自然语言处理入门实战2:基于深度学习的文本分类
自然语言处理入门实战2:基于深度学习的文本分类
- 数据集
- 数据预处理
- 模型
- 模型训练
- 模型测试
- 参考
本文参考复旦大学自然语言处理入门练习,主要是实现基于深度学习的文本分类。
环境:python3.7
版本:pytorch1.2
数据集:
数据集采用gaussic的数据集,https://github.com/gaussic/text-classification-cnn-rnn
链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1hugrfRu 密码: qfud
数据集有十个类别,分别是:
体育|娱乐|家居|房产|教育|时尚|时政|游戏|科技|财经
数据集
cnews:
cnews.train.txt
cnews.val.txt

cnews.test.txt
数据预处理
cnews_loader.py:
read_file(): 读取文件数据;
build_vocab(): 构建词汇表,使用字符级的表示,这一函数会将词汇表存储下来,避免每一次重复处理;
read_vocab(): 读取上一步存储的词汇表,转换为**{词:id}表示;
read_category(): 将分类目录固定,转换为{类别: id}**表示;
to_words(): 将一条由id表示的数据重新转换为文字;
process_file(): 将数据集从文字转换为固定长度的id序列表示;
batch_iter(): 为神经网络的训练准备经过shuffle的批次的数据。
# coding: utf-8
import sys
from collections import Counter
import numpy as np
#import tensorflow.keras as kr
import os
import keras
try:
reload(sys)
sys.setdefaultencoding("utf-8")
is_py3 = False
except NameError:
is_py3 = True
def native_word(word, encoding='utf-8'):
"""如果在python2下面使用python3训练的模型,可考虑调用此函数转化一下字符编码"""
if not is_py3:
return word.encode(encoding)
else:
return word
def native_content(content):
if not is_py3:
return content.decode('utf-8')
else:
return content
def open_file(filename, mode='r'):
"""
常用文件操作,可在python2和python3间切换.
mode: 'r' or 'w' for read or write
"""
if is_py3:
return open(filename, mode, encoding='utf-8', errors='ignore')
else:
return open(filename, mode)
def read_file(filename):
"""读取文件数据"""
contents, labels = [], []
with open_file(filename) as f:
for line in f:
try:
label, content = line.strip().split('\t')
if content:
contents.append(list(native_content(content)))
labels.append(native_content(label))
except:
pass
return contents, labels
def build_vocab(train_dir, vocab_dir, vocab_size=5000):
"""根据训练集构建词汇表,存储"""
data_train, _ = read_file(train_dir)
all_data = []
for content in data_train:
all_data.extend(content)
counter = Counter(all_data)
count_pairs = counter.most_common(vocab_size - 1) #统计最常出现的字
# print(count_pairs)
words, _ = list(zip(*count_pairs))
# print(words)
# 添加一个 来将所有文本pad为同一长度
words = ['' ] + list(words)
open_file(vocab_dir, mode='w').write('\n'.join(words) + '\n')
def read_vocab(vocab_dir):
"""读取词汇表"""
# words = open_file(vocab_dir).read().strip().split('\n')
with open_file(vocab_dir) as fp:
# 如果是py2 则每个值都转化为unicode
words = [native_content(_.strip()) for _ in fp.readlines()]
word_to_id = dict(zip(words, range(len(words))))
return words, word_to_id
def read_category():
"""读取分类目录,固定"""
categories = ['体育', '财经', '房产', '家居', '教育', '科技', '时尚', '时政', '游戏', '娱乐']
categories = [native_content(x) for x in categories]
cat_to_id = dict(zip(categories, range(len(categories))))
return categories, cat_to_id
def to_words(content, words):
"""将id表示的内容转换为文字"""
return ''.join(words[x] for x in content)
def process_file(filename, word_to_id, cat_to_id, max_length=600):
"""将文件转换为id表示"""
contents, labels = read_file(filename)
data_id, label_id = [], []
for i in range(len(contents)):
data_id.append([word_to_id[x] for x in contents[i] if x in word_to_id])
label_id.append(cat_to_id[labels[i]])
# 使用keras提供的pad_sequences来将文本pad为固定长度
#x_pad = kr.preprocessing.sequence.pad_sequences(data_id, max_length)
#y_pad = kr.utils.to_categorical(label_id, num_classes=len(cat_to_id)) # 将标签转换为one-hot表示
#x_pad = nn.utils.rnn.pack_padded_sequence(data_id, max_length)
x_pad = keras.preprocessing.sequence.pad_sequences(data_id, max_length)
y_pad = keras.utils.to_categorical(label_id, num_classes=len(cat_to_id)) # 将标签转换为one-hot表示
return x_pad, y_pad
def batch_iter(x, y, batch_size=64):
"""生成批次数据"""
# print('inter')
data_len = len(x)
num_batch = int((data_len - 1) / batch_size) + 1
indices = np.random.permutation(np.arange(data_len))
# print(indices)
x_shuffle = x[indices]
# print(x_shuffle)
y_shuffle = y[indices]
