基于Android 7.0源码分析
以最基本的MotionEvent(touchsreen single pointer)为例分析
InputReader读取输入事件分发给InputDispatcher的过程
下面从InputReader的loopOnce()开始分析
void InputReader::loopOnce() {
int32_t oldGeneration;
int32_t timeoutMillis;
bool inputDevicesChanged = false;
Vector inputDevices;
......
// 获取驱动上报的输入事件,返回读取的事件数
size_t count = mEventHub->getEvents(timeoutMillis, mEventBuffer, EVENT_BUFFER_SIZE);
{ // acquire lock
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
mReaderIsAliveCondition.broadcast();
if (count) {
// 处理输入事件
processEventsLocked(mEventBuffer, count);
}
......
}
......
// 发送事件给InputDispatcher
mQueuedListener->flush();
}
size_t EventHub::getEvents(int timeoutMillis, RawEvent* buffer, size_t bufferSize) {
ALOG_ASSERT(bufferSize >= 1);
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
struct input_event readBuffer[bufferSize];
RawEvent* event = buffer;
size_t capacity = bufferSize;
bool awoken = false;
for (;;) {
......
// Grab the next input event.
// 读取输入事件
bool deviceChanged = false;
while (mPendingEventIndex < mPendingEventCount) {
......
ssize_t deviceIndex = mDevices.indexOfKey(eventItem.data.u32);
if (deviceIndex < 0) {
ALOGW("Received unexpected epoll event 0x%08x for unknown device id %d.",
eventItem.events, eventItem.data.u32);
continue;
}
// 找到上报事件的设备
Device* device = mDevices.valueAt(deviceIndex);
if (eventItem.events & EPOLLIN) {
// 读取输入事件
int32_t readSize = read(device->fd, readBuffer,
sizeof(struct input_event) * capacity);
if (readSize == 0 || (readSize < 0 && errno == ENODEV)) {
// Device was removed before INotify noticed.
// 读取失败,设备已经移除
ALOGW("could not get event, removed? (fd: %d size: %" PRId32
" bufferSize: %zu capacity: %zu errno: %d)\n",
device->fd, readSize, bufferSize, capacity, errno);
deviceChanged = true;
closeDeviceLocked(device);
} else if (readSize < 0) {
if (errno != EAGAIN && errno != EINTR) {
ALOGW("could not get event (errno=%d)", errno);
}
} else if ((readSize % sizeof(struct input_event)) != 0) {
// 输入事件不完整
ALOGE("could not get event (wrong size: %d)", readSize);
} else {
int32_t deviceId = device->id == mBuiltInKeyboardId ? 0 : device->id;
size_t count = size_t(readSize) / sizeof(struct input_event);
for (size_t i = 0; i < count; i++) {
// 解析读取的事件,封装为RawEvent
struct input_event& iev = readBuffer[i];
......
event->deviceId = deviceId;
event->type = iev.type;
event->code = iev.code;
event->value = iev.value;
event += 1;
capacity -= 1;
}
}
}
}
......
// 读取到一些事件立即返回
// Return now if we have collected any events or if we were explicitly awoken.
if (event != buffer || awoken) {
break;
}
}
......
// All done, return the number of events we read.
return event - buffer;
}
-
RawEvent中的时间使用的是驱动上报事件的时间,更加精确;另外还要防止输入设备时钟源切换引入的问题
下面分析processEventsLocked()的实现
void InputReader::processEventsLocked(const RawEvent* rawEvents, size_t count) {
for (const RawEvent* rawEvent = rawEvents; count;) {
int32_t type = rawEvent->type;
size_t batchSize = 1;
if (type < EventHubInterface::FIRST_SYNTHETIC_EVENT) {
int32_t deviceId = rawEvent->deviceId;
// 统计同一设备普通输入事件
while (batchSize < count) {
if (rawEvent[batchSize].type >= EventHubInterface::FIRST_SYNTHETIC_EVENT
|| rawEvent[batchSize].deviceId != deviceId) {
break;
}
batchSize += 1;
}
......
// 处理普通的输入事件,同一设备的事件一起处理
processEventsForDeviceLocked(deviceId, rawEvent, batchSize);
} else {
......
