Android 8.0 NestedScrollingChild2与NestedScrollingParent2实现RecyclerView阻尼回弹效果
前言
NestedScrolling机制是Android 5.0开始就有的新特性。嵌套滑动子View只需要实现NestedScrollChild,父View需实现NestedScrollParent。用法还是容易理解核心逻辑就是在子View消费之前与之后,向父View发出通知,看看父View是否对这此有何处理,然后再将结果返还给子View。但是有一个问题,对于fling的传递,Google的处理似乎并不那么好。在8.0之前,child只是简单的将fling结果抛给parent。它的处理只有两种结果,要么child消费fling,要么parent消费fling,但它并不能让child消费一部分,再由parent消费剩余fling这样的消费效果,如下图。而在8.0之后,也就是我们今天的主题,NestedScrolling2代(下文直接称呼它为NestedScroll2),它解决了这样的问题,如下图。
8.0之前-NestedScroll
8.0之后-NestedScroll2
其实并不复杂,但是需要先了解NestedScrollChild和NestedScrollParent,不了解的同学进传送门,这里我附一张NestedScroll2的消费传递路径图(画的有点乱见谅)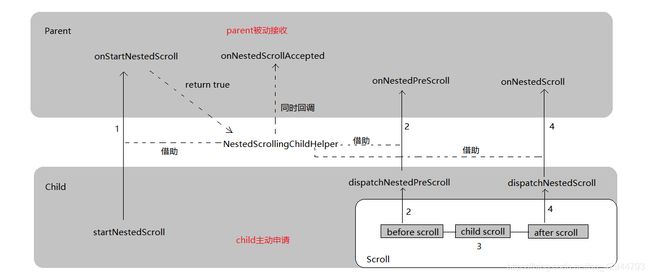
变化
先来看看NestedScrollChild与NestedScrollChild2
public interface NestedScrollingChild {
void setNestedScrollingEnabled(boolean enabled);
boolean isNestedScrollingEnabled();
boolean startNestedScroll(int axes);
void stopNestedScroll();
boolean hasNestedScrollingParent();
boolean dispatchNestedScroll(int dxConsumed, int dyConsumed, int dxUnconsumed, int dyUnconsumed, @Nullable int[] offsetInWindow);
boolean dispatchNestedPreScroll(int dx, int dy, @Nullable int[] consumed, @Nullable int[] offsetInWindow);
boolean dispatchNestedFling(float velocityX, float velocityY, boolean consumed);
boolean dispatchNestedPreFling(float velocityX, float velocityY);
}
public interface NestedScrollingChild2 extends NestedScrollingChild {
boolean startNestedScroll(int axes, int type);
void stopNestedScroll(int type);
boolean hasNestedScrollingParent(int type);
boolean dispatchNestedScroll(int dxConsumed, int dyConsumed, int dxUnconsumed, int dyUnconsumed, @Nullable int[] offsetInWindow, int type);
boolean dispatchNestedPreScroll(int dx, int dy, @Nullable int[] consumed, @Nullable int[] offsetInWindow, int type);
}
什么?只是多了个type?我们再来看看NestedScrollParent与NestedScrollParent2
public interface NestedScrollingParent {
boolean onStartNestedScroll(@NonNull View child, @NonNull View target, int nestedScrollAxes);
void onNestedScrollAccepted(@NonNull View child, @NonNull View target, int axes);
void onStopNestedScroll(@NonNull View target);
void onNestedScroll(@NonNull View target, int dxConsumed, int dyConsumed, int dxUnconsumed, int dyUnconsumed);
void onNestedPreScroll(@NonNull View target, int dx, int dy, @NonNull int[] consumed);
boolean onNestedFling(@NonNull View target, float velocityX, float velocityY, boolean var4);
boolean onNestedPreFling(@NonNull View target, float velocityX, float velocityY);
int getNestedScrollAxes();
}
public interface NestedScrollingParent2 extends NestedScrollingParent {
boolean onStartNestedScroll(@NonNull View child, @NonNull View target, int nestedScrollAxes, int type);
void onNestedScrollAccepted(@NonNull View child, @NonNull View target, int nestedScrollAxes, int type);
void onStopNestedScroll(@NonNull View target, int type);
void onNestedScroll(@NonNull View target, int dxConsumed, int dyConsumed, int dxUnconsumed, int dyUnconsumed, int type);
void onNestedPreScroll(@NonNull View target, int dx, int dy, @NonNull int[] consumed, int type);
}
果然,一对一,都加了一个type,那么这个type是什么呢?下面是ViewCompat源码中的标识
public static final int TYPE_TOUCH = 0;
public static final int TYPE_NON_TOUCH = 1;
TYPE_TOUCH 标识手指触碰 Scroll
TYPE_NON_TOUCH 标识非手指触碰 Fling
好了,大致已经清楚了Google的解决方式了,用一个type标志着当前进行的是Scroll还是Fling,然后在parent中区分进行逻辑处理。
实例
下面我将通过一个实例进行讲解NestedScrollChild2与NestedScrollParent2的联系与用法。
创建一个parent,实现NestedScrollParent2接口,嵌套RecyclerView(RecyclerView已经默认实现了NestedScrollChild2,自己创建child需实现NestedScrollChild2接口)进行滑动,并有类似iOS橡皮筋滑动的阻尼效果。
