LeetCode题目解析
LeetCode —— 两数之和
给定一个整数数组和一个目标值,找出数组中和为目标值的两个数。
你可以假设每个输入只对应一种答案,且同样的元素不能被重复利用。
示例:给定 nums = [2, 7, 11, 15], target = 22,因为 nums[1] + nums[3] = 7 + 15 = 22,所以返回 [1, 3]
简单解法
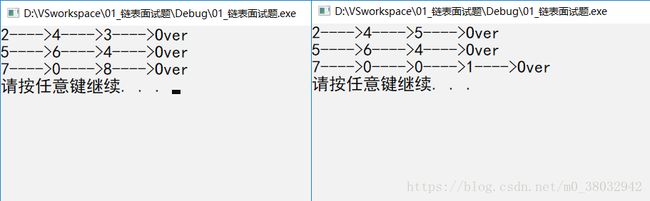
#include 优化版
主要是去掉重复比较元素,j = i + 1这一句代码
#include 结果差异
链表逆数相加
给定两个非空链表来表示两个非负整数。位数按照逆序方式存储,它们的每个节点只存储单个数字。将两数相加返回一个新的链表。
你可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数字都不会以零开头。
示例:
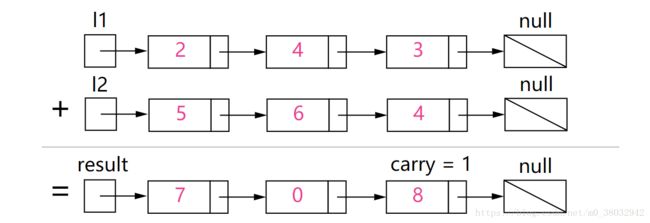
输入:(2 -> 4 -> 3) + (5 -> 6 -> 4)
输出:7 -> 0 -> 8
原因:342 + 465 = 807
本题目中需要重点考虑两点问题:
- 在执行加法运算的过程中可能会遇到进位,这个时候需要把进位的数字与不进位的数字分别处理
- 在两条链表都加结束时,可能还是需要进位,这样的情况下就需要新增节点存储进位
- 在链表的长度不一致的时候多余的节点被丢弃
这是定义的链表,使用pList指针类型维护链表
typedef int DataType;
typedef struct Node{
DataType data;
struct Node *next;
}Node, *pNode, List, *pList;
//初始化
void InitList(pList *ppl);
//尾部插入
void PushBack(pList *ppl, DataType d);
//打印链表
void PrintList(pList pl);
//链表加法
pList addTwoNumbers(pList list1, pList list2);
核心代码
pList addTwoNumbers(pList list1, pList list2)
{
pList newlist = NULL;
pNode newNode = NULL;
int flag = 0;//是否进位
int sum = 0;//两个data域之和
pNode tail = newlist;//维护尾插的指针
pNode cur = NULL;//寻找尾节点前一个节点的指针
//其中一条链表为空就直接返回NULL
if (list1 == NULL || list2 == NULL)
return NULL;
while (list1 != NULL && list2 != NULL)
{
sum = list1->data + list2->data;
if (flag)
sum++; //之前有进位则还要加1
//加了之后是否还需要进位的判断
if (sum >= 10)
flag = 1;
else
flag = 0;
//申请新节点
newNode = BuyNode(sum % 10);
//尾部插入(当然这里可以直接使用尾插的函数)
if (newlist == NULL)
{
newlist = newNode;
tail = newlist;
}
else
{
tail->next = newNode;
tail = tail->next;
}
//指针同时向后走
list1 = list1->next;
list2 = list2->next;
}
//如果加到最后还是需要进位的处理
if (flag == 1){
//printf("sum = %d\n", sum);
cur = newlist;
while (cur->next != NULL)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
cur->data = sum % 10;//修改最后一个元素
//追加进位的节点
newNode = BuyNode(1);
tail->next = newNode;
}
return newlist;
}
测试函数
void test()
{
pList plist1 = NULL;
pList plist2 = NULL;
pList newlist = NULL;
InitList(&plist1);
InitList(&plist2);
PushBack(&plist1, 2);
PushBack(&plist1, 4);
PushBack(&plist1, 3);
//PushBack(&plist1, 5); //测试最后进位新增节点
PushBack(&plist2, 5);
PushBack(&plist2, 6);
PushBack(&plist2, 4);
PrintList(plist1);
PrintList(plist2);
newlist = addTwoNumbers(plist1, plist2);
PrintList(newlist);
}
上面只是完成了基本操作,接下来才是重点
自己优化后的代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* addTwoNumbers(struct ListNode* l1, struct ListNode* l2) {
struct ListNode* newlist = NULL;
struct ListNode* newNode = NULL;
struct ListNode* tail = NULL;
int flag = 0;//是否进位
//其中一条链表为空就直接返回NULL
if (l1 == NULL || l2 == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
while (l1 != NULL && l2 != NULL)
{
if ((l1->val + l2->val + flag) >= 10)
