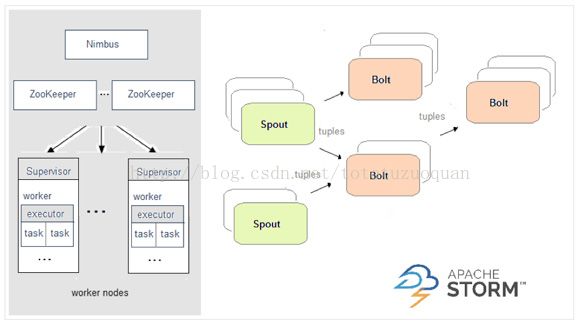
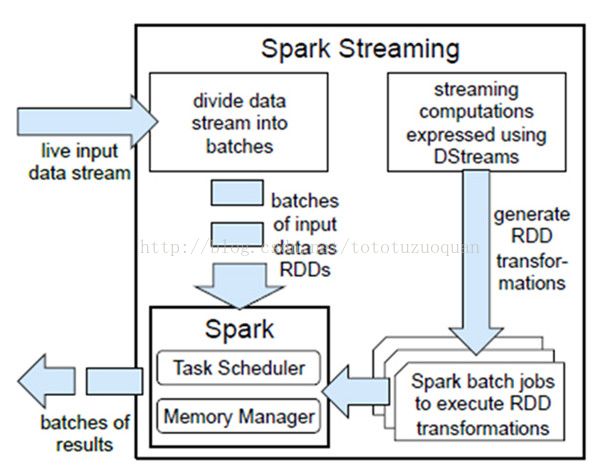
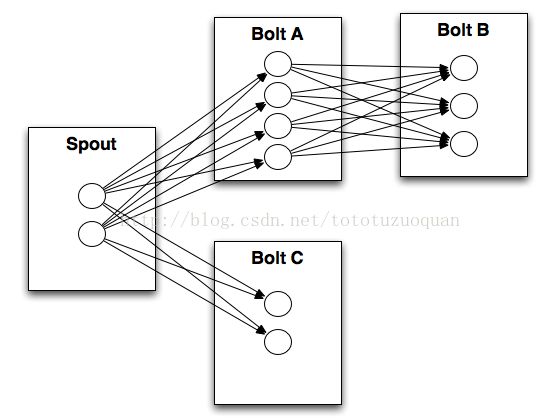
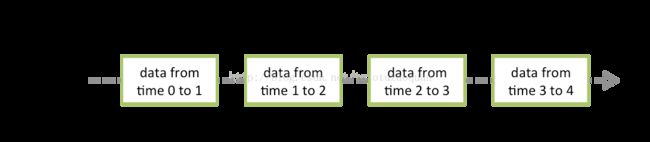
- 工业大模型应用报告:新机遇、挑战与未来展望
花生糖@
AIGC学习资料库大模型人工智能应用扩展屏应用开发AI机器学习
大模型在工业智能化发展中的新机遇、挑战与展望。以下是报告的核心内容概述:大模型为工业智能化发展带来新机遇大模型开启人工智能应用新时代,推动技术创新和应用。大模型有望成为驱动工业智能化的引擎,提高研发效率、拓展生产制造智能化应用边界、提升经营管理水平。大模型应用落地需要深度适配工业场景,解决行业知识和企业特定环境的理解问题。大模型和小模型在工业领域将长期并存小模型应用呈现倒U型分布,主要集中在生产制
- 游戏UI开发之路:复盘从Flash黄金时代到Unity UI Toolkit的漫漫长路(5)
伽蓝_游戏
游戏UI开发游戏uiunity
第五章:终章与新篇——在永无止境的道路上,眺望下一个十年从Flash页游的喧嚣时代,到引擎王权的更迭与“第三极”的百家争鸣,我们一同穿越了游戏UI技术发展史上波澜壮阔的十余年。当历史的尘埃落定,回望这条漫漫长路,几条清晰而深刻的技术脉络,如山脉般贯穿了整个时代,并清晰地指向了未来的方向。5.1历史的回响:驱动技术演进的三大主旋律在这场永不停歇的技术演进中,有三个核心的“主旋律”在反复奏响,它们是理
- 飞算JavaAI:Java开发者的智能革命,从代码生成到架构重塑
目录一、Java开发困局:效率与质量的双重挑战二、技术架构解析:三层智能引擎驱动开发革命1.智能语义理解层2.代码智能生成层3.运行时智能优化层三、核心功能矩阵:从需求到部署的全流程覆盖1.智能需求分析2.自动化软件设计3.工程化代码输出4.智能重构引擎四、实战场景解析:从初创项目到老系统改造场景1:初创项目快速验证场景2:老系统迭代升级场景3:高并发系统优化五、开发者价值重构:从代码工人到系统设
- FPGA芯片厂商及关键的开发测试工具
Chip Design
xPUChipDesignfpga开发
以下是结合2025年技术动态整理的。一、FPGA芯片主要厂商及产品系列厂商芯片系列典型特点目标市场AMD/XilinxVersal,Kintex,Artix,Zynq高性能异构计算(AI引擎+FPGA+CPU)数据中心、5G、航空航天Intel(Altera)Stratix,Arria,Agilex,Cyclone高带宽内存集成(HBM),支持CXL协议网络加速、边缘计算LatticeCertus
