SparkCore之运行架构
参考官网:http://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/cluster-overview.html
Cluster Mode Overview
集群模式概述
This document gives a short overview of how Spark runs on clusters, to make it easier to understand the components involved. Read through the application submission guide to learn about launching applications on a cluster.
这篇文档简短概述了Spark如何在集群上运行,以便理解所涉及到的组件更加容易一些。阅读应用程序提交指南 ,了解有关在群集上启动应用程序的信息。
Components
组件
Spark applications run as independent sets of processes on a cluster, coordinated by the SparkContext object in your main program (called the driver program).
sets of processes:进程的集合
Spark应用程序在集群上以独立的进程集合运行,由主程序(称作驱动程序)中的SparkContext对象来协调和组织。一个Spark应用程序包括一个driver和多个executors。
分析:Spark应用程序是一组独立的进程,这些进程有哪些?一个driver program进程和多个executors进程组成。
Specifically, to run on a cluster, the SparkContext can connect to several types of cluster managers (either Spark’s own standalone cluster manager, Mesos or YARN), which allocate resources across applications. Once connected, Spark acquires executors on nodes in the cluster, which are processes that run computations and store data for your application. Next, it sends your application code (defined by JAR or Python files passed to SparkContext) to the executors. Finally, SparkContext sends tasks to the executors to run.
具体来说,集群模式下,SparkContext 能够连接不同类型的cluster managers集群管理器,比如说Spark自己的standalone cluster manager, Mesos或者YARN,而这些cluster managers所扮演的角色是在各个应用程序application之间分配资源。一旦Spark连接上这些cluster managers,Spark就获得了分布在集群各个节点上的executors,这些executors其实是一系列的进程,这些进程负责执行我们的应用程序application中的计算并存储相关的数据。接着,SparkContext将我们的应用程序代码发送给executors,这些应用程序代码是由JAR或者Python文件所定义并且传给SparkContext。最后,SparkContext把tasks发送给executors去执行。
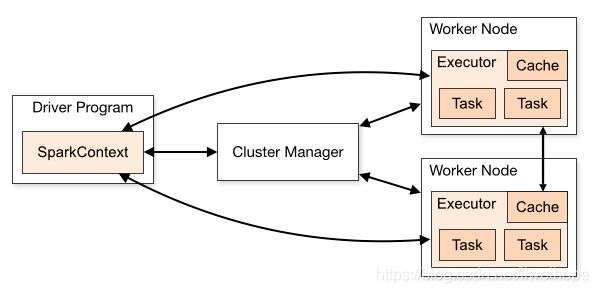
Driver program里面包含SparkContext,它为了能够在集群上去运行,能够把作业运行到集群上面,需要SparkContext需要通过Cluster manager去集群上申请资源,比如去了两个节点上面申请了两个executors。一旦连接上,拿到了资源,获得了分布在集群各个节点上的executors后,SparkContext就可以将我们的应用程序代码发送给executors。最后,SparkContext把tasks发送给executors去执行。
关于这个体系结构,需要注意以下几点:
-
1.Each application gets its own executor processes, which stay up for the duration of the whole application and run tasks in multiple threads. This has the benefit of isolating applications from each other, on both the scheduling side (each driver schedules its own tasks) and executor side (tasks from different applications run in different JVMs). However, it also means that data cannot be shared across different Spark applications (instances of SparkContext) without writing it to an external storage system.
每个Spark应用程序都有属于它自己本身的executor进程,这些进程在这个Spark应用程序的整个生命周期都一直存活着,并且以多线程的方式来执行内部的多个tasks。这样做的好处是使各个应用之间相互隔离,无论是在调度层面scheduling side还是在执行层面executor side都是相互隔离的,从调度层面来看,每个driver调度属于它自身的tasks,从执行层面上来看,属于不同applications的tasks运行在不同的JVM上,(假如现在有两个Spark应用程序,分别有多个executors,这些executors分布在各个节点之上,假如两个Spark应用程序的其中分别有一个executor,它俩是可以在同一个节点上运行的,而且互不影响) 。然而,这也意味着不同的Spark applications(就是SparkContext的实例)之间是不能共享各自所属的数据,除非,你把数据写到外部存储系统。还有一个方法可以不用写到外部存储系统,比如说Alluxio内存高速虚拟分布式存储系统。 -
2.Spark is agnostic to the underlying cluster manager. As long as it can acquire executor processes, and these communicate with each other, it is relatively easy to run it even on a cluster manager that also supports other applications (e.g. Mesos/YARN).
