光流 | 近十年光流参考文献总结
博主github:https://github.com/MichaelBeechan
博主CSDN:https://blog.csdn.net/u011344545
[1]Bruhn A, Weickert J, Kohlberger T, et al. A Multigrid Platform for Real-Time Motion Computation with Discontinuity-Preserving Variational Methods[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2006, 70(3):257-277. 2区 4.270 较难
针对变分方法的实时性能问题提出解决方法:提出基于双向多网格的数值框架方法来加速不同不变性和平滑性假设下的变分光流。
数据项:规定了图像特征的时间不变性,如灰度等
平滑项:数据项附加的平滑假设
[2]Bruhn A, Weickert J, Schnörr C. Combining the Advantages of Local and Global Optic Flow Methods[C]// Pattern Recognition, Dagm Symposium, Zurich, Switzerland, September 16-18, 2002, Proceedings. DBLP, 2002:454-462. 2区 3.399 较易
[3]Bruhn, A., Weickert, J. & Schnörr, C. Lucas/Kanade Meets Horn/Schunck: Combining Local and Global Optic Flow Methods[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2005, 61(3): 211-231.
在局部邻域内集成约束提高了密集光流的精度
差分方法:局部方法:Lucas-Kanade[6]技术和Bigun[4]的结构张量方法:对噪声具有更好的鲁棒性
全局方法:Horn-Schunck方法[5]以及改进方法:产生100%的稠密光流
并置了局部和全局差分方法的光流计算的平滑项作用,结合全局和局部光流的方法的优点,产生鲁棒性好且稠密的光流。
差分方法是图像序列光流估计的应用最广的技术,基于图像时空导数的计算。
[4]Bigün J, Granlund G H, Wiklund J. Multidimensional Orientation Estimation with Applications to Texture Analysis and Optical Flow[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 1991, 13(8):775-790. 1区 6.077 很难
[5]Horn B K P,Schunck B G. Determining optical flow[J]. Artificial Intelligence, 1981; 17: 185-204. 2区 3.333 较易
对光流估计引入亮度恒定假设和空间平滑约束,然而their quadratic formulation assumes Gaussian statistics and is not robust to outliers caused by reflection, occlusion, motion boundaries etc.
[6]Lucas B D, Kanade T. An iterative image registration technique with an application to stereo vision[C]// International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc. 1981:674-679.
提出一种图像配准技术——利用图像的空间梯度使用牛顿-拉夫逊迭代法找到一个很好的匹配,此技术能够推广到处理旋转,缩放和剪切问题。
[7]Brox T, Bregler C, Malik J. Large displacement optical flow[J]. IEEE Computer Society, 2009, 33(3):41-48.
目前文献提供了两种方式来建立图像与移动物体之间的点对应:
能量最小化的方法:能非常精确的产生稠密的光流场,但是不能处理大位移场
描述符匹配:允许大位移,但是光流场稀疏不精确,并且由于缺少规则约束,存在许多异常值
本文提出的方法是:结合两种匹配策略优点的方法,建立两个图像区域层次结构。描述符匹配为对应区域提供一组稀疏假设,他们被集成到变分方法中,并将局部优化引导到解决大位移方案中。利用几何约束和所有可用的图像信息,变分优化在假设之间进行选择,并提供密集和子像素准确的估计。
为了获得更准确,密集的光流场,我们将匹配假设整合到变分方法中,将其与原始图像数据的局部信息和先前的平滑度相结合。
Bruhn A.Variational optic flow computation: accurate modelling and efficient numerics [D]. Germany: Saarland University,2006.
(Abstract:The recovery of the displacement field between two consecutive frames of an image sequence – the so-called optic flow – is one of the central problems in computer vision. Allowing a mathematical sound integration of different concepts into a single minimisation framework, variational methods belong to the best performing and best understood techniques for solving this task. They can be designed in such a way that they preserve motion boundaries, treat large displacements correctly, are robust with respect to illumi- nation changes or perform favourably in the presence of noise and occlusions. However, they are hardly used in practical applications, since they require to solve large linear or nonlinear systems of equations. In particular, they are considered to be too slow for those tasks where real-time performance is needed. In this thesis we make two important contributions to the field of variational optic flow computation: Firstly, we provide a systematic toolkit for the design of accurate variational methods. Thereby, we demonstrate that this toolkit allows the construction of the currently most precise optic flow approaches in the literature. Secondly, we present a multigrid framework for the efficient solution of the resulting linear and nonlinear systems of equa- tions. This framework does not only outperform frequently used numerical schemes by up to four orders of magnitude, it even allows the first real-time computation of variational optic flow ever. The first part of this thesis is dedicated to variational optic flow methods for small displacements. Thereby we investigate the systematic design of convex approaches by discussing a variety of established models. In this context, we also introduce several new ideas that improve the quality of the estimation with respect to noise, outliers and varying illumination. Moreover, we present a compact notation for variational optic flow methods that is based on motion and diffusion tensors. This notation proves to be useful in two respects: Firstly, it allows the systematic construction of novel approaches. This is demonstrated by the example of two advanced optic flow techniques. Secondly, it forms the basis of our numerical framework for the design of efficient bidirectional multigrid methods. By resampling these tensors instead of the original image sequence, we present a novel way to create a suitable coarse grid representation that is both computationally efficient and accurate at the same time. Extensive qualitative and quantitative benchmarks for seven different models and six different numerical prototypes show the accuracy and the efficiency of the proposed