- InnoDB引擎B+树索引使用和新特性
蜜獾互联网
MySqlb树数据结构
B+树索引的管理我们在InnoDB引擎中常用的索引基本都是B+树索引。创建和删除索引它的创建和删除有两种方法:#方式一:altertable,此时index和key均可以,如果要求所有值均不重复,加上uniquealtertabletbl_nameadd[unique]index|keyindex_name(index_col_name,...);altertabletbl_namedropind
- 【MySQL】性能优化实战指南:释放数据库潜能的艺术
文章目录MySQL性能优化实战指南:释放数据库潜能的艺术引言为什么需要MySQL性能优化?性能优化基础知识MySQL性能瓶颈分析1.硬件资源瓶颈2.MySQL内部瓶颈优化配置策略大全内存配置优化InnoDB缓冲池配置查询缓存配置连接和线程配置磁盘I/O优化InnoDB存储引擎配置临时表配置独特优化创意配置创意1:分层存储优化创意2:动态配置自适应创意3:负载感知配置高级优化技巧并行处理优化索引和查
- GEO + SEO+SMO:AI时代全域组合营销
智***O
人工智能GEO优化大数据GEOAI搜索
在信息爆炸的时代,用户每一次搜索的背后,都是一次决策的起点。当AI工具逐渐成为人们获取答案的首选,如何让你的品牌在AI生成的回答中占据核心位置?如何让用户在不同平台搜索时,始终选择你?智火营销SEO+GEO+SMO组合营销策略,让品牌成为用户与“搜索”之间的桥梁。智火营销GEO服务一、SEO:巩固搜索生态的信任基石在AI工具与社交平台崛起的当下,传统搜索引擎仍是用户验证信息的重要场景。SEO(搜索
- linux安装Node.js 环境,Docker 环境,Ruby 环境,MongoDB 环境,PostgreSQL 数据库,Go 开发环境,Python 虚拟环境
2401_87017622
数据库linuxnode.js
在Linux上安装其他常见的开发环境可以根据具体需求而定,以下是一些常见的安装步骤:1.Node.js环境Node.js是一个基于ChromeV8引擎的JavaScript运行环境,适用于服务器端开发。安装Node.js:通过包管理器安装:sudoyuminstall-ygcc-c++makecurl-sLhttps://rpm.nodesource.com/setup_14.x|sudo-Eba
- 5大核心技术+3大交互革命!Java如何让虚拟世界‘活过来’?——附代码实战+防坑指南!