}
count -= batchSize;
rawEvent += batchSize;
}
}
void InputReader::processEventsForDeviceLocked(int32_t deviceId,
const RawEvent* rawEvents, size_t count) {
ssize_t deviceIndex = mDevices.indexOfKey(deviceId);
if (deviceIndex < 0) {
ALOGW("Discarding event for unknown deviceId %d.", deviceId);
return;
}
// 找到对应的设备
InputDevice* device = mDevices.valueAt(deviceIndex);
if (device->isIgnored()) {
//ALOGD("Discarding event for ignored deviceId %d.", deviceId);
return;
}
// 调用InputDevice的process处理
device->process(rawEvents, count);
}
void InputDevice::process(const RawEvent* rawEvents, size_t count) {
// Process all of the events in order for each mapper.
// We cannot simply ask each mapper to process them in bulk because mappers may
// have side-effects that must be interleaved. For example, joystick movement events and
// gamepad button presses are handled by different mappers but they should be dispatched
// in the order received.
size_t numMappers = mMappers.size();
for (const RawEvent* rawEvent = rawEvents; count--; rawEvent++) {
......
for (size_t i = 0; i < numMappers; i++) {
InputMapper* mapper = mMappers[i];
// 对于MotionEvent, 由MultiTouchInputMapper处理
mapper->process(rawEvent);
}
......
}
}
在分析MultiTouchInputMapper的process()实现之前,先简单了解下touchscreen驱动上报的原始输入事件的格式。
Down/Move事件类似:
1) report (EV_ABS, ABS_MT_SLOT) // 存放事件的SLOT
2) report (EV_ABS, ABS_MT_TRACKING_ID(非负)) // touch轨迹id
3) report (EV_ABS, ABS_MT_TOOL_TYPE = 0) // touch设备类型
4) report (EV_ABS, ABS_MT_POSITION_X(x坐标)) // touch区域(椭圆)的中心点的X坐标
5) report (EV_ABS, ABS_MT_POSITION_Y(Y坐标)) // touch区域(椭圆)的中心点的Y坐标
6) report (EV_SYN, SYN_REPORT) // 完整事件标示
Up事件:
1) report (EV_ABS, ABS_MT_SLOT)
2) report (EV_ABS, ABS_MT_TRACKING_ID(-1))
3) report (EV_SYN, SYN_REPORT)
更多信息请参考kernel multi-touch-protocol.txt文档
- 不同的touchscreen驱动会有所差异
下面看process()实现
void MultiTouchInputMapper::process(const RawEvent* rawEvent) {
// 原始事件处理
TouchInputMapper::process(rawEvent);
// 根据multi-touch protocol,解析原始事件存放到slot中
mMultiTouchMotionAccumulator.process(rawEvent);
}
void MultiTouchMotionAccumulator::process(const RawEvent* rawEvent) {
// 绝对坐标事件
if (rawEvent->type == EV_ABS) {
bool newSlot = false;
if (mUsingSlotsProtocol) {
// 获取SLOT位置,一次Touch,Down/Move/.../Up通常使用一个SLOT存储
if (rawEvent->code == ABS_MT_SLOT) {
mCurrentSlot = rawEvent->value;
newSlot = true;
}
} else if (mCurrentSlot < 0) {
mCurrentSlot = 0;
}
......
} else {
Slot* slot = &mSlots[mCurrentSlot];
switch (rawEvent->code) {
// 一般只有Down/Move有坐标信息
// X坐标
case ABS_MT_POSITION_X:
slot->mInUse = true;
slot->mAbsMTPositionX = rawEvent->value;
break;
// Y坐标
case ABS_MT_POSITION_Y:
slot->mInUse = true;
slot->mAbsMTPositionY = rawEvent->value;
break;
case ABS_MT_TOUCH_MAJOR:
slot->mInUse = true;
slot->mAbsMTTouchMajor = rawEvent->value;
break;
case ABS_MT_TOUCH_MINOR:
slot->mInUse = true;
slot->mAbsMTTouchMinor = rawEvent->value;
slot->mHaveAbsMTTouchMinor = true;
break;
......
case ABS_MT_TRACKING_ID:
// 通常Down/Move事件 id为非负,Up事件id = -1
if (mUsingSlotsProtocol && rawEvent->value < 0) {
// The slot is no longer in use but it retains its previous contents,
// which may be reused for subsequent touches.
