【WEB】struts2整合spring原理以及源码剖析
一、原理概述
1. struts和spring整合,到底是谁整合谁?
是struts整合spring还是spring整合struts?这个问题重要吗?有必要讨论吗?
说struts整合spring,是因为struts比spring晚出现,所以只能是struts整合spring,貌似有一定的道理,但是不绝对正确。一个框架的流行取决于市场的接受程度,在struts很流行的前提下如果spring没有那么流行,那么无论是谁先出现谁后出现,恐怕spring为了自身的发展也会要去整合struts。
事实上的确是struts整合spring,但原因不是两个框剪出现的时间,而是两个框架提供了什么样的jar包。struts和spring整合后的运行环境不再只是单纯的JVM,而是WEB服务器,spring提供接入web的jar包是spring-web-x.x.x.RELEASE.jar,这个jar包的作用是将spring容器整合到WEB容器(见上一篇博文:《【Spring】Spring&WEB整合原理及源码剖析》),而struts提供的jar包是struts2-spring-plugin-x.x.x.x.jar,这个jar包里面改写了struts默认的对象工厂ObjectFactory,重新提供了一个新的对象工厂SpringObjectFactory,在这个工厂类里面你会看到出现spring框架中的类和对象,也就是struts通过这个jar包,把spring整合到了自己的框架里面,从而享受spring带来的便利。
2. struts是表现层MVC框架,而spring是业务层框架,struts整合spring,整合的到底是什么东西?
spring的核心是IOC和AOP(加多spring MVC和spring JDBC/事务),通俗的讲spring是框架的框架,他自己本身就是一个框架,但是他主要服务于其他框架。所以整合的核心就落点于spring的”服务“,spring为其他框架提供了什么样的服务?换言之,struts需要把什么东西托管给spring,从而获得更好的服务?
这一切谜题的答案就在struts框架提供整合spring的jar包之中:struts2-spring-plugin-x.x.x.x.jar。
这个jar包里面主要提供了SpringObjectFactory这个对象工厂,将原来struts对象工厂创建的实例交由spring IOC容器来创建和管理,从而首先享受了spring提供的IOC服务,因为从spring容器获得bean实例,从而又享受到了spring带来的其他诸如AOP、spring JDBC、spring事务管理等等服务。
所以,struts整合spring,是将spring的IOC整合到了自己的框架里面!
3. 整合步骤如概述
1. spring整合web,参看上一篇文章《【Spring】Spring&WEB整合原理及源码剖析》,主要由spring框架提供的jar包完成:spring-web-x.x.x.RELEASE.jar;
2. struts接入spring,将原来struts自己ObjectFactory创建的对象交由SpringObjectFactory来创建并缓存,主要由struts提供的jar包完成:struts2-spring-plugin-2.3.15.3.jar;
3. 最后,不要忘记struts的Action托管给spring,并且设置scope="ptototype";
二、实现细节&源码code实现
一句话struts整合spring:配置好web.xml(spring接入web,struts配置过滤器,剩下的交由两个jar包处理即可,是不是太TM的简单了?一切就是那么简单!),导入spring-web-x.x.x.RELEASE.jar,导入struts2-spring-plugin-2.3.15.3.jar,完成!