multigrid implementations. The second part of this thesis extends our previous contributions to the case of large displacements. To this end, we introduce an eighth prototype that is based on a nonconvex approach. In order to solve the resulting minimisation problem we derive an incremental coarse-to-fine fixed point iteration that allows to avoid local minima. In this context, we also succeed to provide a theoretical justification for the well-known warping technique that has been motivated only on an algorithmic basis so far. Moreover, we define a new motion tensor equivalent for the case of large displacements. This allows us to extend our compact notation and therewith our highly efficient multigrid framework that we devel- oped before. Quality and efficiency benchmarks show the success of this generalisation: While the speedups are similar than in the case of small displacements, the accuracy is even higher.图像序列的两个连续帧之间的位移场的恢复 - 所谓的光流 - 是计算机视觉中的核心问题之一。允许将不同概念的数学声音整合到单个最小化框架中,变分方法属于解决此任务的最佳性能和最佳理解技术。它们的设计方式可以保持运动边界,正确地处理大的位移,在照明变化方面是稳健的,或者在存在噪声和遮挡的情况下表现良好。然而,它们在实际应用中几乎不被使用,因为它们需要求解大的线性或非线性方程组。特别地,对于那些需要实时性能的任务来说,它们被认为太慢了。在本论文中,我们对变分光流计算领域做出了两个重要贡献:首先,我们为精确变分方法的设计提供了一个系统的工具包。因此,我们证明,该工具包允许在文献中构建目前最精确的光流方法。其次,我们提出了一个多网格框架,用于有效解决所得到的线性和非线性方程组。该框架不仅优于经常使用的数字方案达四个数量级,甚至允许先前实时计算变分光流。本论文的第一部分专门用于小位移的变分光学流动方法。因此,我们通过讨论各种建立的模型来研究凸方法的系统设计。在这方面,我们还介绍了几个新的想法,提高噪声,异常值和不同照明方面的估计质量。此外,我们提出了基于运动和扩散张量的变分光学流动方法的紧凑符号。这个表示法在两个方面证明是有用的:首先,它允许系统地构建新的方法。这通过两个先进的光学流技术的示例来证明。其次,它构成了高效双向多网格方法设计数值框架的基础。通过重新采样这些张量而不是原始图像序列,我们提出了一种新颖的方法来创建同时计算高效和准确的合适的粗网格表示。七种不同型号和六种不同数字原型的广泛定性和定量基准显示了所提出的多栅格实现的准确性和效率。本论文的第二部分将我们以前的贡献扩大到大型流离失所的情况。为此,我们引入了基于非凸方法的第八个原型。为了解决所产生的最小化问题,我们得到允许避免局部最小值的增量粗到精定点迭代。在这种情况下,我们还成功地为迄今为止仅以算法为基础的知名翘曲技术提供了理论上的理由。此外,我们定义一个新的运动张量相当于大位移的情况。这使我们能够扩展我们的紧凑型符号,同时也扩展了我们以前开发的高效多网格框架。质量和效率基准显示了这种泛化的成功:虽然加速比与小位移的情况相似,但精度更高。)
[8]Ummenhofer B. Large Displacement Optical Flow for Volumetric Image Sequences[M]// Pattern Recognition. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2011:432-437.
[9]Brox T, Malik J. Large Displacement Optical Flow: Descriptor Matching in Variational Motion Estimation[J]. Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence IEEE Transactions on, 2010, 33(3):500-513.
[10]Brox T, Bruhn A, Papenberg N, et al. High Accuracy Optical Flow Estimation Based on a Theory for Warping[J]. Computer Vision - ECCV, 2004, 3024(:10):25-36.
结合三种假设研究了计算光流的能量方程:亮度不变性假设,梯度不变性假设,不连续保持时空平滑约束。提出了基于两个嵌套定点迭代的一致性数值方案,评估表明,此方法得出的光流估计角度误差更小。对参数变化非常不敏感,在噪声下具有更好的鲁棒性。为了最小化光照变化的影响扩展亮度不变性假设到高阶(梯度和Hessian)。
[11]Sun D, Roth S, Lewis J P, et al. Learning Optical Flow.[C]// Computer Vision - ECCV 2008, European Conference on Computer Vision, Marseille, France, October 12-18, 2008, Proceedings. DBLP, 2008:83-97.
Sun D, Roth S, Lewis J P, et al. Learning Optical Flow[J]. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 2008, 5304:83-97.
大多数光流估计方法是以亮度不变性假设和空间平滑假设为基础的。不同于标准的heuristic formulations(启发式算法),我们依据图像序列的真实光流场提出了一结合亮度不变性误差和空间特性的统计学习模型——光流全概率模型。我们也将此模型推广到了高阶不变性假设。
主要贡献:First 探索图像亮度边界提高运动边界附近的光流精度——Nagel and Enkelmann[12](引进导向平滑,防止图像边界光流模糊化——各向异性扩散方法)
Second 数据项学习统计模型
Steerable Random field(SRF)[14]——空间平滑模型(模拟光流和图像序列之间统计关系的条件)
Markov random field (MRF)—|—Gaussian scale mixtures(GSM)
[12]Nagel H H, Enkelmann W. An Investigation of Smoothness Constraints for the Estimation of Displacement Vector Fields from Image Sequences[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 1986, 8(5):565.
[13]Bao W, Li H, Li N, et al. A liveness detection method for face recognition based on optical flow field[C]// International Conference on Image Analysis and Signal Processing. IEEE Xplore, 2009:233-236.
[14]Roth S, Black M J. Steerable Random Fields[C]// IEEE, International Conference on Computer Vision. IEEE, 2007:1-8.
[15]Black M J, Jepson A D. Estimating optical flow in segmented images using variable-order parametric models with local deformations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 1996, 18(10):972-986.
基于平面区域和局部变形运动提出了新的光流估计模型。该方法利用亮度信息来组织和约束运动的解释,通过使用分段平滑亮度的分段区域来假设场景中的平面区域。
场景中光流估计包含深度变化,独立运动或者关节对象需要将场景分割成相干运动的区域。
参数+变形模型(the parametric+deformation model)
实验表明,参数+变形模型产生准确的流量估计,而亮度分割的结合提供了运动边界的精确定位。
[16]Enric M L, Javier S, Daniel K. Horn-Schunck Optical Flow with a Multi-Scale Strategy[J]. Image Processing on Line, 2013, 20:151–172.
实现了原始HS方法,为了处理大位移介绍了多尺度策略(建立了降采样图像的金字塔结构,用一个非线性公式改变了光流约束方程,用线性化和迭代每个尺度的方法处理非线性方程)。即:用迭代的方法计算运动增量 or 依照迭代增量在迭代期间计算完整光流。解决方案是在所有尺度上逐步完善的。这种金字塔结构是很多光流方法的标准工具。
H-S的开创性工作是第一次提出了光流估计的变分方法。介绍了一个新的光流计算框架:最小化问题的解决方案。光流约束方程的推导是基于像素强度不变假设的。方程涉及图像的导数。有无穷多向量场满足光流约束——不适定问题。
[17]Javier S, Nelson M, Agustin S. Robust Optical Flow Estimation[J]. Image Processing on Line, 2013, 3: 252-270
描述了Brox et al(2004)[10]变分光流的实现过,用较短的运行时间产生了精确的光流。对于Horn和Schunck的方法,它有几个好处:对存在异常值更好的鲁棒性,产生分段光滑的光流场,能处理亮度变化。也概括了L1泛函的使用,有助于减轻异常值的影响并创建一个总变异(TV)正则化。此外也引入一种简单的时间正则化方案,增强光流场连续时间的相干性。
[18]Zach C, Pock T, Bischof H. A Duality Based Approach for Realtime TV-L, 1 Optical Flow[J]. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 2007, 4713(5):214-223.
