Matlab——离散点的随机区域分配
Matlab——离散点的随机区域分配
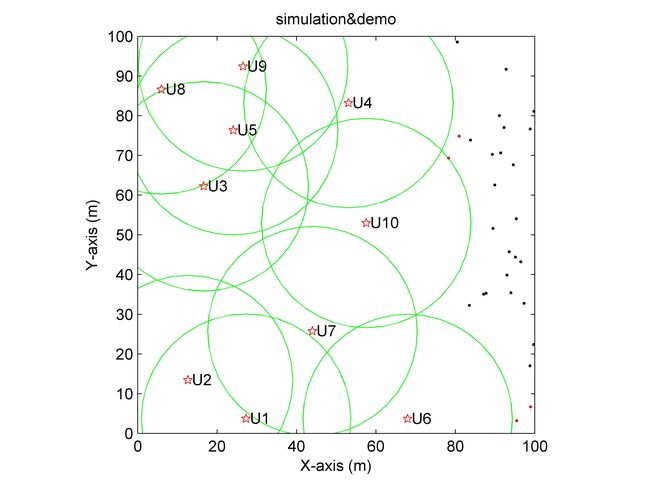
假设待定区域现在有200个离散点,我们随机挑选出10个离散点,并以这10个点为中心画半径为R(任意取)的圆。我们知道这10个圆在没有任何交集的情况下,共有10个区域,每个区域中的离散点统计起来都很简单。但是,如果这10个区域存在交集,假设两个圆U1,U2相交,得到三个区域,如用Area_1,Area_2,与Area_12表示,此时获取这三个区域的离散点也不是太难。如果选取的中心点增多时,比如下图,此时交集比较难确定,我们先直观感受一下:
图 1 离散点随机区域划分结果
解释说明:
(1)黑色的点为200个随机离散点,具有标号1~200;
(2)标有红色五角星的黑色点:被选中的10个随机点(当然,数字10也可以任意选取);
(3)绿色的圆形区域:10个中心点在半径R下所画的圆;
(4)红线:10个点中,两两间距小于2R的中中心点连线;
(5)U1~U10:表示10个初始区域。
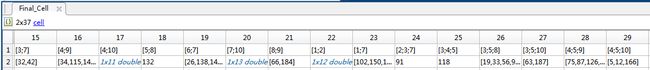
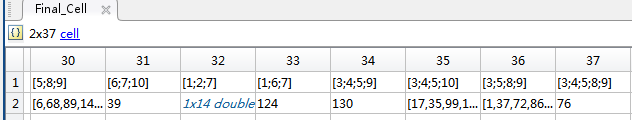
问题来了,那些密密麻麻的交集如何表示?还需要求每个交集中的离散点,有的存在离散点,有的没有!这里我选择用Matlab里面的元胞来表示!运行结果如下:
这个元胞的具体含义为:
(1)横坐标为交集区域的一种描述,如第33列的第一行[1,6,7]表示该区域为Area_1,Area_6与Area_7的交集;
(2)纵坐标为指定区域中的离散点编号,如第33列的第二行中的124表示编号为124的离散点。
我们可以借助上图证实一下,确实如此。
有时候,我们或许对那些不在目标区域内部的离散点(离群点)感兴趣,首先我们将在目标区域的离散点删掉,即下图2(红色点为边界点,具体见代码),再画一个凸包然后得到下图3。
图 2 删除目标区域内部点的效果
图 3 非目标区域离散点的凸包
其中运行过程的所有结果为myResults.mat文件,下载地址为离散点的随机区域分配
matlab的运行代码(命令文件)如下:
close all;
clear;
clc;%%寻找交区域
%% 绘制区域图
xm = 100; %横坐标长度
ym = 100; %纵坐标长度
sink.x = xm/2; %基站横坐标
sink.y = ym+50; %基站纵坐标
density = 1/50; %节点密度
n = xm*ym*density; %节点个数
Eo = 0.5; %初始能量
packetLength = 3000; %数据报长度
ctrPacketLength = 300; %控制数据报
Eelec = 50*0.000000001;
ETX = 50*0.000000001; %电路发送一比特所需能量
ERX = 50*0.000000001;
Efs = 10*0.000000000001; %自由空间模型发送一比特数据功放所需能量
Emp = 0.0013*0.000000000001; %多径衰落模型功放
EDA = 5*0.000000001; %数据汇聚所需能量
INFINITY = 999999999999999;
rmax = 8000 ; %最大迭代轮数
do = sqrt(Efs/Emp); %传输距离>do为多径衰落模型,<则为自由空间模型
% d_to_BS=((sink.y-ym) + (sink.y))/2;
% n_CH_opt=sqrt(n/2*pi)*sqrt(Efs/Emp)*sqrt(xm*ym)/d_to_BS^2;
% R = sqrt(xm*ym/(pi*n_CH_opt)); %节点通信半径
d_to_BS = (abs(sink.y-ym)+sqrt(sink.x^2+sink.y^2))/2;
n_CH_opt = sqrt(n/(2*pi))*sqrt(Efs/Emp)*sqrt(xm*ym)/(d_to_BS^2);
R = sqrt(xm*ym/(n_CH_opt*pi));
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% END OF PARAMETERS %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
for i = 1:n
S(i).xd = rand(1,1)*xm;%坐标
S(i).yd = rand(1,1)*ym;
S(i).G = 0; %=0表示有资格成为簇头
S(i).cl = 0;%成为簇头的次数
S(i).type = 'N';%普通节点
S(i).E = Eo;
S(i).Dis = 'n';
end
S(n+1).xd = sink.x;
S(n+1).yd = sink.y;
figure(1);
for i = 1:n
plot(S(i).xd,S(i).yd,'k.');
hold on;
end
plot(S(n+1).xd,S(n+1).yd,'bp');
ylabel('Y-axis (m)','fontsize',10);
xlabel('X-axis (m)','fontsize',10);
title('simulation&demo');
hold on
%load d:\wu\mat\Init;
%load C:\Users\Zhangwei\Documents\MATLAB\mat\Init;
%% 加入特殊点
Unique_num = 10 ;%%待输入的值
Unique_node = 100*rand(Unique_num,2);
CH=[10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100];
%Unique_num = length(CH);
temp = [];
temp1 = [];
for i=1:length(CH)
