RabbitMQ入门(六)RabbitMQ交换器之fanout
前言
本章讲解RabbitMQ常用交换器的最后一个类型——fanout
方法
1.概念
fanout(广播),顾名思义,其可以不依赖路由键,向所有绑定了的队列发送消息。
广播的含义就是将消息发送给所有订阅该频道的听众。
需求:我们的用户下订单之后,我们会做如下的两步操作:发短信、推送订单,在以前的模式上,我们下订单的业务逻辑和发短信,推送订单的逻辑是强耦合的,当我们使用RabbitMQ之后,情况将变得十分乐观。我们可以为发短信和推送订单业务各设立一个队列,当用户下订单的时候,会将消息同时传递给这两个队列,进而进行后续的发短信和推送订单业务,实现解耦。
2.环境搭建
1)创建Provider和Consumer工程
2)修改pom文件
4.0.0
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
2.1.7.RELEASE
cn.edu.ccut
rabbitmq-fanout-consumer
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
1.8
3.1.0
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-amqp
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-devtools
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
cn.edu.ccut.App
3)修改application.properties
Provider:
spring.application.name=springboot-rabbitmq
#rabbitmq config
spring.rabbitmq.host=192.168.1.108
spring.rabbitmq.port=5672
spring.rabbitmq.username=jwang
spring.rabbitmq.password=123456
#exchange config
mq.config.exchange=order.fanoutConsumer:
spring.application.name=springboot-rabbitmq
#rabbitmq config
spring.rabbitmq.host=192.168.1.108
spring.rabbitmq.port=5672
spring.rabbitmq.username=jwang
spring.rabbitmq.password=123456
#exchange config
mq.config.exchange=order.fanout
mq.config.queue.sms=order.sms
mq.config.queue.push=order.push3.编写Consumer代码
创建两个Consumer类,PushConsumer和SmsConsumer来分别处理订单的推送和短信功能
注意:广播模式不需要路由键啦!
PushConsumer:
package cn.edu.ccut;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.ExchangeTypes;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.Exchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.Queue;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.QueueBinding;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@RabbitListener(bindings=
@QueueBinding(
value=@Queue(name="${mq.config.queue.push}",autoDelete="true"),
exchange=@Exchange(name="${mq.config.exchange}",type=ExchangeTypes.FANOUT)
)
)
public class PushConsumer {
@RabbitHandler
public void receiveMsg(String msg){
System.out.println("Push Message is "+msg);
}
}SmsConsumer:
package cn.edu.ccut;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.ExchangeTypes;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.Exchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.Queue;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.QueueBinding;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@RabbitListener(bindings=
@QueueBinding(
value=@Queue(name="${mq.config.queue.sms}",autoDelete="true"),
exchange=@Exchange(name="${mq.config.exchange}",type=ExchangeTypes.FANOUT)
)
)
public class SmsConsumer {
@RabbitHandler
public void receiveMsg(String msg){
System.out.println("Sms Message is "+msg);
}
}4.编写Provider
Provider:
package cn.edu.ccut;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.AmqpTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Provider {
@Autowired
private AmqpTemplate rabbitTemplate;
@Value("${mq.config.exchange}")
private String exchange;
public void sendMsg(String msg){
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchange, "", msg);
}
}注意:此处不需要传递路由键啦!
5.编写测试代码进行测试
package cn.edu.ccut;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes=App.class)
public class RabbitMQTest {
@Autowired
private Provider provider;
@Test
public void testSendMsg() throws Exception{
provider.sendMsg("hello rabbitmq !");
}
}
接下来我们首先启动消费者端:
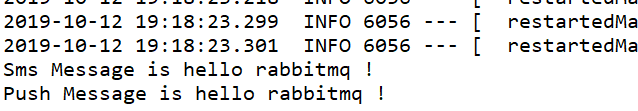
再次运行我们测试代码,观察控制台效果:
我们发现,SMS和Push端都接收到了消息,可见我们的测试是成功的。