提出一个更有效的TV-L1光流方法。[19]实现
[19]Pérez J S. TV-L1 Optical Flow Estimation[J]. Image Processing on Line, 2012, 2(4):137-150.
[20]桂本烨, 钱徽, 朱淼良. 一种优化梯度计算的改进HS光流算法[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2005, 10(8):1052-1058.
针对HS方法中不准确的灰度梯度,提出一种改进的HS算法——循环求精的梯度算法,减少了光流计算的迭代次数。
[21]Botelho S, Correa U B, Lautenschlager W I. Vision-Based Motion Detection Using C-NLPCA Approach[C]// Neural Networks, 2006. SBRN '06. Ninth Brazilian Symposium on. IEEE Xplore, 2006:214-219. 2区 3.216 较易
提出了一个基于视觉的运动检测方法——应用于自动机器人环境探索,信息获取和解决运动定位导航问题。(C-NLPCA Approach)级联非线性主成分分析方法。
[22]Tu Z G. Variational Optical Flow Algorithms for Motion Estimation[D]. Utrecht University, 2015.
[23]Chen D, Sheng H, Chen Y, et al. Fractional-order variational optical flow model for motion estimation.[J]. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci, 2013, 371(1990):20120148.
[24]Stoll M, Volz S, Bruhn A. Adaptive Integration of Feature Matches into Variational Optical Flow Methods[M]// Computer Vision – ACCV 2012. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2013:1-14.
[25]Baker S, Scharstein D, Lewis J P, et al. A Database and Evaluation Methodology for Optical Flow[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2011, 92(1):1-31.
[26]Baker S, Roth S, Scharstein D, et al. A Database and Evaluation Methodology for Optical Flow[C]// IEEE, International Conference on Computer Vision. IEEE, 2007:1-8.
为下一代光流估计算法建立一系列新的标准。估计the performance of several well-known methods,用当前最先进的估计数据建立一个Database: http://vision.middlebury.edu/flow/。
{ we contribute four types of data to test different aspects of optical flow algorithms: sequences with nonrigid motion where the ground-truth flow is determined by tracking hidden fluorescent texture; realistic synthetic sequences; high frame-rate video used to study interpolation error; and modified stereo sequences of static scenes.}——the average angular error、the absolute flow endpoint error、 frame interpolation error
Our solution is to collect four different datasets, each of which satisfies a different subset of the desirable properties above. The combination of these datasets provides a basis for a rigorous evaluation of current optical flow algorithms. Moreover, the relative performance of algorithms on the different datatypes should stimulate further research in the field.(1.Real imagery of nonrigidly moving scenes, where dense ground-truth flow is obtained using hidden fluorescent texture painted on the scene. 2.Realistic synthetic imagery.3.Imagery for frame interpolation where intermediate frames are withheld and used as ground truth.4.Real stereo imagery of rigid scenes)
In this paper we present two kinds of ground truth; ground-truth motion fields and intermediate images for the evaluation of apparent motion.
We have developed a technique for capturing imagery of nonrigid scenes with ground-truth optical flow.
[27]Weinzaepfel P, Revaud J, Harchaoui Z, et al. DeepFlow: Large Displacement Optical Flow with Deep Matching[C]// IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. IEEE, 2013:1385-1392.
[28]Timofte R, Gool L V. Sparse Flow: Sparse Matching for Small to Large Displacement Optical Flow[C]// Applications of Computer Vision. IEEE, 2015:1100-1106.
[29]Sun D, Roth S, Black M J. Secrets of optical flow estimation and their principles[J]. 2010, 1:2432-2439.
[30]Kennedy R, Taylor C J. Optical Flow with Geometric Occlusion Estimation and Fusion of Multiple Frames[M]// Energy Minimization Methods in Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Springer International Publishing, 2015:364-377.
[31]Vogel C, Roth S, Schindler K. An Evaluation of Data Costs for Optical Flow[J]. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 2013, 8142:343-353.
[32]Xu L, Jia J, Matsushita Y. Motion detail preserving optical flow estimation.[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 2012, 34(9):1744-57.
[33]Bao L, Yang Q, Jin H. Fast Edge-Preserving PatchMatch for Large Displacement Optical Flow[C]// IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. IEEE Computer Society, 2014:3534-3541.
[34]Revaud J, Weinzaepfel P, Harchaoui Z, et al. EpicFlow: Edge-preserving interpolation of correspondences for optical flow[J]. Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition, 2015:1164-1172.
[35]Brox T, Malik J. Large Displacement Optical Flow: Descriptor Matching in Variational Motion Estimation[J]. Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence IEEE Transactions on, 2010, 33(3):500-513.
[36]Chen Z, Jin H, Lin Z, et al. Large Displacement Optical Flow from Nearest Neighbor Fields[C]// Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. IEEE, 2013:2443-2450.
[37]Bailer C, Taetz B, Stricker D. Flow Fields: Dense Correspondence Fields for Highly Accurate Large Displacement Optical Flow Estimation[C]// IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. IEEE, 2015:4015-4023.
[38]Hu Y, Song R, Li Y. Efficient Coarse-to-Fine Patch Match for Large Displacement Optical Flow[C]// IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. IEEE, 2016:5704-5712.
[39]Lu Z, Wei L. The Compensated HS Optical Flow Estimation Based on Matching Harris Corner Points[C]// International Conference on Electrical and Control Engineering. IEEE, 2010:2279-2282.
[40]Senst T, Eiselein V, Sikora T. Robust Local Optical Flow for Feature Tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits & Systems for Video Technology, 2012, 22(9):1377-1387.
[41]Yamaoka D, Ogawa Y, Ishimura K, et al. Motion segmentation using pulse-coupled neural network[C]// Sice 2003 Conference. IEEE, 2003:2778-2783 Vol.3.
关注于PCNN的图像分割能力,并应用PCNN解决光流分割问题。
[42]黄金杰, 赵飞. 一种改进的彩色图像序列光流场计算方法[J]. 哈尔滨理工大学学报, 2009, 14(a01):24-26.