{
//PushBack(&newlist, (list1->data + list2->data + flag) % 10);
newNode = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
newNode->val = (l1->val + l2->val + flag) % 10;
newNode->next = NULL;
tail = newlist;
if (newlist == NULL)
{
newlist = newNode;
}
else
{
while (tail->next)
{
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = newNode;
}
flag = 1;
}
else
{
//PushBack(&newlist, list1->data + list2->data+ flag);
newNode = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
newNode->val = l1->val + l2->val + flag;
newNode->next = NULL;
tail = newlist;
if (newlist == NULL)
{
newlist = newNode;
}
else
{
while (tail->next)
{
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = newNode;
}
flag = 0;
}
l1 = l1->next;
l2 = l2->next;
}
//开始处理多余部分
//printf("lis1t1 %d\n",list1->data);
while (l1 != NULL)
{
//使用指针找到链表的末尾
tail = newlist;
while (tail->next != NULL)
{
tail = tail->next;
}
//如果之前没有进位
if (flag == 0)
{
tail->next = l1;
return newlist;
}
//flag == 1
if (l1->val + 1 >= 10)
{
//PushBack(&newlist, (l1->val + 1) % 10);
newNode = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
newNode->val =(l1->val + 1) % 10;
newNode->next = NULL;
tail = newlist;
if (newlist == NULL)
{
newlist = newNode;
}
else
{
while (tail->next)
{
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = newNode;
}
flag = 1;
}
else
{
//PushBack(&newlist, l1->val + 1);
newNode = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
newNode->val = l1->val + 1;
newNode->next = NULL;
tail = newlist;
if (newlist == NULL)
{
newlist = newNode;
}
else
{
while (tail->next)
{
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = newNode;
}
flag = 0;
}
l1 = l1->next;
}
while (l2 != NULL)
{
//使用指针找到链表的末尾
tail = newlist;
while (tail->next != NULL)
tail = tail->next;
//如果之前没有进位
if (flag == 0)
{
tail->next = l2;
return newlist;
}
//flag == 1
if (l2->val + 1 >= 10)
{
//PushBack(&newlist, (l2->val + 1) % 10);
newNode = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
newNode->val = (l2->val + 1) % 10;
newNode->next = NULL;
tail = newlist;
if (newlist == NULL)
{
newlist = newNode;
}
else
{
while (tail->next)
{
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = newNode;
}
flag = 1;
}
else
{
//PushBack(&newlist, l2->val + 1);
newNode = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
newNode->val = l2->val + 1;
newNode->next = NULL;
tail = newlist;
if (newlist == NULL)
{
newlist = newNode;
}
else
{
while (tail->next)
{
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = newNode;
}
flag = 0;
}
l2 = l2->next;
}
//最后追加
if (flag == 1)
{
newNode = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
newNode->val = 1;
newNode->next = NULL;