// 注意对于Up事件,mInUse为false
slot->mInUse = false;
} else {
slot->mInUse = true;
slot->mAbsMTTrackingId = rawEvent->value;
}
break;
}
}
} else if (rawEvent->type == EV_SYN && rawEvent->code == SYN_MT_REPORT) {
// MultiTouch Sync: The driver has returned all data for *one* of the pointers.
mCurrentSlot += 1;
}
}
下面看TouchInputMapper的process()实现
void TouchInputMapper::process(const RawEvent* rawEvent) {
mCursorButtonAccumulator.process(rawEvent);
mCursorScrollAccumulator.process(rawEvent);
mTouchButtonAccumulator.process(rawEvent);
if (rawEvent->type == EV_SYN && rawEvent->code == SYN_REPORT) {
// 获得一个完整事件,处理事件后分发给监听者
sync(rawEvent->when);
}
}
void TouchInputMapper::sync(nsecs_t when) {
const RawState* last = mRawStatesPending.isEmpty() ?
&mCurrentRawState : &mRawStatesPending.top();
// Push a new state.
// 创建一个RawState
mRawStatesPending.push();
RawState* next = &mRawStatesPending.editTop();
next->clear();
next->when = when;
......
// Sync touch
// 调用MultiTouchInputMapper的syncTouch,将SLOT中的原始事件保存到next中
syncTouch(when, next);
// Assign pointer ids.
// 对于Up事件,由于pointer数为0,不分配id
if (!mHavePointerIds) {
assignPointerIds(last, next);
}
......
// 处理分发原始事件
processRawTouches(false /*timeout*/);
}
下面首先看syncTouch()的实现,然后分析处理分发原始事件。
void MultiTouchInputMapper::syncTouch(nsecs_t when, RawState* outState) {
size_t inCount = mMultiTouchMotionAccumulator.getSlotCount();
size_t outCount = 0;
BitSet32 newPointerIdBits;
for (size_t inIndex = 0; inIndex < inCount; inIndex++) {
const MultiTouchMotionAccumulator::Slot* inSlot =
mMultiTouchMotionAccumulator.getSlot(inIndex);
// Up事件跳过
if (!inSlot->isInUse()) {
continue;
}
......
// SLOT中的原始事件信息保存到outState中
RawPointerData::Pointer& outPointer = outState->rawPointerData.pointers[outCount];
outPointer.x = inSlot->getX();
outPointer.y = inSlot->getY();
outPointer.pressure = inSlot->getPressure();
outPointer.touchMajor = inSlot->getTouchMajor();
outPointer.touchMinor = inSlot->getTouchMinor();
outPointer.toolMajor = inSlot->getToolMajor();
outPointer.toolMinor = inSlot->getToolMinor();
outPointer.orientation = inSlot->getOrientation();
outPointer.distance = inSlot->getDistance();
outPointer.tiltX = 0;
outPointer.tiltY = 0;
......
// Assign pointer id using tracking id if available.
mHavePointerIds = true;
int32_t trackingId = inSlot->getTrackingId();
int32_t id = -1;
if (trackingId >= 0) {
// 查找当前事件的trackingId在mPointerTrackingIdMap中的索引
for (BitSet32 idBits(mPointerIdBits); !idBits.isEmpty(); ) {
uint32_t n = idBits.clearFirstMarkedBit();
// mPointerTrackingIdMap用于根据id快速访问trackingId
if (mPointerTrackingIdMap[n] == trackingId) {
id = n;
}
}
if (id < 0 && !mPointerIdBits.isFull()) {
id = mPointerIdBits.markFirstUnmarkedBit();
mPointerTrackingIdMap[id] = trackingId;
}
}
if (id < 0) {
mHavePointerIds = false;
outState->rawPointerData.clearIdBits();
newPointerIdBits.clear();
} else {
// 记录id(single pointer时通常为0)
outPointer.id = id;
outState->rawPointerData.idToIndex[id] = outCount;
// 标记id掩码
outState->rawPointerData.markIdBit(id, isHovering);
newPointerIdBits.markBit(id);
}
outCount += 1;
}
// pointer数这里为1
outState->rawPointerData.pointerCount = outCount;
// 更新全局id掩码
mPointerIdBits = newPointerIdBits;
mMultiTouchMotionAccumulator.finishSync();
}
- 对于Down/Move事件,SLOT中的原始事件信息保存到
outState中,但是对于Up事件,outState处于初始状态
下面分析processRawTouches()
void TouchInputMapper::processRawTouches(bool timeout) {
if (mDeviceMode == DEVICE_MODE_DISABLED) {
// Drop all input if the device is disabled.
