flink分析使用之七任务的启动
一、flink的任务
在前面已经分析过了作业对任务的分发,那么,现在就可以分析任务的启动和执行了。任务可以通过RPC分发到指定位置。所以在此处需要对任务的分发有一个管理TaskManager,从宏观上看,Flink的每个TaskManager都是一个独立的JVM进程,为了更好的管理JVM进程,又要对TaskManager进行细化的管理,这时候儿就需要另外一个对象TaskSlot来负责对细节的管控。
这样的优势就在于,如果JOBMaster通过分发而来的作业,可以独立的在不同的Slot中执行。有一点类似于资源的隔离,这样,就可以尽可能的提高整个资源的效率。但是需要注意的是,在Slot中目前还没有做到CPU资源的隔离。通过动态的对槽的大小和数量的调整,就可以把任务的执行较好的并行起来。
在子任务同属一个JOB时,Flink还允许共享Slot。之所以允许共享,主要是因为既可以迅速的执行一些占用资源较小的任务,又可以从逻辑上抽离对并行计算是资源的消耗的多余计算(这点和虚拟内存有异曲同工之妙)。通过Map-reduce的映射来更好的进行作业和任务的执行。
在前面的章节分析过,JobMaster 将 JobGraph 转换为 ExecutionGraph,ExecutionGraph 是 JobGraph 的并行版本.而通过一系列的分析,才可以最终把任务分发到相关的任务槽中。槽可以根据CPU的数量提前指定出来,可以最大限度的利用CPU的计算资源。如果Slot耗尽,也就意味着新分发的作业任务是无法执行的。
二、任务流程
看一下任务和Slot二者的关系,看下图:
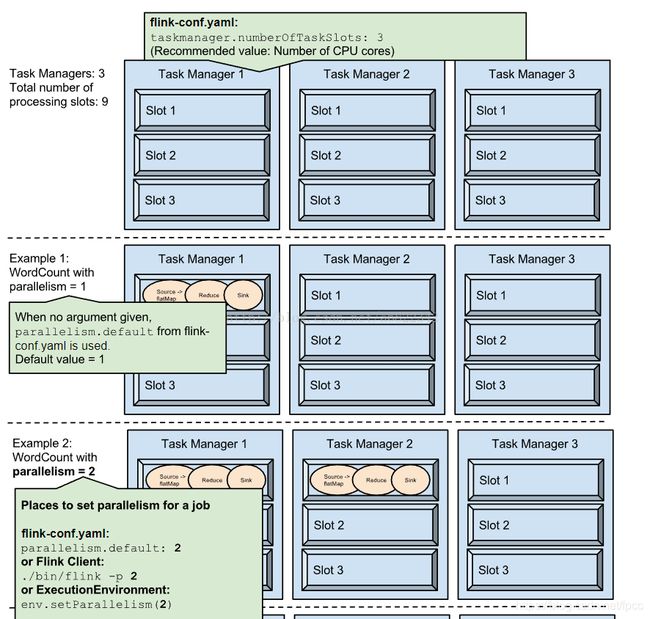
一般来说,任务的流程就是通过作业分发到TaskManager,然后再分发到指定的Slot进行执行。是不是可以把Slot当成任务执行的最小执行单位?再看一下任务执行的流程:
三、源码分析
任务有主要有两大块,一块是任务的管理,一块是任务的执行,这映射到源码中,就是taskmanager和taskexecutor两个包中。
先不管他们两个,来看一下,任务的启动:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// startup checks and logging
......
try {
SecurityUtils.getInstalledContext().runSecured(new Callable<Void>() {
@Override
public Void call() throws Exception {
//在主函数中调用这个函数启动任务管理
runTaskManager(configuration, ResourceID.generate());
return null;
}
});
} catch (Throwable t) {
final Throwable strippedThrowable = ExceptionUtils.stripException(t, UndeclaredThrowableException.class);
LOG.error("TaskManager initialization failed.", strippedThrowable);
System.exit(STARTUP_FAILURE_RETURN_CODE);
}
}
//最终会调用:TaskManagerRunner.java
public TaskManagerRunner(Configuration configuration, ResourceID resourceId) throws Exception {
this.configuration = checkNotNull(configuration);
this.resourceId = checkNotNull(resourceId);
timeout = AkkaUtils.getTimeoutAsTime(configuration);
this.executor = java.util.concurrent.Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(
Hardware.getNumberCPUCores(),
new ExecutorThreadFactory("taskmanager-future"));
highAvailabilityServices = HighAvailabilityServicesUtils.createHighAvailabilityServices(
configuration,
executor,
HighAvailabilityServicesUtils.AddressResolution.TRY_ADDRESS_RESOLUTION);
rpcService = createRpcService(configuration, highAvailabilityServices);
metricQueryServiceActorSystem = MetricUtils.startMetricsActorSystem(configuration, rpcService.getAddress(), LOG);
HeartbeatServices heartbeatServices = HeartbeatServices.fromConfiguration(configuration);
metricRegistry = new MetricRegistryImpl(MetricRegistryConfiguration.fromConfiguration(configuration));
// TODO: Temporary hack until the MetricQueryService has been ported to RpcEndpoint
metricRegistry.startQueryService(metricQueryServiceActorSystem, resourceId);
blobCacheService = new BlobCacheService(
configuration, highAvailabilityServices.createBlobStore(), null
);
//会启动相关的服务,包括调用TaskManagerServices
taskManager = startTaskManager(
this.configuration,
this.resourceId,
rpcService,
highAvailabilityServices,
heartbeatServices,
metricRegistry,
blobCacheService,
false,
this);
this.terminationFuture = new CompletableFuture<>();
this.shutdown = false;
MemoryLogger.startIfConfigured(LOG, configuration, metricQueryServiceActorSystem);
}
//承接上最后的启动启动任务函数
public static TaskExecutor startTaskManager(
Configuration configuration,
ResourceID resourceID,
RpcService rpcService,
HighAvailabilityServices highAvailabilityServices,
HeartbeatServices heartbeatServices,
MetricRegistry metricRegistry,
BlobCacheService blobCacheService,
boolean localCommunicationOnly,
FatalErrorHandler fatalErrorHandler) throws Exception {
checkNotNull(configuration);
checkNotNull(resourceID);
checkNotNull(rpcService);
checkNotNull(highAvailabilityServices);
LOG.info("Starting TaskManager with ResourceID: {}", resourceID);
InetAddress remoteAddress = InetAddress.getByName(rpcService.getAddress());
TaskManagerServicesConfiguration taskManagerServicesConfiguration =
TaskManagerServicesConfiguration.fromConfiguration(
configuration,
remoteAddress,
localCommunicationOnly);
TaskManagerServices taskManagerServices = TaskManagerServices.fromConfiguration(
taskManagerServicesConfiguration,
resourceID,
rpcService.getExecutor(), // TODO replace this later with some dedicated executor for io.