# print(y_shuffle)
for i in range(num_batch):
start_id = i * batch_size
end_id = min((i + 1) * batch_size, data_len)
yield x_shuffle[start_id:end_id], y_shuffle[start_id:end_id]
if __name__ == '__main__':
base_dir = 'cnews'
train_dir = os.path.join(base_dir, 'cnews.train.txt')
test_dir = os.path.join(base_dir, 'cnews.test.txt')
val_dir = os.path.join(base_dir, 'cnews.val.txt')
vocab_dir = os.path.join(base_dir, 'cnews.vocab.txt')
categories, cat_to_id = read_category()
words, word_to_id = read_vocab(vocab_dir)
x_val, y_val = process_file(val_dir, word_to_id, cat_to_id,600)
print('start')
batch_val = batch_iter(x_val, y_val, 64)
f = 0
for i,j in batch_val:
f+=1
print(f)
模型
torch_model.py:
此部分构建了两个模型,分别是基于RNN的和基于CNN的,
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import torch
from torch import nn
import numpy as np
from torch.autograd import Variable
import torch.nn.functional as F
class TextRNN(nn.Module):
"""文本分类,RNN模型"""
def __init__(self):
super(TextRNN, self).__init__()
# 三个待输入的数据
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(5000, 64) # 进行词嵌入
self.rnn = nn.LSTM(input_size=64, hidden_size=128, bidirectional=True)
# self.rnn = nn.GRU(input_size=64, hidden_size=128, num_layers=2, bidirectional=True)
self.f1 = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(256, 10),
nn.Softmax())
def forward(self, x):
x = self.embedding(x) # batch_size x text_len x embedding_size 64*600*64
x= x.permute(1, 0, 2) # text_len x batch_size x embedding_size 600*64*64
x, (h_n, c_n)= self.rnn(x) #x为600*64*256, h_n为2*64*128 lstm_out Sentence_length * Batch_size * (hidden_layers * 2 [bio-direct]) h_n (num_layers * 2) * Batch_size * hidden_layers
final_feature_map = F.dropout(h_n, 0.8)
feature_map = torch.cat([final_feature_map[i, :, :] for i in range(final_feature_map.shape[0])], dim=1) #64*256 Batch_size * (hidden_size * hidden_layers * 2)
final_out = self.f1(feature_map) #64*10 batch_size * class_num
return final_out
class TextCNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(TextCNN, self).__init__()
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(5000, 64)
self.conv = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv1d(in_channels=64,
out_channels=256,
kernel_size=5),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool1d(kernel_size=596))
self.f1 = nn.Linear(256, 10)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.embedding(x) # batch_size x text_len x embedding_size 64*600*64
x = x.permute(0, 2, 1) #64*64*600
x = self.conv(x) #Conv1后64*256*596,ReLU后不变,NaxPool1d后64*256*1
x = x.view(-1, x.size(1)) #64*256
x = F.dropout(x, 0.8)
x = self.f1(x) #64*10 batch_size * class_num
return x
if __name__ == '__main__':
net = TextRNN()
print(net)
模型训练
此部分可以选择使用RNN或者CNN模型进行训练,可以选择损失函数和优化器等等。
将训练好的模型保存在 model_params.pkl中
# coding: utf-8
from __future__ import print_function
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch import optim
from torch.autograd import Variable
import os
import numpy as np
from torch_model import TextRNN, TextCNN
from cnews_loader import read_vocab, read_category, batch_iter, process_file, build_vocab
def evaluate(model, Loss, x_val, y_val):
"""测试集上准确率评估"""
batch_val = batch_iter(x_val, y_val, 64)
acc = 0
los = 0
for x_batch, y_batch in batch_val:
size = len(x_batch)
x = np.array(x_batch)
y = np.array(y_batch)
x = torch.LongTensor(x)
y = torch.Tensor(y)
# y = torch.LongTensor(y)
# x = Variable(x)
# y = Variable(y)
out = model(x)
loss = Loss(out, y)
# optimizer.zero_grad()
# loss.backward()
# optimizer.step()
loss_value = np.mean(loss.detach().numpy())
accracy = np.mean((torch.argmax(out, 1) == torch.argmax(y, 1)).numpy())
acc +=accracy*size
los +=loss_value*size
return los/len(x_val), acc/len(x_val)
base_dir = 'cnews'