Spark并不关心底层的cluster manager。只要Spark可以获取得到executor进程,并且这些executor进程能够互相通信,那么这个Spark应用程序即使运行在 同样支持其他applications的cluster manager(比如Mesos/YARN)上面相对来说也是比较容易的。
就是说spark可以跑在好多个地方,但是它并不去关心你的底层,不管你是standalone 还是Mesos还是YARN,它的代码都是一样的。 -
3.The driver program must listen for and accept incoming connections from its executors throughout its lifetime (e.g., see spark.driver.port in the network config section). As such, the driver program must be network addressable from the worker nodes.
在driver program的整个生命周期中,它一直在监听并且接收来自其executors的连接。(可以查看spark.driver.port in the network config sectio)。因此,driver program必须跟各个worker nodes节点网络互通。 -
4.Because the driver schedules tasks on the cluster, it should be run close to the worker nodes, preferably on the same local area network. If you’d like to send requests to the cluster remotely, it’s better to open an RPC to the driver and have it submit operations from nearby than to run a driver far away from the worker nodes.
由于driver是在集群上调度各个任务的,所以它应该靠近工作节点运行,最好是在同一局域网上运行。如果你想发送请求给远端的集群,最好向驱动程序打开RPC并让它从附近提交操作,而不是远离工作节点运行驱动程序。
Cluster Manager Types
集群管理类型
The system currently supports several cluster managers:
- Standalone – a simple cluster manager included with Spark that makes it easy to set up a cluster.
- Apache Mesos – a general cluster manager that can also run Hadoop MapReduce and service applications.
- Hadoop YARN – the resource manager in Hadoop 2.
- Kubernetes – an open-source system for automating deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications.
Spark现在直接支持以下几种集群管理器:
- Standalone – 一个简单的cluster manager,Spark内置的,使得我们设置一个集群变得很容易。
- Apache Mesos – 一个通用的cluster manager,它也可以运行Hadoop MapReduce以及service applications。
- Hadoop YARN – Hadoop 2.x中的resource manager。
- Kubernetes – 一个开源的项目,用于自动部署,扩容以及容器内部应用的管理。
Submitting Applications
Applications can be submitted to a cluster of any type using the spark-submit script. The application submission guide describes how to do this.
通过spark-submit脚本,我们可以把应用Applications提交到任何类型的集群上。这篇 application submission guide 文章描述了具体的实现方式。
Monitoring
Each driver program has a web UI, typically on port 4040, that displays information about running tasks, executors, and storage usage. Simply go to http://:4040 in a web browser to access this UI. The monitoring guide also describes other monitoring options.
每个驱动程序有一个web UI,典型的是在4040端口,你可以看到有关运行的任务、executors和存储空间大小等信息。我们可以通过浏览器访问http://:4040来浏览这个UI界面。这篇monitoring guide文章详细介绍了其他监控选项。
Job Scheduling
Spark gives control over resource allocation both across applications (at the level of the cluster manager) and within applications (if multiple computations are happening on the same SparkContext). The job scheduling overview describes this in more detail.
