Data exploration (1): Data Visualization with ggplot2
Goal

A Graphing Template
ggplot(data=)+
(mapping=aes())
Aesthetic Mappings
An aesthetic is a visual property of the objects in your plot,
including the size, the shape, or the color of points.
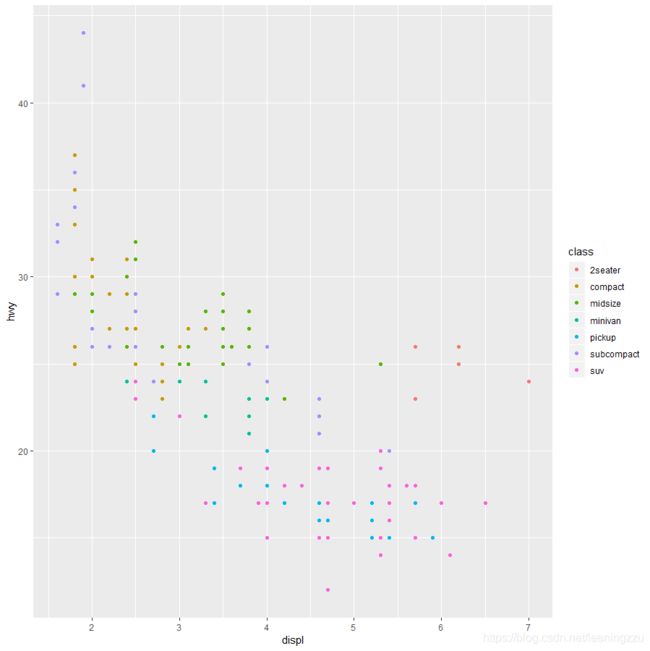
For example, map the colors of points to the class variable
library(tidyverse)
ggplot(data=mpg)+
geom_point(mapping=aes(x=displ,y=hwy,color=class)) # alpha=class 透明度, shape=class 形状, size=class 大小
Facets
> Two ways to add additional variables:
1. with aesthetics
2. split plot into facets (particularly for categorical variables)
For example,
ggplot(data=mpg)+
geom_point(mapping=aes(x=displ,y=hwy)) +
facet_wrap(~ class, nrow=2)

For the combination of two variables, using facet_grid()
ggplot(data=mpg)+
geom_point(mapping=aes(x=displ,y=hwy)) +
facet_grid(drv ~ cyl)

Geometric Objects
A geom is the geometrical object that a plot use to represent data. Such as bar geoms, point geoms, box geoms
For example
ggplot(data=mpg,mapping=aes(x=displ,y=hwy,color=drv))+
geom_point()+
geom_smooth()

Smooth all the class points
ggplot(data=mpg,mapping=aes(x=displ,y=hwy))+
geom_point(mapping=aes(color=class))+
geom_smooth()

Smooth a subst of the class points
ggplot(data=mpg,mapping=aes(x=displ,y=hwy))+
geom_point(mapping=aes(color=class))+
geom_smooth(data=filter(mpg,class=="subcompact"), se=FALSE)

# 1图
ggplot(data=mpg,mapping=aes(x=displ,y=hwy))+
geom_point()+
geom_smooth(se=FALSE)
# 2图
ggplot(data=mpg,mapping=aes(x=displ,y=hwy))+
geom_point()+
geom_smooth(mapping=aes(group=drv),se=FALSE)
# 3图
ggplot(data=mpg,mapping=aes(x=displ,y=hwy,color=drv))+
geom_point()+
geom_smooth(mapping=aes(group=drv),se=FALSE)
# 4图
ggplot(data=mpg,mapping=aes(x=displ,y=hwy))+
geom_point(mapping=aes(color=drv))+
geom_smooth(se=FALSE)
# 5图
ggplot(data=mpg,mapping=aes(x=displ,y=hwy,color=drv))+
geom_point()+
geom_smooth(mapping=aes(linetype=drv),se=FALSE)
# 6图 做反了?
ggplot(data=mpg,mapping=aes(x=displ,y=hwy))+
geom_point(aes(color=drv),size=4)+
geom_point(color="white",size=0.6)

Statistical Transformations
Statistical transformation is also called stat: the algorithm used to calculate new values for a graph
For example, geom_bar and stat_count are interchangeable.
ggplot(data=diamonds,aes(x=cut))+
stat_count()
#指定统计变换
demo <- tribble(~a,~b,"bar_1",20,"bar_2",30,"bar_3",40)
ggplot(data=demo,aes(a,b))+
geom_bar(sta="identity")

Position Adjustments
# 面积颜色相同,边框颜色表示不同分类
ggplot(diamonds,aes(x=cut,color=clarity))+
geom_bar(alpha=1/5,position="identity)
# 边框颜色固定,面积颜色表示不同分类
ggplot(diamonds,aes(x=cut,fill=clarity))+
geom_bar(alpha=1/5,position="identity",color="black")

# fill
ggplot(diamonds,aes(x=cut,fill=clarity))+
geom_bar(alpha=0.5,,position="fill")
#identity
ggplot(diamonds,aes(x=cut,fill=clarity))+
geom_bar(alpha=0.5,,position="identity")
#dodge
ggplot(diamonds,aes(x=cut,fill=clarity))+
geom_bar(alpha=0.5,,position="dodge")

Coordinate Systems
coord_flip坐标翻转,coord_quickmap等比例放缩,coord_polar极坐标转换
The Layered Grammar of Graphics
Code template:
ggplot(data=<DATA>)+
<GEOM_FUNCTION>(mapping=aes(<MAPPINGGS>),stat=<STAT>,position=<POSITION>) +
<COORDINATE FUNCTION> +
<FACET_FUNCTION>