提出一种基于HSI颜色模型的光流场计算方法,避免了传统光流算法增加约束条件来解决孔径问题的复杂度。
[43]屠大维, 江济良. 改进的光流运动图像分析方法及其应用[J]. 光学精密工程, 2011, 19(5):1159-1164. EI 1.925
[44]张永亮, 卢焕章, 高劼,等. 一种改进的Lucas-Kanade光流估计方法[J]. 海军航空工程学院学报, 2009, 24(4):443-446.
针对图像纹理欠丰富区域CFLK算法光流估计结果较差(根本原因在于这些区域像素灰度时空域的变化都不明显,运动信息难以获取),提出了一种改进的CFLK算法:计算跟踪置信度因子;通过阈值检测剔除不可靠光流估计结果;邻域填充。
序列图像光流计算是计算机视觉领域运动估计的重要组成部分,主要应用在两个方面:二维图像的快速配准和运动目标检测;作为中间介质重建三维物体的运动和结构。
[45]武理静, 明军. 一种改进的光流估计方法[J]. 国外电子测量技术, 2006, 25(12):6-8.
针对光流法在亮度突变条件下运动参数估计不准确的弱点,基于图像的边缘变化特征,对平滑约束项加以改进,给出了一种基于区域平滑约束的光流估计算法。
[46]Black M J, Anandan P. The Robust Estimation of Multiple Motions: Parametric and Piecewise-Smooth Flow Fields[J]. Computer Vision & Image Understanding, 1996, 63(1):75-104.
3区 2.134 容易
用于估计光流的大多数方法假设在有限图像区域内仅存在单个运动。这种单一运动假设在涉及透明度,深度不连续性,独立移动物体,阴影和镜面反射的常见情况下被违反。为了鲁棒地估计光流,单一运动假设必须放松。本文提出了一种基于鲁棒估计的框架,其解决了由多个运动引起的亮度恒定性和空间平滑度假设的违规。
[47]Roth S, Black M J. On the Spatial Statistics of Optical Flow[C]// Tenth IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. IEEE Computer Society, 2005:42-49.
用高阶MRF模拟了光流场的空间结构——Field of Experts (FoE),学习了训练数据的参数。
[48]Fermüller C, Shulman D, Aloimonos Y. The Statistics of Optical Flow[J]. Computer Vision & Image Understanding, 2001, 82(1):1-32. 3区 2.134 容易
分析了噪声对光流估计的影响,但并没有试图从例子中学习光流统计
[49]Simoncelli E P, Adelson E H, Heeger D J. Probability distributions of optical flow[C]// Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 1991. Proceedings CVPR '91. IEEE Computer Society Conference on. IEEE, 2001:310-315.
formulated an early probabilistic model of optical flow and modeled the statistics of the deviation of the estimated flow from the true flow.首次阐述了光流的概率模型,从真实光流中模拟了估计光流统计的偏差。
[50]Black M J, Yacoob Y, Jepson A D, et al. Learning Parameterized Models of Image Motion[C]// Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. IEEE Computer Society, 1997:561.
proposed an MRF model that coupled edges in the flow field with edges in the brightness images. This model, however, was hand designed and tuned.
[51]Fleet D J, Black M J, Nestares O. Bayesian Inference of Visual Motion Boundaries[J]. Exploring Artificial Intelligence in the New Millennium, 2003:139--174.
learned a statistical model relating image edge orientation and amplitude to flow boundaries in the context of a patch-based motion discontinuity model.
[52]Alvarez L, Deriche R, Papadopoulo T, et al. Symmetrical Dense Optical Flow Estimation with Occlusions Detection[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2007, 75(3):371-385.
修改了Nagel-Enkelmann[12]的方法,以至于不执行平滑光流估计也可以接近图像边缘。启发式地确定了沿边界和跨越边界的平滑量。
提出一种结合遮挡估计与光流检测的方法。
[53]Mayer N, Ilg E, Häusser P, et al. A Large Dataset to Train Convolutional Networks for Disparity, Optical Flow, and Scene Flow Estimation[J]. Computer Science, 2015:4040-4048
(一种用于训练卷积网络的大型数据集,用于视差,光流和场景流估计)
光流估计可以被表述为一种监督学习过程,并且成功的可以用卷积网络解决。所谓的FlowNet训练是由大型的综合数据集实现的。本文通过卷积网络将光流估计的概念扩展到视差和场景流估计。 为此,提出了三个足够真实的,可变的,大小足够的综合立体视频数据集,以成功地训练大型网络。 我们的数据集是第一个能够训练和评估场景流方法的大型数据集。 除了数据集之外,我们提出了一个实时差异估计的卷积网络,提供了最先进的结果。 通过组合流量和差异估计网络并联合训练,我们演示了使用卷积网络的第一个场景流量估计。
立体视频:估计场景流——深度,3D运动矢量。Last decades子任务:光流估计和视差估计。Research over the last decades has focused on its subtasks, namely disparity estimation and optical flow estimation, with considerable success.
提出一种场景流估计网络并且并在足够大的测试集上提供了全场景流的第一个定量数字。
[54]Fischer P, Dosovitskiy A, Ilg E, et al. FlowNet: Learning Optical Flow with Convolutional Networks[J]. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2015:2758-2766.
光流估计可视为一种监督学习过程并且可以被大型网络解决。为了训练他们的网络,他们创建了一个简单的合成二维数据集飞行椅,这被证明足以预测一般视频中的精确光流。这些结果也表明视差和场景光流可以通过卷积网络估计Ideally jointly, efficiently, and in real-time。实现这一想法缺少的是一个大型数据集,具有足够的现实性和可变性来训练这样的网络并评估其性能。
[55]Butler D J, Wulff J, Stanley G B, et al. A Naturalistic Open Source Movie for Optical Flow Evaluation[M]// Computer Vision – ECCV 2012. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2012:611-625.
MPI Sintel——一个完全合成的数据集,源自一个短的开源动画3D电影。 它为光流提供了密集的地面真相。
[56]Revaud J, Weinzaepfel P, Harchaoui Z, et al. EpicFlow: Edge-preserving interpolation of correspondences for optical flow[J]. Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition, 2015:1164-1172.
[57]Geiger A, Lenz P, Stiller C, et al. Vision meets robotics: The KITTI dataset[J]. International Journal of Robotics Research, 2013, 32(11):1231-1237. 2区 2.489 较易
[58]Menze M, Geiger A. Object scene flow for autonomous vehicles[C]// Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. IEEE, 2015:3061-3070.