墨瑾轩
Java乐园交互java开发语言
关注墨瑾轩,带你探索编程的奥秘!超萌技术攻略,轻松晋级编程高手技术宝库已备好,就等你来挖掘订阅墨瑾轩,智趣学习不孤单即刻启航,编程之旅更有趣从“木头人”到“交互大师”的Java魔法之旅一、Java的“五大核心技术”——虚拟世界的“五感开关”1.1核心技术1:JOGL渲染引擎——“视觉中枢”作用:用OpenGL实现3D场景渲染代码示例://JOGL渲染循环:画一个旋转的立方体importjavax.
- MySQL 索引详解:从原理到实战的全方位指南
一切皆有迹可循
mysqlmysql数据库后端javasql
前言索引是MySQL高性能查询的核心驱动力,合理设计索引能将查询性能提升几个数量级,而不当使用则可能导致严重的性能瓶颈。本文从索引的基础概念出发,深入解析数据结构、分类特性、设计原则及实战优化,帮助开发者掌握索引的核心原理与最佳实践。一、索引基础概念1.索引定义与本质索引是存储引擎用于快速查找数据的一种数据结构,本质是「数据项→数据地址」的映射表类比:相当于书籍的目录,通过目录(索引)快速定位章节
- MySQL 锁详解:从原理到实战的并发控制指南
一切皆有迹可循
mysqlmysql数据库后端javasql
前言在高并发场景下,锁是MySQL保证数据一致性的核心机制。正确理解锁的类型、行为及适用场景,能有效避免数据竞争、死锁等问题,是构建可靠数据库应用的关键。本文从锁的分类、存储引擎差异到实战优化,结合代码示例,系统解析MySQL锁机制的核心原理与最佳实践。一、锁分类:按粒度与功能划分1.按锁粒度划分(1)全局锁(GlobalLock)作用范围:锁定整个数据库实例典型场景:全库逻辑备份(FLUSHTA
- Python 数据分析与可视化:从基础到进阶的技术实现与优化策略
女码农的重启
python数据分析开发语言
数据分析与可视化是数据科学领域的核心技能,Python凭借其丰富的库生态和灵活的编程范式,成为该领域的首选工具。本文将系统讲解Python数据分析与可视化的技术栈实现,从基础操作到性能优化,结合实战场景提供可复用的解决方案。数据分析核心库技术解析Pandas数据处理引擎原理Pandas作为数据分析的基石,其核心优势在于基于NumPy的矢量运算和高效的内存管理。与Excel的单元格级操作不同,Pan
- 浅谈MySQL SQL优化的底层原理
干净的坏蛋
mysqlsql数据库
深入理解MySQL的SQL优化底层原理,需要从查询的执行流程出发,结合优化器原理、执行计划生成机制、索引原理和存储引擎行为全面剖析。以下是完整的底层视角分析:✅一、MySQLSQL查询的底层执行流程客户端->SQL解析器->查询优化器->执行器->存储引擎(如InnoDB)1.SQL解析(Parser)词法分析+语法分析→生成抽象语法树(AST)比如:识别出SELECT、FROM、WHERE、字段
- MySQL MVCC解密:多版本并发控制的魔法世界
码农技术栈
MySQLmysql数据库开发语言javajvm后端性能优化
当多个用户同时读写数据库时,MySQL如何避免数据混乱?本文将揭开MVCC的神秘面纱,带你探索这个让数据库高并发运行的魔法引擎!一、为什么需要MVCC?并发控制的困境想象图书馆借阅场景:传统方式:一本书只能一个人看(锁机制)MVCC方式:复印多份,每人看不同版本(多版本控制)传统锁机制的痛点:事务A读数据加锁事务B写数据等待锁释放长时间等待系统卡顿二、MVCC是什么?时间旅行的艺术MVCC核心概念
- 24.park和unpark方法
卷土重来…
java并发编程java
1.park方法可以暂停线程,线程状态为wait。2.unpark方法可以恢复线程,线程状态为runnable。3.LockSupport的静态方法。4.park和unpark方法调用不分先后,unpark先调用,park后执行也可以恢复线程。publicclassParkDemo{publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args){Threadt1=newThread(()->
- 网络爬虫:技术原理、应用场景与合法使用全攻略
程序小武
python爬虫入门爬虫网络
