MVP、MVVM,MVC设计模式的实例分析
简单介绍
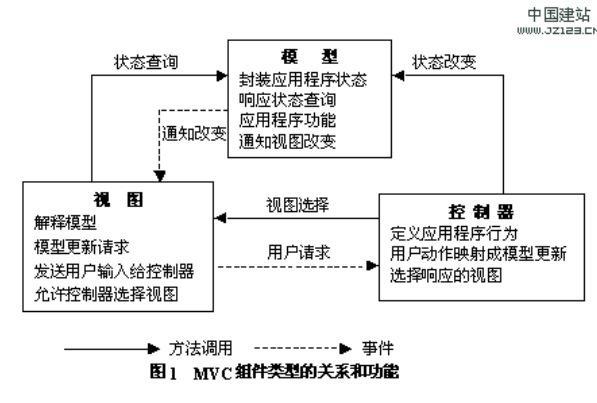
一个典型的MVC的模式
可以看到,这个是非常自然的想法。也无怪乎是人类第一种提出来的方案。这个的问题就是用久了的话,
MVC的使用非常常见,可以看一下经典的SpringMVC
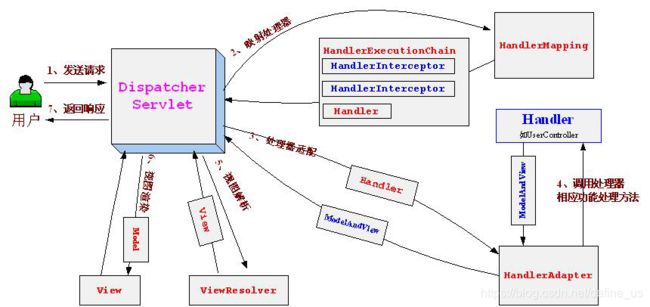
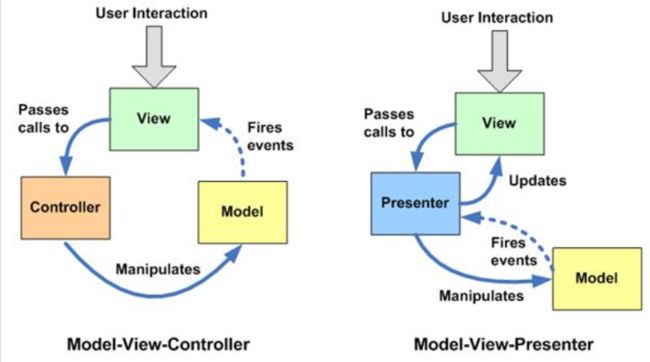
controller会变得非常复杂,因为主要的业务逻辑都会集中在controller里,controller既要负责更新数据,又要负责选择视图,又要负责处理用户请求。另一个问题,view是依赖于model的。代码很有可能导致view根据model的数据进行业务逻辑判断后进行展示。所以,有人又提出了MVVM
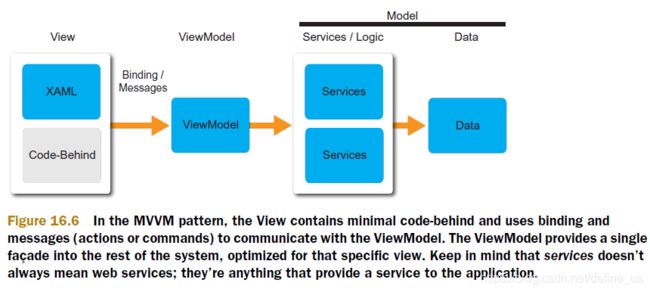
这种情况下,前端界面和ViewModel严格绑定。这样杜绝了View中掺杂业务逻辑。Controller(现在的ViewModel)的部分逻辑拆入到了Service当中,保证ViewModel的代码足够简洁。
实例
先只考虑V和P的分离,在这里,我们用接口实现
首先,程序先实例化V,主函数代码如下
static class Program
{
///
/// 应用程序的主入口点。
///
[STAThread]
static void Main()
{
Application.EnableVisualStyles();
Application.SetCompatibleTextRenderingDefault(false);
Application.Run(new FrmTestMvp());
}
}
然后,我们让V去实例化P,将对自己的引用传给P
VIEW代码如下
public partial class FrmTestMvp : Form, ITestMvpView
{
private TestMvpPresenter _testMvpPresenter;
public FrmTestMvp()
{
InitializeComponent();
//注意构造Presenter时需把自身传过去
this._testMvpPresenter = new TestMvpPresenter(this);
}
//单击按钮事件
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (Click != null)
{
Click();
}
}
#region ITestMvpView 成员
//实现接口属性方法
public TextBox TextBox1
{
get { return this.textBox1; }
}
//委托事件
public new event Button1_Click Click;
#endregion
}
VIEW实现了如下接口。这让我们的Presenter可以支持多个VIEW,只要他作出了对接口的实现
//声明了一个委托类型,并在接口安上了和这个委托类型相关的事件
public delegate void Button1_Click();
interface ITestMvpView
{
//声明控件
TextBox TextBox1{get;}
//事件
event Button1_Click Click;
}
最后就是我们的Presenter部分,利用界面给它的接口来访问界面。
class TestMvpPresenter
{
private ITestMvpView _testMvpView;
///
/// 构造函数,出入视图接口
///
/// ITestMvpView接口
public TestMvpPresenter(ITestMvpView testMvpView)
{
this._testMvpView = testMvpView;
this.InitEvent();
}
//加载委托事件
private void InitEvent()
{
this._testMvpView.Click += new Button1_Click(_testMvpView_Click);
}
//处理事件
void _testMvpView_Click()
{
if (CheckValue())
{
this.ShowMessage(this._testMvpView.TextBox1.Text);
}
else
{
this.ShowMessage("输入的值不能为空!");
this._testMvpView.TextBox1.Focus();
}
}
//检查TestBox1的输入值是否合法
private bool CheckValue()
{
if (this._testMvpView.TextBox1.Text.ToString() == "")
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
private void ShowMessage(string message)
{
MessageBox.Show(message);
}
}
实际上,上面的例子是先初始化view,然后初始化presenter的方式,我们成为view-first。反过来当然也一样,叫做presenter-first方式。
另外一个例子,首先,在来看我们的Model,model是一个只包含属性的实体类.书写如下
public class TestMvpModel
{
public string Name { get; set; }
}
然后写我们的view类
View类中依赖model,并负责model和view的绑定
public partial class FrmTestMvp : Form
{
private TestMvpModel model;
public TestMvpModel Model
{
get
{
return model as TestMvpModel;
}
set
{
model = value as TestMvpModel;
label1.Text = model.Name;
}
}
public FrmTestMvp()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