The KITTI dataset was produced in 2012 [57] and extended in 2015 [58].它包含来自安装在汽车上的校准的摄像机对道路场景的立体视频。光流和视差的地面实况是从与汽车的自动运动数据结合的3D激光扫描仪获得的。虽然数据集包含实际数据,但采集方法将场地真实性限制在场景的静态部分。此外,激光器只提供一定距离和高度的稀疏数据。对于最新版本,汽车的3D模型被安装到点云以获得更密集的标签并且还包括移动物体。但是,这些领域的地面实况仍然是近似的。
[59]Jure Žbontar, Lecun Y. Stereo Matching by Training a Convolutional Neural Network to Compare Image Patches[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2015, 17(1):2287-2318.
视差估计方法——使用Siamese网络计算图像斑块之间的匹配距离。
[60]Vedula S, Baker S, Collins R, et al. Three-dimensional scene flow.[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 2005, 27(3):475-480.
场景光流估计首次受到欢迎是由于[60]的工作——分析不同可能场景的问题。
[61]肖军, 朱世鹏, 黄杭,等. 基于光流法的运动目标检测与跟踪算法[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 37(6):770-774. EI 0.706
用Harris角点作跟踪对象,映入尺度空间的概念,提取尺度上的Harris角点,并进行曲率非极大值抑制,滤除“伪角点”,提高角点检测对尺度变化的抗干扰能力。跟踪算法采用结合图像金字塔的光流法,迭代计算光流,并提出光流误差的跟踪算法。
图像金字塔是一个图像集合,集合中所有的图像都源于同一个原始图像,而且是通过对原始图像连续降采样获得,直至达到某一个终止条件停止采样[63]。传统光流法采用小窗口跟踪目标以满足空间一致假设,因而当跟踪运动过快的物体时,跟踪效果不理想。
[62]Harris C. A combined corner and edge detector[J]. Proc Alvey Vision Conf, 1988, 1988(3):147-151.
Harris角点检测:由英国学者Harris和Stephens提出[62],角点定义为窗口向任意方向移动都会引起图像灰度变化明显的像素点。(Harris角点检测只在单一尺度下进行特征点检测,因而对图像的尺度变化不具备不变形;Harris角点至少两个边缘相交于一点,其曲率较大)
[63]Tamgade S N, Bora V R. Motion Vector Estimation of Video Image by Pyramidal Implementation of Lucas Kanade Optical Flow[C]// International Conference on Emerging Trends in Engineering & Technology, Icetet 2009, Nagpur, Maharashtra, India, 16-18 December. DBLP, 2009:914-917.
[64]Bergen J R, Burt P J, Hingorani R, et al. A three-frame algorithm for estimating two-component image motion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 1992, 14(9):886-896.
使用迭代注册算法来解释场景中的多个全局运动。
[65]Comg-xuan ZHANG, Ling-ling ZHU, et al. An Improved Evaluation Method for Optical Flow of Endpoint Error[J]. ACRS, 2017,54:312-317.
基于Middlebury基准提出了一种改进的光流估计评价公式。
[66]李秀智, 贾松敏, 尹晓琳,等.视觉光流矢量场估计算法综述[J].北京工业大学学报. 2013(11):
1638- 1643.
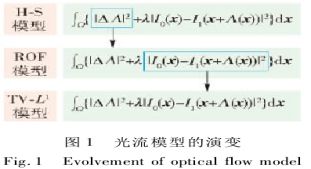
内容涉及(evolving)保边平滑、抗光照变化、大位移光流、异质点滤除和实时性计算(edge preserving smoothing, vary illumination tackling, large displacement optical flow eatimating, outlier removing and real-time computing)。变分法是求解光流的主要方法——用平滑项和数据项构建能量泛函,然后用欧拉-拉格朗日方程求解泛函的最优化解,最终得到致密光流场。变分光流法的优点是模型的通用性好、求解的精确度高且光流致密。(HS模型—>ROF模型(ROF模型的提出是为解决图像复原中的保边去噪问题[67],其中L1范数的正则项比L2范数正则项更有利于分段平滑,有利于在边界处保持灰度的不连续性,这对基于边缘的运动分割与运动与跟踪至关重要)—>TV-L1模型(Alliney[68]和Nikolova[69]提出进一步将ROF模型中的数据项也替换为L1范数)Zach等[18]将其拓展到光流场求解模型中。Chan等[70]最早提出了ROF模型的对偶求法,Chanbolle[71]提供了算法的收敛证明,Pock等[72]在此基础上首次卷积那个对偶方法用于光流计算,通过引入一个辅助变量κ,将其作为被估光流矢量的近似量)
未来研究工作:
1) 当前主流的光流算法所能估计的位移的尺度仍很有限,已成为制约光流技术广泛应用的主要瓶颈,因此,面向大位移的光流算法研究具有迫切的应用需求. 由于传统的图像金字塔算法所能提供的改进空间有限,可以考虑融合其他某些图像特征作为引导信息,以降低最优化搜索的范围及难度.
2) 光照变化的影响十分复杂,是影响光流求解精度的重要因素. 从文献报道看,结构-纹理分解等策略以及高阶梯度约束法能降低光照变化带来的不利影响,但改善的程度尚不明确,能否满足面向机器人导航、跟踪等应用领域的需要还有待定量地考察.
3) 目前光流算法的处理精度及运算效率之间的矛盾依然突出,因此,有必要研究更具普遍适用性的高效优化算法. 由于并行图形图像加速硬件( 如GPU) 和多核处理器成本不断降低,可为实时性系统的构建提供有力的支持.
[67]Rudin L I, Osher S, Fatemi E. Nonlinear total variation based noise removal algorithms[C]// Eleventh International Conference of the Center for Nonlinear Studies on Experimental Mathematics : Computational Issues in Nonlinear Science: Computational Issues in Nonlinear Science. Elsevier North-Holland, Inc. 1992:259-268.
ROF(Rudin-Osher-Fatemi)模型
[68]Alliney S. A property of the minimum vectors of a regularizing functional defined by means of the absolute norm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1997, 45(4):913-917.
[69]Nikolova M. A Variational Approach to Remove Outliers and Impulse Noise[J]. Journal of Mathematical Imaging and Vision, 2004, 20(1):99-120.
[70]Chan T F, Golub G H, Mulet P. A Nonlinear primal dual method for TV-based image restoration[C]// in ICAOS’96, 12th International Conference on Analysis and Optimization of Systems: Images, Wavelets and PDE’s, edited by. 1996.
[71]Chambolle A. An Algorithm for Total Variation Minimization and Applications[M]. Kluwer Academic Publishers, 2004.