爬虫是什么?网络爬虫(WebScraping或WebCrawling)是一种通过自动化方式从网站上抓取公开数据的程序。它通过模拟用户在浏览器中浏览网页的过程,访问网页、提取信息,并将数据保存到本地系统中。爬虫技术广泛应用于搜索引擎、数据收集、市场分析、信息聚合等多个领域。爬虫能做什么?数据收集爬虫可以高效地从互联网上的大量网站收集信息。比如,抓取新闻网站上的文章内容、商品电商平台的价格与库存数据、
- Java 大视界 -- Java 大数据机器学习模型在金融市场情绪指数构建与投资决策支持中的应用(339)
青云交
大数据新视界Java大视界java大数据机器学习金融情绪指数投资决策量化策略情绪分析
Java大视界--Java大数据机器学习模型在金融市场情绪指数构建与投资决策支持中的应用(339)引言:正文:一、Java构建的金融市场情绪数据采集与预处理体系1.1多源异构数据接入引擎1.2数据采集延迟测试报告1.3情绪数据预处理管道二、Java驱动的金融市场情绪指数构建模型2.1多维度情绪指数计算框架2.2情绪指数与投资决策的映射模型三、Java在金融投资决策支持中的实战应用3.1量化私募情绪
- 2018-04-08
viper44
科技就是将复杂的事情简单化,所以智能手机的出现显著降低了我们学习的难度,只要善于使用搜索引擎,几乎能够获得所有的知识,而我们利用这些工具的姿势,会反过来决定我们未来的走向,所以一定不能做伸手党,能查到东西尽量自己去搜索,网上有很多现成的成功,我们要善于搜索,把节约的时间拿去干别的事生活中会面临很多突发状况,要如何才能从容面对呢,培养急智的最简单的方法就是列举出所有可能出现的问题,并对它们制定一些相
- Flask框架入门:快速搭建轻量级Python网页应用
「已注销」
python-AIpython基础网站网络pythonflask后端
转载:Flask框架入门:快速搭建轻量级Python网页应用1.Flask基础Flask是一个使用Python编写的轻量级Web应用框架。它的设计目标是让Web开发变得快速简单,同时保持应用的灵活性。Flask依赖于两个外部库:Werkzeug和Jinja2,Werkzeug作为WSGI工具包处理Web服务的底层细节,Jinja2作为模板引擎渲染模板。安装Flask非常简单,可以使用pip安装命令
- 高效批量单词翻译工具的设计与应用
本文还有配套的精品资源,点击获取简介:在信息技术飞速发展的今天,批量单词翻译工具通过计算机的数据处理能力,大大提高了语言学习和文字处理的效率。用户通过简单输入单词列表到一个文本文件,并运行翻译程序,即可获得翻译结果并保存至指定文件。该工具集成了内置或外部翻译引擎,利用自然语言处理技术实现快速准确的翻译,并可能提供词性识别等附加功能。尽管机器翻译无法完全取代人工校对,但它为用户提供了一种高效的翻译解
- 传统检测响应慢?陌讯多模态引擎提速90+FPS实战
2501_92473147
算法计算机视觉目标检测
开篇痛点:实时目标检测在安防监控中的核心挑战在安防监控领域,实时目标检测是保障公共安全的关键技术。然而,传统算法如YOLOv5或开源框架MMDetection常面临两大痛点:误报率高(复杂光照或遮挡场景下检测不稳定)和响应延迟(高分辨率视频流处理FPS低于30)。实测数据显示,城市交通监控系统误报率达15%,导致安保资源浪费;客户反馈表明,延迟超100ms时,目标跟踪可能失效。这些问题源于算法泛化
- InnoDB引擎行存储结构
InnoDB引擎行存储结构文章目录InnoDB引擎行存储结构1.存储引擎2.InnoDB页的概念3.InnoDB行格式3.1指定行格式3.2COMPACT格式3.3REDUNDANT行格式3.4溢出列3.5DYNAMIC行格式和COMPRESSED行格式1.存储引擎[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-Y7BY5kOU-1643188470321)(C:\U
- 400多个免费在线编程与计算机科学课程
zhufafa
基础理论课程理论计算机基础免费
