蓝桥杯复习——广度优先搜索总结
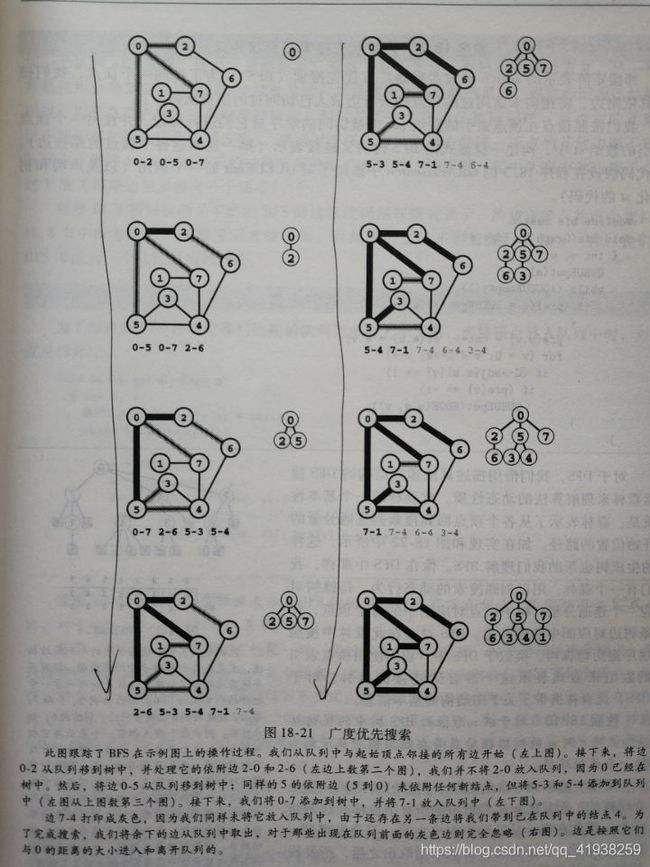
前些日子在刷DFS(深度优先搜索)的题目,而最近在练习BFS(广度优先搜索),现在我对我这一段时间的学习做个总结。BFS类似于树的层次遍历,而DFS则是类似树的先根遍历。我拍了《算法C实现》这本书的讲解,作为BFS的示意图,看的顺序是从上到下,从左到右,如下所示:
BFS会使用到队列这个数据结构,队列是一个先进先出的数据结构。队列是作为一个缓冲区而存在的。先将当前遍历的节点弹出队列,再将所有与他连通的下一跳入队,以此为循环直到队列为空,则遍历结束,这张图的遍历顺序如下所示。
- 以这张图为例,先将0入队,再将其连通的所有下一跳(2、5、7)分别入队,再将0弹出,此时队列里是257,2为队头,7为队尾。
- 将2的所有连通下一跳入队(6),再将2弹出队,此时是576。
- 再将5的下一跳入队(3、4),再将5弹出队,此时队列里是7634。
- 将7的下一跳入队(1),4不入队因为已经入过了。
- 此时全部入队完成,逐一将对里的元素出队到空队为止。
依照这个可以写出如下的代码:
#include
#include
using namespace std;
vector Adj[1000];//建立邻接表存放点的连通信息,当然也可以使用二维数组
int n;//顶点数
bool flag[1000] = { false };//标记是否入过队列,false没有,true则是入了队的
void bfs(int u)
{
queueq;
//入队
q.push(u);
//入队就标记
flag[u] = true;
//循环入队、出队
while (!q.empty())
{
//先取出队头元素再出队
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
//遍历队头元素的所有没入过队的下一跳
//循环入队操作
for (int i = 0; i < Adj[u].size(); i++)
{
//取出下一跳
int v = Adj[u][i];
//没有入过队的才可以入队
if (flag[v] == false)
{
q.push(v);
flag[v] = true;
}
}
}
}
int main(void)
{
//实际功能部分
return 0;
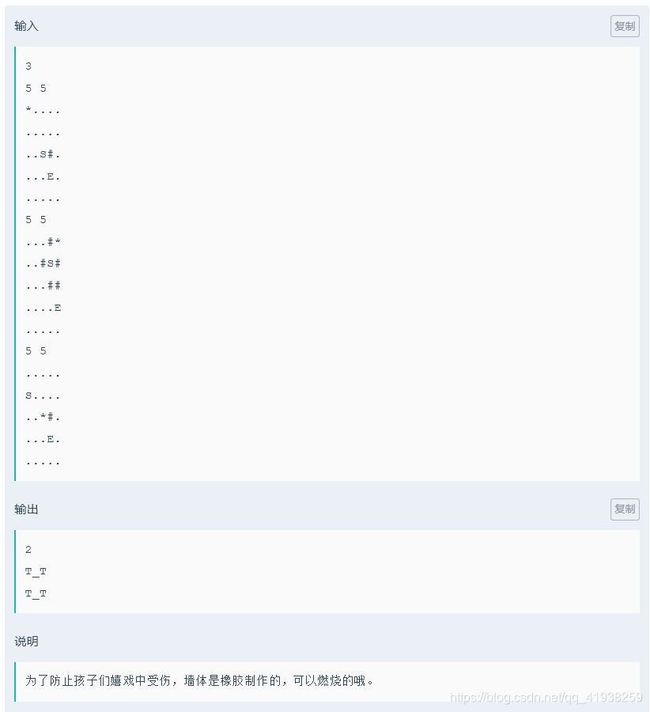
} 如果要求最小路径的话,看这题:
给出BFS代码:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
struct node
{
int x, y;
int step;
}S,E,fire,Node;
bool flag;
bool testunit[35][35];
int n, m;
char map[35][35];
int dr[4] = { -1, 0, 1, 0 };
int dc[4] = { 0, 1, 0, -1 };
float distance(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2)
{
return sqrt(pow(x1 - x2, 2) + pow(y1 - y2, 2));
}
bool test(int x, int y)
{
if (x < 0 && x >= n && y < 0 && y >= m)return false;
if (testunit[x][y] == true)return false;
if (map[x][y] == '#')return false;
return true;
}
int bfs()
{
queue Q;
Q.push(S);
while (!Q.empty())
{
node top = Q.front();
Q.pop();
if (top.x == E.x && top.y == E.y)return top.step;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int X = top.x + dr[i];
int Y = top.y + dc[i];
if (test(X, Y))
{
Node.x = X;
Node.y = Y;
Node.step = top.step + 1;
Q.push(Node);
testunit[X][Y] = true;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
int main(void)