EnvironmentInformation.getSizeOfFreeHeapMemoryWithDefrag(),
EnvironmentInformation.getMaxJvmHeapMemory());
TaskManagerMetricGroup taskManagerMetricGroup = MetricUtils.instantiateTaskManagerMetricGroup(
metricRegistry,
taskManagerServices.getTaskManagerLocation(),
taskManagerServices.getNetworkEnvironment(),
taskManagerServicesConfiguration.getSystemResourceMetricsProbingInterval());
TaskManagerConfiguration taskManagerConfiguration = TaskManagerConfiguration.fromConfiguration(configuration);
String metricQueryServicePath = metricRegistry.getMetricQueryServicePath();
return new TaskExecutor(
rpcService,
taskManagerConfiguration,
highAvailabilityServices,
taskManagerServices,
heartbeatServices,
taskManagerMetricGroup,
metricQueryServicePath,
blobCacheService,
fatalErrorHandler);
}
通过上面的三个函数从主函数到任务管理到管理的启动,可以发现这玩意儿和前面的JobMaster启动的过程没啥太大区别啊。看来,写程序的人还是一家。而槽的分配管理就在TaskManagerServices.java中:
public class TaskManagerServices {
private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(TaskManagerServices.class);
@VisibleForTesting
public static final String LOCAL_STATE_SUB_DIRECTORY_ROOT = "localState";
/** TaskManager services. */
private final TaskManagerLocation taskManagerLocation;
private final MemoryManager memoryManager;
private final IOManager ioManager;
private final NetworkEnvironment networkEnvironment;
private final BroadcastVariableManager broadcastVariableManager;
private final TaskSlotTable taskSlotTable;
private final JobManagerTable jobManagerTable;
private final JobLeaderService jobLeaderService;
private final TaskExecutorLocalStateStoresManager taskManagerStateStore;
TaskManagerServices(
TaskManagerLocation taskManagerLocation,
MemoryManager memoryManager,
IOManager ioManager,
NetworkEnvironment networkEnvironment,
BroadcastVariableManager broadcastVariableManager,
TaskSlotTable taskSlotTable,
JobManagerTable jobManagerTable,
JobLeaderService jobLeaderService,
TaskExecutorLocalStateStoresManager taskManagerStateStore) {
this.taskManagerLocation = Preconditions.checkNotNull(taskManagerLocation);
this.memoryManager = Preconditions.checkNotNull(memoryManager);
this.ioManager = Preconditions.checkNotNull(ioManager);
this.networkEnvironment = Preconditions.checkNotNull(networkEnvironment);
this.broadcastVariableManager = Preconditions.checkNotNull(broadcastVariableManager);
//达里创建任务槽的表映射
this.taskSlotTable = Preconditions.checkNotNull(taskSlotTable);
this.jobManagerTable = Preconditions.checkNotNull(jobManagerTable);
this.jobLeaderService = Preconditions.checkNotNull(jobLeaderService);
this.taskManagerStateStore = Preconditions.checkNotNull(taskManagerStateStore);
}
......
}
//具体的创建过程
public static TaskManagerServices fromConfiguration(
TaskManagerServicesConfiguration taskManagerServicesConfiguration,
ResourceID resourceID,
Executor taskIOExecutor,
long freeHeapMemoryWithDefrag,
long maxJvmHeapMemory) throws Exception {
// pre-start checks
checkTempDirs(taskManagerServicesConfiguration.getTmpDirPaths());
final NetworkEnvironment network = createNetworkEnvironment(taskManagerServicesConfiguration, maxJvmHeapMemory);
network.start();
final TaskManagerLocation taskManagerLocation = new TaskManagerLocation(
resourceID,
taskManagerServicesConfiguration.getTaskManagerAddress(),
network.getConnectionManager().getDataPort());
// this call has to happen strictly after the network stack has been initialized
final MemoryManager memoryManager = createMemoryManager(taskManagerServicesConfiguration, freeHeapMemoryWithDefrag, maxJvmHeapMemory);
// start the I/O manager, it will create some temp directories.
final IOManager ioManager = new IOManagerAsync(taskManagerServicesConfiguration.getTmpDirPaths());
final BroadcastVariableManager broadcastVariableManager = new BroadcastVariableManager();
final List<ResourceProfile> resourceProfiles = new ArrayList<>(taskManagerServicesConfiguration.getNumberOfSlots());
for (int i = 0; i < taskManagerServicesConfiguration.getNumberOfSlots(); i++) {
resourceProfiles.add(ResourceProfile.ANY);
}
final TimerService<AllocationID> timerService = new TimerService<>(
new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(1),
taskManagerServicesConfiguration.getTimerServiceShutdownTimeout());
final TaskSlotTable taskSlotTable = new TaskSlotTable(resourceProfiles, timerService);
final JobManagerTable jobManagerTable = new JobManagerTable();
final JobLeaderService jobLeaderService = new JobLeaderService(taskManagerLocation, taskManagerServicesConfiguration.getRetryingRegistrationConfiguration());
final String[] stateRootDirectoryStrings = taskManagerServicesConfiguration.getLocalRecoveryStateRootDirectories();
final File[] stateRootDirectoryFiles = new File[stateRootDirectoryStrings.length];
for (int i = 0; i < stateRootDirectoryStrings.length; ++i) {
stateRootDirectoryFiles[i] = new File(stateRootDirectoryStrings[i], LOCAL_STATE_SUB_DIRECTORY_ROOT);
}
final TaskExecutorLocalStateStoresManager taskStateManager = new TaskExecutorLocalStateStoresManager(
taskManagerServicesConfiguration.isLocalRecoveryEnabled(),
stateRootDirectoryFiles,
taskIOExecutor);
return new TaskManagerServices(
taskManagerLocation,
memoryManager,
ioManager,
network,
broadcastVariableManager,
taskSlotTable,
jobManagerTable,
jobLeaderService,
taskStateManager);
}
在任务启动后,就是相关的任务的分配调度了,在任务的管理中,有一个TaskExecutorGateway接口,它用来通过RPC分配任务槽,或者说分配任务的资源:
在JobMaster和ResourceManager中都有类似于registerTaskManager的调用:
public CompletableFuture<RegistrationResponse> registerTaskManager(
final String taskManagerRpcAddress,
final TaskManagerLocation taskManagerLocation,
final Time timeout) {
final ResourceID taskManagerId = taskManagerLocation.getResourceID();
if (registeredTaskManagers.containsKey(taskManagerId)) {