Spark在跨应用程序(在集群管理器的级别)和应用程序内(在同一个SparkContext上运行多个计算)中,对资源分配进行控制。 job scheduling overview 更加详细的描述了这个特性。
Glossary(术语)
| Term | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Application | User program built on Spark. Consists of a driver program and executors on the cluster. |
| Application jar | A jar containing the user’s Spark application. In some cases users will want to create an “uber jar” containing their application along with its dependencies. The user’s jar should never include Hadoop or Spark libraries, however, these will be added at runtime. |
| Driver program | The process running the main() function of the application and creating the SparkContext |
| Cluster manager | An external service for acquiring resources on the cluster (e.g. standalone manager, Mesos, YARN) |
| Deploy mode | Distinguishes where the driver process runs. In “cluster” mode, the framework launches the driver inside of the cluster. In “client” mode, the submitter launches the driver outside of the cluster. |
| Worker node | Any node that can run application code in the cluster |
| Executor | A process launched for an application on a worker node, that runs tasks and keeps data in memory or disk storage across them. Each application has its own executors. |
| Task | A unit of work that will be sent to one executor |
| Job | A parallel computation consisting of multiple tasks that gets spawned in response to a Spark action (e.g. save, collect); you’ll see this term used in the driver’s logs. |
| Stage | Each job gets divided into smaller sets of tasks called stages that depend on each other (similar to the map and reduce stages in MapReduce); you’ll see this term used in the driver’s logs. |
| 术语 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| Application | 基于Spark进行构建的用户程序 。由集群中的一个driver program以及多个executors组成。 |
| Application jar | 包含用户的Spark应用程序的Jar包。在某些场景下,用户可能想创建“Uber jar”,它包含用户的应用程序和它的依赖。用户的Jar不应该包含Hadoop和Spark的类库。不过这些类库将会在运行时被加载。 |
| Driver program | Driver program是一个进程,它运行应用程序application里面的main()函数,并在main函数里面创建SparkContext |
| Cluster manager | 一个外部服务,用于获取集群资源(比如: standalone manager, Mesos, YARN ) |
| Deploy mode | 区分驱动程序进程的运行位置。在“集群”模式下,框架在集群内部启动驱动程序。在“客户端”模式下,提交者在集群外部启动驱动程序,在本地local启动driver,就是你在哪里提交,在哪台机器上提交,就在哪台机器上运行这个driver program。 |
| Worker node | 任何可以在群集中运行应用程序代码的节点 |
| Executor | 在worker node上启动应用程序的进程,这个进程可以运行多个任务并将数据保存在内存或磁盘存储中。每个Spark应用程序都有它自己的一组executors。 |
| Task | 被发送给一个executor的工作单元。每个executor上面可以跑多个task。 |
| Job | 由Spark action触发的由多个tasks组成的并行计算。当一个Spark action(如save, collect)被触发,一个包含很多个tasks的并行计算的job将会生成。你可以在driver’s logs看到这个术语。就是说只要Spark 程序触发了一个action,它就是一个job。 |
| Stage | 每个job被切分成小的任务集,这些小的任务集叫做stages,并且他们之间相互依赖(类似于MapReduce中的map和reduce阶段)。你可以在driver’s logs看到这个术语。 |
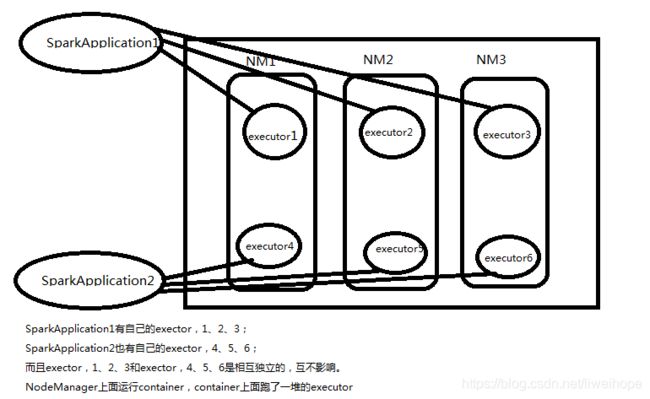
总结一下,所谓的Spark应用程序,它包含一个driver加上多个executor。所谓的driver,它是运行我们的Spark应用程序里面的main方法,并且在里面创建SparkContext的一个进程。所谓的Cluster manager,它是一个外部服务,用于申请集群资源。所谓的Deploy mode,它分为两种模式,client和cluster模式,client模式下,就是driver跑在本地,如果是cluster模式,就是driver跑在集群里面。所谓的Worker node,就是在它上面可以跑executor进程,对于Yarn来说,就是NM上面运行container。所谓的executor,它是一个进程,这个进程可以运行多个任务并将数据保存在内存或磁盘存储中,每个Spark应用程序都有它自己的一组executors。所谓的job,就是当一个Spark应用程序遇到一个action的时候,就会创建一个job,job里面会有很多个task,task是进行计算的最小单元,task将会被发送到executor上面去执行。