temp = [temp S(CH(i)).xd];
temp1 = [temp1 S(CH(i)).yd];
end
Unique_node = [temp' temp1'];
Unique_node_x = Unique_node(:,1);
Unique_node_y = Unique_node(:,2);
hold on;
for i = 1:Unique_num
theta = 0:pi/20:2*pi;
Circle1 = Unique_node(i,1)+R*cos(theta);
Circle2 = Unique_node(i,2)+R*sin(theta);
plot(Circle1,Circle2,'g-');
hold on
end
axis equal
for ii = 1:Unique_num
text(Unique_node_x(ii)+1,Unique_node_y(ii),strcat('U',num2str(ii)),'fontsize',10);
end
hold on
plot(Unique_node_x,Unique_node_y,'rp');
axis([0 100 0 100]);%%设置图的大小
hold on
%% 求特殊点之间的距离(若两点距离小于2*R,连边便于观察)
Unique_dis = zeros(Unique_num-1,Unique_num);
for ii = 1:Unique_num
for jj = ii+1:Unique_num
Unique_dis(ii,jj) = sqrt((Unique_node_x(ii)-Unique_node_x(jj)).^2+(Unique_node_y(ii)-Unique_node_y(jj)).^2);
if(Unique_dis(ii,jj)<=2*R)
plot([Unique_node_x(ii) Unique_node_x(jj)],[Unique_node_y(ii) Unique_node_y(jj)],'r-');
hold on
end
end
end
%%%获取普通点的x与y坐标
Ordinary_node_x = cat(1,S.xd);
Ordinary_node_y = cat(1,S.yd);
Ordinary_node = [Ordinary_node_x Ordinary_node_y]';
for i=1:length(CH)
temp = ismember(Ordinary_node, [S(CH(i)).xd;S(CH(i)).yd])*(-1)+1;
Ordinary_node = Ordinary_node.*temp;
end
Ordinary_num = 200;
%% 进行判断
if(Unique_num == 0)
disp(' 没有特殊点! 请修改参数!');
end
% %%特殊点个数为1的情况
% UandO_dis = zeros(1,Ordinary_num);
% U1_x = [];U1_y = []; U1_UO_dis = [];
% if(Unique_num == 1)
% for jj = 1:Ordinary_num
% UandO_dis(jj) = sqrt((Ordinary_node_x(jj)-Unique_node(1,1)).^2+(Ordinary_node_y(jj)-Unique_node(1,2)).^2);
% if( UandO_dis(jj) <= R)
% U1_x = [U1_x Ordinary_node_x(jj)];
% U1_y = [U1_y Ordinary_node_y(jj)];
% U1_UO_dis = [U1_UO_dis UandO_dis(jj)];
% end
% end
% %%U1中的点的集合
% U1 = [U1_x;U1_y;U1_UO_dis];%%第一行为横坐标,第二行为纵坐标,第三行为普通点与特殊点之间的距离
% % fprintf('当只有一个特殊点U1时,有%d个点在圆内或圆上!\n',length(U1));
% % return;
% U1= U1'
% end
%% 特殊点的个数大于等于1的情况(其实包括个数为1的情况)
%if(Unique_num>=1)
if(Unique_num>=1)
for i = 1:Unique_num
for k = 1:Ordinary_num
UandO_dis(i,k) = sqrt((Ordinary_node_x(k)-Unique_node(i,1)).^2+(Ordinary_node_y(k)-Unique_node(i,2)).^2);
if( UandO_dis(i,k)<=R)
U(i,k) = k;
else
U(i,k) = 0;
end
end
end
end
%% 返回每个普通点所在区域的个数num、交集Intersection 、交集区域内的点IntersectionPoints
%%% Intersection 指的是Unique_num个区域内普通点的具体分布矩阵,例如:第一行的第二列的值为0,代表第2个普通点不在U1内。
Intersection = [];
IntersectionPoints = [];
Intersection_1 = [];
IntersectionPoints_1 = [];
Intersection_0 = [];
IntersectionPoints_0 = [];
for k = 1:Ordinary_num
AllNodes_num(k) = length(find(U(1:Unique_num,k) ~= 0));
if(length(find(U(1:Unique_num,k))) == 0)
Intersection_0 = [Intersection_0 k];
IntersectionPoints_0 = [IntersectionPoints_0 Ordinary_node(:,k)];
end