// 设备被禁止,丢弃输入事件
mCurrentRawState.clear();
mRawStatesPending.clear();
return;
}
......
const size_t N = mRawStatesPending.size();
size_t count;
for(count = 0; count < N; count++) {
const RawState& next = mRawStatesPending[count];
// A failure to assign the stylus id means that we're waiting on stylus data
// and so should defer the rest of the pipeline.
if (assignExternalStylusId(next, timeout)) {
break;
}
// All ready to go.
clearStylusDataPendingFlags();
// 原始事件信息拷贝至mCurrentRawState
mCurrentRawState.copyFrom(next);
if (mCurrentRawState.when < mLastRawState.when) {
mCurrentRawState.when = mLastRawState.when;
}
// 校准分发事件
cookAndDispatch(mCurrentRawState.when);
}
if (count != 0) {
// 移除处理完成的事件
mRawStatesPending.removeItemsAt(0, count);
}
......
}
下面看cookAndDispatch()的实现
void TouchInputMapper::cookAndDispatch(nsecs_t when) {
// Always start with a clean state.
mCurrentCookedState.clear();
......
// Cook pointer data. This call populates the mCurrentCookedState.cookedPointerData structure
// with cooked pointer data that has the same ids and indices as the raw data.
// The following code can use either the raw or cooked data, as needed.
// 校准原始事件数据存放到mCurrentCookedState, Up事件,pointer数为0无需校准
cookPointerData();
......
if (mDeviceMode == DEVICE_MODE_POINTER) {
......
} else {
......
if (!mCurrentMotionAborted) {
dispatchButtonRelease(when, policyFlags);
dispatchHoverExit(when, policyFlags);
// 分发Touch事件
dispatchTouches(when, policyFlags);
dispatchHoverEnterAndMove(when, policyFlags);
dispatchButtonPress(when, policyFlags);
}
}
......
// Copy current touch to last touch in preparation for the next cycle.
// 当前事件处理完成,拷贝至mLastRawState及mLastCookedState
mLastRawState.copyFrom(mCurrentRawState);
mLastCookedState.copyFrom(mCurrentCookedState);
}
void TouchInputMapper::dispatchTouches(nsecs_t when, uint32_t policyFlags) {
// 当前事件的id掩码
BitSet32 currentIdBits = mCurrentCookedState.cookedPointerData.touchingIdBits;
// 先前的事件的id掩码
BitSet32 lastIdBits = mLastCookedState.cookedPointerData.touchingIdBits;
int32_t metaState = getContext()->getGlobalMetaState();
int32_t buttonState = mCurrentCookedState.buttonState;
if (currentIdBits == lastIdBits) {
if (!currentIdBits.isEmpty()) {
// id掩码相等且非零,那么current为Move事件
// No pointer id changes so this is a move event.
// The listener takes care of batching moves so we don't have to deal with that here.
dispatchMotion(when, policyFlags, mSource,
AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_MOVE, 0, 0, metaState, buttonState,
AMOTION_EVENT_EDGE_FLAG_NONE,
mCurrentCookedState.cookedPointerData.pointerProperties,
mCurrentCookedState.cookedPointerData.pointerCoords,
mCurrentCookedState.cookedPointerData.idToIndex,
currentIdBits, -1,
mOrientedXPrecision, mOrientedYPrecision, mDownTime);
}
} else {
// There may be pointers going up and pointers going down and pointers moving
// all at the same time.
// 考虑single pointer事件
// 1) Up事件(lastIdBits.value非0,currentIdBits.value为0)
// 2) Down事件(lastIdBits.value为0,currentIdBits.value非0)
BitSet32 upIdBits(lastIdBits.value & ~currentIdBits.value);
BitSet32 downIdBits(currentIdBits.value & ~lastIdBits.value);
BitSet32 moveIdBits(lastIdBits.value & currentIdBits.value);
BitSet32 dispatchedIdBits(lastIdBits.value);
......
// Dispatch pointer up events.
// 分发Up事件,这里注意Up事件信息使用mLastCookedState(例如,Up事件的坐标是前驱事件的坐标)
while (!upIdBits.isEmpty()) {
uint32_t upId = upIdBits.clearFirstMarkedBit();
dispatchMotion(when, policyFlags, mSource,
AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_POINTER_UP, 0, 0, metaState, buttonState, 0,
mLastCookedState.cookedPointerData.pointerProperties,
mLastCookedState.cookedPointerData.pointerCoords,
mLastCookedState.cookedPointerData.idToIndex,
dispatchedIdBits, upId, mOrientedXPrecision, mOrientedYPrecision, mDownTime);
dispatchedIdBits.clearBit(upId);
}
......