因为spring整合web上一次有过详细讨论,这一次主要讨论的是struts提供的jar包,也即struts对象工厂的替换。
1. 怎么实现工厂替换
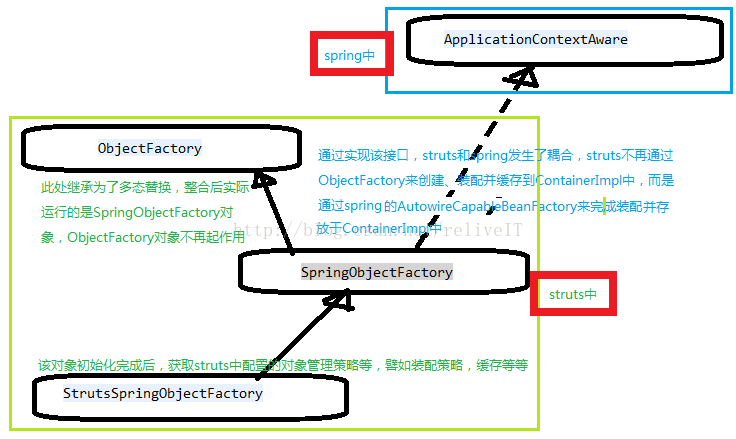
struts默认的对象工厂是ObjectFactory,该工厂提供了在struts启动的时候实例化、装配bean的操作,主要是struts-default.xml中配好的bean/result/interceptor(缓存在ContainerImpl中),以及运行期的action及其参数注入。
SpringObjectFactory是ObjectFactory的子类,要想替换ObjectFactory,利用面向对象三大特性“多态”即可完成。要想完成替换,需要告知struts你的意图,替换的开关在最先加载的框架起配置文件default.properties中,即struts.objectFactory = spring。要想打开这个开关,你可以在struts-default.xml、struts-plugin.xml、struts.xml、struts.properties、web.xml总共五处完成操作,当然struts-default.xml和struts-plugin.xml是不能修改的,除非系统已经提供。毋庸置疑,既然struts整合spring,那么struts提供的整合插件必然打开了这个开关,不需要你再手动配置。
struts.xml中对象工厂替换配置内容,默认开关是关闭的。
### if specified, the default object factory can be overridden here
### Note: short-hand notation is supported in some cases, such as "spring"
### Alternatively, you can provide a com.opensymphony.xwork2.ObjectFactory subclass name here
# struts.objectFactory = spring(看我看我看我看我看我,我就是开关,默认是关闭的,已经在struts-spring-plugin-xxx.jar中打开了,引入了该jar包即可,剩下的什么也不用操作)
### specifies the autoWiring logic when using the SpringObjectFactory.
### valid values are: name, type, auto, and constructor (name is the default)
struts.objectFactory.spring.autoWire = name
### indicates to the struts-spring integration if Class instances should be cached
### this should, until a future Spring release makes it possible, be left as true
### unless you know exactly what you are doing!
### valid values are: true, false (true is the default)
struts.objectFactory.spring.useClassCache = true
### ensures the autowire strategy is always respected.
### valid values are: true, false (false is the default)
struts.objectFactory.spring.autoWire.alwaysRespect = false
2. 替换了哪些内容
struts的默认工厂ObjectFactory里面提供了一堆的buildXXX方法,但是所有的buildXXX方法最终都通过调用buildBean来实现。其中涉及类的关系统如下所示。
更多细节,请参看源码注解。
package org.apache.struts2.spring;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.inject.Container;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.inject.Inject;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.spring.SpringObjectFactory;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.logging.Logger;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.logging.LoggerFactory;
import org.apache.struts2.StrutsConstants;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.AutowireCapableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
/**
* Struts object factory that integrates with Spring.
*
* Spring should be loaded using a web context listener
* org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener defined in web.xml.
*
*/
public class StrutsSpringObjectFactory extends SpringObjectFactory {
private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(StrutsSpringObjectFactory.class);
//@Inject
//public StrutsSpringObjectFactory(
// @Inject(value=StrutsConstants.STRUTS_OBJECTFACTORY_SPRING_AUTOWIRE,required=false) String autoWire,
// @Inject(value=StrutsConstants.STRUTS_OBJECTFACTORY_SPRING_USE_CLASS_CACHE,required=false) String useClassCacheStr,
// @Inject ServletContext servletContext) {
// this(autoWire, "false", useClassCacheStr, servletContext);
//}
/**
* Constructs the spring object factory
* @param autoWire The type of autowiring to use
* @param alwaysAutoWire Whether to always respect the autowiring or not
* @param useClassCacheStr Whether to use the class cache or not
* @param servletContext The servlet context
* @since 2.1.3
*/
@Inject
public StrutsSpringObjectFactory(
@Inject(value=StrutsConstants.STRUTS_OBJECTFACTORY_SPRING_AUTOWIRE,required=false) String autoWire,
@Inject(value=StrutsConstants.STRUTS_OBJECTFACTORY_SPRING_AUTOWIRE_ALWAYS_RESPECT,required=false) String alwaysAutoWire,
@Inject(value=StrutsConstants.STRUTS_OBJECTFACTORY_SPRING_USE_CLASS_CACHE,required=false) String useClassCacheStr,
@Inject ServletContext servletContext,
@Inject(StrutsConstants.STRUTS_DEVMODE) String devMode,
@Inject Container container) {
super();
boolean useClassCache = "true".equals(useClassCacheStr);
if (LOG.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOG.info("Initializing Struts-Spring integration...");
}
/**
* 从ServletContext中获取spring IOC容器
* 该容器在spring web的jar包中创建完成并放入ServletContext,具体代码在ContextLoader类中
*/
Object rootWebApplicationContext = servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE);
