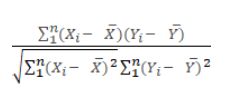Pytorch相似度计算
1 余弦相似度
余弦相似度是一种我们较为常用的计算向量相似度的方法。下面就是计算余弦相似度的公式:

import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import math
class ConineSimilarity(nn.Module):
def forward(self, tensor_1,tensor_2):
normalized_tensor_1=tensor_1/tensor_1.norm(dim=-1,keepdim=True)
normalized_tensor_2=tensor_2/tensor_2.norm(dim=-1,keepdim=True)
return (normalized_tensor_1*normalized_tensor_2).sum(dim=-1)
input_1=torch.randn(3,5,requires_grad=True)
print(input_1)
input_2=torch.randn(3,5,requires_grad=True)
print(input_2)
con=ConineSimilarity()
CS=con(input_1,input_2)
CS2=torch.cosine_similarity(input_1,input_2)
print(CS)
print(CS2)
输出:
tensor([[ 0.5389, 1.7485, -0.5183, 1.5721, -0.3880],
[-1.3460, 1.8793, -1.9676, 0.8554, -2.6176],
[-0.5190, -0.4626, -1.5462, 0.5101, -0.3836]], requires_grad=True)
tensor([[-0.3151, 0.0500, -0.2004, -0.8795, 0.2460],
[ 0.1276, 1.0000, 0.6290, -0.0722, -0.1960],
[-0.6387, -0.7833, -0.1992, 0.3575, 0.7043]], requires_grad=True)
tensor([-0.5903, 0.1863, 0.3887], grad_fn=)
tensor([-0.5903, 0.1863, 0.3887], grad_fn=)
1.1 余弦相似度(改进版)
class CosineSimilarity(nn.Module):
def forward(self, tensor_1, tensor_2):
norm_tensor_1=tensor_1.norm(dim=-1, keepdim=True)
norm_tensor_2=tensor_2.norm(dim=-1, keepdim=True)
norm_tensor_1=norm_tensor_1.numpy()
norm_tensor_2=norm_tensor_2.numpy()
for i,vec2 in enumerate(norm_tensor_1[0]) :
for j,scalar in enumerate(vec2):
if scalar==0:
norm_tensor_1[0][i][j]=1
for i, vec2 in enumerate(norm_tensor_2[0]):
for j, scalar in enumerate(vec2):
if scalar == 0:
norm_tensor_2[0][i][j]=1
norm_tensor_1=torch.tensor(norm_tensor_1)
norm_tensor_2 = torch.tensor(norm_tensor_2)
normalized_tensor_1 = tensor_1 / norm_tensor_1
normalized_tensor_2 = tensor_2 / norm_tensor_2
return (normalized_tensor_1*normalized_tensor_2).sum(dim=-1)
tensor_1=torch.randn((1,2,10))
tensor_2=torch.randn((1,2,10))
cos=CosineSimilarity()
c=cos(tensor_1,tensor_2)
print(c)
输出:
tensor([[-0.0684, -0.5751]])
不知道你能不能看出这段代码相较与上面的余弦相似度有何不同。
我也不卖关子了。
使用上面的那个余弦相似度,normalized_tensor_1中存在零值,使用tensor_1除以normalized_tensor_1,然后得到的相似度就会存在NAN值。为了解决这个问题,我们就需要排除零值。
class DotProductSimilarity(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,scale_output=False):
super(DotProductSimilarity,self).__init__()
self.scale_output=scale_output
def forward(self,tensor_1,tensor_2):
result=(tensor_1*tensor_2).sum(dim=-1)
if(self.scale_output):
result/=math.sqrt(tensor_1.size(-1))
return result
input_1=torch.randn(3,5,requires_grad=True)
print(input_1)
input_2=torch.randn(3,5,requires_grad=True)
print(input_2)
con=ConineSimilarity()
CS=con(input_1,input_2)
print(CS)
dot=DotProductSimilarity()
DS=dot(input_1,input_2)
print(DS)
输出:
tensor([[ 0.2148, 0.2645, 0.8717, -1.4637, 1.0932],
[-0.2975, -0.1585, 0.1567, -1.8238, -0.1437],
[-0.8243, -0.0170, -0.7533, -1.7643, 2.2571]], requires_grad=True)
tensor([[-1.8424, -1.4204, -1.5639, 0.2739, 0.7922],
[-0.3378, -2.3861, -1.7581, -0.8220, 0.3456],
[ 0.5536, 0.8324, -1.0632, -1.5567, 0.6374]], requires_grad=True)
tensor([-0.2780, 0.2843, 0.6595], grad_fn=)
tensor([-1.6696, 1.6526, 4.5157], grad_fn=)
余弦相似度的大小固定在-1-1之间,但是点乘却没有。
3 双线性相似度
计算公式如下:
b=x^T W y + b
class BiLinearSimilarity(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,tensor_1_dim,tensor_2_dim,activation=None):
super(BiLinearSimilarity,self).__init__()