public EventHandler ButtonClick;
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (ButtonClick != null)
{
ButtonClick(sender,e);
}
}
}
最后写我们的presenter,负责一切的初始化,和页面逻辑的控制
class TestMvpPresenter
{
public FrmTestMvp View { get; set; }
public TestMvpPresenter(FrmTestMvp view)
{
this.View = view;
this.View.Model = new TestMvpModel() {Name = "GDL" };
this.View.ButtonClick += delegate
{
this.View.Model = new TestMvpModel() { Name = "ABC" };
};
}
}
主程序改为如下
[STAThread]
static void Main()
{
Application.EnableVisualStyles();
Application.SetCompatibleTextRenderingDefault(false);
TestMvpPresenter presenter = new TestMvpPresenter(new FrmTestMvp());
Application.Run(presenter.View);
}
在我的理解中,MVP模式的核心就是将传统VIEW中相互耦合的业务逻辑,页面静态部分,和页面中动态部分分开。页面中不变的静态部分继续放在view里。动态部分放在model里。而业务逻辑放在我们的presenter中。
是不是觉得上面的view代码有点多,还需要手工绑定两件事:
(1)页面动作和presenter中的处理函数
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (ButtonClick != null)
{
ButtonClick(sender,e);
}
}
(2)模型和页面的一致性变化
public TestMvpModel Model
{
get
{
return model as TestMvpModel;
}
set
{
model = value as TestMvpModel;
label1.Text = model.Name;
}
}
所以,微软又推出了WPF。我们来看一下WPF中的view典型写法
显然,在上述的XAML中,已经对前文提到的两件事进行了绑定。在wpf下,我们可以轻松的写出model代码(#region部分为INotifyPropertyChanged
接口添加)
public class PanelPresenterationModel : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
private string name;
public string Name
{
get
{
return this.name;
}
set
{
if (this.name != value)
{
this.name = value;
this.OnPropertyChanged("Name");
}
}
}
#region INotifyPropertyChanged Members
public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;
private void OnPropertyChanged(string propertyName)
{
PropertyChangedEventHandler Handler = PropertyChanged;
if (Handler != null) Handler(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propertyName));
}
#endregion
}
我们给出presenter代码
public class PanelPresenter
{
public PanelPresenter(PanelView view)
{
this.View = view;
//初始化Model
this.View.Model = new PanelPresenterationModel() { Name = "Bao, Jianqiang" };
this.View.ButtonClick += delegate
{
this.View.Model.Name = "Jax.Bao";
};
}
public PanelView View { get; set; }
}
我们看到WPF很成功的实现了MVP。
然而,还有好事者,他们开发了MVVM模式
Simple Mvvm,Mvvm Light和Prism都是MVVM的开源框架
下面只贴上典型的viewmodel的实例
namespace SilverlightApplication2.ViewModels
{
public class StudentViewModel : NotificationObject
{
public StudentViewModel()
{
student = new Student();
}
Student student;
public Student Student
{
get
{
return this.student;
}
private set
{
this.student = value;
this.RaisePropertyChanged(() => this.student);
}
}
public bool CanSubmit
{
get
{
return true;
}
}
public void Submit()
{
student.Mock();
}
}
}
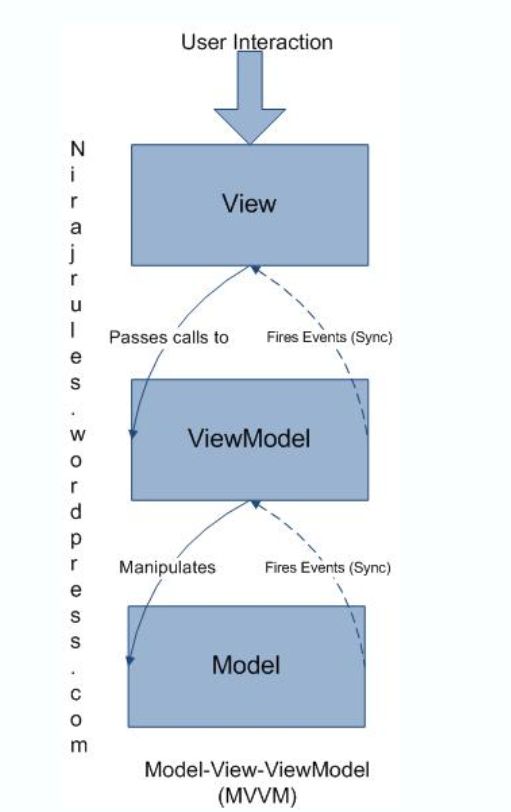
在上代码中可以看见,viewmodel又负责处理view内容的更新,同时也负责对model内容进行同步调整。下面展现了一个一般MVVM系统的架构