spark-事件总线
1、CopyOnWriteArrayList:java的一个集合 implements List, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable,写入时复制。当线程读的时候不上锁,写的时候进行上锁一份复制副本,写入改副本写完替换就对象。在写的过程中其他进程读的就是老数据。
public boolean add(E e) {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock(); //上锁,只能一个线程进来写,其他的等着
try {
Object[] elements = getArray();
int len = elements.length;
Object[] newElements = Arrays.copyOf(elements, len + 1);
newElements[len] = e;
setArray(newElements);
return true;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
2、LinkedBlockingQueue: 一个阻塞的线程安全的队列,底层应该采用链表实现
添加元素的方法有三个:add,put,offer。
public static void main(String args[]){
try {
LinkedBlockingQueue queue=new LinkedBlockingQueue(2);
queue.add("hello");
queue.add("world");
queue.add("yes");
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//运行结果:
java.lang.IllegalStateException: Queue full
at java.util.AbstractQueue.add(Unknown Source)
at com.wjy.test.GrandPather.main(GrandPather.java:12)
public static void main(String args[]){
try {
LinkedBlockingQueue queue=new LinkedBlockingQueue(2);
queue.put("hello");
queue.put("world");
queue.put("yes");
System.out.println("yes");
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//运行结果:
//在queue.put("yes")处发生阻塞
//下面的“yes”无法输出
public static void main(String args[]){
try {
LinkedBlockingQueue queue=new LinkedBlockingQueue(2);
boolean bol1=queue.offer("hello");
boolean bol2=queue.offer("world");
boolean bol3=queue.offer("yes");
System.out.println(queue.toString());
System.out.println(bol1);
System.out.println(bol2);
System.out.println(bol3);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//运行结果:
[hello, world]
true
true
false
从队列中取出并移除头元素的方法有:poll,remove,take。
poll: 若队列为空,返回null。
remove:若队列为空,抛出NoSuchElementException异常。
take:若队列为空,发生阻塞,等待有元素。
==========================================================================================================================================================================================================================================
监听:理解为对某些特定的动作,做一个单独的处理。比如说人吃饭,吃饭这个动作(事件)触发时,我去记录下他的吃饭事件。。。。一个事件的触发引起一些处理。
spark中就有一个事件总线来监听特殊的一些事件发生。为什么要做事件总线,是因为每个方法调用自己去实现代码很复杂,也不好管理。
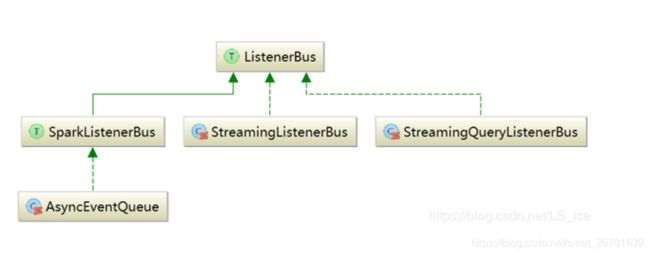
总体结构如下:这个是到 LiveListenerBus 这个类,对外的统一的类。
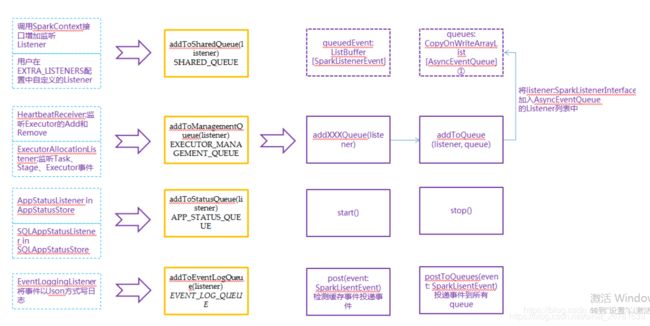
父类 ListenerBus,
SparkListenerBus:用于将SparkListenerEvent类型的事件投递到SparkListenerInterface类型的监听器;
StreamingQueryListenerBus:用于将StreamingQueryListener.Event类型的事件投递到StreamingQueryListener类型的监听器,此外还会将StreamingQueryListener.Event类型的事件交给SparkListenerBus;
StreamingListenerBus:用于将StreamingListenerEvent类型的事件投递到StreamingListener类型的监听器,此外还会将StreamingListenerEvent类型的事件交给SparkListenerBus。
