引子:
- 在 dubbo剖析:二 服务引用 中,我们讲到了
RegistryProtocol.refer过程中有一个关键步骤,即在监听到服务提供者url时触发RegistryDirectory.notify()方法。 -
RegistryDirectory.notify()方法调用refreshInvoker()方法将服务提供者urls转换为对应的远程invoker,最终调用到DubboProtocol.refer()方法生成对应的DubboInvoker。 -
DubboInvoker的构造方法中有一项入参ExchangeClient[] clients,即对应本文要讲的网络客户端Client。DubboInvoker就是通过调用client.request()方法完成网络通信的请求发送和响应接收功能。 -
Client的具体生成过程就是通过DubboProtocol的initClient(URL url)方法创建了一个HeaderExchangeClient。 - 本章我们就来介绍
HeaderExchangeClient的 设计架构 和 功能实现 。
一、入口流程
服务引用过程中,RegistryProtocol会调用到DubboProtocol的refer()方法,用于创建一个DubboInvoker完成客户端的启动并和服务提供方建连。
public Invoker refer(Class serviceType, URL url) throws RpcException {
// create rpc invoker.
DubboInvoker invoker = new DubboInvoker(serviceType, url, getClients(url), invokers);
invokers.add(invoker);
return invoker;
}
其中DubboProtocol的getClients()方法完成了Client的创建过程:
private ExchangeClient[] getClients(URL url) {
//...判断是否共享连接...
ExchangeClient[] clients = new ExchangeClient[connections];
for (int i = 0; i < clients.length; i++) {
if (service_share_connect) {
clients[i] = getSharedClient(url);
} else {
//关键代码,生成Client
clients[i] = initClient(url);
}
}
return clients;
}
/**
* 创建新连接.
*/
private ExchangeClient initClient(URL url) {
// ...省略部分非关键代码...
ExchangeClient client;
try {
//设置连接应该是lazy的
if (url.getParameter(Constants.LAZY_CONNECT_KEY, false)) {
client = new LazyConnectExchangeClient(url, requestHandler);
} else {
//关键代码:通过Exchangers创建HeaderExchangeClient
client = Exchangers.connect(url, requestHandler);
}
} catch (RemotingException e) {
throw new RpcException("Fail to create remoting client for service(" + url
+ "): " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
return client;
}
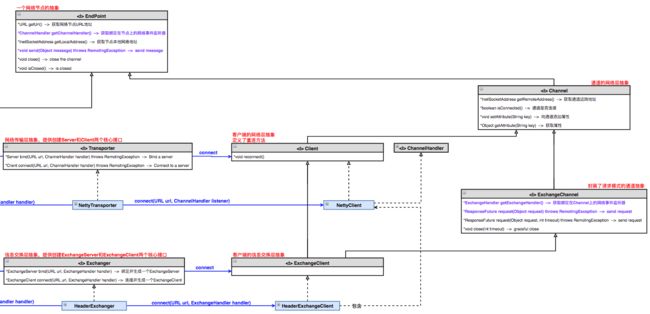
二、Client端网络层结构
2.1 网络传输层
-
ChannelHandler为网络事件处理器接口,定义了Server端监听到各种类型的网络事件时的处理方法(connected、disconnected、sent、received、caught),Netty中也有类似定义。 -
EndPoint为网络端点的抽象接口,定义了获取网络端点地址、连接、及最原始的发送消息的方法。 -
Channel为网络通道的抽象接口,继承了EndPoint的功能,并扩展了绑定获取属性和判断通道是否连接的方法。 -
Client为网络客户端的抽象接口,继承了Channel的功能,并扩展了重连方法reconnect()。 -
Transporter为网络传输层的抽象接口,核心作用就是提供了创建Server和Client两个核心接口实现类的方法。
2.2 信息交换层
-
ExchangeHandler,在ChannelHandler接口基础上,添加了 响应请求的方法。 -
ExchangeChannel,在Channel接口的基础上,扩展了请求响应模式的功能,并能获取绑定在通道上的网络事件监听器。 -
ExchangeClient,在Client接口基础上,继承了ExchangeChannel接口,将Channel扩展为ExchangeChannel。 -
Exchanger为信息交换层的抽象接口,核心作用就是提供了创建ExchangeServer和ExchangeClient两个核心接口实现类的方法。
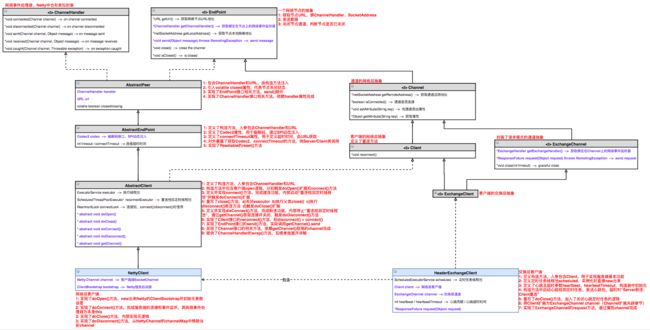
三 HeaderExchangeClient & NettyClient实现详解
3.1 网络层
AbstractPeer类(网络事件处理器和网络节点的通用实现):
- 定义了属性
ChannelHandler和URL,作为构造方法入参注入; - 实现了
ChannelHandler和EndPoint接口,ChannelHandler接口的相关方法依赖其channelHandler属性完成实现;
AbstractEndPoint类(加入编解码功能):
- 定义了构造方法,入参包含属性
ChannelHandler和URL; - 定义了属性
