订单有限状态机架构设计
有限状态机
有限状态机(Finite-state machine, FSM),是表示有限个状态以及在这些状态之间的转移和动作等行为的数学模型。主要用来是描述对象在它的生命周期内所经历的状态序列,以及如何响应来自外界的各种事件。
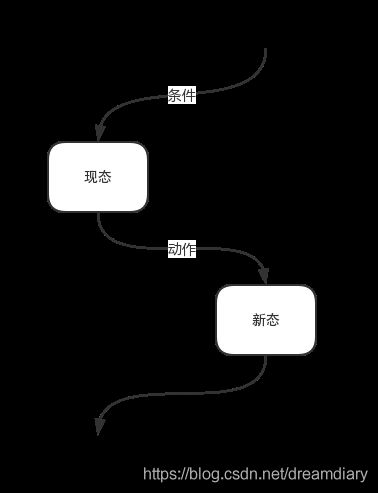
状态机可归纳为4个要素,即现态、条件、动作、新态。其中“现态”和“条件”是因,“动作”和“次态”是果。
- **现态:**是指当前所处的状态。
- **事件:**又称为“条件”。当一个事件发生,将会触发一个动作,或者执行一次状态的迁移。
- **动作:**条件满足后执行的动作。动作执行完毕后,可以迁移到新的状态,也可以仍旧保持原状态。动作不是必需的,当条件满足后,也可以不执行任何动作,直接迁移到新状态。
- **次态:**条件满足后要迁往的新状态。“次态”是相对于“现态”而言的,“次态”一旦被激活,就转变成新的“现态”了。
例如,当订单处于“待动作”状态时,收到了支付平台的支付成功回调通知,这就是订单的现态和条件。这时候,系统会执行拆分订单、推送订单到供应链系统等操作,这就是“动作”。最后再把订单的状态标记为已完成,这就是这一次状态变更的“次态”。
按这个模式,整个订单系统的逻辑都可以抽象成为一系统的状态、状态变更的条件、状态变更的动作。
订单状态转移表
根据实际业务场景,按以下格式整理出一份订单的状态转移表。这里增加前置动作和后置动作两个概念,前置动作是指在修改状态之前要执行的动作,例如创建订单前需要锁定库存。执行一系列前置动作时,如果某个动作失败了,需要把前面的前置动作做回滚。后置动作是订单指的是转移到新状态后自动触发的事件,例如支付成功后的拆单和推送等。后置动作执行失败也不需要做回滚,但是需要加上重试机制。
| 当前状态 | 事件 | 前置动作 | 新状态 | 后置动作 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 未创建 | 确认下单 | 锁定库存 创建订单 |
待支付 | |
| 待支付 | 支付成功 | 修改订单状态 | 拆分订单 推送订单 |
已支付 |
| 待支付 | 手动取消 | 修改订单状态 | 已取消 | |
| 待支付 | 超时取消 | 修改订单状态 | 已取消 |
核心代码
状态定义
枚举定义全部的订单状态,订单状态应该尽量订得很细,即使两个状态之间只有细微的区别也可以分开来。因为在这个架构下,事件和动作都是可以重用的,不同的状态转移过程通过配置来区分就可以。
这里的示例是只用一个主状态字段来表示所有的订单状态,也可以分成把多种状态分别用不同的字段来表示,例如支付状态、发货状态、售后状态都用单独的字段和枚举变量。
class Orderstatus extends BaseEnum
{
//未创建
const NOT_CREATED = -200;
//售后状态
const REFUND_APPLIED = -100
const REFUND_CONFIRM = -101
//关闭状态
const CANCELED = 0;
//商城端状态
const CREATED = 100;//已创建
const PAY_SUCCESS = 110;// 支付成功
const ORDER_SPLITED = 120;// 已拆单
//推送状态
const PUSH_SUCCESS = 200;// 推送成功
const PUSH_FAILURE = 201;// 権送失败
//物流状态
const NOT_DELIVER = 300;// 未发貸
const PART_DELIVER = 301;// 已麦貸
const ALL_DELIVER = 302;// 全部宏貸
const SELF_MENTION = 303;// 到店百提
//完成状态
const FINISHED = 400;
const REVIEWED = 410;
}
事件定义
首先定义事件的枚举类
class OrderEventType extends BaseEnum
{
const CANCEL = 0; // 取消订单
const CLOSE = 5; // 关闭订单
const CREATE = 10; // 创建订单
const PAY_SUCCESS = 110; // 支付成功
const PAY_FAILURE = 120; // 支付失败
const SHIPPING_DELIVER = 210; // 订单发货
const SHIPPING_RECEIPT = 220; // 确认收货
}
然后每个事件写一个类,继承事件基类
class PaySuccess extends OrderEvent
{
protected $eventType = OrderEventType::PAY_SUCCESS;
}
class OrderEvent
{
protected $eventType = '';
protected $orderId = 0;
protected $eventData = [];
public function getEventType()
{
return $this->eventType;
}
public function getOrderId(): int
{
return $this->orderId;
}
public function setOrderId(int $orderId): void
{
$this->orderId = $orderId;
}
public function getEventData(): array
{
return $this->eventData;
}
public function setEventData(array $eventData): void
{
$this->eventData = $eventData;
}
}
操作类
前置动作、后置动作、回滚操作都继承相同的基类OrderOperation,分别放到不同的目录下。
class OrderOperation
{
protected $event = null;
protected $order = null;
protected $data = [];
public function handle(OrderEvent $event, $order = null)
{
$this->setEvent($event);
$this->setOrder($order);
// 获取传的参数
$this->data = $event->getEventData();
}
protected function throwException($message = '', $code = 0)
{
$exception = new StateMachineException($message, $code);