从外部调用post后的代码流程。
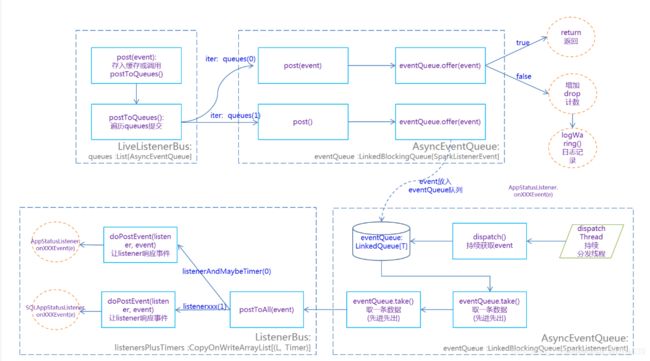
LiveListenerBus:
private val queues = new CopyOnWriteArrayListAsyncEventQueue
该queues存放了 AsyncEventQueue
private class AsyncEventQueue(
val name: String,
conf: SparkConf,
metrics: LiveListenerBusMetrics,
bus: LiveListenerBus)
extends SparkListenerBus
目前有四种name:
def addToSharedQueue(listener: SparkListenerInterface): Unit = {
addToQueue(listener, SHARED_QUEUE)
}
/** Add a listener to the executor management queue. */
def addToManagementQueue(listener: SparkListenerInterface): Unit = {
addToQueue(listener, EXECUTOR_MANAGEMENT_QUEUE)
}
/** Add a listener to the application status queue. */
def addToStatusQueue(listener: SparkListenerInterface): Unit = {
addToQueue(listener, APP_STATUS_QUEUE)
}
/** Add a listener to the event log queue. */
def addToEventLogQueue(listener: SparkListenerInterface): Unit = {
addToQueue(listener, EVENT_LOG_QUEUE)
}
就是通过LiveListenerBus的addto…Queue初始化 AsyncEventQueue 。
然后调用post
/** Post an event to all queues. */
def post(event: SparkListenerEvent): Unit = {
if (stopped.get()) {
return
}
metrics.numEventsPosted.inc()
// If the event buffer is null, it means the bus has been started and we can avoid
// synchronization and post events directly to the queues. This should be the most
// common case during the life of the bus.
if (queuedEvents == null) {
postToQueues(event)
return
}
// Otherwise, need to synchronize to check whether the bus is started, to make sure the thread
// calling start() picks up the new event.
synchronized {
if (!started.get()) {
queuedEvents += event
return
}
}
// If the bus was already started when the check above was made, just post directly to the
// queues.
// 把事件丢入所有的queue
postToQueues(event)
}
private def postToQueues(event: SparkListenerEvent): Unit = {
val it = queues.iterator()
while (it.hasNext()) {
it.next().post(event)
}
}
比如这样 listenerBus.post(SparkListenerBlockUpdated(BlockUpdatedInfo(_updateBlockInfo)))。
相当于把 SparkListenerBlockUpdated 丢给总线中的所有queue。然后queue中的dispatch会做执行,具体会到具体监听的类,,,,
// 线程运行
private val dispatchThread = new Thread(s"spark-listener-group-$name") {
setDaemon(true)
override def run(): Unit = Utils.tryOrStopSparkContext(sc) {
dispatch()
}
}
private def dispatch(): Unit = LiveListenerBus.withinListenerThread.withValue(true) {
var next: SparkListenerEvent = eventQueue.take()
while (next != POISON_PILL) {
val ctx = processingTime.time()
try {
super.postToAll(next)
} finally {
ctx.stop()
}
eventCount.decrementAndGet()
next = eventQueue.take()
}
eventCount.decrementAndGet()
}