Spring+ehcache+redis两级缓存--缓存实战篇(1)
在上篇《性能优化-缓存篇》中已经从理论上介绍了缓存,其实,缓存简单易用,更多精力关注的是根据实际业务的选择缓存策略。
本文主要介绍为什么要构建ehcache+redis两级缓存?以及在实战中如何实现?思考如何配置缓存策略更合适?这样的方案可能遗留什么问题?JUST DO IT! GO!
问题描述
场景:我们的应用系统是分布式集群的,可横向扩展的。应用中某个接口操作满足以下一个或多个条件:
1. 接口运行复杂代价大,
2. 接口返回数据量大,
3. 接口的数据基本不会更改,
4. 接口数据一致性要求不高(只需满足最终一致)。
此时,我们会考虑将这个接口的返回值做缓存。考虑到上述条件,我们需要一套高可用分布式的缓存集群,并具备持久化功能,备选的有ehcache集群或redis主备(sentinel)。
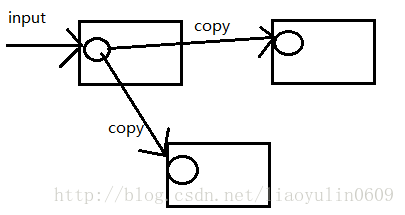
- ehcache集群因为节点之间数据同步通过组播的方式,可能带来的问题:节点间大量的数据复制带来额外的开销,在节点多的情况下此问题越发严重,N个节点会出现N-1次网络传输数据进行同步。(见下图,缓存集群中有三台机器,其中一台机器接收到数据,需要拷贝到其他机器,一次input后需要copy两次,两次copy是需要网络传输消耗的)
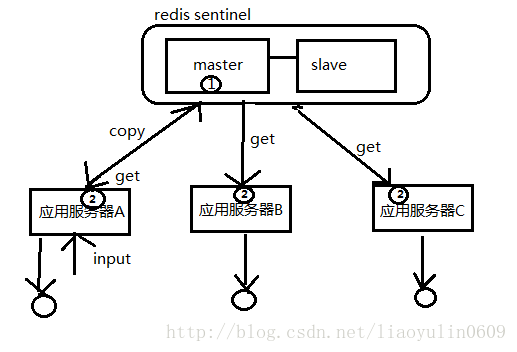
- redis主备由于作为中心节点提供缓存,其他节点都向redis中心节点取数据,所以,一次网络传输即可。(当然此处的一次网络代价跟组播的代价是不一样的)但是,随着访问量增大,大量的缓存数据访问使得应用服务器和缓存服务器之间的网络I/O消耗越大。(见下图,同样三台应用服务器,redis sentinel作为中心节点缓存。所谓中心,即所有应用服务器以redis为缓存中心,不再像ehcache集群,缓存是分散存放在应用服务器中,需要互相同步的,任何一台应用服务器的input,都会经过一次copy网络传输到redis,由于redis是中心共享的,那么就可以不用同步的步骤,其他应用服务器需要只需去get取即可。但是,我们会发现多了N台服务器的get的网络开销。)
提出方案
那么要怎么处理呢?所以两级缓存的思想诞生了,在redis的方案上做一步优化,在缓存到远程redis的同时,缓存一份到本地进程ehcache(此处的ehcache不用做集群,避免组播带来的开销),取缓存的时候会先取本地,没有会向redis请求,这样会减少应用服务器<–>缓存服务器redis之间的网络开销。(见下图,为了减少get这几条网络传输,我们会在每个应用服务器上增加本地的ehcache缓存作为二级缓存,即第一次get到的数据存入ehcache,后面output输出即可从本地ehcache中获取,不用再访问redis了,所以就减少了以后get的网络开销。get开销只要一次,后续不需要了,除非本地缓存过期需要再get。)
如果用过j2cache的都应该知道,oschina用j2cache这种两级缓存,实践证明了该方案是可行的。该篇使用spring+ehcache+redis实现更加简洁。
方案实施
1、 spring和ehcache集成
主要获取ehcache作为操作ehcache的对象。
ehcache.xml 代码如下:
<ehcache updateCheck="false" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="http://ehcache.sf.net/ehcache.xsd">
<diskStore path="java.io.tmpdir/ehcache"/>
<defaultCache maxElementsInMemory="10000"
eternal="false"
timeToIdleSeconds="3600"
timeToLiveSeconds="3600"
overflowToDisk="true"
diskPersistent="false"
diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU"/>
<cache name="userCache"
maxElementsInMemory="1000"
eternal="true"
overflowToDisk="false"
timeToIdleSeconds="0"
timeToLiveSeconds="0"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LFU">
cache>
<cacheManagerPeerProviderFactory
class="net.sf.ehcache.distribution.RMICacheManagerPeerProviderFactory"
properties="peerDiscovery=automatic,
multicastGroupAddress=230.0.0.1,
multicastGroupPort=4546, timeToLive=1"/>
<cache name="webCache_LT"
maxElementsInMemory="10000"
eternal="false"
overflowToDisk="false"
timeToIdleSeconds="3600"
timeToLiveSeconds="3600"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU">
<cacheEventListenerFactory
class="net.sf.ehcache.distribution.RMICacheReplicatorFactory"
properties="replicateRemovals=true"/>
<bootstrapCacheLoaderFactory
class="net.sf.ehcache.distribution.RMIBootstrapCacheLoaderFactory"/>