if(rootWebApplicationContext instanceof RuntimeException){
RuntimeException runtimeException = (RuntimeException)rootWebApplicationContext;
LOG.fatal(runtimeException.getMessage());
return;
}
//强转成父类型
ApplicationContext appContext = (ApplicationContext) rootWebApplicationContext;
if (appContext == null) {
// uh oh! looks like the lifecycle listener wasn't installed. Let's inform the user
String message = "********** FATAL ERROR STARTING UP STRUTS-SPRING INTEGRATION **********\n" +
"Looks like the Spring listener was not configured for your web app! \n" +
"Nothing will work until WebApplicationContextUtils returns a valid ApplicationContext.\n" +
"You might need to add the following to web.xml: \n" +
" \n" +
" org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener \n" +
" ";
LOG.fatal(message);
return;
}
//从struts容器中获取一些开发模式的实例
String watchList = container.getInstance(String.class, "struts.class.reloading.watchList");
String acceptClasses = container.getInstance(String.class, "struts.class.reloading.acceptClasses");
String reloadConfig = container.getInstance(String.class, "struts.class.reloading.reloadConfig");
//对于开发模式的处理
if ("true".equals(devMode)
&& StringUtils.isNotBlank(watchList)
&& appContext instanceof ClassReloadingXMLWebApplicationContext) {
//prevent class caching
useClassCache = false;
ClassReloadingXMLWebApplicationContext reloadingContext = (ClassReloadingXMLWebApplicationContext) appContext;
reloadingContext.setupReloading(watchList.split(","), acceptClasses, servletContext, "true".equals(reloadConfig));
if (LOG.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOG.info("Class reloading is enabled. Make sure this is not used on a production environment!", watchList);
}
setClassLoader(reloadingContext.getReloadingClassLoader());
//we need to reload the context, so our isntance of the factory is picked up
reloadingContext.refresh();
}
/**
* 为SpringObjectFactory设置容器(替代ContainerImpl)
* 方法setApplicationContext来自父类SpringObjectFactory
* SpringObjectFactory中方法重写了ApplicationContextAware(spring中的类)
* 此时,struts开始和spring发生耦合,struts获得了spring的IOC容器
*/
this.setApplicationContext(appContext);
/**
* 开启spring工厂开关后,struts配置文件default.properties中关于springObjectFactory开始生效
* 默认是按照name进行装配 struts.objectFactory.spring.autoWire = name
* 提供的装配类型有:
* name(名字装配)、type(类型装配)、constructor(按构造器装配)、auto(自动装配)、no(不自动装配)
*/
int type = AutowireCapableBeanFactory.AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME; // default
if ("name".equals(autoWire)) {
type = AutowireCapableBeanFactory.AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME;
} else if ("type".equals(autoWire)) {
type = AutowireCapableBeanFactory.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE;
} else if ("auto".equals(autoWire)) {
type = AutowireCapableBeanFactory.AUTOWIRE_AUTODETECT;
} else if ("constructor".equals(autoWire)) {
type = AutowireCapableBeanFactory.AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR;
} else if ("no".equals(autoWire)) {
type = AutowireCapableBeanFactory.AUTOWIRE_NO;
}
this.setAutowireStrategy(type);
this.setUseClassCache(useClassCache);
this.setAlwaysRespectAutowireStrategy("true".equalsIgnoreCase(alwaysAutoWire));
if (LOG.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOG.info("... initialized Struts-Spring integration successfully");
}
}
}package com.opensymphony.xwork2.spring;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ObjectFactory;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.inject.Inject;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.logging.Logger;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.logging.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.UnsatisfiedDependencyException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.AutowireCapableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* Simple implementation of the ObjectFactory that makes use of Spring's application context if one has been configured,
* before falling back on the default mechanism of instantiating a new class using the class name. In order to use
* this class in your application, you will need to instantiate a copy of this class and set it as XWork's ObjectFactory
* before the xwork.xml file is parsed. In a servlet environment, this could be done using a ServletContextListener.