Chambolle A.An Algorithm for Total Variation Minimization and Applications[J].Math Imaging Vis,2004,20:89-97.
[72]Pock T, Urschler M, Zach C, et al. A duality based algorithm for TV-L1-optical-flow image registration[C]// International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Springer-Verlag, 2007:511-518.
[73]程爱灵, 黄昶, 李小雨. 运动目标检测算法研究综述[J]. 信息通信, 2017(1):12-14.
[74]刘博文, 魏伟波, 潘振宽,等. 大位移变分光流计算的快速算法[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2017, 22(1):66-74.
针对多尺度方法在解决传统HS算法不能计算大位移光流的问题中出现的迭代速度慢的问题,应用Split Bregman方法,对偶方法和交替方向乘子法到大位移光流计算中加快迭代收敛。
多尺度方法:由于基于微分的光流算法利用了泰勒展开式,前提条件是变化量趋于0,因此微分光流算法只能计算小位移光流。而在图像中,位移的单位为像素,位移量的大小表现为相隔的像素的个数,像素又与图像分辨率直接相关,因此,可对原图像进行缩小,将原来的大位移运动变为小位移运动。将原图像缩小不同尺寸,得到许多个小分辨率的图像,原来整个的大位移变为一个个的小位移,然后再将小位移合并得到大位移光流。![]() (尺度变换公式)——双线性插值
(尺度变换公式)——双线性插值
M-HS-TV模型:
Dual方法
对于变分模型中计算复杂的光滑项,Split Bregman方法采用分裂的思想,用辅助变量ω代替计算▽u。而对偶方法定义了对偶空间:
![]() .....(2)
.....(2)
使用对偶项
![]() .....(3)
.....(3)
代替光滑项
![]() .....(4)
.....(4)
对于模型式( 10) ,需要引入辅助变量 ![]() ,利用
,利用![]() 计算光流矢量
计算光流矢量 ![]() ,得到
,得到
固定 dv,对 p 和 du 进行求解,得到问题
上式对du的变分导(函)数为
计算得到
原始解法:
上式是一个约束问题,可将其转为无约束问题
对上式求欧拉-拉格朗日方程得到
[75]Fortun D, Bouthemy P, Kervrann C. Optical flow modeling and computation: A survey[J]. Computer Vision & Image Understanding, 2015, 134:1-21.
文章总结了近几年光流技术。提出了一个光流估计的调查,分析了这一演变过程中阐述的主要原理,特别关注近期的发展。我们深入了解建模和优化技术的动机,兴趣和局限性,并强调方法之间的相似之处,以便能够清楚地了解其行为。提出对现有主要方法原则的综合分类,特别是对最近的发展。
运动分析是计算机视觉的主要任务之一。(目标跟踪,量化变形,检索主运动,检测异常行为)
论文不是告诉整个光流的演变过程,也不是对现有方法给出一个详尽的清单。我们提出存在的主要方法原则的综合分类,特别关注给出最近的发展。
![]()
![]()
AE对小误差估计即发生小位移非常敏感,而EPE几乎对非常接近的运动矢量没有区别。反之,AE趋于估计大位移运动运动矢量的距离,而EPE对大位移估计误差有强的惩罚性。
[76]Wedel A, Pock T, Zach C, et al. An Improved Algorithm for TV-L1 Optical Flow[M]// Statistical and Geometrical Approaches to Visual Motion Analysis. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2009:23-45.
ROF模型应用于光流。
[77]王琦, 潘振宽, 魏伟波. 多相图像分割的Split-Bregman方法及对偶方法[J]. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2010, 22(9):1561-1569.
对偶方法通过引入对偶变量将问题转化为对偶变量的半隐式迭代计算和主变量的精确计算公式。
[78]刘德春. 对偶算法的有效改进[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2006, 11(4):465-468.
应用块匹配的法的基本原理,提出实用的快速算法——最大梯度及多重循环对偶法。块匹配法是一种基于模式匹配的位移估值法。目前常用的匹配准则有均方误差(MSE)、平均绝对值误差(MSD)和绝对值误差(SAD)准则等。
其中,![]() 表示第
表示第![]() 帧灰度值,
帧灰度值,![]() ,
,![]() 分别为水平、垂直方向的偏移量。
分别为水平、垂直方向的偏移量。
[79]张俊, 顾广泽, 杨余飞. 基于改进的Chambolle对偶迭代的图像分割方法[J]. 湖南大学学报(自科版), 2013, 40(5):99-102.
为了克服基于对偶迭代的分割方法在要求达到较高精度的分割时收敛较慢的缺点,提出了对二相位分片常数Mumford-Shah模型的一个字问题采用改进的Chambolle对偶迭代进行求解。
基于边缘的图像分割方法对于噪声是非鲁棒性的,一般带噪声的图像不得不进行光滑。而基于区域的图像分割方法利用了区域和边缘的信息,它对噪声是鲁棒的。
[80]CHAN T F, VESE L A.Active contours without edges[J]. IEEE T Image Process, 2001,10(2):266-277.
提出二相位分片常数Munford-Shah模型,即CV模型,并提出了CV模型的水平集构造。
[81]VESE L A, CHAN T F. Amultiphase level set frarnewerk for image seynertation using the munford and shah model international[J]. Journal of Computer Vision, 2002, 50(3): 271-293.
多相位分片常数Munford-Shah模型的分割。
[82]涂志刚. 变分光流法在序列图像运动分析中的研究[D]. 武汉大学, 2013.
变分光流法,由于其具备完整的数值理论体系,并且可以获得较为准确的较高时空分辨率的致密运动场,而成为运动估计技术的优先选项。但由于光流法自身的受约束因素,致使变分光流技术在针对复杂情况(如:噪声,大位移,光照的均匀性,运动遮挡等)与标准光流产生较大的偏差,使估计精度下降。
处理噪声污染——中值滤波技术
处理大位移——Coarse-to-Fine技术
处理噪声、多运动目标——Robust函数
获取更高计算精度——图像插值技术(双线性插值),混合求导法
(光流模型、光流有效性检测技术、修正光流分量、权重选择(通过设置误差评估阈值获取最优权重)、权重中值滤波和双边滤波(更适合遮挡区域:运动特征分解成边缘区和遮挡区)结合)
[83]Ayvaci A, Raptis M, Soatto S. Sparse Occlusion Detection with Optical Flow[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2012, 97(3):322-338.