来源:medium作者:DhawalShah五年前,麻省理工学院和斯坦福大学等学校首先向公众开放免费的在线课程。如今,全球有700多所学校创造了数以千计的免费在线课程。从入门到精通系列,是作者通过ClassCentral的课程数据库整理的400多个免费在线课程的简介和链接(来源于ClassCentral,一个在线课程搜索引擎),根据课程难度分为入门、进阶和高阶三大类,每门课程还有星级评分(统计自C
- AI MCP教程之 什么是 MCP?利用本地 LLM 、MCP、DeepSeek 集成构建您自己的 AI 驱动工具
知识大胖
NVIDIAGPU和大语言模型开发教程人工智能mcpdeepseek
介绍利用模型上下文协议(MCP)的工具吸引了我们的注意力—将AI变成触手可及的生产力引擎。它们巧妙、高效,让人难以抗拒。但如果您可以将这样的功能添加到自己的工具中,会怎么样呢?在本指南中,我将引导您构建一个具有本地运行的大型语言模型(LLM)和MCP集成的AI工具-让您以类似的方式自动执行利用MCP的工具您喜欢的任务。推荐文章《AnythingLLM教程系列之12AnythingLLM上的Olla
- 使用 DeepSeek R1 和 Ollama 开发 RAG 系统 使用 DeepSeek R1 和 Ollama 构建强大的 RAG 系统。了解开发智能 AI 解决方案的设置过程、最佳实践和技巧。
知识大胖
NVIDIAGPU和大语言模型开发教程人工智能deepseekollama
简介DeepSeekR1和Ollama提供了用于构建检索增强生成(RAG)系统的强大工具。本指南介绍了使用这些技术开发RAG应用程序的设置、实施和最佳实践。为什么RAG系统会改变游戏规则检索增强生成(RAG)系统结合了搜索和生成AI的优点,可实现精确且准确的情境感知响应。借助DeepSeekR1和Ollama等工具,创建RAG系统不再令人生畏。无论您是构建聊天机器人、知识助手还是AI驱动的搜索引擎
- AI技术正在深刻重塑A/B测试优化的流程、效率和价值,推动其从传统的“手动实验”向“智能优化引擎”跃迁。
zzywxc787
人工智能
AI技术正在深刻重塑A/B测试优化的流程、效率和价值,推动其从传统的“手动实验”向“智能优化引擎”跃迁。以下是具体变革方向及实际影响:1.实验设计智能化:告别“猜猜看”传统痛点:依赖经验选择测试变量(如按钮颜色、文案),忽略潜在高价值组合。AI解决方案:多臂老虎机算法(MAB):动态分配流量至表现最优的变体(如:80%流量给当前最优,20%探索新选项),减少流量浪费高达70%(Netflix案例)
- Elasticsearch搜索引擎存储:从原理到实践的全景解析
Python×CATIA工业智造
搜索引擎elasticsearch大数据
引言在大数据时代,数据规模呈指数级增长,传统数据库的模糊查询、实时分析能力逐渐成为瓶颈。Elasticsearch(简称ES)凭借其分布式架构、实时搜索和灵活的数据分析能力,成为企业级搜索与存储的核心引擎。截至2025年,ES在全球日志分析、电商搜索、实时监控等场景的市场占有率超过60%。本文将从存储架构、核心技术、应用场景及优化策略四个维度,深入解析Elasticsearch的设计哲学与实践价值
- UnrealEngine5游戏引擎实践(C++)
KENYCHEN奉孝
C++服务器c++游戏引擎
目录目录目录UnrealEngine是什么?UnrealEngine5简介核心技术特性应用场景扩展兼容性与生态系统UnrealEngine安装下载EpicGamesLauncher启动UnrealEngine选择安装版本和路径选择组件开始安装验证安装配置项目模板(可选)更新和插件管理UE游戏引擎动作捕捉与动画系统程序化生成与AI技术物理与破坏系统音频与本地化技术性能优化导入静态网格体材质实例创建与
- NodeJS VM2沙箱逃逸漏洞分析【CVE-2023-29199】
R3s3arcm
NodeJS漏洞分析node.js安全安全威胁分析
NodeJSVM2沙箱逃逸漏洞分析【CVE-2023-29199】简介Node.js是一个基于V8引擎的开源、跨平台的JavaScript运行环境,它可以在多个操作系统上运行,包括Windows、macOS和Linux等。Node.js提供了一个运行在服务器端的JavaScript环境,使得开发者可以编写并发的、高效的服务器端应用程序。Node.js使用事件驱动、非阻塞I/O模型来支持并发运行。它