tail = newlist;
if (newlist == NULL)
{
newlist = newNode;
}
else
{
while (tail->next)
{
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = newNode;
}
}
return newlist;
}
优化的代码
我自己的执行时间为24ms,但是接下来这种方式执行时间更快,为20ms
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* addTwoNumbers(struct ListNode* l1, struct ListNode* l2) {
struct ListNode *head,*p,*q;
p=NULL;
q=NULL;
int sum=0,c=0;
while(l1!=NULL||l2!=NULL)
{
if(l1==NULL&&l2==NULL)
{
if(c==1)
{
p=(struct ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
if(p!=NULL)
{
p->val=c;
p->next=NULL;
if(q==NULL)
{
head=p;
q=p;
}
else
{
q->next=p;
q=p;
}
}
}
}
else if(l1!=NULL&&l2!=NULL)
{
sum=c+l1->val+l2->val;
c=sum/10;
p=(struct ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
if(p!=NULL)
{
p->val=sum%10;
p->next=NULL;
if(q==NULL)
{
head=p;
q=p;
}
else
{
q->next=p;
q=p;
}
}
}
else
{
sum=c+(l1!=NULL?l1->val:l2->val);
c=sum/10;
p=(struct ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
if(p!=NULL)
{
p->val=sum%10;
p->next=NULL;
if(q==NULL)
{
head=p;
q=p;
}
else
{
q->next=p;
q=p;
}
}
}
if(l1!=NULL)
l1=l1->next;
if(l2!=NULL)
l2=l2->next;
}
if(c==1)
{
p=(struct ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
if(p!=NULL)
{
p->val=c;
p->next=NULL;
if(q==NULL)
{
head=p;
q=p;
}
else
{
q->next=p;
q=p;
}
}
}
return head;
}
给定一个字符串,找出不含有重复字符的最长子串的长度。
示例:
给定 "abcabcbb" ,没有重复字符的最长子串是 "abc",那么长度就是3。
给定"bbbbb",最长的子串就是"b" ,长度是1。
给定"pwwkew" ,最长子串是 "wke" ,长度是3。请注意答案必须是一个子串,"pwke" 是子序列 而不是子串。
个人思路
首先我想到的是直接比对,就拿"abcabcbb"这个字符串来说:
首先使用两个指针来记录比较位置,start指针作为开头,一直往后移动,end指针接着start向后移动,遇到其中包含重复元素就停止向前走,等下一轮start指针向后移动一步的时候再走,然后使用tmp_len来保存临时长度,max_len记录最大长度,这样直到start指针走到最后即可判断出最大的无重复元素的长度,但是时间复杂度较大!,下面给出代码:
#include虽然这样做不是特别快,LeetCode运行时间为264ms,效率是很低的,但是最大的优点就是节省空间,下面这种哈希表的方式效率很快,但是空间也是浪费了不少,等于是在拿空间换时间吧,而且更加容易理解的方式!
哈希的方式
只用哈希表无疑是解决这类办法的最优解,将一个存储127个元素的数组视为Hash表,先初始化为-1,遇到重复的则会开始新的一轮的计数:
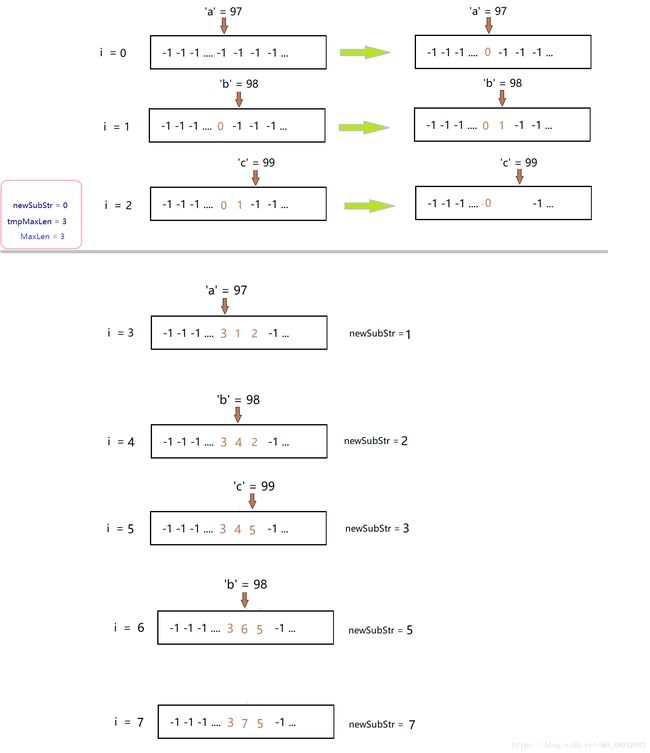
int lengthOfLongestSubstring(char* s) {
int hashTab[CHAR_MAX] = { 0 }; //0-- index 1--len
int i = 0, j = 0, strLen = 0, maxLen = 0, tmpMaxLen = 0;
int newSubStr = 0; //假设如果只有一个字符 那么上次找到的地方就是前面
if (NULL == s)
{
return 0;
}
strLen = strlen(s);
for (i = 0; i < CHAR_MAX; i++)
{
hashTab[i] = -1;
}
for (i = 0; i < strLen; i++)
{
if ((hashTab[*(s + i)] < newSubStr))
{
hashTab[*(s + i)] = i;
tmpMaxLen++;
}
else { //meet a same
/*计算原来的*/
maxLen = tmpMaxLen > maxLen ? tmpMaxLen : maxLen;
//代表新的一轮计数开始
newSubStr = hashTab[*(s + i)] + 1;
tmpMaxLen = i - newSubStr + 1;//代表新的一轮计数开始 +1是因为new和i都是新的长度
hashTab[*(s + i)] = i;
}
}
maxLen = tmpMaxLen > maxLen ? tmpMaxLen : maxLen;
return maxLen;
}
最优解复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度(Table):O(m)O(m),mm 是字符集的大小。