Insert语句的语法
文档地址:http://docs.oracle.com/cd/B19306_01/server.102/b14200/statements_9014.htm#i2064185
(DML_table_expression_clause::=)
values_clause::=

Description of the illustrationvalues_clause.gif
--可见values里头的语法:只有表达式 或者 默认 (既是如果columnlist中有存在列在设计表的时候有默认值,那么可以使用DEFAULT来代替任何值在 values_clause子句中。见下英文说明)
values_clause
For a single-table insert operation,specify a row of values to be inserted into the table or view. Youmust specify a value in the values_clause for each column inthe column list. If you omit the column list, then thevalues_clause must providevalues for every column in the table.
For a multitable insert operation, each expression inthe values_clause must refer tocolumns returned by the select list of the subquery. If you omitthe values_clause, then the selectlist of the subquery determines the values to be inserted, so itmust have the same number of columns as the column list of thecorresponding insert_into_clause. If you donot specify a column list in the insert_into_clause, then thecomputed row must provide values for all columns in the targettable.
For both types of insert operations, if you specify a column listin the insert_into_clause, then thedatabase assigns to each column in the list a corresponding valuefrom the values clause or the subquery. You can specify DEFAULT for any value in thevalues_clause.If you have specified a default value for thecorresponding column of the table or view, then that value isinserted.
If no default value for the corresponding column hasbeen specified, then the database inserts null.
--这说法似乎有点问题。当相关列不允许空值的时候,数据库插入操作会失败。需要说明各个列为空。这时候,你不指定默认值,那么插入就为NULL。
Please refer to "About SQL Expressions"and SELECT for syntax of valid expressions.
Note:
Parallel direct-path
INSERT supports only the subquerysyntax of the
INSERT statement, not the
values_clause. Please refer to
OracleDatabase Concepts for information on serial and paralleldirect-path
INSERT.
Restrictions onInserted Values The value are subject tothe following restrictions:
-
You cannot insert a
BFILEvalue until you haveinitialized theBFILElocator to null or to adirectory name and filename.See Also:
-
BFILENAME for information on initializing
BFILEvalues and for an example of inserting into aBFILE -
OracleCall Interface Programmer's Guide and Oracle Database Application Developer's Guide -Fundamentals for information on initializing
BFILElocators
-
-
When inserting into a list-partitioned table, you cannot inserta value into the partitioning key column that does not alreadyexist in the
partition_valuelist of one ofthe partitions. -
You cannot specify
DEFAULTwhen inserting into aview. -
If you insert string literals into a
RAWcolumn,then during subsequent queries Oracle Database will perform a fulltable scan rather than using any index that might exist on theRAWcolumn.
See Also:
-
"Using XML in SQL Statements" for information on insertingvalues into an XMLType table
-
"Inserting into a Substitutable Tables and Columns: Examples","Inserting Using the TO_LOB Function: Example", "Inserting Sequence Values: Example", and "Inserting Using Bind Variables: Example"
文档地址:http://docs.oracle.com/cd/B19306_01/appdev.102/b14261/insert_statement.htm#LNPLS01325
---下边是比较重要的INSERT的语法。
INSERT Statement
TheINSERT statement adds one or more new rows of data toa database table. For a full description of the INSERTstatement, see Oracle Database SQL Reference.
Syntax
insert statement ::=
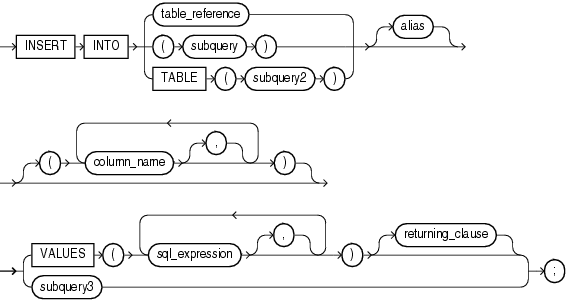
Description of the illustrationinsert_statement.gif
Keyword and ParameterDescription
alias
Another (usually short) name for the referenced table orview.
column_name[, column_name]...
A list of columns in a database table or view. The columns canbe listed in any order, as long as the expressions in theVALUES clause are listed in the same order. Eachcolumn name can only be listed once. If the list does not includeall the columns in a table, each missing columns is set toNULL or to a default value specified in theCREATE TABLE statement.
returning_clause
Returns values from inserted rows, eliminating the need toSELECT the rows afterward. You can retrieve the columnvalues into variables or into collections. You cannot use theRETURNING clause for remote or parallel inserts. Ifthe statement does not affect any rows, the values of the variablesspecified in the RETURNING clause are undefined. Forthe syntax of returning_clause, see "RETURNING INTO Clause".
sql_expression
Any expression valid in SQL. For example, it could be aliteral, a PL/SQL variable, or a SQL query that returns a singlevalue. For more information, see OracleDatabase SQL Reference. PL/SQL alsolets you use a record variable here.
---在SQL中任意一个表达式都有效。例如:可以是一个字符、一个PL/SQL变量、或者能够返回单独值的一个SQL查询。
subquery
A SELECT statement that provides a set of rows forprocessing. Its syntax is like that ofselect_into_statement without the INTOclause. See "SELECT INTO Statement".
subquery3
A SELECT statement that returns a set of rows. Eachrow returned by the select statement is inserted into the table.The subquery must return a value for every column in the columnlist, or for every column in the table if there is no columnlist.
table_reference
A table or view that must be accessible when you execute theINSERT statement, and for which you must haveINSERT privileges. For the syntax oftable_reference, see "DELETE Statement".
TABLE (subquery2)
The operand of TABLE is a SELECTstatement that returns a single column value representing a nestedtable. This operator specifies that the value is a collection, nota scalar value.
VALUES (...)
Assigns the values of expressions to corresponding columns inthe column list. If there is no column list, the first value isinserted into the first column defined by the CREATETABLE statement, the second value is inserted into thesecond column, and so on. There must be one value for each columnin the column list. The datatypes of the values being inserted mustbe compatible with the datatypes of corresponding columns in thecolumn list.
Usage Notes
Character and date literals in the VALUES list mustbe enclosed by single quotes ('). Numeric literals are not enclosedby quotes.
The implicit cursor SQL and the cursor attributes%NOTFOUND, %FOUND,%ROWCOUNT, and %ISOPEN let you accessuseful information about the execution of an INSERTstatement.