- 在ARM46+KylinOS下安装配置Docker的详细步骤
Q_Daniooi
docker容器运维
目录一、安装前准备(一)环境检查(二)依赖准备二、Docker安装步骤(一)添加Docker官方源(以Debian分支银河麒麟为例,RPM系类似调整)(二)安装Docker引擎(三)启动与基础配置三、Docker优化配置(可选但推荐)(一)镜像加速(二)存储驱动优化四、注意事项(一)系统兼容性(二)网络与镜像源(三)权限与安全(四)ARM架构特殊点五、经常遇见的问题及解决方法六、学习经验分享一、前
- java杨辉三角
3213213333332132
java基础
package com.algorithm;
/**
* @Description 杨辉三角
* @author FuJianyong
* 2015-1-22上午10:10:59
*/
public class YangHui {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//初始化二维数组长度
int[][] y
- 《大话重构》之大布局的辛酸历史
白糖_
重构
《大话重构》中提到“大布局你伤不起”,如果企图重构一个陈旧的大型系统是有非常大的风险,重构不是想象中那么简单。我目前所在公司正好对产品做了一次“大布局重构”,下面我就分享这个“大布局”项目经验给大家。
背景
公司专注于企业级管理产品软件,企业有大中小之分,在2000年初公司用JSP/Servlet开发了一套针对中
- 电驴链接在线视频播放源码
dubinwei
源码电驴播放器视频ed2k
本项目是个搜索电驴(ed2k)链接的应用,借助于磁力视频播放器(官网:
http://loveandroid.duapp.com/ 开放平台),可以实现在线播放视频,也可以用迅雷或者其他下载工具下载。
项目源码:
http://git.oschina.net/svo/Emule,动态更新。也可从附件中下载。
项目源码依赖于两个库项目,库项目一链接:
http://git.oschina.
- Javascript中函数的toString()方法
周凡杨
JavaScriptjstoStringfunctionobject
简述
The toString() method returns a string representing the source code of the function.
简译之,Javascript的toString()方法返回一个代表函数源代码的字符串。
句法
function.
- struts处理自定义异常
g21121
struts
很多时候我们会用到自定义异常来表示特定的错误情况,自定义异常比较简单,只要分清是运行时异常还是非运行时异常即可,运行时异常不需要捕获,继承自RuntimeException,是由容器自己抛出,例如空指针异常。
非运行时异常继承自Exception,在抛出后需要捕获,例如文件未找到异常。
此处我们用的是非运行时异常,首先定义一个异常LoginException:
/**
* 类描述:登录相
- Linux中find常见用法示例
510888780
linux
Linux中find常见用法示例
·find path -option [ -print ] [ -exec -ok command ] {} \;
find命令的参数;
- SpringMVC的各种参数绑定方式
Harry642
springMVC绑定表单
1. 基本数据类型(以int为例,其他类似):
Controller代码:
@RequestMapping("saysth.do")
public void test(int count) {
}
表单代码:
<form action="saysth.do" method="post&q
- Java 获取Oracle ROWID
aijuans
javaoracle
A ROWID is an identification tag unique for each row of an Oracle Database table. The ROWID can be thought of as a virtual column, containing the ID for each row.