final RegistrationResponse response = new JMTMRegistrationSuccess(resourceId);
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(response);
} else {
return getRpcService()
.connect(taskManagerRpcAddress, TaskExecutorGateway.class)
.handleAsync(
(TaskExecutorGateway taskExecutorGateway, Throwable throwable) -> {
if (throwable != null) {
return new RegistrationResponse.Decline(throwable.getMessage());
}
slotPool.registerTaskManager(taskManagerId);
registeredTaskManagers.put(taskManagerId, Tuple2.of(taskManagerLocation, taskExecutorGateway));
// monitor the task manager as heartbeat target
taskManagerHeartbeatManager.monitorTarget(taskManagerId, new HeartbeatTarget<Void>() {
@Override
public void receiveHeartbeat(ResourceID resourceID, Void payload) {
// the task manager will not request heartbeat, so this method will never be called currently
}
@Override
public void requestHeartbeat(ResourceID resourceID, Void payload) {
taskExecutorGateway.heartbeatFromJobManager(resourceID);
}
});
return new JMTMRegistrationSuccess(resourceId);
},
//启动主线程中RPC服务
getMainThreadExecutor());
}
}
在执行图的最终分发上,可以看到下面的代码:
public class ExecutionJobVertex implements AccessExecutionJobVertex, Archiveable<ArchivedExecutionJobVertex> {
/** Use the same log for all ExecutionGraph classes. */
private static final Logger LOG = ExecutionGraph.LOG;
public static final int VALUE_NOT_SET = -1;
private final Object stateMonitor = new Object();
private final ExecutionGraph graph;
private final JobVertex jobVertex;
private final List<OperatorID> operatorIDs;
private final List<OperatorID> userDefinedOperatorIds;
private final ExecutionVertex[] taskVertices;
private final IntermediateResult[] producedDataSets;
private final List<IntermediateResult> inputs;
private final int parallelism;
private final SlotSharingGroup slotSharingGroup;
private final CoLocationGroup coLocationGroup;
private final InputSplit[] inputSplits;
private final boolean maxParallelismConfigured;
private int maxParallelism;
private Either<SerializedValue<TaskInformation>, PermanentBlobKey> taskInformationOrBlobKey = null;
private InputSplitAssigner splitAssigner;
@VisibleForTesting
ExecutionJobVertex(
ExecutionGraph graph,
JobVertex jobVertex,
int defaultParallelism,
Time timeout) throws JobException {
this(graph, jobVertex, defaultParallelism, timeout, 1L, System.currentTimeMillis());
}
public ExecutionJobVertex(
ExecutionGraph graph,
JobVertex jobVertex,
int defaultParallelism,
Time timeout,
long initialGlobalModVersion,
long createTimestamp) throws JobException {
if (graph == null || jobVertex == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
this.graph = graph;
this.jobVertex = jobVertex;
int vertexParallelism = jobVertex.getParallelism();
int numTaskVertices = vertexParallelism > 0 ? vertexParallelism : defaultParallelism;
final int configuredMaxParallelism = jobVertex.getMaxParallelism();
this.maxParallelismConfigured = (VALUE_NOT_SET != configuredMaxParallelism);
// if no max parallelism was configured by the user, we calculate and set a default
setMaxParallelismInternal(maxParallelismConfigured ?
configuredMaxParallelism : KeyGroupRangeAssignment.computeDefaultMaxParallelism(numTaskVertices));
// verify that our parallelism is not higher than the maximum parallelism
if (numTaskVertices > maxParallelism) {
throw new JobException(
String.format("Vertex %s's parallelism (%s) is higher than the max parallelism (%s). Please lower the parallelism or increase the max parallelism.",
jobVertex.getName(),
numTaskVertices,
maxParallelism));
}
this.parallelism = numTaskVertices;
this.taskVertices = new ExecutionVertex[numTaskVertices];
this.operatorIDs = Collections.unmodifiableList(jobVertex.getOperatorIDs());
this.userDefinedOperatorIds = Collections.unmodifiableList(jobVertex.getUserDefinedOperatorIDs());
this.inputs = new ArrayList<>(jobVertex.getInputs().size());
// take the sharing group
this.slotSharingGroup = jobVertex.getSlotSharingGroup();
this.coLocationGroup = jobVertex.getCoLocationGroup();
// setup the coLocation group
if (coLocationGroup != null && slotSharingGroup == null) {
throw new JobException("Vertex uses a co-location constraint without using slot sharing");
}
// create the intermediate results
this.producedDataSets = new IntermediateResult[jobVertex.getNumberOfProducedIntermediateDataSets()];
for (int i = 0; i < jobVertex.getProducedDataSets().size(); i++) {
final IntermediateDataSet result = jobVertex.getProducedDataSets().get(i);
this.producedDataSets[i] = new IntermediateResult(
result.getId(),
this,
numTaskVertices,
result.getResultType());
}
Configuration jobConfiguration = graph.getJobConfiguration();
int maxPriorAttemptsHistoryLength = jobConfiguration != null ?
jobConfiguration.getInteger(JobManagerOptions.MAX_ATTEMPTS_HISTORY_SIZE) :
JobManagerOptions.MAX_ATTEMPTS_HISTORY_SIZE.defaultValue();
// create all task vertices
for (int i = 0; i < numTaskVertices; i++) {
ExecutionVertex vertex = new ExecutionVertex(
this,
i,
producedDataSets,
timeout,
initialGlobalModVersion,
createTimestamp,
maxPriorAttemptsHistoryLength);
this.taskVertices[i] = vertex;
}
// sanity check for the double referencing between intermediate result partitions and execution vertices
for (IntermediateResult ir : this.producedDataSets) {
if (ir.getNumberOfAssignedPartitions() != parallelism) {
throw new RuntimeException("The intermediate result's partitions were not correctly assigned.");
}
}
// set up the input splits, if the vertex has any
try {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
InputSplitSource<InputSplit> splitSource = (InputSplitSource<InputSplit>) jobVertex.getInputSplitSource();
......
}
......