解决视频流中遮挡检测问题。
光流:共同可见的场景的部分可以通过域变形映射到彼此
光流满足条件:1.朗伯反射 2.恒定光照:ego-motion(帧间运动:场景不是相对光源运动的) 3.场景的可见性常数不变
[84]Gibson J, Marques O. Sparse Regularization of TV-L 1, Optical Flow[M]// Image and Signal Processing. Springer International Publishing, 2014:460-467.
[85]董国华. Horn-Schunck 光流理论研究[D].国防科技技术大学.2013(博士)
Guohua Dong. Contributions to Horn-Schunck’s Theory on Optical Flow[D]. National University of Defense technology. 2013
Horn-Schunck光流存在的问题:方程组的适定性和可解耦性、方程组解的规则性和输入图像序列规则性之间的关系、收敛性证明等等。
用二阶椭圆方程组理论证明了Horn-Schunck方程组并不存在适定性现象的可能性。
Gibson:We see because we move; we move because we see。
[86]陈鹏光. 基于稀疏模型的运动跟踪识别算法[D].东南理工大学.2016(博士)
运动跟踪识别是计算机视觉的基础和关键技术。论文研究了运动跟踪识别中光流和遮挡的计算检测、运动目标的跟踪和动作识别三个问题。
稀疏表示的特征是具有稳定重构性和充分降维性。能有效表示图像视频数据中本质的有意义的关键内容,抑制噪声和遮挡的影响。基于稀疏表示的最小化,能有效地提高运算的效率和鲁棒性。
对于遮挡问题,遮挡区域有意义信息过少导致运动物体出现模糊。论文组合了时空域和变换域中的稀疏特征表示遮挡,采用Stein-Weiss解析函数作为变分模型正则化函数和稀疏模型的变换函数,建立一个统一的没有经由稀疏转换的稀疏模型和伴随有稀疏转换的稀疏模型的光流框架。
光流法是运动估计的重要方法。光流是三维速度场在二维平面的投影向量,是运动目标像素运动产生的瞬时速度场。
稀疏表示的方法融合到计算光流。学习字典
稀疏表示的模型
在稀疏模型中,原始的正则化条件定义:
![]()
其中,![]() 定义为计算变量中非零项数目的函数,即期望所求的变量是稀疏的。
定义为计算变量中非零项数目的函数,即期望所求的变量是稀疏的。
[87]刘龙. 基于Kalman-BP组合模型的变形分析与预测方法研究[D]. 西南交通大学, 2015.
[88]于洪丽. 基于全变分模型的图像去噪方法研究[D]. 沈阳工业大学, 2015.
[89]连晓峰. 移动机器人及室内环境三维模型重建技术[M]. 国防工业出版社, 2010.
[90]贾松敏, 王可, 李秀智,等. 基于变分模型的单目视觉三维重建方法[J]. 光学学报, 2014, 34(4):162-168.
[91]秦宝岭. 基于光流—场景流的单目视觉三维重建研究[D]. 北京工业大学, 2016.
[92]李秀智, 杨爱林, 秦宝岭,等. 基于光流反馈的单目视觉三维重建[J]. 光学学报, 2015, 35(5):228-236.
[93]王可.基于变分模型的移动机器人三维环境建模方法研究[D]. 北京工业大学, 2016.(博士)
[94]Gageik N, Strohmeier M, Montenegro S. An Autonomous UAV with an Optical Flow Sensor for Positioning and Navigation[J]. International Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems, 2013, 10(4):1.
[95]陈赛. 基于稀疏表示的在线字典学习模型目标跟踪算法研究[D]. 江南大学, 2017.
[96]王可. 基于变分模型的移动机器人三维环境建模方法研究[D].北京工业大学, 2016.
[97]罗文峰. 光流计算方法, Optical flow calculation method:, CN 106204637 A[P]. 2016.
[98]王凌, 冯华君, 徐之海,等. 一种基于光流场的复杂背景下人脸定位方法[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2003, 39(8):68-70.
[99]赵光灿. 基于光流和惯性导航的小型无人机定位方法[J]. 工程技术:引文版, 2016(11):00315-00315.
[100]刘小明, 邢晓岚, 陈万春. 一种光流多传感器和惯导器件信息融合配置方法:, CN 102506892 A[P]. 2012.
[101]孙黎明. 图像稀疏去噪算法的并行改进研究[D]. 重庆大学, 2011.
[102]Raghunath D R, Kumar P V P, Pradeep C H M, et al. Video denoising using Optical flow estimation & Regularized non-local means[J]. International Journal of Advanced Research in Innovative Discoveries in Engineering and Applications[IJARIDEA], 2017, 2(2): 78-82.
提出一种新的视频去噪计算方法。
- 空间视频去噪策略
- 短暂视频去噪技术
[103]Ho H W, Croon G D, Chu Q P. Distance and velocity estimation using optical flow from a monocular camera[C]// International MICRO Air Vehicles Conferences and Competitions. 2016.
光流不直接提供运动物体的距离和速度,但可以提供其变化率。
论文主旨:利用单目相机测得的光流估计运动物体的距离和速度。算法使用扩展的卡尔曼滤波器(EKF)估计运动状态,并用其估计控制运动物体着陆。
四种已知的方法从光流中估计距离:
- 增加传感器直接或者间接测量距离,速度或者加速度。选择正确的滤波器并且融合可以得到距离估计。
- 当执行完美的恒定流量发散着陆时,控制输入(推力)或所谓的效应复制随着时间推移具有特定的单调递减函数,可用于估计距离[104]。他们通过将摄像机沿着轨道移动到图像场景来演示这种方法,以首先估计初始距离。由于恒流分散控制将导致距离的指数衰减,因此在获得初始值之后,将估计问题简化为距离的指数传播。
[104]Van B F, Morgansen K, Dickinson M H. Monocular distance estimation from optic flow during active landing maneuvers.[J]. Bioinspiration & Biomimetics, 2014, 9(2):771-778.
[105]Croon G C. Monocular distance estimation with optical flow maneuvers and efference copies: a stability-based strategy[J]. Bioinspiration & Biomimetics, 2016, 11(1):016004.
[106]Ho H W, De Croon G C H E, Van Kampen E, et al. Adaptive Control Strategy for Constant Optical Flow Divergence Landing[J]. 2016.
卡尔曼滤波自适应背景模型
[107] Karmann K P. Achim von Brandt. Moving Object Recognition Using an Adaptive Background Memory[C]// Time-varying Image Processing & Moving Object Recognition. 1990.
