【多线程高并发】线程池初始化过程、线程池中的阻塞队列
多线程高并发一定少不了线程池技术。
作用
-
提升性能
线程的创建和销毁都会消耗一定的性能,通过线程池可以减少线程 的创建和销毁带来的性能消耗。 -
便于管理
方便对线程进行统一的维护管理,比如定时开启,周期执行,并发数控制等
参数及含义
-
corePoolSize
核心线程数,队列没满时,线程最大的并发数 -
maximumPoolSize
线程池最大线程数,队列满时,线程最大并发数 -
keepAliveTime
空闲线程的最大存活时间,系统默认只回收非核心线程,核心线程可以通过 设置 threadPoolExecutor.allowCoreThreadTimeOut(true);来运行核心 线程的销毁。 -
TimeUnit
空闲时间的时间单位 -
BlockingQueue workQueue
线程池中的阻塞队列类型(下面详细介绍各种阻塞队列的区别) -
ThreadFactory threadFactory
线程工厂,用于创建线程 -
RejectedExecutionHandler handler
拒绝策略,当线程池数量达到最大线程数限制时,采取的具体执行措施
线程池的初始化过程
当调用线程池执行任务时,要进行如下的步骤:
1、当线程池中线程数小于corePoolSize时,新提交任务将创建一个新线程执行任务,即使此时线程池中存在空闲线程。
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("name = " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
};
//核心线程数为5,最大线程数为10
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(5,10,
5, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(10));
threadPoolExecutor.execute(runnable);
threadPoolExecutor.execute(runnable);
threadPoolExecutor.execute(runnable);
System.out.println("核心线程数 = " + threadPoolExecutor.getCorePoolSize());
System.out.println("当前线程池线程数 = "+threadPoolExecutor.getPoolSize());
System.out.println("maxPoolNum = " + threadPoolExecutor.getMaximumPoolSize());
System.out.println("当前队列中的任务数 queue size = " + threadPoolExecutor.getQueue().size());
}
只启动了3个线程执行任务,如果再来一个任务,无论之前的线程是否空闲线程池会再开启一个线程执行。
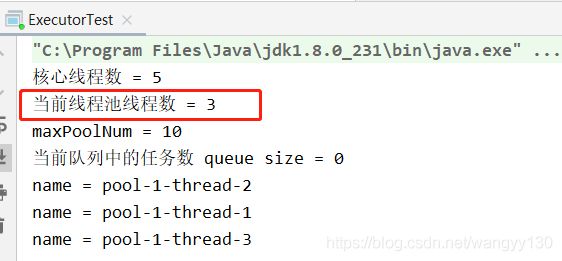
2、当线程池中线程数达到corePoolSize时,新提交任务将被放入workQueue中,等待线程池中任务调度执行 。
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("name = " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
};
//核心线程数为5,最大线程数为10
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(5,10,
5, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(10));
//开启8个任务
threadPoolExecutor.execute(runnable);
threadPoolExecutor.execute(runnable);
threadPoolExecutor.execute(runnable);
threadPoolExecutor.execute(runnable);
threadPoolExecutor.execute(runnable);
threadPoolExecutor.execute(runnable);
threadPoolExecutor.execute(runnable);
threadPoolExecutor.execute(runnable);