cache>
<cache name="webCache_ST"
maxElementsInMemory="1000"
eternal="false"
overflowToDisk="false"
timeToIdleSeconds="300"
timeToLiveSeconds="300"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU">
<cacheEventListenerFactory
class="net.sf.ehcache.distribution.RMICacheReplicatorFactory"
properties="replicateRemovals=true"/>
<bootstrapCacheLoaderFactory
class="net.sf.ehcache.distribution.RMIBootstrapCacheLoaderFactory"/>
cache>
ehcache>
spring.xml中注入ehcacheManager和ehCache对象,ehcacheManager是需要加载ehcache.xml配置信息,创建ehcache.xml中配置不同策略的cache。
<bean id="ehcacheManager" class="org.springframework.cache.ehcache.EhCacheManagerFactoryBean">
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:ehcache.xml" />
<property name="shared" value="true" />
<property name="cacheManagerName" value="ehcacheManager" />
bean>
<bean id="ehCache" class="org.springframework.cache.ehcache.EhCacheFactoryBean">
<property name="cacheName" value="ehCache"/>
<property name="cacheManager" ref="ehcacheManager"/>
bean>
2、 spring和redis集成
主要获取redisTemplate作为操作redis的对象。
redis.properties配置信息
#host 写入redis服务器地址
redis.ip=127.0.0.1
#Port
redis.port=6379
#Passord
#redis.password=123456
#连接超时30000
redis.timeout=30
#最大分配的对象数
redis.pool.maxActive=100
#最大能够保持idel状态的对象数
redis.pool.maxIdle=30
#当池内没有返回对象时,最大等待时间
redis.pool.maxWait=1000
#当调用borrow Object方法时,是否进行有效性检查
redis.pool.testOnBorrow=true
#当调用return Object方法时,是否进行有效性检查
redis.pool.testOnReturn=true
spring注入jedisPool、redisConnFactory、redisTemplate对象
<bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="locations" value="classpath:redis.properties"/>
bean>
<bean id="jedisPool" class="redis.clients.jedis.JedisPoolConfig">
<property name="maxTotal" value="${redis.pool.maxActive}" />
<property name="maxIdle" value="${redis.pool.maxIdle}" />
<property name="testOnBorrow" value="${redis.pool.testOnBorrow}" />
<property name="testOnReturn" value="${redis.pool.testOnReturn}" />
<property name="maxWaitMillis" value="${redis.pool.maxWait}" />
bean>
<bean id="redisConnFactory"
class="org.springframework.data.redis.connection.jedis.JedisConnectionFactory">
<property name="hostName" value="${redis.ip}" />
<property name="port" value="${redis.port}" />
<property name="timeout" value="${redis.timeout}" />
<property name="poolConfig" ref="jedisPool" />
bean>
<bean id="redisTemplate" class="org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate">
<property name="connectionFactory" ref="redisConnFactory" />
bean>
3、 spring集成ehcache和redis
通过上面两步注入的ehcache和redisTemplate我们就能自定义一个方法将两者整合起来。详见EhRedisCache类。
EhRedisCache.java
/**
* 两级缓存,一级:ehcache,二级为redisCache
* @author yulin
