Pytorch中的Conv1d()和Conv2d()函数
文章目录
- 一、Pytorch中的Conv1d()函数
- 二、Pytorch中的Conv2d()函数
- 三、Pytorch中的MaxPool1d()函数
- 四、pytorch中的MaxPool2d()函数
- 参考资料
一、Pytorch中的Conv1d()函数
class torch.nn.Conv1d(
in_channels,
out_channels,
kernel_size,
stride=1,
padding=0,
dilation=1,
groups=1,
bias=True)
Conv1d()函数就是利用指定大小的一维卷积核对输入的多通道一维输入信号进行一维卷积操作的卷积层。
最简单的情况下,对于输入大小为 ( N , C i n , L i n ) (N, C_{in}, L_{in}) (N,Cin,Lin),输出大小为 ( N , C o u t , L o u t ) (N, C_{out}, L_{out}) (N,Cout,Lout)的一维卷积层,其中, N 代表batch size,C代表通道的数量, L代表信号序列的长度。
- in_channels (int) – 输入通道个数。在文本应用中,即为词向量的维度
- out_channels (int) – 输出通道个数 。有多少个out_channels,就需要多少个一维卷积(也就是卷积核的数量)
- kernel_size(int or tuple) – 卷积核的尺寸;卷积核的第二个维度由in_channels决定,所以实际上卷积核的大小为kernel_size * in_channels
- stride (int or tuple, optional) – 卷积操作的步长。 默认:1
- padding (int or tuple, optional) – 输入数据各维度各边上要补齐0的层数。 默认: 0
- dilation (int or tuple, optional) – 卷积核各元素之间的距离。 默认: 1
- groups (int, optional) – 输入通道与输出通道之间相互隔离的连接的个数。 默认:1
- bias (bool, optional) – 如果被置为True,向输出增加一个偏差量,此偏差是可学习参数。 默认:True
| 一般来说,一维卷积nn.Conv1d()用于文本数据,只对宽度进行卷积,对高度不卷积。通常,输入大小为word_embedding_dim * max_sent_length,其中,word_embedding_dim为词向量的维度,max_sent_length为句子的最大长度。卷积核窗口在句子长度的方向上滑动,进行卷积操作。 |
示例:
输入:批大小为50,句子的最大长度为35,词向量维度为300
目标:句子分类,共2类
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
# max_sent_len=35, batch_size=50, embedding_size=300
conv1 = nn.Conv1d(in_channels=300, out_channels=100, kernel_size=3)
input = torch.randn(50, 35, 300)
# batch_size x max_sent_len x embedding_size -> batch_size x embedding_size x max_sent_len
input = input.permute(0, 2, 1)
print("input:", input.size())
output = conv1(input)
print("output:", output.size())
# 最大池化
pool1d = nn.MaxPool1d(kernel_size=35-3+1)
pool1d_value = pool1d(output)
print("最大池化输出:", pool1d_value.size())
# 全连接
fc = nn.Linear(in_features=100, out_features=2)
fc_inp = pool1d_value.view(-1, pool1d_value.size(1))
print("全连接输入:", fc_inp.size())
fc_outp = fc(fc_inp)
print("全连接输出:", fc_outp.size())
# softmax
m = nn.Softmax()
out = m(fc_outp)
print("输出结果值:", out)
- 原始输入大小为(50, 35, 300),经过permute(0, 2, 1)操作后,输入的大小变为(50, 300, 35);
- 使用1个window_size为3的卷积核进行卷积,因为一维卷积是在最后维度上扫的,最后output的大小即为:50*100*(35-3+1)=50*100*33
- output经过最大池化操作后,得到了数据维度为:(50,100,1)
- 经过(输入特征=100,输出特征=2)的全连接层,数据维度就变为了:(50,2)
- 再经过softmax函数就得到了属于两个类别的概率值
二、Pytorch中的Conv2d()函数
class torch.nn.Conv2d(
in_channels,
out_channels,
kernel_size,
stride=1,
padding=0,
dilation=1,
groups=1,
bias=True)
该函数是利用指定大小的二维卷积核对输入的多通道二维输入信号进行二维卷积操作的卷积层。
在最简单的情况下,对于输入大小为 ( N , C i n , H , W ) (N, C_{in}, H, W) (N,Cin,H,W),输出大小为 ( N , C o u t , H o u t , W o u t ) (N, C_{out}, H_{out}, W_{out}) (N,Cout,Hout,Wout)的二维维卷积层,其卷积计算过程可以如下表述:
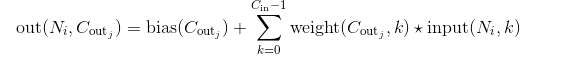
N N N is a batch size, 代表通道的数量, H H H是输入的二维数据的像素高度, W W W是输入的二维数据的像素宽度。
如果要用二维卷积来实现文本的处理也是可以的,还是上面的那个任务,用二维卷积来做的话,代码如下所示:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
# max_sent_len=35, batch_size=50, embedding_dim=300
conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1, out_channels=100, kernel_size=(3, 300))
# batch_size x 1 × max_sent_len x embedding_dim
input = torch.randn(50, 1, 35, 300)
print("input:", input.size())
output = conv2(input)
# batch_size × kernel_num × H × 1,其中H=max_sent_len-kernel_size+1
print("output:", output.size())
# 最大池化
# pool = nn.MaxPool1d(kernel_size=35-3+1)
output = output.squeeze(3)
pool1d_value = F.max_pool1d(output, output.size(2))
print("最大池化输出:", pool1d_value.size())
# 全连接
fc = nn.Linear(in_features=100, out_features=2)
fc_inp = pool1d_value.view(-1, pool1d_value.size(1))
print("全连接输入:", fc_inp.size())
fc_outp = fc(fc_inp)
print("全连接输出:", fc_outp.size())
# softmax
out = F.softmax(fc_outp, dim=1)
print("输出结果值:", out)
- 二维卷积输入大小为(50, 1,35, 300),
- 使用1个window_size为3的卷积核进行二维卷积,最后output的大小即为:50*100*(35-3+1)*1=50*100*33*1
- output经过最大池化操作后,得到了数据维度为:(50,100,1)
- 经过(输入特征=100,输出特征=2)的全连接层,数据维度就变为了:(50,2)
- 再经过softmax函数就得到了属于两个类别的概率值
三、Pytorch中的MaxPool1d()函数
class torch.nn.MaxPool1d(
kernel_size,
stride=None,
padding=0,
dilation=1,
return_indices=False,
ceil_mode=False)
该函数对输入的多通道信号执行一维最大池化操作。
最简单的情况下,对于输入大小为 ( N , C , L i n ) (N, C, L_{in}) (N,C,Lin) ,输出大小为 ( N , C , L o u t ) (N, C, L_{out}) (N,C,Lout) 的池化操作,此池化过程可表述如下:

参数说明:
- kernel_size – 最大池化操作的滑动窗大小
- stride – 滑动窗的步长,默认值是 kernel_size
- padding – 要在输入信号的各维度各边上要补齐0的层数
- dilation – 滑动窗中各元素之间的距离
- return_indices – 如果此参数被设置为True, 那么此池化层在返回输出信号的同时还会返回一连串滑动窗最大值的索引位置,即每个滑动窗的最大值位置信息。这些信息可以在后面的上采样torch.nn.MaxUnpool1d中被用到。
- ceil_mode – 如果此参数被设置为True,计算输出信号大小的时候,会使用向上取整,代替默认的向下取整的操作

四、pytorch中的MaxPool2d()函数
class torch.nn.MaxPool2d(
kernel_size,
stride=None,
padding=0,
dilation=1,
return_indices=False,
ceil_mode=False)
该函数是对输入的多通道信号执行二维最大池化操作。
最简单的情况下,对于输入大小为 ( N , C , H , W ) (N, C, H, W) (N,C,H,W) ,输出大小为 ( N , C , H o u t , W o u t ) (N, C, H_{out}, W_{out}) (N,C,Hout,Wout),kernel_size为 ( k H , k W ) (kH, kW) (kH,kW)的池化操作.

示例:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
# pool of square window of size=3, stride=2
# m = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2)
# pool of non-square window
m = nn.MaxPool2d((5, 2))
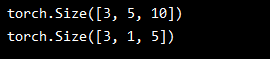
input = torch.randn(3, 5, 10)
print(input.size())
output = m(input)
print(output.size())
参考资料
- pytorch中文文档: https://pytorch.apachecn.org/docs/1.2/nn.html#conv1d
- 博客:https://www.jianshu.com/p/45a26d278473