*
* @author Simon Stewart ([email protected])
*/
public class SpringObjectFactory extends ObjectFactory implements ApplicationContextAware {
private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SpringObjectFactory.class);
protected ApplicationContext appContext;//spring IOC容器
protected AutowireCapableBeanFactory autoWiringFactory;//spring中用于自动装配的类
protected int autowireStrategy = AutowireCapableBeanFactory.AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME;//默认按照name进行装配,配置项在default.properties中
private final Map classes = new HashMap();
private boolean useClassCache = true;
private boolean alwaysRespectAutowireStrategy = false;
@Inject(value="applicationContextPath",required=false)
public void setApplicationContextPath(String ctx) {
if (ctx != null) {
setApplicationContext(new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(ctx));
}
}
/**
* Set the Spring ApplicationContext that should be used to look beans up with.
*
* @param appContext The Spring ApplicationContext that should be used to look beans up with.
*/
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext appContext)
throws BeansException {
this.appContext = appContext;
autoWiringFactory = findAutoWiringBeanFactory(this.appContext);
}
/**
* Sets the autowiring strategy
* 装配策略
* @param autowireStrategy
*/
public void setAutowireStrategy(int autowireStrategy) {
switch (autowireStrategy) {
case AutowireCapableBeanFactory.AUTOWIRE_AUTODETECT:
if (LOG.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOG.info("Setting autowire strategy to autodetect");
}
this.autowireStrategy = autowireStrategy;
break;
case AutowireCapableBeanFactory.AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME:
if (LOG.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOG.info("Setting autowire strategy to name");
}
this.autowireStrategy = autowireStrategy;
break;
case AutowireCapableBeanFactory.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE:
if (LOG.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOG.info("Setting autowire strategy to type");
}
this.autowireStrategy = autowireStrategy;
break;
case AutowireCapableBeanFactory.AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR:
if (LOG.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOG.info("Setting autowire strategy to constructor");
}
this.autowireStrategy = autowireStrategy;
break;
case AutowireCapableBeanFactory.AUTOWIRE_NO:
if (LOG.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOG.info("Setting autowire strategy to none");
}
this.autowireStrategy = autowireStrategy;
break;
default:
throw new IllegalStateException("Invalid autowire type set");
}
}
public int getAutowireStrategy() {
return autowireStrategy;
}
/**
* If the given context is assignable to AutowireCapbleBeanFactory or contains a parent or a factory that is, then
* set the autoWiringFactory appropriately.
*
* @param context
*/
protected AutowireCapableBeanFactory findAutoWiringBeanFactory(ApplicationContext context) {
if (context instanceof AutowireCapableBeanFactory) {
// Check the context
return (AutowireCapableBeanFactory) context;
} else if (context instanceof ConfigurableApplicationContext) {
// Try and grab the beanFactory
return ((ConfigurableApplicationContext) context).getBeanFactory();
} else if (context.getParent() != null) {
// And if all else fails, try again with the parent context
return findAutoWiringBeanFactory(context.getParent());
}
return null;
}
/**
* Looks up beans using Spring's application context before falling back to the method defined in the {@link
* ObjectFactory}.
*
* @param beanName The name of the bean to look up in the application context
* @param extraContext
* @return A bean from Spring or the result of calling the overridden
* method.
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public Object buildBean(String beanName, Map extraContext, boolean injectInternal) throws Exception {
Object o;
if (appContext.containsBean(beanName)) {
o = appContext.getBean(beanName);
} else {
Class beanClazz = getClassInstance(beanName);
o = buildBean(beanClazz, extraContext);
}
if (injectInternal) {
injectInternalBeans(o);
}
return o;
}
/**
* @param clazz
* @param extraContext
* @throws Exception
* 所有创建和装配对象的最终方法,也是最重要的方法
* 不再由struts创建并缓存
* 而是由spring的自动装配类autoWiringFactory来创建和装配,最后
*/
@Override
public Object buildBean(Class clazz, Map extraContext) throws Exception {
Object bean;
try {
// Decide to follow autowire strategy or use the legacy approach which mixes injection strategies
if (alwaysRespectAutowireStrategy) {
// Leave the creation up to Spring
bean = autoWiringFactory.createBean(clazz, autowireStrategy, false);
injectApplicationContext(bean);
return injectInternalBeans(bean);//放入容器
} else {
bean = autoWiringFactory.autowire(clazz, AutowireCapableBeanFactory.AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR, false);
bean = autoWiringFactory.applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(bean, bean.getClass().getName());
// We don't need to call the init-method since one won't be registered.