$exception->setOrderEvent($this->event);
$exception->setOrderModel($this->order);
$operationFile = $exception->getTrace()[0]['file'];
$operationName = basename($operationFile, '.php');
$exception->setOperation('App\Domain\PlatformOrder\Services\StateMachine\BeforeOperation\\' . $operationName);
throw $exception;
}
}
class LockSaleableStock extends OrderOperation
{
public function handle(OrderEvent $event, $order = null)
{
parent::handle($event, $order);
//具体处理逻辑
...
}
}
状态转移配置
首先用事件类型作为数组的key进行配置,对应的value是可以响应这个事件的状态列表,如果一个事件可能有多种状态转移方式,就需要配置多个状态定义。
状态的conditions是指可以响应这个Event的状态,配置的多个状态是“或”关系。
private $statusTransition = [
// 支付成功
OrderEventType::PAY_SUCCESS => [
[
'conditions' => [OrderStatus::CREATED], //仅未支付的状态才允许触发,
'beforeOperation' => [
ChangeSaleableStock::class, // 扣库存
],
// 后置操作
'afterOperation' => [
AddSaleCount::class
],
// 新状态变更
'newStatus' => OrderStatus::PAY_SUCCESSED
],
],
];
核心代码
event = $event;
$matched = false;
if (isset($this->statusTransition[$this->event->getEventType()])) {
$transitions = $this->statusTransition[$this->event->getEventType()];
// 事件支持
$matched = null;
/** @var Order $order */
$orderId = $this->event->getOrderId();
if ($orderId) {
$this->order = $this->subOrderModel->find($orderId);
}
foreach ($transitions as $transition) {
if ($this->checkCondition($transition['conditions'])) {
// 事件支持 并且 状态支持
$matched = true;
try {
// 更新状态的前置操作
$this->callOperation($transition['beforeOperation']);
// 更新订单状态
if ($this->order && !empty($transition['newStatus'])) {
$this->order->update($transition['newStatus']);
}
// 更新状态的后置操作
$this->callOperation($transition['afterOperation']);
} catch (StateMachineException $exception) {
$this->beforeRollback($transition['beforeOperation'], $exception);
throw $exception;
}
break;
}
}
}
if ($matched === false) {
throw new StateMachineException("订单状态机不支持的事件类型");
} elseif ($matched === null) {
throw new StateMachineException("该订单状态不允许当前操作");
}
}
protected function beforeRollback($operation, $exception)
{
// 检查哪些需要回滚的
$rollbackOperation = [];
foreach ($operation as $op) {
if ($op !== $exception->getOperation()) {
array_unshift($rollbackOperation, str_replace('BeforeOperation', 'RollbackOperation', $op));
} else {
break;
}
}
// 回滚操作
foreach ($rollbackOperation ?? [] as $op) {
if (class_exists($op)) {
$operationService = app($op);
$operationService->handle($this->event, $this->order);
}
}
}
protected function checkCondition($conditions)
{
if (empty($conditions) || empty($this->order)) {
return true;
}
foreach ($conditions as $condition) {
$matchCount = 0;
foreach ($condition as $field => $value) {
if ($this->order->getAttribute($field) === $value) {
$matchCount++;
} else {
break;
}
}
if ($matchCount == count($condition)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
protected function callOperation($operation = [])
{
foreach ($operation ?? [] as $op) {
/** @var OrderOperation $operationService */
$operationService = app($op);
$operationService->handle($this->event, $this->order);
}
}
}