JAVA程序设计:设计跳表(LeetCode:1206)
不使用任何库函数,设计一个跳表。
跳表是在 O(log(n)) 时间内完成增加、删除、搜索操作的数据结构。跳表相比于树堆与红黑树,其功能与性能相当,并且跳表的代码长度相较下更短,其设计思想与链表相似。
例如,一个跳表包含 [30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 90],然后增加 80、45 到跳表中,以下图的方式操作:
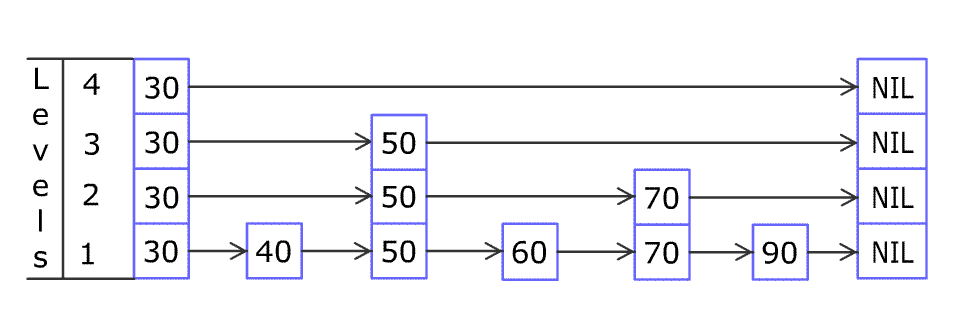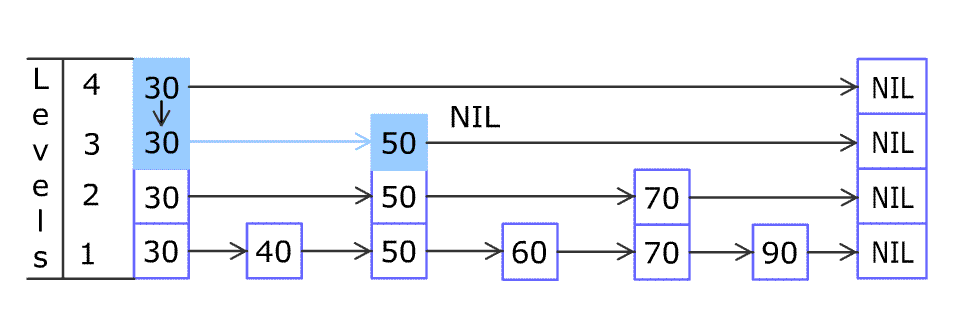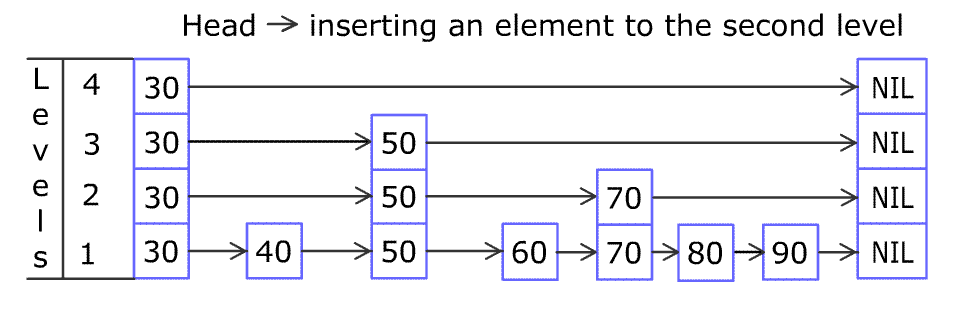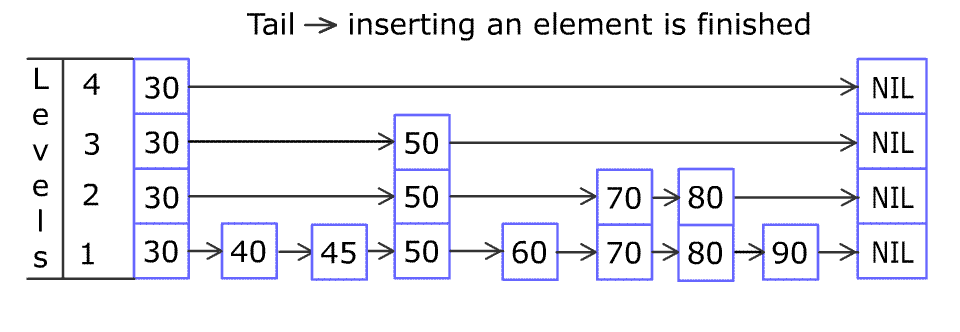
Artyom Kalinin [CC BY-SA 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons
跳表中有很多层,每一层是一个短的链表。在第一层的作用下,增加、删除和搜索操作的时间复杂度不超过 O(n)。跳表的每一个操作的平均时间复杂度是 O(log(n)),空间复杂度是 O(n)。
在本题中,你的设计应该要包含这些函数:
bool search(int target) : 返回target是否存在于跳表中。
void add(int num): 插入一个元素到跳表。
bool erase(int num): 在跳表中删除一个值,如果 num 不存在,直接返回false. 如果存在多个 num ,删除其中任意一个即可。
了解更多 : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Skip_list
注意,跳表中可能存在多个相同的值,你的代码需要处理这种情况。
样例:
Skiplist skiplist = new Skiplist();
skiplist.add(1);
skiplist.add(2);
skiplist.add(3);
skiplist.search(0); // 返回 false
skiplist.add(4);
skiplist.search(1); // 返回 true
skiplist.erase(0); // 返回 false,0 不在跳表中
skiplist.erase(1); // 返回 true
skiplist.search(1); // 返回 false,1 已被擦除
约束条件:
0 <= num, target <= 20000
最多调用 50000 次 search, add, 以及 erase操作。
方法一:用数组+set实现快速插入,删除以及查询操作,并且能够做到比跳表更优,不过违背了本题的初衷。
class Skiplist {
int[] nums;
Set st;
public Skiplist() {
nums = new int[20005];
st = new HashSet<>();
}
public boolean search(int target) {
return st.contains(target);
}
public void add(int num) {
st.add(num);
nums[num]++;
}
public boolean erase(int num) {
if (nums[num] == 0)
return false;
nums[num]--;