*
*/
public class EhRedisCache implements Cache{
private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(UserServiceImpl.class);
private String name;
private net.sf.ehcache.Cache ehCache;
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
private long liveTime = 1*60*60; //默认1h=1*60*60
@Override
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
@Override
public Object getNativeCache() {
return this;
}
@Override
public ValueWrapper get(Object key) {
Element value = ehCache.get(key);
LOG.info("Cache L1 (ehcache) :{}={}",key,value);
if (value!=null) {
return (value != null ? new SimpleValueWrapper(value.getObjectValue()) : null);
}
//TODO 这样会不会更好?访问10次EhCache 强制访问一次redis 使得数据不失效
final String keyStr = key.toString();
Object objectValue = redisTemplate.execute(new RedisCallback spring注入自定义缓存
<bean id="ehRedisCacheManager" class="org.springframework.cache.support.SimpleCacheManager">
<property name="caches">
<set>
<bean id="ehRedisCache" class="org.musicmaster.yulin.ercache.EhRedisCache">
<property name="redisTemplate" ref="redisTemplate" />
<property name="ehCache" ref="ehCache"/>
<property name="name" value="userCache"/>
bean>
set>
property>
bean>
<cache:annotation-driven cache-manager="ehRedisCacheManager"
proxy-target-class="true" />
4、 模拟问题中提到的接口
此处假设该接口满足上述条件。
UserService.java
public interface UserService {
User findById(long id);
List findByPage(int startIndex, int limit);
List findBySex(Sex sex);
List findByAge(int lessAge);
List findByUsers(List users);
boolean update(User user);
boolean deleteById(long id);
}
UserServiceImpl.java
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{
private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(UserServiceImpl.class);
@Cacheable("userCache")
@Override
public User findById(long id) {
LOG.info("visit business service findById,id:{}",id);
User user = new User();
user.setId(id);
user.setUserName("tony");
user.setPassWord("******");
user.setSex(Sex.M);
user.setAge(32);
//耗时操作
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return user;
}
@Override
public List findByPage(int startIndex, int limit) {
return null;
}
@Cacheable("userCache")
@Override
public List findBySex(Sex sex) {
LOG.info("visit business service findBySex,sex:{}",sex);
List users = new ArrayList();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
User user = new User();
user.setId(i);
user.setUserName("tony"+i);
user.setPassWord("******");
user.setSex(sex);
user.setAge(32+i);
users.add(user);
}
return users;
}
@Override
public List findByAge(int lessAge) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return null;
}
//FIXME 此处将list参数的地址作为key存储,是否有问题?