// Dispatch pointer down events using the new pointer locations.
// 分发Down事件
while (!downIdBits.isEmpty()) {
uint32_t downId = downIdBits.clearFirstMarkedBit();
dispatchedIdBits.markBit(downId);
if (dispatchedIdBits.count() == 1) {
// First pointer is going down. Set down time.
mDownTime = when;
}
dispatchMotion(when, policyFlags, mSource,
AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_POINTER_DOWN, 0, 0, metaState, buttonState, 0,
mCurrentCookedState.cookedPointerData.pointerProperties,
mCurrentCookedState.cookedPointerData.pointerCoords,
mCurrentCookedState.cookedPointerData.idToIndex,
dispatchedIdBits, downId, mOrientedXPrecision, mOrientedYPrecision, mDownTime);
}
}
}
下面看dispatchMotion()的实现
void TouchInputMapper::dispatchMotion(nsecs_t when, uint32_t policyFlags, uint32_t source,
int32_t action, int32_t actionButton, int32_t flags,
int32_t metaState, int32_t buttonState, int32_t edgeFlags,
const PointerProperties* properties, const PointerCoords* coords,
const uint32_t* idToIndex, BitSet32 idBits, int32_t changedId,
float xPrecision, float yPrecision, nsecs_t downTime) {
PointerCoords pointerCoords[MAX_POINTERS];
PointerProperties pointerProperties[MAX_POINTERS];
uint32_t pointerCount = 0;
// 拷贝指尖属性及坐标数据
while (!idBits.isEmpty()) {
uint32_t id = idBits.clearFirstMarkedBit();
uint32_t index = idToIndex[id];
pointerProperties[pointerCount].copyFrom(properties[index]);
pointerCoords[pointerCount].copyFrom(coords[index]);
if (changedId >= 0 && id == uint32_t(changedId)) {
action |= pointerCount << AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_POINTER_INDEX_SHIFT;
}
pointerCount += 1;
}
......
if (changedId >= 0 && pointerCount == 1) {
// Replace initial down and final up action.
// We can compare the action without masking off the changed pointer index
// because we know the index is 0.
// 修改single pointer Down/Up事件的action
if (action == AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_POINTER_DOWN) {
action = AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_DOWN;
} else if (action == AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_POINTER_UP) {
action = AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_UP;
} else {
// Can't happen.
ALOG_ASSERT(false);
}
}
// 向监听者(QueuedInputListener)发送事件
NotifyMotionArgs args(when, getDeviceId(), source, policyFlags,
action, actionButton, flags, metaState, buttonState, edgeFlags,
mViewport.displayId, pointerCount, pointerProperties, pointerCoords,
xPrecision, yPrecision, downTime);
getListener()->notifyMotion(&args);
}
// NotifyMotionArgs存放到mArgsQueue容器中
void QueuedInputListener::notifyMotion(const NotifyMotionArgs* args) {
mArgsQueue.push(new NotifyMotionArgs(*args));
}
- PointerCoords 保存指尖坐标数据
- PointerProperties 保存指尖属性信息
- NotifyMotionArgs 描述一个Motion事件,采用命令模式
这里QueuedInputListener只是将事件封装成NotifyArgs存放到容器中。回到InputReader的loopOnce()中,驱动上报的事件都放到容器中后,QueuedInputListener调用flush()分发给InputDispatcher。
void QueuedInputListener::flush() {
size_t count = mArgsQueue.size();
for (size_t i = 0; i < count; i++) {
NotifyArgs* args = mArgsQueue[i];
// mInnerListener为InputDispatcher
// 这里args为NotifyMotionArgs
args->notify(mInnerListener);
delete args;
}
mArgsQueue.clear();
}
void NotifyMotionArgs::notify(const sp& listener) const {
// 调用InputDispatcher的notifyMotion
listener->notifyMotion(this);
}
下面分析InputDispatcher的notifyMotion()
void InputDispatcher::notifyMotion(const NotifyMotionArgs* args) {
// 检查MotionEvent是否合法
if (!validateMotionEvent(args->action, args->actionButton,
args->pointerCount, args->pointerProperties)) {
return;
}
uint32_t policyFlags = args->policyFlags;
policyFlags |= POLICY_FLAG_TRUSTED;
// mPolicy为NativeInputManager
// 检查系统是否需要拦截事件
mPolicy->interceptMotionBeforeQueueing(args->eventTime, /*byref*/ policyFlags);
bool needWake;
{ // acquire lock
mLock.lock();
......