train_dir = os.path.join(base_dir, 'cnews.train.txt')
test_dir = os.path.join(base_dir, 'cnews.test.txt')
val_dir = os.path.join(base_dir, 'cnews.val.txt')
vocab_dir = os.path.join(base_dir, 'cnews.vocab.txt')
def train():
x_train, y_train = process_file(train_dir, word_to_id, cat_to_id,600)#获取训练数据每个字的id和对应标签的oe-hot形式
x_val, y_val = process_file(val_dir, word_to_id, cat_to_id,600)
#使用LSTM或者CNN
model = TextRNN()
# model = TextCNN()
#选择损失函数
Loss = nn.MultiLabelSoftMarginLoss()
# Loss = nn.BCELoss()
# Loss = nn.MSELoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(),lr=0.001)
best_val_acc = 0
for epoch in range(100):
i = 0
print('epoch:{}'.format(epoch))
batch_train = batch_iter(x_train, y_train,64)
for x_batch, y_batch in batch_train:
i +=1
# print(i)
x = np.array(x_batch)
y = np.array(y_batch)
x = torch.LongTensor(x)
y = torch.Tensor(y)
# y = torch.LongTensor(y)
# x = Variable(x)
# y = Variable(y)
out = model(x)
loss = Loss(out,y)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# 对模型进行验证
if i % 90 == 0:
los, accracy = evaluate(model, Loss, x_val, y_val)
#los, accracy = evaluate(model, Loss, optimizer, x_val, y_val)
print('loss:{},accracy:{}'.format(los, accracy))
if accracy > best_val_acc:
torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'model_params.pkl')
best_val_acc = accracy
if __name__ == '__main__':
#获取文本的类别及其对应id的字典
categories, cat_to_id = read_category()
#获取训练文本中所有出现过的字及其所对应的id
words, word_to_id = read_vocab(vocab_dir)
#获取字数
vocab_size = len(words)
print('train')
train()
由于训练时间过长,所以仅训练三轮,结果如下:
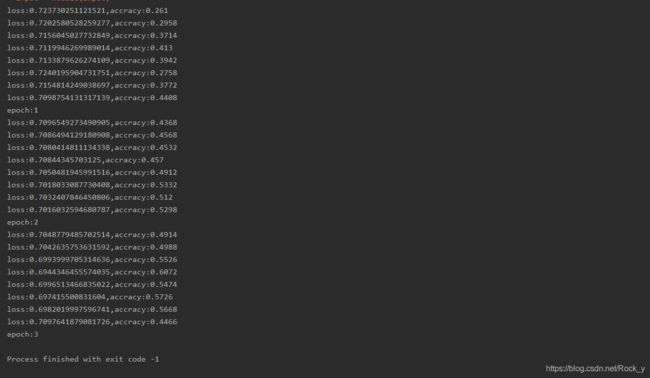
可以看到三轮过后,准确度最高达到了60%(由于训练次数较少所以准确度较低)
模型测试
torch_test.py:
提供CNN和RNN两种模型的预测,加载训练得到的模型model.state_dict
# coding: utf-8
from __future__ import print_function
import os
import tensorflow.contrib.keras as kr
import torch
from torch import nn
from cnews_loader import read_category, read_vocab
from torch_model import TextCNN,TextRNN
from torch.autograd import Variable
import numpy as np
try:
bool(type(unicode))
except NameError:
unicode = str
base_dir = 'cnews'
vocab_dir = os.path.join(base_dir, 'cnews.vocab.txt')
class CnnModel:
def __init__(self):
self.categories, self.cat_to_id = read_category()
self.words, self.word_to_id = read_vocab(vocab_dir)
self.model = TextCNN()
self.model.load_state_dict(torch.load('model_params.pkl'))
def predict(self, message):
# 支持不论在python2还是python3下训练的模型都可以在2或者3的环境下运行
content = unicode(message)
data = [self.word_to_id[x] for x in content if x in self.word_to_id]
data = kr.preprocessing.sequence.pad_sequences([data], 600)
data = torch.LongTensor(data)
y_pred_cls = self.model(data)
print(y_pred_cls)
class_index = torch.argmax(y_pred_cls[0]).item()
return self.categories[class_index]
class RnnModel:
def __init__(self):
self.categories, self.cat_to_id = read_category()
self.words, self.word_to_id = read_vocab(vocab_dir)
self.model = TextRNN()
self.model.load_state_dict(torch.load('model_params.pkl'))
def predict(self, message):
# 支持不论在python2还是python3下训练的模型都可以在2或者3的环境下运行
content = unicode(message)
data = [self.word_to_id[x] for x in content if x in self.word_to_id]
data = kr.preprocessing.sequence.pad_sequences([data], 600)
data = torch.LongTensor(data)
y_pred_cls = self.model(data)
class_index = torch.argmax(y_pred_cls[0]).item()
return self.categories[class_index]
if __name__ == '__main__':
# model = CnnModel()
model = RnnModel()
test_demo = ['三星ST550以全新的拍摄方式超越了以往任何一款数码相机',
'热火vs骑士前瞻:皇帝回乡二番战 东部次席唾手可得新浪体育讯北京时间3月30日7:00']
for i in test_demo:
print(i,":",model.predict(i))
三星ST550以全新的拍摄方式超越了以往任何一款数码相机 : 科技
热火vs骑士前瞻:皇帝回乡二番战 东部次席唾手可得新浪体育讯北京时间3月30日7:00 : 游戏
可以看到第一条数据预测正确,第二条数据错误,由于模型训练次数的原因
参考
https://github.com/Alic-yuan/nlp-beginner-finish/tree/master/task2
https://github.com/gaussic/text-classification-cnn-rnn