@Cacheable("userCache")
@Override
public List findByUsers(List users) {
LOG.info("visit business service findByUsers,users:{}",users);
return users;
}
@CacheEvict("userCache")
@Override
public boolean update(User user) {
return true;
}
@CacheEvict("userCache")
@Override
public boolean deleteById(long id) {
return false;
}
}
User.java
public class User implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public enum Sex{
M,FM
}
private long id;
private String userName;
private String passWord;
private int age;
private Sex sex;
public long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public String getPassWord() {
return passWord;
}
public void setPassWord(String passWord) {
this.passWord = passWord;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Sex getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(Sex sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [id=" + id + ", userName=" + userName + ", passWord="
+ passWord + ", age=" + age + ", sex=" + sex + "]";
}
}
实施结果
我们写个测试类来模拟下
TestEhRedisCache.java
public class TestEhRedisCache{
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-ehRedisCache.xml");
UserService userService= (UserService) context.getBean("userServiceImpl");
System.out.println(userService.findById(5l));
System.out.println(userService.findById(5l));
System.out.println(userService.findById(5l));
System.out.println(userService.findById(5l));
System.out.println(userService.findById(5l));
}
}
TEST1 输出结果:
Cache L1 (ehcache) :UserServiceImpl/findById/5=null
Cache L2 (redis) :UserServiceImpl/findById/5=null
visit business service findById,id:5
User [id=5, userName=tony, passWord=******, age=32, sex=M]
Cache L1 (ehcache) :UserServiceImpl/findById/5=User [id=5, userName=tony, passWord=******, age=32, sex=M]
User [id=5, userName=tony, passWord=******, age=32, sex=M]
Cache L1 (ehcache) :UserServiceImpl/findById/5=User [id=5, userName=tony, passWord=******, age=32, sex=M]
User [id=5, userName=tony, passWord=******, age=32, sex=M]
Cache L1 (ehcache) :UserServiceImpl/findById/5=User [id=5, userName=tony, passWord=******, age=32, sex=M]
User [id=5, userName=tony, passWord=******, age=32, sex=M]
Cache L1 (ehcache) :UserServiceImpl/findById/5=User [id=5, userName=tony, passWord=******, age=32, sex=M]
User [id=5, userName=tony, passWord=******, age=32, sex=M]
上面第一次访问,一级缓存ehcache和二级缓存redis都没有数据,访问接口耗时操作,打印日志:
visit business service findById,id:5
第二次之后的访问,都会访问一级缓存ehcache,此时响应速度很快。
TEST2 在TEST1结束后,我们在liveTime的时间内,也就是redis缓存还未过期再次执行,会出现以下结果
Cache L1 (ehcache) :UserServiceImpl/findById/5=null
Cache L2 (redis) :UserServiceImpl/findById/5=User [id=5, userName=tony, passWord=******, age=32, sex=M]
User [id=5, userName=tony, passWord=******, age=32, sex=M]
Cache L1 (ehcache) :UserServiceImpl/findById/5=User [id=5, userName=tony, passWord=******, age=32, sex=M]
User [id=5, userName=tony, passWord=******, age=32, sex=M]
Cache L1 (ehcache) :UserServiceImpl/findById/5=User [id=5, userName=tony, passWord=******, age=32, sex=M]
User [id=5, userName=tony, passWord=******, age=32, sex=M]
Cache L1 (ehcache) :UserServiceImpl/findById/5=User [id=5, userName=tony, passWord=******, age=32, sex=M]
User [id=5, userName=tony, passWord=******, age=32, sex=M]
Cache L1 (ehcache) :UserServiceImpl/findById/5=User [id=5, userName=tony, passWord=******, age=32, sex=M]
User [id=5, userName=tony, passWord=******, age=32, sex=M]
由于TEST1执行完结束后,ehcache为进程间的缓存,自然随着运行结束而释放,所以TEST2出现:
Cache L1 (ehcache) :UserServiceImpl/findById/5=null
然而在第二次访问二级缓存redis,还未到缓存过期时间,所以在redis中找到数据(同时数据入一级缓存ehcache):
Cache L2 (redis) :UserServiceImpl/findById/5=User [id=5, userName=tony, passWord=**, age=32, sex=M]
此处不会visit….没有经过接口的耗时操作,接下来数据都可以在本地缓存ehcache中获取。
总结
经过demo实践结果符合预期效果,还需更大规模的测试。遗留了几个问题,在代码处的TODO和FIXME中,留给大家一起来思考,一起来探讨解决。问题解决和源码下载:《spring + ehcache + redis两级缓存实战篇(2)》