}
回过头来看一下TaskManager:
public class Task implements Runnable, TaskActions, CheckpointListener {
/** The class logger. */
private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Task.class);
/** The tread group that contains all task threads. */
private static final ThreadGroup TASK_THREADS_GROUP = new ThreadGroup("Flink Task Threads");
/** For atomic state updates. */
private static final AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater<Task, ExecutionState> STATE_UPDATER =
AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater.newUpdater(Task.class, ExecutionState.class, "executionState");
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Constant fields that are part of the initial Task construction
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------
/** The job that the task belongs to. */
private final JobID jobId;
/** The vertex in the JobGraph whose code the task executes. */
private final JobVertexID vertexId;
/** The execution attempt of the parallel subtask. */
private final ExecutionAttemptID executionId;
/** ID which identifies the slot in which the task is supposed to run. */
private final AllocationID allocationId;
/** TaskInfo object for this task. */
private final TaskInfo taskInfo;
/** The name of the task, including subtask indexes. */
private final String taskNameWithSubtask;
/** The job-wide configuration object. */
private final Configuration jobConfiguration;
/** The task-specific configuration. */
private final Configuration taskConfiguration;
/** The jar files used by this task. */
private final Collection<PermanentBlobKey> requiredJarFiles;
/** The classpaths used by this task. */
private final Collection<URL> requiredClasspaths;
/** The name of the class that holds the invokable code. */
private final String nameOfInvokableClass;
/** Access to task manager configuration and host names. */
private final TaskManagerRuntimeInfo taskManagerConfig;
/** The memory manager to be used by this task. */
private final MemoryManager memoryManager;
/** The I/O manager to be used by this task. */
private final IOManager ioManager;
/** The BroadcastVariableManager to be used by this task. */
private final BroadcastVariableManager broadcastVariableManager;
/** The manager for state of operators running in this task/slot. */
private final TaskStateManager taskStateManager;
/** Serialized version of the job specific execution configuration (see {@link ExecutionConfig}). */
private final SerializedValue<ExecutionConfig> serializedExecutionConfig;
private final ResultPartition[] producedPartitions;
private final SingleInputGate[] inputGates;
private final Map<IntermediateDataSetID, SingleInputGate> inputGatesById;
/** Connection to the task manager. */
private final TaskManagerActions taskManagerActions;
/** Input split provider for the task. */
private final InputSplitProvider inputSplitProvider;
/** Checkpoint notifier used to communicate with the CheckpointCoordinator. */
private final CheckpointResponder checkpointResponder;
/** GlobalAggregateManager used to update aggregates on the JobMaster. */
private final GlobalAggregateManager aggregateManager;
/** The BLOB cache, from which the task can request BLOB files. */
private final BlobCacheService blobService;
/** The library cache, from which the task can request its class loader. */
private final LibraryCacheManager libraryCache;
/** The cache for user-defined files that the invokable requires. */
private final FileCache fileCache;
/** The gateway to the network stack, which handles inputs and produced results. */
private final NetworkEnvironment network;
/** The registry of this task which enables live reporting of accumulators. */
private final AccumulatorRegistry accumulatorRegistry;
/** The thread that executes the task. */
private final Thread executingThread;
/** Parent group for all metrics of this task. */
private final TaskMetricGroup metrics;
/** Partition producer state checker to request partition states from. */
private final PartitionProducerStateChecker partitionProducerStateChecker;
/** Executor to run future callbacks. */
private final Executor executor;
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Fields that control the task execution. All these fields are volatile
// (which means that they introduce memory barriers), to establish
// proper happens-before semantics on parallel modification
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------
/** atomic flag that makes sure the invokable is canceled exactly once upon error. */
private final AtomicBoolean invokableHasBeenCanceled;
/** The invokable of this task, if initialized. All accesses must copy the reference and
* check for null, as this field is cleared as part of the disposal logic. */
@Nullable
private volatile AbstractInvokable invokable;
/** The current execution state of the task. */
private volatile ExecutionState executionState = ExecutionState.CREATED;
/** The observed exception, in case the task execution failed. */
private volatile Throwable failureCause;
/** Serial executor for asynchronous calls (checkpoints, etc), lazily initialized. */
private volatile ExecutorService asyncCallDispatcher;
/** Initialized from the Flink configuration. May also be set at the ExecutionConfig */
private long taskCancellationInterval;
/** Initialized from the Flink configuration. May also be set at the ExecutionConfig */
private long taskCancellationTimeout;
/**
* This class loader should be set as the context class loader of the threads in
* {@link #asyncCallDispatcher} because user code may dynamically load classes in all callbacks.
*/
private ClassLoader userCodeClassLoader;
/**
* IMPORTANT: This constructor may not start any work that would need to
* be undone in the case of a failing task deployment.