bean = autoWiringFactory.applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(bean, bean.getClass().getName());
return autoWireBean(bean, autoWiringFactory);//自动装配bean,并放入容器
}
} catch (UnsatisfiedDependencyException e) {
if (LOG.isErrorEnabled())
LOG.error("Error building bean", e);
// Fall back
return autoWireBean(super.buildBean(clazz, extraContext), autoWiringFactory);
}
}
public Object autoWireBean(Object bean) {
return autoWireBean(bean, autoWiringFactory);
}
/**
* @param bean
* @param autoWiringFactory
*/
public Object autoWireBean(Object bean, AutowireCapableBeanFactory autoWiringFactory) {
if (autoWiringFactory != null) {
autoWiringFactory.autowireBeanProperties(bean,
autowireStrategy, false);
}
injectApplicationContext(bean);
injectInternalBeans(bean);
return bean;
}
private void injectApplicationContext(Object bean) {
if (bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware) {
((ApplicationContextAware) bean).setApplicationContext(appContext);
}
}
public Class getClassInstance(String className) throws ClassNotFoundException {
Class clazz = null;
if (useClassCache) {
synchronized(classes) {
// this cache of classes is needed because Spring sucks at dealing with situations where the
// class instance changes
clazz = (Class) classes.get(className);
}
}
if (clazz == null) {
if (appContext.containsBean(className)) {
clazz = appContext.getBean(className).getClass();
} else {
clazz = super.getClassInstance(className);
}
if (useClassCache) {
synchronized(classes) {
classes.put(className, clazz);
}
}
}
return clazz;
}
/**
* This method sets the ObjectFactory used by XWork to this object. It's best used as the "init-method" of a Spring
* bean definition in order to hook Spring and XWork together properly (as an alternative to the
* org.apache.struts2.spring.lifecycle.SpringObjectFactoryListener)
* @deprecated Since 2.1 as it isn't necessary
*/
@Deprecated public void initObjectFactory() {
// not necessary anymore
}
/**
* Allows for ObjectFactory implementations that support
* Actions without no-arg constructors.
*
* @return false
*/
@Override
public boolean isNoArgConstructorRequired() {
return false;
}
/**
* Enable / disable caching of classes loaded by Spring.
*
* @param useClassCache
*/
public void setUseClassCache(boolean useClassCache) {
this.useClassCache = useClassCache;
}
/**
* Determines if the autowire strategy is always followed when creating beans
*
* @param alwaysRespectAutowireStrategy True if the strategy is always used
*/
public void setAlwaysRespectAutowireStrategy(boolean alwaysRespectAutowireStrategy) {
this.alwaysRespectAutowireStrategy = alwaysRespectAutowireStrategy;
}
} 3. 带来的效果
struts中的Action, Inteceptor, Result, Converter, Validator的创建和装配交由Spring,struts自己创建的对象允许spring装配。
4. 启动顺序
web容器、spring、struts三者的启动顺序,web容器(ServletContext)会最先启动,接着是spring,最后才是struts。
从启动类型来看。web容器的启动依赖于web.xml,而xml中的配置加载顺序是context-param>listener>filter>servlet,context-param加载后会以KV形式set到web容器ServletContext中,所以web容器最先启动;接着是listener,spring 2.4以后只提供了listener方式整合web,因此接着启动的是spring;最后是通过filter实现拦截HTTP的struts。
从依赖关系来看。struts启动依赖于对象工厂,而struts的对象工厂依赖于spring的WebApplicationContext,而spring的WebApplicationContext的创建则依赖于ServletContext,因此最先启动的是web容器,接着是spring和struts。
5. 伪类名
action要交由spring创建和注入,则需要在struts中配置的时候起class属性采用伪类名,即applicationContext.xml中bean的属性id,否则是由struts自己创建action,但是是spring来装配。
三、整合实现范例
如上所述,一句话struts整合spring,配置文件的参考范例如下,亲测无误。
1. web.xml
ss01
contextConfigLocation
classpath:applicationContext.xml
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener
struts2
org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ng.filter.StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter
struts2
/*
index.jsp
2. applicationContext.xml
3. struts.xml
/WEB-INF/jsp/succ.jsp
附注:
本文如有错漏,烦请不吝指正,谢谢!