The oracle.sql.ROWID class i
- java获取方法的参数名
antlove
javajdkparametermethodreflect
reflect.ClassInformationUtil.java
package reflect;
import javassist.ClassPool;
import javassist.CtClass;
import javassist.CtMethod;
import javassist.Modifier;
import javassist.bytecode.CodeAtt
- JAVA正则表达式匹配 查找 替换 提取操作
百合不是茶
java正则表达式替换提取查找
正则表达式的查找;主要是用到String类中的split();
String str;
str.split();方法中传入按照什么规则截取,返回一个String数组
常见的截取规则:
str.split("\\.")按照.来截取
str.
- Java中equals()与hashCode()方法详解
bijian1013
javasetequals()hashCode()
一.equals()方法详解
equals()方法在object类中定义如下:
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
return (this == obj);
}
很明显是对两个对象的地址值进行的比较(即比较引用是否相同)。但是我们知道,String 、Math、I
- 精通Oracle10编程SQL(4)使用SQL语句
bijian1013
oracle数据库plsql
--工资级别表
create table SALGRADE
(
GRADE NUMBER(10),
LOSAL NUMBER(10,2),
HISAL NUMBER(10,2)
)
insert into SALGRADE values(1,0,100);
insert into SALGRADE values(2,100,200);
inser
- 【Nginx二】Nginx作为静态文件HTTP服务器
bit1129
HTTP服务器
Nginx作为静态文件HTTP服务器
在本地系统中创建/data/www目录,存放html文件(包括index.html)
创建/data/images目录,存放imags图片
在主配置文件中添加http指令
http {
server {
listen 80;
server_name
- kafka获得最新partition offset
blackproof
kafkapartitionoffset最新
kafka获得partition下标,需要用到kafka的simpleconsumer
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.
- centos 7安装docker两种方式
ronin47
第一种是采用yum 方式
yum install -y docker
- java-60-在O(1)时间删除链表结点
bylijinnan
java
public class DeleteNode_O1_Time {
/**
* Q 60 在O(1)时间删除链表结点
* 给定链表的头指针和一个结点指针(!!),在O(1)时间删除该结点
*
* Assume the list is:
* head->...->nodeToDelete->mNode->nNode->..
- nginx利用proxy_cache来缓存文件
cfyme
cache
user zhangy users;
worker_processes 10;
error_log /var/vlogs/nginx_error.log crit;
pid /var/vlogs/nginx.pid;
#Specifies the value for ma
- [JWFD开源工作流]JWFD嵌入式语法分析器负号的使用问题
comsci
嵌入式
假如我们需要用JWFD的语法分析模块定义一个带负号的方程式,直接在方程式之前添加负号是不正确的,而必须这样做:
string str01 = "a=3.14;b=2.71;c=0;c-((a*a)+(b*b))"
定义一个0整数c,然后用这个整数c去
- 如何集成支付宝官方文档
dai_lm
android
官方文档下载地址
https://b.alipay.com/order/productDetail.htm?productId=2012120700377310&tabId=4#ps-tabinfo-hash
集成的必要条件
1. 需要有自己的Server接收支付宝的消息
2. 需要先制作app,然后提交支付宝审核,通过后才能集成
调试的时候估计会真的扣款,请注意
- 应该在什么时候使用Hadoop
datamachine
hadoop
原帖地址:http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-301743-id-3925358.html
存档,某些观点与我不谋而合,过度技术化不可取,且hadoop并非万能。
--------------------------------------------万能的分割线--------------------------------
有人问我,“你在大数据和Hado
- 在GridView中对于有外键的字段使用关联模型进行搜索和排序
dcj3sjt126com
yii
在GridView中使用关联模型进行搜索和排序
首先我们有两个模型它们直接有关联:
class Author extends CActiveRecord {
...