*/
public Task(
JobInformation jobInformation,
TaskInformation taskInformation,
ExecutionAttemptID executionAttemptID,
AllocationID slotAllocationId,
int subtaskIndex,
int attemptNumber,
Collection<ResultPartitionDeploymentDescriptor> resultPartitionDeploymentDescriptors,
Collection<InputGateDeploymentDescriptor> inputGateDeploymentDescriptors,
int targetSlotNumber,
MemoryManager memManager,
IOManager ioManager,
NetworkEnvironment networkEnvironment,
BroadcastVariableManager bcVarManager,
TaskStateManager taskStateManager,
TaskManagerActions taskManagerActions,
InputSplitProvider inputSplitProvider,
CheckpointResponder checkpointResponder,
GlobalAggregateManager aggregateManager,
BlobCacheService blobService,
LibraryCacheManager libraryCache,
FileCache fileCache,
TaskManagerRuntimeInfo taskManagerConfig,
@Nonnull TaskMetricGroup metricGroup,
ResultPartitionConsumableNotifier resultPartitionConsumableNotifier,
PartitionProducerStateChecker partitionProducerStateChecker,
Executor executor) {
Preconditions.checkNotNull(jobInformation);
Preconditions.checkNotNull(taskInformation);
Preconditions.checkArgument(0 <= subtaskIndex, "The subtask index must be positive.");
Preconditions.checkArgument(0 <= attemptNumber, "The attempt number must be positive.");
Preconditions.checkArgument(0 <= targetSlotNumber, "The target slot number must be positive.");
this.taskInfo = new TaskInfo(
taskInformation.getTaskName(),
taskInformation.getMaxNumberOfSubtaks(),
subtaskIndex,
taskInformation.getNumberOfSubtasks(),
attemptNumber,
String.valueOf(slotAllocationId));
this.jobId = jobInformation.getJobId();
this.vertexId = taskInformation.getJobVertexId();
this.executionId = Preconditions.checkNotNull(executionAttemptID);
this.allocationId = Preconditions.checkNotNull(slotAllocationId);
this.taskNameWithSubtask = taskInfo.getTaskNameWithSubtasks();
this.jobConfiguration = jobInformation.getJobConfiguration();
this.taskConfiguration = taskInformation.getTaskConfiguration();
this.requiredJarFiles = jobInformation.getRequiredJarFileBlobKeys();
this.requiredClasspaths = jobInformation.getRequiredClasspathURLs();
this.nameOfInvokableClass = taskInformation.getInvokableClassName();
this.serializedExecutionConfig = jobInformation.getSerializedExecutionConfig();
Configuration tmConfig = taskManagerConfig.getConfiguration();
this.taskCancellationInterval = tmConfig.getLong(TaskManagerOptions.TASK_CANCELLATION_INTERVAL);
this.taskCancellationTimeout = tmConfig.getLong(TaskManagerOptions.TASK_CANCELLATION_TIMEOUT);
this.memoryManager = Preconditions.checkNotNull(memManager);
this.ioManager = Preconditions.checkNotNull(ioManager);
this.broadcastVariableManager = Preconditions.checkNotNull(bcVarManager);
this.taskStateManager = Preconditions.checkNotNull(taskStateManager);
this.accumulatorRegistry = new AccumulatorRegistry(jobId, executionId);
this.inputSplitProvider = Preconditions.checkNotNull(inputSplitProvider);
this.checkpointResponder = Preconditions.checkNotNull(checkpointResponder);
this.aggregateManager = Preconditions.checkNotNull(aggregateManager);
this.taskManagerActions = checkNotNull(taskManagerActions);
this.blobService = Preconditions.checkNotNull(blobService);
this.libraryCache = Preconditions.checkNotNull(libraryCache);
this.fileCache = Preconditions.checkNotNull(fileCache);
this.network = Preconditions.checkNotNull(networkEnvironment);
this.taskManagerConfig = Preconditions.checkNotNull(taskManagerConfig);
this.metrics = metricGroup;
this.partitionProducerStateChecker = Preconditions.checkNotNull(partitionProducerStateChecker);
this.executor = Preconditions.checkNotNull(executor);
// create the reader and writer structures
final String taskNameWithSubtaskAndId = taskNameWithSubtask + " (" + executionId + ')';
// Produced intermediate result partitions
this.producedPartitions = new ResultPartition[resultPartitionDeploymentDescriptors.size()];
int counter = 0;
for (ResultPartitionDeploymentDescriptor desc: resultPartitionDeploymentDescriptors) {
ResultPartitionID partitionId = new ResultPartitionID(desc.getPartitionId(), executionId);
this.producedPartitions[counter] = new ResultPartition(
taskNameWithSubtaskAndId,
this,
jobId,
partitionId,
desc.getPartitionType(),
desc.getNumberOfSubpartitions(),
desc.getMaxParallelism(),
networkEnvironment.getResultPartitionManager(),
resultPartitionConsumableNotifier,
ioManager,
desc.sendScheduleOrUpdateConsumersMessage());
++counter;
}
// Consumed intermediate result partitions
this.inputGates = new SingleInputGate[inputGateDeploymentDescriptors.size()];
this.inputGatesById = new HashMap<>();
counter = 0;
for (InputGateDeploymentDescriptor inputGateDeploymentDescriptor: inputGateDeploymentDescriptors) {
SingleInputGate gate = SingleInputGate.create(
taskNameWithSubtaskAndId,
jobId,
executionId,
inputGateDeploymentDescriptor,
networkEnvironment,
this,
metricGroup.getIOMetricGroup());
inputGates[counter] = gate;
inputGatesById.put(gate.getConsumedResultId(), gate);
++counter;
}
invokableHasBeenCanceled = new AtomicBoolean(false);
// finally, create the executing thread, but do not start it
executingThread = new Thread(TASK_THREADS_GROUP, this, taskNameWithSubtask);
}
......
}
这个包下的其它几个类基本都是围绕着Manager来展开的,包括相关资源的ID,执行状态,相关信息,而真正的执行在taskexecutor这个包下,这个包还包含有rpc、slot以及exception三个,最后一个可以略过。在slot的包下,有三个类很重要:TaskSlot,TaskSlotTable和SlotOffer。
public class TaskSlot {
/** Index of the task slot. */
private final int index;
/** Resource characteristics for this slot. */
private final ResourceProfile resourceProfile;
/** Tasks running in this slot. */
private final Map<ExecutionAttemptID, Task> tasks;
/** State of this slot. */
private TaskSlotState state;
/** Job id to which the slot has been allocated; null if not allocated. */
private JobID jobId;
/** Allocation id of this slot; null if not allocated. */
private AllocationID allocationId;
TaskSlot(final int index, final ResourceProfile resourceProfile) {
Preconditions.checkArgument(0 <= index, "The index must be greater than 0.");
this.index = index;
this.resourceProfile = Preconditions.checkNotNull(resourceProfile);
this.tasks = new HashMap<>(4);
this.state = TaskSlotState.FREE;
this.jobId = null;
this.allocationId = null;
}
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// State accessors
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
public int getIndex() {
return index;
}
public ResourceProfile getResourceProfile() {
return resourceProfile;
}
public JobID getJobId() {
return jobId;
}
public AllocationID getAllocationId() {
return allocationId;
}
TaskSlotState getState() {
return state;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return tasks.isEmpty();
}
public boolean isFree() {
return TaskSlotState.FREE == state;
}
public boolean isActive(JobID activeJobId, AllocationID activeAllocationId) {
Preconditions.checkNotNull(activeJobId);
Preconditions.checkNotNull(activeAllocationId);
return TaskSlotState.ACTIVE == state &&
activeJobId.equals(jobId) &&
activeAllocationId.equals(allocationId);
}
public boolean isAllocated(JobID jobIdToCheck, AllocationID allocationIDToCheck) {
Preconditions.checkNotNull(jobIdToCheck);
Preconditions.checkNotNull(allocationIDToCheck);
return jobIdToCheck.equals(jobId) && allocationIDToCheck.equals(allocationId) &&
(TaskSlotState.ACTIVE == state || TaskSlotState.ALLOCATED == state);
}
public boolean isReleasing() {
return TaskSlotState.RELEASING == state;
}
/**
* Get all tasks running in this task slot.