Codec2,用于编解码,通过SPI动态注入; - 定义了timeout/connectTimeout相关超时属性,由
URL解析赋值; - 对外暴露了获取
Codec2和超时相关属性的方法,供上层依赖调用;
AbastractClient类(网络客户端通用抽象,实现了open、connect、disConnect、close、send的公共流程,并提供了doOpen、doConnect、doDisconnect、doClose、getChannel的扩展):
- 定义了构造方法,入参包含属性
ChannelHandler和URL,并触发doOpen()和connect()方法; - 重写
AbstractPeer的close()方法,加入了disconnect()和doClose()扩展方法的触发逻辑; - 定义并实现
connect()方法,完成建连功能。内部逻辑为启动“心跳检测定时任务”并触发doConnect()扩展方法; - 定义并实现
disconnect()方法,完成断连功能。内部逻辑为停止“心跳检测定时任务”、通过getChannel()获取连接并关闭、并触发doDisconnect()扩展方法; - 实现了
Client接口的reconnect()方法,实际调用disconnect()+connect(); - 实现了
EndPoint接口的send()方法,实际调用getChannel().send()完成; - 实现了
Channel接口的相关方法,实际依赖getChannel()取得的channel完成; - 提供了对
ChannelHandler的wrap()方法,后续单独展开讲解;
NettyClient类(网络客户端Netty实现类,实现了doOpen、doConnect、doDisconnect、doClose、getChannel这五个关键扩展方法):
- 实现了
doOpen()扩展方法,new出来Netty的ClientBootstrap并初始化参数设置; - 实现了
doConnect()扩展方法,使用ClientBootstrap完成服务端的廉价和事件监听,其网络事件处理器为本身this的包装; - 实现了
doDisconnect()扩展方法,从NettyChannel的channelMap中移除当前的断连channel; - 实现了
doClose()扩展方法,内部无实际逻辑; - 实现了
getChannel()扩展方法,由NettyChannel类将客户端的Netty原生Channel包装后放入channelMap并返回;
protected void doOpen() throws Throwable {
NettyHelper.setNettyLoggerFactory();
bootstrap = new ClientBootstrap(channelFactory);
// config
// @see org.jboss.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannelConfig
bootstrap.setOption("keepAlive", true);
bootstrap.setOption("tcpNoDelay", true);
bootstrap.setOption("connectTimeoutMillis", getTimeout());
final NettyHandler nettyHandler = new NettyHandler(getUrl(), this);
bootstrap.setPipelineFactory(new ChannelPipelineFactory() {
public ChannelPipeline getPipeline() {
NettyCodecAdapter adapter = new NettyCodecAdapter(getCodec(), getUrl(), NettyClient.this);
ChannelPipeline pipeline = Channels.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast("decoder", adapter.getDecoder());
pipeline.addLast("encoder", adapter.getEncoder());
pipeline.addLast("handler", nettyHandler);
return pipeline;
}
});
}
protected void doConnect() throws Throwable {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.connect(getConnectAddress());
try {
boolean ret = future.awaitUninterruptibly(getConnectTimeout(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
if (ret && future.isSuccess()) {
Channel newChannel = future.getChannel();
newChannel.setInterestOps(Channel.OP_READ_WRITE);
try {
// 关闭旧的连接
Channel oldChannel = NettyClient.this.channel; // copy reference
if (oldChannel != null) {
try {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Close old netty channel " + oldChannel + " on create new netty channel " + newChannel);
}
oldChannel.close();
} finally {
NettyChannel.removeChannelIfDisconnected(oldChannel);
}
}
} finally {
if (NettyClient.this.isClosed()) {