}
class Post extends CActiveRecord {
...
function relations() {
return array(
'
- 使用NSString 的格式化大全
dcj3sjt126com
Objective-C
格式定义The format specifiers supported by the NSString formatting methods and CFString formatting functions follow the IEEE printf specification; the specifiers are summarized in Table 1. Note that you c
- 使用activeX插件对象object滚动有重影
蕃薯耀
activeX插件滚动有重影
使用activeX插件对象object滚动有重影 <object style="width:0;" id="abc" classid="CLSID:D3E3970F-2927-9680-BBB4-5D0889909DF6" codebase="activex/OAX339.CAB#
- SpringMVC4零配置
hanqunfeng
springmvc4
基于Servlet3.0规范和SpringMVC4注解式配置方式,实现零xml配置,弄了个小demo,供交流讨论。
项目说明如下:
1.db.sql是项目中用到的表,数据库使用的是oracle11g
2.该项目使用mvn进行管理,私服为自搭建nexus,项目只用到一个第三方 jar,就是oracle的驱动;
3.默认项目为零配置启动,如果需要更改启动方式,请
- 《开源框架那点事儿16》:缓存相关代码的演变
j2eetop
开源框架
问题引入
上次我参与某个大型项目的优化工作,由于系统要求有比较高的TPS,因此就免不了要使用缓冲。
该项目中用的缓冲比较多,有MemCache,有Redis,有的还需要提供二级缓冲,也就是说应用服务器这层也可以设置一些缓冲。
当然去看相关实现代代码的时候,大致是下面的样子。
[java]
view plain
copy
print
?
public vo
- AngularJS浅析
kvhur
JavaScript
概念
AngularJS is a structural framework for dynamic web apps.
了解更多详情请见原文链接:http://www.gbtags.com/gb/share/5726.htm
Directive
扩展html,给html添加声明语句,以便实现自己的需求。对于页面中html元素以ng为前缀的属性名称,ng是angular的命名空间
- 架构师之jdk的bug排查(一)---------------split的点号陷阱
nannan408
split
1.前言.
jdk1.6的lang包的split方法是有bug的,它不能有效识别A.b.c这种类型,导致截取长度始终是0.而对于其他字符,则无此问题.不知道官方有没有修复这个bug.
2.代码
String[] paths = "object.object2.prop11".split("'");
System.ou
- 如何对10亿数据量级的mongoDB作高效的全表扫描
quentinXXZ
mongodb
本文链接:
http://quentinXXZ.iteye.com/blog/2149440
一、正常情况下,不应该有这种需求
首先,大家应该有个概念,标题中的这个问题,在大多情况下是一个伪命题,不应该被提出来。要知道,对于一般较大数据量的数据库,全表查询,这种操作一般情况下是不应该出现的,在做正常查询的时候,如果是范围查询,你至少应该要加上limit。
说一下,
- C语言算法之水仙花数
qiufeihu
c算法
/**
* 水仙花数
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#define N 10
int main()
{
int x,y,z;
for(x=1;x<=N;x++)
for(y=0;y<=N;y++)
for(z=0;z<=N;z++)
if(x*100+y*10+z == x*x*x
- JSP指令
wyzuomumu
jsp
jsp指令的一般语法格式: <%@ 指令名 属性 =”值 ” %>
常用的三种指令: page,include,taglib
page指令语法形式: <%@ page 属性 1=”值 1” 属性 2=”值 2”%>
include指令语法形式: <%@include file=”relative url”%> (jsp可以通过 include