*
* @return Iterator to all currently contained tasks in this task slot.
*/
public Iterator<Task> getTasks() {
return tasks.values().iterator();
}
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// State changing methods
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* Add the given task to the task slot. This is only possible if there is not already another
* task with the same execution attempt id added to the task slot. In this case, the method
* returns true. Otherwise the task slot is left unchanged and false is returned.
*
* In case that the task slot state is not active an {@link IllegalStateException} is thrown.
* In case that the task's job id and allocation id don't match with the job id and allocation
* id for which the task slot has been allocated, an {@link IllegalArgumentException} is thrown.
*
* @param task to be added to the task slot
* @throws IllegalStateException if the task slot is not in state active
* @return true if the task was added to the task slot; otherwise false
*/
public boolean add(Task task) {
// Check that this slot has been assigned to the job sending this task
Preconditions.checkArgument(task.getJobID().equals(jobId), "The task's job id does not match the " +
"job id for which the slot has been allocated.");
Preconditions.checkArgument(task.getAllocationId().equals(allocationId), "The task's allocation " +
"id does not match the allocation id for which the slot has been allocated.");
Preconditions.checkState(TaskSlotState.ACTIVE == state, "The task slot is not in state active.");
Task oldTask = tasks.put(task.getExecutionId(), task);
if (oldTask != null) {
tasks.put(task.getExecutionId(), oldTask);
return false;
} else {
return true;
}
}
/**
* Remove the task identified by the given execution attempt id.
*
* @param executionAttemptId identifying the task to be removed
* @return The removed task if there was any; otherwise null.
*/
public Task remove(ExecutionAttemptID executionAttemptId) {
return tasks.remove(executionAttemptId);
}
/**
* Removes all tasks from this task slot.
*/
public void clear() {
tasks.clear();
}
/**
* Allocate the task slot for the given job and allocation id. If the slot could be allocated,
* or is already allocated/active for the given job and allocation id, then the method returns
* true. Otherwise it returns false.
*
* A slot can only be allocated if it's current state is free.
*
* @param newJobId to allocate the slot for
* @param newAllocationId to identify the slot allocation
* @return True if the slot was allocated for the given job and allocation id; otherwise false
*/
public boolean allocate(JobID newJobId, AllocationID newAllocationId) {
if (TaskSlotState.FREE == state) {
// sanity checks
Preconditions.checkState(allocationId == null);
Preconditions.checkState(jobId == null);
this.jobId = Preconditions.checkNotNull(newJobId);
this.allocationId = Preconditions.checkNotNull(newAllocationId);
state = TaskSlotState.ALLOCATED;
return true;
} else if (TaskSlotState.ALLOCATED == state || TaskSlotState.ACTIVE == state) {
Preconditions.checkNotNull(newJobId);
Preconditions.checkNotNull(newAllocationId);
return newJobId.equals(jobId) && newAllocationId.equals(allocationId);
} else {
return false;
}
}
/**
* Mark this slot as active. A slot can only be marked active if it's in state allocated.
*
* The method returns true if the slot was set to active. Otherwise it returns false.
*
* @return True if the new state of the slot is active; otherwise false
*/
public boolean markActive() {
if (TaskSlotState.ALLOCATED == state || TaskSlotState.ACTIVE == state) {
state = TaskSlotState.ACTIVE;
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
/**
* Mark the slot as inactive/allocated. A slot can only be marked as inactive/allocated if it's
* in state allocated or active.
*
* @return True if the new state of the slot is allocated; otherwise false
*/
public boolean markInactive() {
if (TaskSlotState.ACTIVE == state || TaskSlotState.ALLOCATED == state) {
state = TaskSlotState.ALLOCATED;
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
/**
* Mark the slot as free. A slot can only be marked as free if it's empty.
*
* @return True if the new state is free; otherwise false
*/
public boolean markFree() {
if (isEmpty()) {
state = TaskSlotState.FREE;
this.jobId = null;
this.allocationId = null;
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
/**
* Mark this slot as releasing. A slot can always be marked as releasing.
*
* @return True
*/
public boolean markReleasing() {
state = TaskSlotState.RELEASING;
return true;
}
/**
* Generate the slot offer from this TaskSlot.
*
* @return The sot offer which this task slot can provide
*/
public SlotOffer generateSlotOffer() {
Preconditions.checkState(TaskSlotState.ACTIVE == state || TaskSlotState.ALLOCATED == state,
"The task slot is not in state active or allocated.");
Preconditions.checkState(allocationId != null, "The task slot are not allocated");
return new SlotOffer(allocationId, index, resourceProfile);
}
......
}
而真正的任务重点在TaskExecutor、TaskManagerRunner和TaskManagerServices这三个类中。在一开始其实已经看到了这三者相互依存,启动工作的过程,下面看一下执行的过程:
public static RpcService createRpcService(
final Configuration configuration,
final HighAvailabilityServices haServices) throws Exception {
checkNotNull(configuration);
checkNotNull(haServices);
final String taskManagerAddress = determineTaskManagerBindAddress(configuration, haServices);
final String portRangeDefinition = configuration.getString(TaskManagerOptions.RPC_PORT);
return AkkaRpcServiceUtils.createRpcService(taskManagerAddress, portRangeDefinition, configuration);
}
再看一下TaskManagerServices.java中的相关代码:
private static MemoryManager createMemoryManager(
TaskManagerServicesConfiguration taskManagerServicesConfiguration,
long freeHeapMemoryWithDefrag,
long maxJvmHeapMemory) throws Exception {
// computing the amount of memory to use depends on how much memory is available
// it strictly needs to happen AFTER the network stack has been initialized
// check if a value has been configured
long configuredMemory = taskManagerServicesConfiguration.getConfiguredMemory();
MemoryType memType = taskManagerServicesConfiguration.getMemoryType();
final long memorySize;
boolean preAllocateMemory = taskManagerServicesConfiguration.isPreAllocateMemory();
if (configuredMemory > 0) {
if (preAllocateMemory) {
LOG.info("Using {} MB for managed memory." , configuredMemory);
} else {
LOG.info("Limiting managed memory to {} MB, memory will be allocated lazily." , configuredMemory);
}
memorySize = configuredMemory << 20; // megabytes to bytes
} else {
// similar to #calculateNetworkBufferMemory(TaskManagerServicesConfiguration tmConfig)
float memoryFraction = taskManagerServicesConfiguration.getMemoryFraction();
if (memType == MemoryType.HEAP) {
// network buffers allocated off-heap -> use memoryFraction of the available heap:
long relativeMemSize = (long) (freeHeapMemoryWithDefrag * memoryFraction);
if (preAllocateMemory) {
LOG.info("Using {} of the currently free heap space for managed heap memory ({} MB)." ,
memoryFraction , relativeMemSize >> 20);
} else {
LOG.info("Limiting managed memory to {} of the currently free heap space ({} MB), " +
"memory will be allocated lazily." , memoryFraction , relativeMemSize >> 20);
}
memorySize = relativeMemSize;
} else if (memType == MemoryType.OFF_HEAP) {
// The maximum heap memory has been adjusted according to the fraction (see
// calculateHeapSizeMB(long totalJavaMemorySizeMB, Configuration config)), i.e.