if(length(find(U(1:Unique_num,k))) == 1)
Intersection_1 = [ Intersection_1 U(1:Unique_num,k)];
IntersectionPoints_1 = [IntersectionPoints_1 Ordinary_node(:,k)];
end
if(length(find(U(1:Unique_num,k))) >= 2)
Intersection = [ Intersection U(1:Unique_num,k)];
IntersectionPoints = [IntersectionPoints Ordinary_node(:,k)];
end
end
%删除重复特殊点
for i=1:length(CH)
[temp1 temp2]=find(Intersection==CH(i));
Intersection(:,temp2)=[];
end
for i=1:length(CH)
[temp1 temp2]=find(Intersection_0==CH(i));
Intersection_0(:,temp2)=[];
end
for i=1:length(CH)
[temp1 temp2]=find(Intersection_1==CH(i));
Intersection_1(:,temp2)=[];
end
%% 完善Intersection矩阵,因为一个点可以同时在多个区域
% for ii = 1:length(Intersection)
% if(length(find(Intersection(:,ii)~=0)) >= 3)
% [Final_Intersection{ii}] = GetSubsetAndMerge(Intersection(:,ii));
% end
% end
% UU=[];
% for i = 1:length(Final_Intersection)
% idx = cellfun(@(x)~isempty(x),Final_Intersection,'UniformOutput',true);
% if(idx(i) == 1)
% UU = [UU Final_Intersection{i}{1}];
% end
% end
% Intersection = [unique([Intersection UU]','rows')]';%%删除Intersection中的重复列
%% 特殊情况讨论
if(Unique_num == 1)
FinalNullAreaNodes_cell = {};
FinalOneAreaNodes_cell = cell(2,Unique_num);
FinalNullAreaNodes_cell{1,1} = 0;
FinalNullAreaNodes_cell{2,1} = Intersection_0';
for i = 1:Unique_num
FinalOneAreaNodes_cell{1,i} = i ;%特殊点编号所在的位置
for j =1:length(Intersection_1(1,:))
if(Intersection_1(i,j) ~= 0)
FinalOneAreaNodes_cell{2,i} = [FinalOneAreaNodes_cell{2,i} Intersection_1(i,j)];%相应特殊点内的普通点
end
end
end
Final_Cell = cat(2,cat(2, FinalNullAreaNodes_cell, FinalOneAreaNodes_cell));
elseif(Unique_num >=2 && length(Intersection)==0)
FinalNullAreaNodes_cell = {};
FinalOneAreaNodes_cell = cell(2,Unique_num);
FinalNullAreaNodes_cell{1,1} = 0;
FinalNullAreaNodes_cell{2,1} = Intersection_0';
FinalOneAreaNodes_cell = cell(2,Unique_num);
for i = 1:Unique_num
FinalOneAreaNodes_cell{1,i} = i ;%特殊点编号所在的位置
for j =1:length(Intersection_1(1,:))
if(Intersection_1(i,j) ~= 0)
FinalOneAreaNodes_cell{2,i} = [FinalOneAreaNodes_cell{2,i} Intersection_1(i,j)];%相应特殊点内的普通点
end
end
end
Final_Cell = cat(2,cat(2, FinalNullAreaNodes_cell, FinalOneAreaNodes_cell));
elseif(length(Intersection)~=0)
Points = [];
if (length(Intersection)>0)
Point_cell = cell(1,length(Intersection(1,:)));
for j = 1:length(Intersection(1,:)) %修改Intersection_1
Points(j) = max(sort(Intersection(1:Unique_num,j)));
Point_cell{1,j} = find(Intersection(1:Unique_num,j) ~= 0);
end
end
%%元胞数组删除重复项
[~,k] = unique(cellfun(@char,cellfun(@getByteStreamFromArray,Point_cell,'un',0),'un',0));
IntersectionArea = Point_cell(k);
%%确定相交区域每个元胞中的普通点数
