ng-bootstrap/ng-bootstrap';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import { WeatherComponent } from './weather/weather.component';
describe('AppComponent', () => {
beforeEach(async(() => {
TestBed.configureTestingModule({
imports: [
RouterTestingModule,
ReactiveFormsModule,
NgbModule
],
declarations: [
AppComponent,
WeatherComponent
],
}).compileComponents();
}));
it('should create the app', () => {
const fixture = TestBed.createComponent(AppComponent);
const app = fixture.debugElement.componentInstance;
expect(app).toBeTruthy();
});
it(`should have as title 'WeatherClient'`, () => {
const fixture = TestBed.createComponent(AppComponent);
const app = fixture.debugElement.componentInstance;
expect(app.title).toEqual('WeatherClient');
});
});如果你和以前的代码进行比较,你可以看到主要的变化是固定的导入,如import WeatherComponent,import ReactiveFormsModule和import NgbMoudle。此外,除了默认测试用例,“应该创建应用程序”,添加一个新的,“应该有标题' WeatherClient'”。
让我们再次通过“ng test”运行测试。
看,app.component.spec.ts中的所有错误都消失了,这意味着app.component.ts通过了测试。
单元测试城市服务
接下来,我们修复cityservice.spec.ts,用以下代码替换默认代码:
import { async, TestBed } from '@angular/core/testing';
import { HttpClientTestingModule, HttpTestingController, TestRequest }
from '@angular/common/http/testing';
import { Constants } from '../../../app/app.constants';
import { CityService } from './city.service';
import { ErrorHandleService } from './error-handle.service';
import { CityMetaData } from '../models/city-meta-data';
import { City } from '../models/city';
describe('CityService', () => {
let service: CityService;
let httpTestingController: HttpTestingController;
beforeEach(async(() => {
TestBed.configureTestingModule({
imports: [HttpClientTestingModule],
providers: [CityService, ErrorHandleService]
});
service = TestBed.get(CityService);
httpTestingController = TestBed.get(HttpTestingController);
}));
afterEach(() => {
httpTestingController.verify();
});
it('should create', () => {
expect(service).toBeTruthy();
});
it('should get last accessed city', () => {
const result = { id: '26216', name: 'Melbourne', countryId: 'AU' } as CityMetaData;
service.getLastAccessedCity()
.subscribe(
(data: City) => expect(data.Key).toEqual('26216'),
(err) => expect(err).toBeNull()
);
const uri = decodeURIComponent(`${Constants.cityAPIUrl}`);
const req: TestRequest = httpTestingController.expectOne(req => req.url.includes(uri));
expect(req.request.method).toEqual('GET');
req.flush(result);
});
});在这里,需要提及的一件事是如何测试http get服务。
设置
我们设置了TestBed导入HttpClientTestingModule和提供HttpTestingController。当然,我们也提供我们正在测试的服务CityService。
我们还运行HttpTestingController#verify以确保没有未完成的请求:
afterEach(() => { httpTestingController.verify(); });模拟
您可以使用HttpTestingController模拟请求和flush方法来提供虚拟值作为响应。当HTTP请求方法返回Observable时,我们订阅它并在回调方法中创建我们的期望:
it('should get last accessed city', () => {
const result = { id: '26216', name: 'Melbourne', countryId: 'AU' } as CityMetaData;
service.getLastAccessedCity()
.subscribe(
(data: City) => expect(data.Key).toEqual('26216'),
(err) => expect(err).toBeNull()
);
const uri = decodeURIComponent(`${Constants.cityAPIUrl}`);
const req: TestRequest = httpTestingController.expectOne(req => req.url.includes(uri));
expect(req.request.method).toEqual('GET');
req.flush(result);
});使用expectOne,expectNone或match模拟请求。
我们准备模拟数据:
const result = {id: '26216', name: 'Melbourne', countryId: 'AU'} as CityMetaData;然后,flush这个模拟数据到http请求。