// maxJvmHeap = jvmTotalNoNet - jvmTotalNoNet * memoryFraction = jvmTotalNoNet * (1 - memoryFraction)
// directMemorySize = jvmTotalNoNet * memoryFraction
long directMemorySize = (long) (maxJvmHeapMemory / (1.0 - memoryFraction) * memoryFraction);
if (preAllocateMemory) {
LOG.info("Using {} of the maximum memory size for managed off-heap memory ({} MB)." ,
memoryFraction, directMemorySize >> 20);
} else {
LOG.info("Limiting managed memory to {} of the maximum memory size ({} MB)," +
" memory will be allocated lazily.", memoryFraction, directMemorySize >> 20);
}
memorySize = directMemorySize;
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("No supported memory type detected.");
}
}
// now start the memory manager
final MemoryManager memoryManager;
try {
memoryManager = new MemoryManager(
memorySize,
taskManagerServicesConfiguration.getNumberOfSlots(),
taskManagerServicesConfiguration.getNetworkConfig().networkBufferSize(),
memType,
preAllocateMemory);
} catch (OutOfMemoryError e) {
if (memType == MemoryType.HEAP) {
throw new Exception("OutOfMemory error (" + e.getMessage() +
") while allocating the TaskManager heap memory (" + memorySize + " bytes).", e);
} else if (memType == MemoryType.OFF_HEAP) {
throw new Exception("OutOfMemory error (" + e.getMessage() +
") while allocating the TaskManager off-heap memory (" + memorySize +
" bytes).Try increasing the maximum direct memory (-XX:MaxDirectMemorySize)", e);
} else {
throw e;
}
}
return memoryManager;
}
/**
* Creates the {@link NetworkEnvironment} from the given {@link TaskManagerServicesConfiguration}.
*
* @param taskManagerServicesConfiguration to construct the network environment from
* @param maxJvmHeapMemory the maximum JVM heap size
* @return Network environment
* @throws IOException
*/
private static NetworkEnvironment createNetworkEnvironment(
TaskManagerServicesConfiguration taskManagerServicesConfiguration,
long maxJvmHeapMemory) {
NetworkEnvironmentConfiguration networkEnvironmentConfiguration = taskManagerServicesConfiguration.getNetworkConfig();
final long networkBuf = calculateNetworkBufferMemory(taskManagerServicesConfiguration, maxJvmHeapMemory);
int segmentSize = networkEnvironmentConfiguration.networkBufferSize();
// tolerate offcuts between intended and allocated memory due to segmentation (will be available to the user-space memory)
final long numNetBuffersLong = networkBuf / segmentSize;
if (numNetBuffersLong > Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("The given number of memory bytes (" + networkBuf
+ ") corresponds to more than MAX_INT pages.");
}
NetworkBufferPool networkBufferPool = new NetworkBufferPool(
(int) numNetBuffersLong,
segmentSize);
ConnectionManager connectionManager;
boolean enableCreditBased = false;
NettyConfig nettyConfig = networkEnvironmentConfiguration.nettyConfig();
if (nettyConfig != null) {
connectionManager = new NettyConnectionManager(nettyConfig);
enableCreditBased = nettyConfig.isCreditBasedEnabled();
} else {
connectionManager = new LocalConnectionManager();
}
ResultPartitionManager resultPartitionManager = new ResultPartitionManager();
TaskEventDispatcher taskEventDispatcher = new TaskEventDispatcher();
KvStateRegistry kvStateRegistry = new KvStateRegistry();
QueryableStateConfiguration qsConfig = taskManagerServicesConfiguration.getQueryableStateConfig();
KvStateClientProxy kvClientProxy = null;
KvStateServer kvStateServer = null;
if (qsConfig != null) {
int numProxyServerNetworkThreads = qsConfig.numProxyServerThreads() == 0 ?
taskManagerServicesConfiguration.getNumberOfSlots() : qsConfig.numProxyServerThreads();
int numProxyServerQueryThreads = qsConfig.numProxyQueryThreads() == 0 ?
taskManagerServicesConfiguration.getNumberOfSlots() : qsConfig.numProxyQueryThreads();
kvClientProxy = QueryableStateUtils.createKvStateClientProxy(
taskManagerServicesConfiguration.getTaskManagerAddress(),
qsConfig.getProxyPortRange(),
numProxyServerNetworkThreads,
numProxyServerQueryThreads,
new DisabledKvStateRequestStats());
int numStateServerNetworkThreads = qsConfig.numStateServerThreads() == 0 ?
taskManagerServicesConfiguration.getNumberOfSlots() : qsConfig.numStateServerThreads();
int numStateServerQueryThreads = qsConfig.numStateQueryThreads() == 0 ?