if (nums[num] == 0)
st.remove(num);
return true;
}
} 方法二:我们采用链表实现,每个节点分别存储节点的值、该链上下一个节点以及下一层链表的对应节点。
class Skiplist {
class node {
int val;
node next, down;
public node(int val, node next, node down) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
this.down = down;
}
}
private node head;
public Skiplist() {
head = new node(-1, null, null);
}
public boolean search(int target) {
node now = head;
while (now != null) {
while (now.next != null && now.next.val < target)
now = now.next;
if (now.next == null || now.next.val > target)
now = now.down;
else
return true;
}
return false;
}
public void add(int num) {
List list = new ArrayList<>();
node now = head;
while (now != null) {
while (now.next != null && now.next.val < num)
now = now.next;
list.add(now);
now = now.down;
}
node downNode = null;
boolean insertUp = true;
int index = list.size() - 1;
while (insertUp && index >= 0) {
node curInsert = list.get(index);
list.remove(index--);
curInsert.next = new node(num, curInsert.next, downNode);
downNode = curInsert.next;
int randint = (int) (1 + Math.random() * (10 - 1 + 1));
//产生1-10的随机数(只要是偶数长度范围内的随机数即可)
insertUp = (randint % 2 == 0 ? true : false);//50%的概率在上层插值
}
if (insertUp)
head = new node(-1, new node(num, null, downNode), head);
}
public boolean erase(int num) {
node now = head;
boolean seen = false;
while (now != null) {
while (now.next != null && now.next.val < num)
now = now.next;
if (now.next == null || now.next.val > num)
now = now.down;
else {
seen = true;
now.next = now.next.next;
now = now.down;
}
}
return seen;
}
}