{
memset(testunit, false, sizeof(testunit));
memset(map, '#', sizeof(map));
int N;
cin >> N;
for (int k = 0; k < N; k++)
{
flag = false;
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
char temp;
cin >> temp;
map[i][j] = temp;
if (map[i][j] == 'E') { E.x = i; E.y = j; }
if (map[i][j] == 'S') { S.x = i; S.y = j; }
if (map[i][j] == '*') { fire.x = i; fire.y = j; }
}
int result = -1;
if (distance(E.x, E.y, S.x, S.y) < distance(fire.x, fire.y, E.x, E.y))
{
result = bfs();
}
testunit[S.x][S.y] = true;
if (result == -1)cout << "T_T" << endl;
else cout << result << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
当然太暴力了没有任何优化是AC不了的,可以看下面这个代码是可以AC的。
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int n, m;
int dir[4][2] = { {1,0},{-1,0},{0,1},{0,-1} };
char mp[31][31];
int vis[31][31], f[31][31];
struct node
{
int x;
int y;
int step;
};
int sx, sy, fx, fy;
queueq;
void bfs(int x, int y)
{
queueq;
node a, b, temp1, temp2;
a.x = x;
a.y = y;
a.step = 0;
q.push(a);
while (!q.empty())
{
a = q.front();
q.pop();
//满足条件时
if (mp[a.x][a.y] == 'E')
{
cout << a.step << endl;
return;
}
//这一步是用来简化复杂度的,是回溯算法,
//满足条件的话说明当前循环以前已经运行过了,就跳过当前这一循环。
if (f[a.x][a.y] == a.step) continue;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
//初始化b,其意义不是把a拷贝给b
b = a;
//遍历下一格
b.x = a.x + dir[i][0];
b.y = a.y + dir[i][1];
//这一步好像有点累赘,但是可以看出是用来下面判断是否满足遍历的条件的
int xx = b.x;
int yy = b.y;
//当前加一步
b.step += 1;
//遍历下一格子
if (mp[xx][yy] != '#' && b.step <= f[xx][yy] && !vis[xx][yy] && xx > 0 && xx <= n && yy > 0 && yy <= m)
{
q.push(b);
vis[xx][yy] = 1;
}
}
}
//不满足条件时
cout << "T_T" << endl;
return;
}
int main()
{
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t)
{
while (!q.empty()) q.pop();
memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
{
cin >> mp[i][j];
if (mp[i][j] == 'S')
{
sx = i;
sy = j;
}
if (mp[i][j] == '*')
{
fx = i;
fy = j;
}
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
{
f[i][j] = max(abs(fx - i), abs(fy - j));
}
vis[sx][sy] = 1;
bfs(sx, sy);
t = t - 1;
}
}
END