// Just enqueue a new motion event.
MotionEntry* newEntry = new MotionEntry(args->eventTime,
args->deviceId, args->source, policyFlags,
args->action, args->actionButton, args->flags,
args->metaState, args->buttonState,
args->edgeFlags, args->xPrecision, args->yPrecision, args->downTime,
args->displayId,
args->pointerCount, args->pointerProperties, args->pointerCoords, 0, 0);
// MotionEntry放入InboundQueue中
needWake = enqueueInboundEventLocked(newEntry);
mLock.unlock();
} // release lock
if (needWake) {
// 唤醒InputDispatcher处理事件
mLooper->wake();
}
}
bool InputDispatcher::enqueueInboundEventLocked(EventEntry* entry) {
bool needWake = mInboundQueue.isEmpty();
// 事件放入InboundQueue tail
mInboundQueue.enqueueAtTail(entry);
// 更新systrace中iq信息
traceInboundQueueLengthLocked();
......
}
最终,InputReader线程将事件放入InboundQueue中,如果有必要,唤醒InputDispatcher线程处理事件。
小结
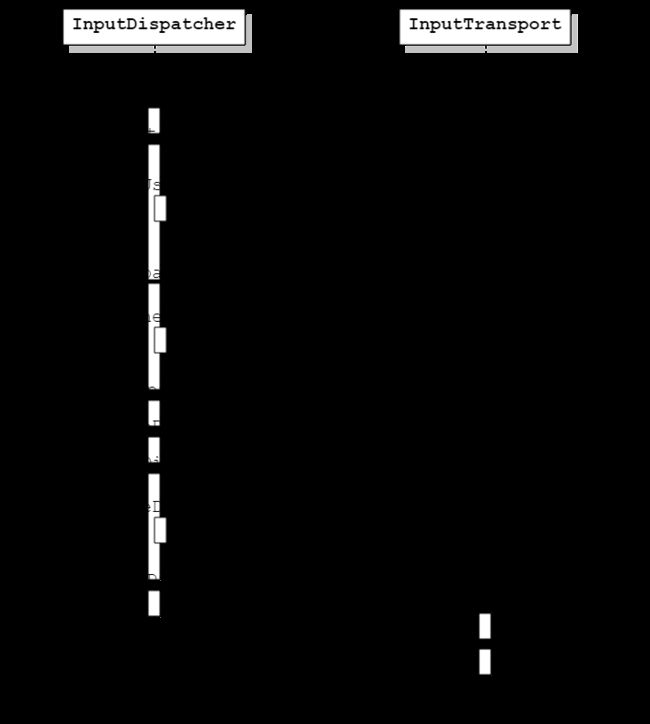
InputDispatcher发送MotionEvent到应用的过程
下面从InputDispatcher的dispatchOnce()开始分析
void InputDispatcher::dispatchOnce() {
nsecs_t nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MAX;
{ // acquire lock
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
mDispatcherIsAliveCondition.broadcast();
// Run a dispatch loop if there are no pending commands.
// The dispatch loop might enqueue commands to run afterwards.
// 如果没有待处理的命令,分发事件(此过程中可能产生命令)
if (!haveCommandsLocked()) {
dispatchOnceInnerLocked(&nextWakeupTime);
}
......
}
// Wait for callback or timeout or wake. (make sure we round up, not down)
nsecs_t currentTime = now();
int timeoutMillis = toMillisecondTimeoutDelay(currentTime, nextWakeupTime);
// 如果被唤醒,从此返回
mLooper->pollOnce(timeoutMillis);
}
下面看dispatchOnceInnerLocked()的实现
void InputDispatcher::dispatchOnceInnerLocked(nsecs_t* nextWakeupTime) {
nsecs_t currentTime = now();
......
// If dispatching is frozen, do not process timeouts or try to deliver any new events.
// 事件分发冻住直接返回
if (mDispatchFrozen) {
#if DEBUG_FOCUS
ALOGD("Dispatch frozen. Waiting some more.");
#endif
return;
}
// Optimize latency of app switches.