try {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Close new netty channel " + newChannel + ", because the client closed.");
}
newChannel.close();
} finally {
NettyClient.this.channel = null;
NettyChannel.removeChannelIfDisconnected(newChannel);
}
} else {
NettyClient.this.channel = newChannel;
}
}
} else if (future.getCause() != null) {
throw new RemotingException(this, "client(url: " + getUrl() + ") failed to connect to server "
+ getRemoteAddress() + ", error message is:" + future.getCause().getMessage(), future.getCause());
} else {
throw new RemotingException(this, "client(url: " + getUrl() + ") failed to connect to server "
+ getRemoteAddress() + " client-side timeout "
+ getConnectTimeout() + "ms (elapsed: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) + "ms) from netty client "
+ NetUtils.getLocalHost() + " using dubbo version " + Version.getVersion());
}
} finally {
if (!isConnected()) {
future.cancel();
}
}
}
NettyChannel类(内部含有一个netty.Channel,实现了EndPoint接口的send()方法):
- 内部包含了netty的原始通道
netty.Channel,该属性由NettyClient.doConnect()执行完成时产生; - 其
send()方法底层最终使用netty原生通道完成数据的发送;
public void send(Object message, boolean sent) throws RemotingException {
super.send(message, sent);
boolean success = true;
int timeout = 0;
try {
//关键代码,使用netty的原始channel完成数据发送
ChannelFuture future = channel.write(message);
if (sent) {
timeout = getUrl().getPositiveParameter(Constants.TIMEOUT_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_TIMEOUT);
success = future.await(timeout);
}
Throwable cause = future.getCause();
if (cause != null) {
throw cause;
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new RemotingException(this, "Failed to send message " + message + " to " + getRemoteAddress() + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
if (!success) {
throw new RemotingException(this, "Failed to send message " + message + " to " + getRemoteAddress()
+ "in timeout(" + timeout + "ms) limit");
}
}
3.2 发送请求数据(网络层)
当“服务引用方客户端”需要向“服务提供方服务端”发送请求时,会通过交换层最终调用NettyClient.send(Object message)方法:
-
NettyClient.send(Object message):依赖getChannel()方法获取到NettyChannel对象,然后调用它的send(Object message)方法; -
NettyChannel:由NettyClient.getChannel()方法中构建生成,入参包括URL、netty.Channel、ChannelHandler,均由NettyClient传入。NettyChannel.send()方法最终调用其内部netty.Channel完成请求数据的发送;
3.3 交换层
HeaderExchangeClient类(交换层客户端,将网络层的Channel扩展为交换层的ExchangeChannel、通过exchangeChannel实现了具有请求响应功能的request()方法,并加入心跳检测功能):
- 定义了构造方法,入参包含属性
Client,用于实现客户端网络层功能; - 定义了属性
定时任务线程池scheduled,用于执行“定时心跳收发及心跳超时监测”任务; - 定义了
hearbeat / heartbeatTieout相关心跳属性,由URL解析赋值; - 构造方法中启动“定时心跳收发及心跳超时监测”任务,
doClose()方法中关闭任务,任务逻辑为超时时“Server断连、Client断连重连”; - 将
Client扩展为交换层ExchangeChannel,并通过ExchangeChannel实现了request()方法,具体实现后续另辟章节;