FinalMultiAreaNodes_cell = cell(2,length(IntersectionArea));
for i=1:Unique_num
for j =1:length(Intersection(1,:))
for k=1:length(IntersectionArea)
FinalMultiAreaNodes_cell{1,k} = IntersectionArea{1,k};
if(length(find(Intersection(:,j)))==length(IntersectionArea{k}))
if(find(Intersection(:,j))==IntersectionArea{k})
if(Intersection(i,j) ~= 0)
FinalMultiAreaNodes_cell{2,k} = unique([FinalMultiAreaNodes_cell{2,k} Intersection(i,j)]);
end
end
end
end
end
end
%% 返回非交集特殊点区域的节点数
%%%若特殊点区域内无普通点,存在两种情况:本身该区域内无普通点;点都在与其他区域的相交范围内。
FinalOneAreaNodes_cell = cell(2,Unique_num);
for i = 1:Unique_num
FinalOneAreaNodes_cell{1,i} = i ;%特殊点编号所在的位置
for j =1:length(Intersection_1(1,:))
if(Intersection_1(i,j) ~= 0)
FinalOneAreaNodes_cell{2,i} = [FinalOneAreaNodes_cell{2,i} Intersection_1(i,j)];%相应特殊点内的普通点
end
end
end
%% 返回非区域内的点信息以及三种节点的个数输出
FinalNullAreaNodes_cell = {};
FinalNullAreaNodes_cell{1,1} = 0;
FinalNullAreaNodes_cell{2,1} = Intersection_0';
% fprintf('分布在重复特殊点区域的普通点数共有 %d 个!\n',n-length(Intersection_0)-length(Intersection_1));
% fprintf('分布在非重复特殊点区域的普通点数共有 %d 个!\n',length(Intersection_1));
% fprintf('分布在非特殊点区域的普通点数共有 %d 个!\n',length(Intersection_0));
%% 返回每个特殊点区域的普通点序号
Final_Intersection = [Intersection Intersection_1];
Final_IntersectionCell = cell(2,Unique_num);
for i = 1:Unique_num
Final_IntersectionCell{1,i} = i;
temp = Final_Intersection(i,:);
temp(temp==0)=[];
temp = unique(temp);
Final_IntersectionCell{2,i} = temp;
end
Final_Cell = cat(2,cat(2, FinalNullAreaNodes_cell, FinalOneAreaNodes_cell),FinalMultiAreaNodes_cell);
end
Final_Cell{2,1} = Final_Cell{2,1}';
AA=[];
for i=1:length(Final_Cell(1,:))
AA=cat(2,AA,Final_Cell{2,i});
end
BB=unique(AA);
%% 讨论不在特殊点区域的情况
figure(2);
for i = 1:length(Final_Cell{2,1})
temp = Intersection_0(i);
plot(S(temp).xd,S(temp).yd,'k.');
hold on;
end
%plot(S(n+1).xd,S(n+1).yd,'bp');
ylabel('Y-axis (m)','fontsize',10);
xlabel('X-axis (m)','fontsize',10);
title('simulation&demo');
hold on
axis([0 100 0 100]);%%设置图的大小
hold on
for i = 1:Unique_num
theta = 0:pi/20:2*pi;
Circle1 = Unique_node(i,1)+R*cos(theta);
Circle2 = Unique_node(i,2)+R*sin(theta);
plot(Circle1,Circle2,'g-');
hold on
end
axis equal
for ii = 1:Unique_num
text(Unique_node_x(ii)+1,Unique_node_y(ii),strcat('U',num2str(ii)),'fontsize',10);
end
hold on
plot(Unique_node_x,Unique_node_y,'rp');
axis([0 100 0 100]);%%设置图的大小
hold on
%% 分区域,找几何中心
%%第一步:找出边界点
redNodes = [];
for i = 1:length(CH)
for j = 1:length(Final_Cell{2,1})
temp = Intersection_0(j);
O_U_Dis(i,j) = sqrt((Unique_node_x(i)-S(Intersection_0(j)).xd)^2+(S(Intersection_0(j)).yd-Unique_node_y(i))^2);
if( O_U_Dis(i,j)