// Essentially we start a short timeout when an app switch key (HOME / ENDCALL) has
// been pressed. When it expires, we preempt dispatch and drop all other pending events.
// 检查app switch key处理是否超时
bool isAppSwitchDue = mAppSwitchDueTime <= currentTime;
if (mAppSwitchDueTime < *nextWakeupTime) {
*nextWakeupTime = mAppSwitchDueTime;
}
// Ready to start a new event.
// If we don't already have a pending event, go grab one.
if (! mPendingEvent) {
if (mInboundQueue.isEmpty()) {
......
} else {
// Inbound queue has at least one entry.
// 从InboundQueue中取出一个事件
mPendingEvent = mInboundQueue.dequeueAtHead();
// 更新systrace中iq信息
traceInboundQueueLengthLocked();
}
// Poke user activity for this event.
if (mPendingEvent->policyFlags & POLICY_FLAG_PASS_TO_USER) {
// 通知PowerManagerService更新电源状态
pokeUserActivityLocked(mPendingEvent);
}
// Get ready to dispatch the event.
// 重置等待输入目标超时信息
resetANRTimeoutsLocked();
}
......
switch (mPendingEvent->type) {
......
case EventEntry::TYPE_MOTION: {
MotionEntry* typedEntry = static_cast(mPendingEvent);
if (dropReason == DROP_REASON_NOT_DROPPED && isAppSwitchDue) {
// app switch key事件处理超时,丢弃后续事件
dropReason = DROP_REASON_APP_SWITCH;
}
if (dropReason == DROP_REASON_NOT_DROPPED
&& isStaleEventLocked(currentTime, typedEntry)) {
// 丢弃已经超时失效的事件
dropReason = DROP_REASON_STALE;
}
if (dropReason == DROP_REASON_NOT_DROPPED && mNextUnblockedEvent) {
// 丢弃将要发送给不响应的应用的事件
dropReason = DROP_REASON_BLOCKED;
}
// 分发事件
done = dispatchMotionLocked(currentTime, typedEntry,
&dropReason, nextWakeupTime);
break;
}
......
}
if (done) {
// 分发结束清理
if (dropReason != DROP_REASON_NOT_DROPPED) {
dropInboundEventLocked(mPendingEvent, dropReason);
}
mLastDropReason = dropReason;
releasePendingEventLocked();
*nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MIN; // force next poll to wake up immediately
}
}
下面分析dispatchMotionLocked()实现
bool InputDispatcher::dispatchMotionLocked(
nsecs_t currentTime, MotionEntry* entry, DropReason* dropReason, nsecs_t* nextWakeupTime) {
// Preprocessing.
if (! entry->dispatchInProgress) {
// 标记正在分发事件
entry->dispatchInProgress = true;
logOutboundMotionDetailsLocked("dispatchMotion - ", entry);
}
// Clean up if dropping the event.
if (*dropReason != DROP_REASON_NOT_DROPPED) {
// 由于某种原因需要丢弃事件
setInjectionResultLocked(entry, *dropReason == DROP_REASON_POLICY
? INPUT_EVENT_INJECTION_SUCCEEDED : INPUT_EVENT_INJECTION_FAILED);
return true;
}
bool isPointerEvent = entry->source & AINPUT_SOURCE_CLASS_POINTER;
// Identify targets.
Vector inputTargets;
bool conflictingPointerActions = false;
int32_t injectionResult;
if (isPointerEvent) {
// Pointer event. (eg. touchscreen)
// 查找InputTarget
// findTouchedWindowTargetsLocked的实现与WindowManagerService关系密切,这里
// 暂不详细讨论,另外它也处理应用不响应输入ANR的情况
injectionResult = findTouchedWindowTargetsLocked(currentTime,
entry, inputTargets, nextWakeupTime, &conflictingPointerActions);
} else {
......
}
......