taskManagerServicesConfiguration.getNumberOfSlots() : qsConfig.numStateQueryThreads();
kvStateServer = QueryableStateUtils.createKvStateServer(
taskManagerServicesConfiguration.getTaskManagerAddress(),
qsConfig.getStateServerPortRange(),
numStateServerNetworkThreads,
numStateServerQueryThreads,
kvStateRegistry,
new DisabledKvStateRequestStats());
}
// we start the network first, to make sure it can allocate its buffers first
return new NetworkEnvironment(
networkBufferPool,
connectionManager,
resultPartitionManager,
taskEventDispatcher,
kvStateRegistry,
kvStateServer,
kvClientProxy,
networkEnvironmentConfiguration.ioMode(),
networkEnvironmentConfiguration.partitionRequestInitialBackoff(),
networkEnvironmentConfiguration.partitionRequestMaxBackoff(),
networkEnvironmentConfiguration.networkBuffersPerChannel(),
networkEnvironmentConfiguration.floatingNetworkBuffersPerGate(),
enableCreditBased);
}
这其实就是前面的说的内存和网络资源的处理。再看一下TaskExecutor.java中的代码:
public CompletableFuture<Acknowledge> submitTask(
TaskDeploymentDescriptor tdd,
JobMasterId jobMasterId,
Time timeout) {
try {
final JobID jobId = tdd.getJobId();
final JobManagerConnection jobManagerConnection = jobManagerTable.get(jobId);
if (jobManagerConnection == null) {
final String message = "Could not submit task because there is no JobManager " +
"associated for the job " + jobId + '.';
log.debug(message);
throw new TaskSubmissionException(message);
}
if (!Objects.equals(jobManagerConnection.getJobMasterId(), jobMasterId)) {
final String message = "Rejecting the task submission because the job manager leader id " +
jobMasterId + " does not match the expected job manager leader id " +
jobManagerConnection.getJobMasterId() + '.';
log.debug(message);
throw new TaskSubmissionException(message);
}
if (!taskSlotTable.tryMarkSlotActive(jobId, tdd.getAllocationId())) {
final String message = "No task slot allocated for job ID " + jobId +
" and allocation ID " + tdd.getAllocationId() + '.';
log.debug(message);
throw new TaskSubmissionException(message);
}
// re-integrate offloaded data:
try {
tdd.loadBigData(blobCacheService.getPermanentBlobService());
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new TaskSubmissionException("Could not re-integrate offloaded TaskDeploymentDescriptor data.", e);
}
// deserialize the pre-serialized information
final JobInformation jobInformation;
final TaskInformation taskInformation;
try {
jobInformation = tdd.getSerializedJobInformation().deserializeValue(getClass().getClassLoader());
taskInformation = tdd.getSerializedTaskInformation().deserializeValue(getClass().getClassLoader());
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new TaskSubmissionException("Could not deserialize the job or task information.", e);
}
if (!jobId.equals(jobInformation.getJobId())) {
throw new TaskSubmissionException(
"Inconsistent job ID information inside TaskDeploymentDescriptor (" +
tdd.getJobId() + " vs. " + jobInformation.getJobId() + ")");
}
TaskMetricGroup taskMetricGroup = taskManagerMetricGroup.addTaskForJob(
jobInformation.getJobId(),
jobInformation.getJobName(),
taskInformation.getJobVertexId(),
tdd.getExecutionAttemptId(),
taskInformation.getTaskName(),
tdd.getSubtaskIndex(),
tdd.getAttemptNumber());
InputSplitProvider inputSplitProvider = new RpcInputSplitProvider(
jobManagerConnection.getJobManagerGateway(),
taskInformation.getJobVertexId(),
tdd.getExecutionAttemptId(),
taskManagerConfiguration.getTimeout());
TaskManagerActions taskManagerActions = jobManagerConnection.getTaskManagerActions();
CheckpointResponder checkpointResponder = jobManagerConnection.getCheckpointResponder();
GlobalAggregateManager aggregateManager = jobManagerConnection.getGlobalAggregateManager();
LibraryCacheManager libraryCache = jobManagerConnection.getLibraryCacheManager();
ResultPartitionConsumableNotifier resultPartitionConsumableNotifier = jobManagerConnection.getResultPartitionConsumableNotifier();
PartitionProducerStateChecker partitionStateChecker = jobManagerConnection.getPartitionStateChecker();
final TaskLocalStateStore localStateStore = localStateStoresManager.localStateStoreForSubtask(
jobId,
tdd.getAllocationId(),
taskInformation.getJobVertexId(),
tdd.getSubtaskIndex());
final JobManagerTaskRestore taskRestore = tdd.getTaskRestore();
final TaskStateManager taskStateManager = new TaskStateManagerImpl(
jobId,
tdd.getExecutionAttemptId(),
localStateStore,
taskRestore,
checkpointResponder);
Task task = new Task(
jobInformation,
taskInformation,
tdd.getExecutionAttemptId(),
tdd.getAllocationId(),
tdd.getSubtaskIndex(),
tdd.getAttemptNumber(),
tdd.getProducedPartitions(),
tdd.getInputGates(),
tdd.getTargetSlotNumber(),
taskExecutorServices.getMemoryManager(),
taskExecutorServices.getIOManager(),
taskExecutorServices.getNetworkEnvironment(),
taskExecutorServices.getBroadcastVariableManager(),
taskStateManager,
taskManagerActions,
inputSplitProvider,
checkpointResponder,
aggregateManager,
blobCacheService,
libraryCache,
fileCache,
taskManagerConfiguration,
taskMetricGroup,
resultPartitionConsumableNotifier,
partitionStateChecker,
getRpcService().getExecutor());
log.info("Received task {}.", task.getTaskInfo().getTaskNameWithSubtasks());
boolean taskAdded;
try {
taskAdded = taskSlotTable.addTask(task);
} catch (SlotNotFoundException | SlotNotActiveException e) {
throw new TaskSubmissionException("Could not submit task.", e);
}
if (taskAdded) {
task.startTaskThread();
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(Acknowledge.get());
} else {
final String message = "TaskManager already contains a task for id " +
task.getExecutionId() + '.';
log.debug(message);
throw new TaskSubmissionException(message);
}
} catch (TaskSubmissionException e) {
return FutureUtils.completedExceptionally(e);
}
}
提交任务执行的代码是关键的一步了。在这一步里,不但要配置各种任务和分发的方式,同样还要启动大量的监视服务以及其它的辅助性的工作。最后调用任务的异步启动方式来执行任务。这事儿就这基本就把任务搞定了。
//Task.java
//task.startTaskThread()
public void startTaskThread() {
executingThread.start();
}
public synchronized void start() {
/**
* This method is not invoked for the main method thread or "system"
* group threads created/set up by the VM. Any new functionality added
* to this method in the future may have to also be added to the VM.
*
* A zero status value corresponds to state "NEW".
*/
if (threadStatus != 0)
throw new IllegalThreadStateException();
/* Notify the group that this thread is about to be started
* so that it can be added to the group's list of threads
* and the group's unstarted count can be decremented. */
group.add(this);
boolean started = false;
try {
start0();
started = true;
} finally {
try {
if (!started) {
group.threadStartFailed(this);
}
} catch (Throwable ignore) {
/* do nothing. If start0 threw a Throwable then
it will be passed up the call stack */
}
}
}
线程的部分回头再深入分析。
四、总结
任务的启动和执行初步算是分析完成了,再往后就开始深入内部的机制和原理进行分析了。