req.flush(result);单元测试当前条件服务
修复current-conditions.service.spec.ts。用以下内容替换默认代码:
import { async, TestBed } from '@angular/core/testing';
import { HttpClientTestingModule, HttpTestingController, TestRequest }
from '@angular/common/http/testing';
import { Constants } from '../../../app/app.constants';
import { CurrentConditionsService } from './current-conditions.service';
import { ErrorHandleService } from './error-handle.service';
import { CurrentConditions } from '../models/current-conditions';
describe(' CurrentConditionsService', () => {
let service: CurrentConditionsService;
let httpTestingController: HttpTestingController;
beforeEach(async(() => {
TestBed.configureTestingModule({
imports: [HttpClientTestingModule],
providers: [CurrentConditionsService, ErrorHandleService]
});
service = TestBed.get(CurrentConditionsService);
httpTestingController = TestBed.get(HttpTestingController);
}));
afterEach(() => {
httpTestingController.verify();
});
it('should create',
() => {
expect(service).toBeTruthy();
});
it('should get current conditions',
() => {
const result = [
{
LocalObservationDateTime: '',
WeatherText: 'Sunny',
WeatherIcon: 1,
IsDayTime: true,
Temperature: {
Imperial: null,
Metric: {
Unit: 'C',
UnitType: 1,
Value: 36
}
}
}
] as CurrentConditions[];
service.getCurrentConditions('26216')
.subscribe(
(data: CurrentConditions[]) => expect
(data.length === 1 && data[0].WeatherText === 'Sunny').toBeTruthy(),
(err: CurrentConditions[]) => expect(err.length).toEqual(0)
);
const uri = decodeURIComponent(`${Constants.currentConditionsAPIUrl}/
26216?apikey=${Constants.apiKey}`);
const req: TestRequest = httpTestingController.expectOne(req => req.url.includes(uri));
expect(req.request.method).toEqual('GET');
req.flush(result);
});
});单元测试位置服务
修复location.service.spec.ts。用以下内容替换默认代码:
import { async, TestBed } from '@angular/core/testing';
import { HttpClientTestingModule, HttpTestingController, TestRequest }
from '@angular/common/http/testing';
import { Constants } from '../../../app/app.constants';
import { LocationService } from './location.service';
import { ErrorHandleService } from './error-handle.service';
import { Country } from '../../shared/models/country';
import { City } from '../../shared/models/city';
describe('LocationService', () => {
let service: LocationService;
let httpTestingController: HttpTestingController;
beforeEach(async(() => {
TestBed.configureTestingModule({
imports: [HttpClientTestingModule],
providers: [LocationService, ErrorHandleService]
});
service = TestBed.get(LocationService);
httpTestingController = TestBed.get(HttpTestingController);
}));
afterEach(() => {
httpTestingController.verify();
});
it('should create', () => {
expect(service).toBeTruthy();
});
it('should get location', () => {
const result = [{
Key: '26216', EnglishName: 'Melbourne', Type: 'City', Country: {
ID: 'AU',
EnglishName: 'Australia'
}
}] as City[];
service.getCities('melbourne', 'AU')
.subscribe(
(data: City[]) => expect(data.length === 1 && data[0].Key === '26216').toBeTruthy(),
(err: City[]) => expect(err.length).toEqual(0)
);
const uri = decodeURIComponent(
`${Constants.locationAPIUrl}/cities/AU/search?apikey=${Constants.apiKey}&q=melbourne`);
const req: TestRequest = httpTestingController.expectOne(req => req.url.includes(uri));
expect(req.request.method).toEqual('GET');