// 分发事件给inputTargets
dispatchEventLocked(currentTime, entry, inputTargets);
return true;
}
- InputTarget 描述如何将事件分发到特定的窗口,它包含目标窗口的InputChannel以及控制标志等
下面看dispatchEventLocked()的实现
void InputDispatcher::dispatchEventLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,
EventEntry* eventEntry, const Vector& inputTargets) {
#if DEBUG_DISPATCH_CYCLE
ALOGD("dispatchEventToCurrentInputTargets");
#endif
ALOG_ASSERT(eventEntry->dispatchInProgress); // should already have been set to true
pokeUserActivityLocked(eventEntry);
for (size_t i = 0; i < inputTargets.size(); i++) {
const InputTarget& inputTarget = inputTargets.itemAt(i);
ssize_t connectionIndex = getConnectionIndexLocked(inputTarget.inputChannel);
if (connectionIndex >= 0) {
// 通过InputChannel找到Connection
sp connection = mConnectionsByFd.valueAt(connectionIndex);
// 分发事件
prepareDispatchCycleLocked(currentTime, connection, eventEntry, &inputTarget);
} else {
#if DEBUG_FOCUS
ALOGD("Dropping event delivery to target with channel '%s' because it "
"is no longer registered with the input dispatcher.",
inputTarget.inputChannel->getName().string());
#endif
}
}
}
void InputDispatcher::prepareDispatchCycleLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,
const sp& connection, EventEntry* eventEntry, const InputTarget* inputTarget) {
......
// Skip this event if the connection status is not normal.
// We don't want to enqueue additional outbound events if the connection is broken.
// 如果Connection的状态异常,跳过事件
if (connection->status != Connection::STATUS_NORMAL) {
#if DEBUG_DISPATCH_CYCLE
ALOGD("channel '%s' ~ Dropping event because the channel status is %s",
connection->getInputChannelName(), connection->getStatusLabel());
#endif
return;
}
......
// Not splitting. Enqueue dispatch entries for the event as is.
// 分发事件
enqueueDispatchEntriesLocked(currentTime, connection, eventEntry, inputTarget);
}
void InputDispatcher::enqueueDispatchEntriesLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,
const sp& connection, EventEntry* eventEntry, const InputTarget* inputTarget) {
bool wasEmpty = connection->outboundQueue.isEmpty();
......
// 事件封装成DispatchEntry,放入Connection的OutboundQueue中,更新systrace中oq信息
enqueueDispatchEntryLocked(connection, eventEntry, inputTarget,
InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_IS);
......
// If the outbound queue was previously empty, start the dispatch cycle going.
// 如果之前Connection的OutboundQueue为空,启动分发事件
if (wasEmpty && !connection->outboundQueue.isEmpty()) {
startDispatchCycleLocked(currentTime, connection);
}
}
下面看startDispatchCycleLocked()的实现
void InputDispatcher::startDispatchCycleLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,
const sp& connection) {
#if DEBUG_DISPATCH_CYCLE
ALOGD("channel '%s' ~ startDispatchCycle",
connection->getInputChannelName());
#endif
while (connection->status == Connection::STATUS_NORMAL
&& !connection->outboundQueue.isEmpty()) {
DispatchEntry* dispatchEntry = connection->outboundQueue.head;
dispatchEntry->deliveryTime = currentTime;
// Publish the event.
status_t status;
EventEntry* eventEntry = dispatchEntry->eventEntry;
switch (eventEntry->type) {
......
case EventEntry::TYPE_MOTION: {
MotionEntry* motionEntry = static_cast(eventEntry);
PointerCoords scaledCoords[MAX_POINTERS];
const PointerCoords* usingCoords = motionEntry->pointerCoords;
......
// Publish the motion event.
// 通过socket将事件分发给应用
status = connection->inputPublisher.publishMotionEvent(dispatchEntry->seq,
motionEntry->deviceId, motionEntry->source,
dispatchEntry->resolvedAction, motionEntry->actionButton,
dispatchEntry->resolvedFlags, motionEntry->edgeFlags,
motionEntry->metaState, motionEntry->buttonState,
xOffset, yOffset, motionEntry->xPrecision, motionEntry->yPrecision,
motionEntry->downTime, motionEntry->eventTime,
motionEntry->pointerCount, motionEntry->pointerProperties,
usingCoords);
break;
}
default:
ALOG_ASSERT(false);
return;
}
......
// Re-enqueue the event on the wait queue.
// 从Connection的OutboundQueue中删除事件
connection->outboundQueue.dequeue(dispatchEntry);
// 更新systrace中oq信息
traceOutboundQueueLengthLocked(connection);
// 事件添加到WaitQueue中
connection->waitQueue.enqueueAtTail(dispatchEntry);
// 更新systrace中wq信息
traceWaitQueueLengthLocked(connection);
}
}
至此,输入事件从InputDispatcher已经分发到应用。