System.out.println("核心线程数 = " + threadPoolExecutor.getCorePoolSize());
System.out.println("当前线程池线程数 = "+threadPoolExecutor.getPoolSize());
System.out.println("maxPoolNum = " + threadPoolExecutor.getMaximumPoolSize());
System.out.println("当前队列中的任务数 queue size = " + threadPoolExecutor.getQueue().size());
}
当超过核心线程数时(8 > 5),其余任务会放入队列中去。当然这里要根据不同类型的队列会有不同之处。
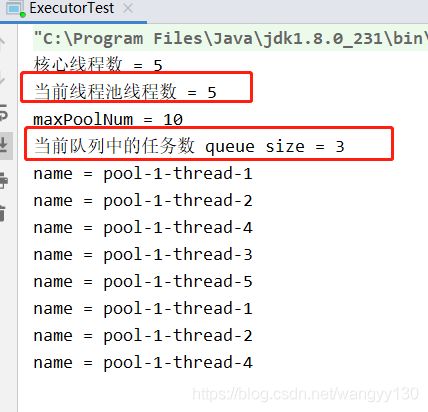
3、当workQueue已满,且maximumPoolSize > corePoolSize时,新提交任务会创建新线程执行任务。
代码同上,当开始18个任务时,结果如下:线程池中的线程数已经成了8个了
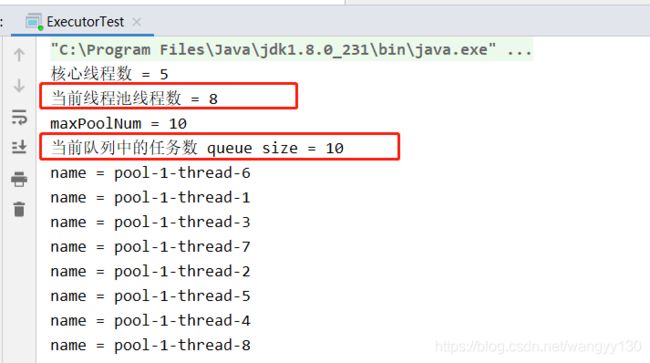
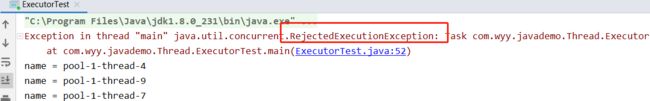
4、当workQueue已满,且提交任务数超过maximumPoolSize,任务由RejectedExecutionHandler处理。
当开启任务超过20个时,会通过拒绝策略来执行,默认拒绝执行抛出异常。
5、当线程池中线程数超过corePoolSize,且超过这部分的空闲时间达到keepAliveTime时,回收这些线程。
6、当设置allowCoreThreadTimeOut(true)时,线程池中corePoolSize范围内的线程空闲时间达到keepAliveTime也将回收。
线程池分类和阻塞队列
- 固定线程池 newFixedThreadPool
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
}
1、队列为LinkedBlockingQueue
2、默认无界队列(可以通过参数设定有限)最大值为Integer.MAX_VALUE
3、核心线程数 = 最大线程数
4、空闲时间为0
5、由于任务队列是无界队列,当并发数很高时,慎用,容易内存溢出。
- 可缓存的线程池 newCachedThreadPool
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
}
1、队列为SynchronousQueue 任务队列中只能存放一个元素,放入一个元素必须消费掉
才可以再放入第二个,否则一直阻塞。
2、核心线程为0,最大为Integer.MAX_VALUE,他是一个可以无限扩大的线程池。
每次新来呀一个任务,总是会新建一个线程来执行,当达到最大线程数时,
可以通过空闲(60s)线程来执行。
3、适用于处理任务时间短,处理速度大于提交速度的场景。对CPU要求高
- 单一线程池 newSingleThreadExecutor
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()));
}
1、队列为LinkedBlockingQueue ,无界队列
2、核心线程数 = 最大线程数 = 1
3、 空闲时间为 0 ,任务队列无界注意OOM
- 定时任务线程池 newScheduledThreadPool
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, NANOSECONDS,
new DelayedWorkQueue());
}
1、队列为DelayedWorkQueue ,有界队列
2、最大线程数无界
3、可以设置定时执行,延时执行等。
-
工作窃取线程池 newWorkStealingPool
1、利用了ForkJoinPool进行实现 2、java1.8提供,适用于比较耗时的并发操作 3、工作窃取线程,当一个线程执行完以后,会去执行其他线程的任务 -
自定义线程池
由于java中提供的线程池会出现各种问题,不一定适用于我们的使用场景,所以我们可以通过根据业务自己设定参数来自定义线程池。
//使用了ArrayBlockingQueue 有界队列,核心线程数为5,最大线程数为10,空闲时间为5s
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(5,10,
5, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(10));