req.flush(result);
});
it('should get countries', () => {
const result = [{
ID: 'AU', EnglishName: 'Australia'
}] as Country[];
service.getCountries()
.subscribe(
(data: Country[]) => expect(data.length === 1 && data[0].ID === 'AU').toBeTruthy(),
(err: Country[]) => expect(err.length).toEqual(0)
);
const uri = decodeURIComponent
(`${Constants.locationAPIUrl}/countries?apikey=${Constants.apiKey}`);
const req: TestRequest = httpTestingController.expectOne(req => req.url.includes(uri));
expect(req.request.method).toEqual('GET');
req.flush(result);
});
});单元测试天气组件
修复weather.component.spec.ts。用以下内容替换默认代码:
import { async, ComponentFixture, TestBed } from '@angular/core/testing';
import { RouterTestingModule } from '@angular/router/testing';
import { HttpClientTestingModule } from '@angular/common/http/testing';
import { ReactiveFormsModule, FormGroup, FormControl, FormBuilder, Validators } from '@angular/forms';
import { NgbModule } from '@ng-bootstrap/ng-bootstrap';
import { WeatherComponent } from './weather.component';
import { LocationService } from '../shared/services/location.service';
import { CurrentConditionsService } from '../shared/services/current-conditions.service';
import { CityService } from '../shared/services/city.service';
import { ErrorHandleService } from '../shared/services/error-handle.service';
describe('WeatherComponent', () => {
let component: WeatherComponent;
let fixture: ComponentFixture;
beforeEach(async(() => {
TestBed.configureTestingModule({
declarations: [WeatherComponent],
imports: [ReactiveFormsModule, NgbModule, RouterTestingModule, HttpClientTestingModule],
providers: [LocationService, CurrentConditionsService, CityService, ErrorHandleService]
})
.compileComponents();
fixture = TestBed.createComponent(WeatherComponent);
component = fixture.componentInstance;
fixture.detectChanges();
}));
it('should create', () => {
expect(component).toBeTruthy();
});
it('should get invalid form when location field is empty ',
() => {
component.ngOnInit();
expect(component.weatherForm.valid).toEqual(false);
});
it('should get valid form when location field has value ',
() => {
component.ngOnInit();
component.cityControl.patchValue("something");
expect(component.weatherForm.valid).toEqual(true);
});
}); 上面的代码将导致编译问题,因为它试图在weather component中访问weatherForm,但是weatherForm是private。因此,只要在weather.component.ts中为weatherForm删除private。
更换:
private weatherForm: FormGroup;和:
weatherForm: FormGroup;在这里,我们有两个测试用例来验证反应表单。返回weather.component.ts,City字段是必需的。
buildForm(): FormGroup {
return this.fb.group({
searchGroup: this.fb.group({
country: [
null
],
city: [
null,
[Validators.required]
],
})
});
}这意味着如果City 输入字段没有值,则表单无效。因为只有一个必填字段,所以当您在此输入中输入内容时,表单将变为有效。
以下两个测试用例涵盖了这种行为:
it('should get invalid form when location field is empty ',
() => {
component.ngOnInit();
expect(component.weatherForm.valid).toEqual(false);
});
it('should get valid form when location field has value ',
() => {
component.ngOnInit();
component.cityControl.patchValue("something");
expect(component.weatherForm.valid).toEqual(true);
});
});总结
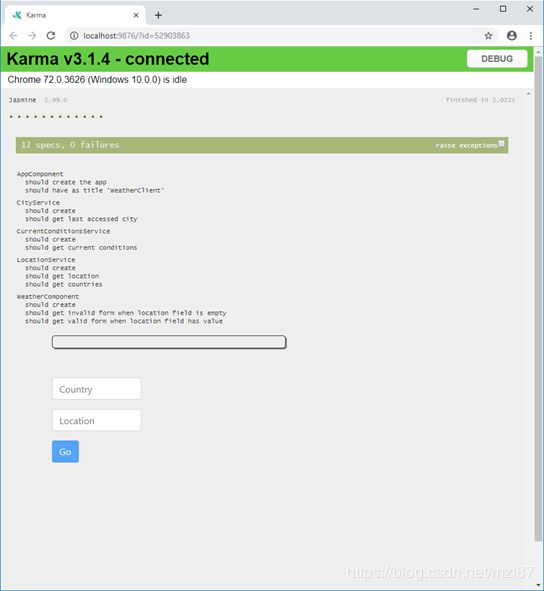
现在我们再次运行ng test,所有测试用例都通过了。
结论
UNIT TESTING是一个软件测试级别,其中测试软件的各个单元/组件。目的是验证软件的每个单元是否按设计执行。在本文中,我讨论了如何在ASP.NET Core和Angular中编写单元测试。
原文地址:https://www.codeproject.com/Articles/1278829/Angular-7-with-NET-Core-2-2-Global-Weather-Part-3