self.weight_matrix=nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(tensor_1_dim,tensor_2_dim))
self.bias=nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(1))
self.activation=activation
self.reset_parameters()
def reset_parameters(self):
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.weight_matrix)
self.bias.data.fill_(0)
def forward(self, tensor_1,tensor_2):
intermediate=torch.matmul(tensor_1,self.weight_matrix)
result=(intermediate*tensor_2).sum(dim=-1)+self.bias
if self.activation is not None:
result=self.activation(result)
return result
input_1=torch.randn(3,5,requires_grad=True)
print(input_1)
input_2=torch.randn(3,5,requires_grad=True)
print(input_2)
con=ConineSimilarity()
CS=con(input_1,input_2)
print(CS)
dot=DotProductSimilarity()
DS=dot(input_1,input_2)
print(DS)
bilinear=BiLinearSimilarity(5,5)
BS=bilinear(input_1,input_2)
print(BS)
bilinear=BiLinearSimilarity(5,5)
BS=bilinear(input_1,input_2)
print(BS)
输出:
tensor([[ 0.1465, -0.8367, 0.5901, -0.7421, 0.7775],
[ 0.2198, 1.5482, 1.5923, 1.0962, -1.6559],
[-1.8222, -0.7740, -0.4819, -1.8031, 1.6413]], requires_grad=True)
tensor([[ 0.0053, 2.1358, 0.9435, 0.2379, 0.0689],
[-0.3503, 1.3089, 0.5033, -2.2339, 1.7092],
[-0.0255, 1.0277, 1.4797, 0.2870, -0.4866]], requires_grad=True)
tensor([-0.3862, -0.2676, -0.4630], grad_fn=)
tensor([-1.3525, -2.5285, -2.7782], grad_fn=)
tensor([ 0.0766, 3.2140, -2.2844], grad_fn=)
从上可见,双线性也并没有取值范围的限定。
以下是我根据自己理解上面的函数写的公式,感觉跟官方一些的对不上。
![]()
4 欧式距离
input_1=torch.randn(3,5,requires_grad=True)
print(input_1)
input_2=torch.randn(3,5,requires_grad=True)
print(input_2)
con=ConineSimilarity()
CS=con(input_1,input_2)
print(CS)
dot=DotProductSimilarity()
DS=dot(input_1,input_2)
print(DS)
bilinear=BiLinearSimilarity(5,5)
BS=bilinear(input_1,input_2)
print(BS)
bilinear=BiLinearSimilarity(5,5)
BS=bilinear(input_1,input_2)
print(BS)
import torch.nn.functional as F
e=F.pairwise_distance(input_1,input_2)
print(e)
输出:
tensor([[-1.0758, 1.2539, -1.4611, -0.5173, -0.3719],
[-0.3430, 1.0673, 0.3724, 0.2630, -0.0029],
[ 0.0570, 0.9101, 0.3809, 0.9970, 0.1919]], requires_grad=True)
tensor([[ 0.0319, -0.7283, -1.2269, 0.0922, 1.3412],
[-1.9286, 0.4859, -1.2347, 2.1949, -0.3295],
[-0.3811, 0.1348, -0.4247, -1.1917, 0.6632]], requires_grad=True)
tensor([ 0.0663, 0.3326, -0.5333], grad_fn=)
tensor([ 0.2986, 1.2986, -1.1216], grad_fn=)
tensor([ 0.4084, -0.2896, -0.4954], grad_fn=)
tensor([ 0.8389, 0.9224, -0.4486], grad_fn=)
tensor([2.9184, 3.0453, 2.5405], grad_fn=)
欧式距离输出范围也是不确定的。
class PearsonCorrelation(nn.Module):
def forward(self,tensor_1,tensor_2):
x = tensor_1
y = tensor_2
vx = x - torch.mean(x)
vy = y - torch.mean(y)
cost = torch.sum(vx * vy) / (torch.sqrt(torch.sum(vx ** 2)) * torch.sqrt(torch.sum(vy ** 2)))
return cost
input_1=torch.randn(3,5,requires_grad=True)
print(input_1)
input_2=torch.randn(3,5,requires_grad=True)
print(input_2)
pearson=PearsonCorrelation()
PC=pearson(input_1,input_2)
print(PC)
输出:
tensor([[-0.3064, 0.5541, 0.5944, 1.2654, 0.0281],
[ 1.0192, -0.8178, 0.2624, -1.4695, 0.3750],
[-1.7883, 0.5552, -0.1381, -0.6302, 0.6420]], requires_grad=True)
tensor([[ 0.8128, -0.3573, -0.8618, 1.2499, 0.5793],
[ 1.7729, 0.1705, -1.6051, -2.5970, 1.2015],
[-0.4328, 0.4294, 0.7364, 1.7886, 0.4203]], requires_grad=True)
tensor(0.4113, grad_fn=)
皮尔逊相关系数的值也限定在【-1,1】之间。
参考文献:
常用的计算向量相似度的函数(pytorch版本)
Pytorch欧式距离euclidean distance实现
皮尔逊在pytorch的应用问题