[108] Karmann K, Brandt A. Moving object recognition using an adaptive background memory. In: Cappellini V ed. Time varying Image Processing and Moving Object Recognition. 2. Elsevier, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1990
自适应的混合高斯背景模型
[109] Stauffer C, Grimson W E L. Adaptive Background Mixture Models for Real-Time Tracking[C]// Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 1999. IEEE Computer Society Conference on. IEEE Xplore, 1999:252 Vol. 2.
[110] Friedman N, Russell S. Image segmentation in video sequences: a probabilistic approach[C]// Thirteenth Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc. 1997:175-181.
[111]Mclachlan G J, Krishnan T. The EM algorithm and extensions[J]. Biometrics, 1997, 382(1):154-156.
Friedman与Russell[110]利用扩展的EM[111](Expectation Maximization)算法,为每个像素建立了混合高斯分类模型,该模型可以自动更新,并能自适应地将每个像素分类为背景、影子或者运动前景,在目标运动速度缓慢的情况下亦能较好地完成运动区域的分割,同时可以有效地消除影子的影响.
[112]Lipton A J. Local Application of Optic Flow to Analyse Rigid versus Non-Rigid Motion[C]// Iccv99 Workshop on Frame-Rate Applications. 1999:99-118.
Lipton[112]通过计算运动区域的残余光流(residual flow)来分析运动实体的刚性和周期性,非刚性的人的运动相对于刚性的车辆运动而言具有较高的平均残余光流,同时它也呈现了周期性的运动特征,据此可以将人区分出来.-
光流的概念是Gibson在1950年首先提出来的。它是空间运动物体在观察成像平面上的像素运动的瞬时速度,是利用图像序列中像素在时间域上的变化以及相邻帧之间的相关性来找到上一帧跟当前帧之间存在的对应关系,从而计算出相邻帧之间物体的运动信息的一种方法。一般而言,光流是由于场景中前景目标本身的移动、相机的运动,或者两者的共同运动所产生的。
目前OpenCV中实现了不少的光流算法。
1. calcOpticalFlowPyrLK
通过金字塔Lucas-Kanade 光流方法计算某些点集的光流(稀疏光流)。理解的话,可以参考这篇论文:”Pyramidal Implementation of the Lucas Kanade Feature TrackerDescription of the algorithm”
2. calcOpticalFlowFarneback
用Gunnar Farneback 的算法计算稠密光流(即图像上所有像素点的光流都计算出来)。它的相关论文是:"Two-Frame Motion Estimation Based on PolynomialExpansion"
3. CalcOpticalFlowBM
通过块匹配的方法来计算光流。
4. CalcOpticalFlowHS
用Horn-Schunck 的算法计算稠密光流。相关论文好像是这篇:”Determining Optical Flow”
5. calcOpticalFlowSF
这一个是2012年欧洲视觉会议的一篇文章的实现:"SimpleFlow: A Non-iterative, Sublinear Optical FlowAlgorithm",工程网站是:http://graphics.berkeley.edu/papers/Tao-SAN-2012-05/ 在OpenCV新版本中有引入。
还有他们的API的使用说明,我们直接参考OpenCV的官方手册就行:
http://www.opencv.org.cn/opencvdoc/2.3.2/html/modules/video/doc/motion_analysis_and_object_tracking.html#calcopticalflowfarneback
IJCV2011有一篇文章,《A Database and Evaluation Methodology for Optical Flow》里面对主流的光流算法做了简要的介绍和对不同算法进行了评估。网址是:http://vision.middlebury.edu/flow/光流定位:
- 【教程】通俗讲法告诉你什么是光流Optical Flow,附算法
http://bbs.elecfans.com/jishu_485979_1_1.html
2. OpenCV学习笔记(九)光流法
http://blog.csdn.net/crzy_sparrow/article/details/7407604
3. 光流法简单介绍
http://blog.csdn.net/carson2005/article/details/7581642
无人机光流定位:
Lucas-Kanade方法解决孔径问题——假设在目标点的邻域内所有点都具有相似的运动。利用一个3*3邻域中的9个点具有相同运动得到9个光流方程,然后采用最小二乘进行拟合求解,最终得到(u,v):
以下内容来自于:孙黎明. 图像稀疏去噪算法的并行改进研究[D]. 重庆大学, 2011.
基于DCT字典图像稀疏去噪算法:
DCT字典的由来:
对于N*N的DCT字典用公式可表示为
其中, 。
。
其中, 。
。
生成64*256大小的DCT字典,matlab代码如下:
DCT = zeros(8, 16);
for k = 0:1:Pn-1
V = cos([0:1:8-1]'*k*pi/16);
if k > 0, V = V-mean(V);
end
DCT(:, k+1) = V/norm(V);
end
DCT = kron(DCT, DCT)
评价图像质量的指标:
MSE(均方误差)
其中, 分别表示待评价图像和原始图像,M,N分别表示图像的长和宽。
分别表示待评价图像和原始图像,M,N分别表示图像的长和宽。
PSNR(峰值信噪比)
其中,Q:表示图像量化的灰度级数
光流
LK光流算法:
L-k算法是在1981年Lucas-Kanade提出来的,开始主要用于求稠密光流,由于该算法能比较好的运用到图像中,后面就发展成为求图像稀疏光流的重要方法。L-K算法需要满足如下3个假设:
1)亮度恒定假设。即假设场景中目标在运动时外观颜色是不变的,也即在图像中的像素在两帧中的亮度保持不变。
2)时间连续或运动是小运动。即图像中物体的运动随时间变化缓慢,在连续的两帧图像间,物体的位移比较小。
3)空间一致性假设。图像中同一物体表面上邻近的像素点的运动是一致的,且这些点一定是聚集在一个区域内的。
假设以M点为中心的灰度区域内的光流均一致,那么对于不同的像素点赋予不同的权值,就可以将光流的计算方程式转化为以下形式: 
-
由于之前的L-K光流法对于大运动的跟踪束手无策,然后有人又提出图像金字塔的方法来解决这个问题。通过建立金字塔,在多尺度下计算光流,使得光流的计算的准确性又跨越了一步。
金字塔光流的思想是对每个图像帧向下采样,分别建立多级金字塔,当采样到足够小以后,相邻的图像帧之间的运动将变得很小,以至于可以看成是物体的运动随时间变化很慢的运动情况,这时候就可以用L-K方法计算目标的光流,再将计算出来的光流向底层投影,计算下一层的光流,直到估算出原图像帧的光流。