先上代码,总览一遍
public class DampLayout extends LinearLayout
implements NestedScrollingParent2 {
private static final int MAX_HEIGHT = 400;
private View headerView;
private View footerView;
private View childView;
private ReboundAnimator animator = null;
private boolean isFirstRunAnim;//针对冗余fling期间,保证回弹动画只执行一次
public DampLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
setOrientation(LinearLayout.VERTICAL);
headerView = new View(context);
footerView = new View(context);
}
@Override
protected void onFinishInflate() {//在setContentView之后、onMeasure之前调用的方法
super.onFinishInflate();
childView = getChildAt(0); //这里的childView将是你xml中嵌套进的子view,我这里是RecyclerView
LayoutParams layoutParams = new LayoutParams(LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, MAX_HEIGHT);
addView(headerView, 0, layoutParams);
addView(footerView, getChildCount(), layoutParams);
// 上移,即隐藏header
scrollBy(0, MAX_HEIGHT);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = childView.getLayoutParams();
params.height = getMeasuredHeight();
}
@Override
public void onNestedScrollAccepted(@NonNull View child, @NonNull View target, int axes, int type) {
if (animator == null) {//初始化动画对象
animator = new ReboundAnimator();
}
}
/**
* 返回true代表处理本次事件
*/
@Override
public boolean onStartNestedScroll(@NonNull View child, @NonNull View target, int nestedScrollAxes, int type) {
return target instanceof RecyclerView;
}
/**
* 复位初始位置
*/
@Override
public void onStopNestedScroll(@NonNull View target, int type) {
isFirstRunAnim = false;
if (getScrollY() != MAX_HEIGHT) {//优化代码执行效率
animator.startOfFloat(target, getScrollY());
}
}
@Override
public void onNestedPreScroll(@NonNull View target, int dx, int dy, @NonNull int[] consumed, int type) {
// 如果在自定义ViewGroup之上还有父View交给我来处理
getParent().requestDisallowInterceptTouchEvent(true);
if (type == ViewCompat.TYPE_TOUCH) {//手指触发的滑动
// dy>0向下scroll dy<0向上scroll
boolean hiddenTop = dy > 0 && getScrollY() < MAX_HEIGHT && !target.canScrollVertically(-1);
boolean showTop = dy < 0 && !target.canScrollVertically(-1);
boolean hiddenBottom = dy < 0 && getScrollY() > MAX_HEIGHT && !target.canScrollVertically(1);
boolean showBottom = dy > 0 && !target.canScrollVertically(1);
if (hiddenTop || showTop || hiddenBottom || showBottom) {
if (animator.isStarted()) {
animator.pause();
}
scrollBy(0, damping(dy));
if (animator.isPaused()) {//手动cancel 避免内存泄漏
animator.cancel();
}
consumed[1] = dy;
}
adjust(dy, target);//调整错位
}
}
@Override
public void onNestedScroll(@NonNull View target, int dxConsumed, int dyConsumed, int dxUnconsumed, int dyUnconsumed, int type) {
getParent().requestDisallowInterceptTouchEvent(true);
if (type == ViewCompat.TYPE_NON_TOUCH) {//非手指触发的滑动,即Filing
//解决冗余fling问题
if (((Math.floor(getScrollY()) == 0) || ((Math.ceil(getScrollY()) == 2 * MAX_HEIGHT))) && !isFirstRunAnim) {
int startY = 0;
if (dyUnconsumed > 0) {
startY = 2 * MAX_HEIGHT;
}
animator.startOfFloat(target, startY);
isFirstRunAnim = true;
}
if (isFirstRunAnim)
return;
// dy>0向下fling dy<0向上fling
boolean showTop = dyUnconsumed < 0 && !target.canScrollVertically(-1);
boolean showBottom = dyUnconsumed > 0 && !target.canScrollVertically(1);
if (showTop || showBottom) {
if (animator.isStarted()) {
animator.pause();
}
scrollBy(0, damping(dyUnconsumed));
if (animator.isPaused()) {//手动cancel 避免内存泄漏
animator.cancel();
}
}
adjust(dyUnconsumed, target);//调整错位
}
}
/**
* 衰减可继续scroll或fling的距离
*/
private int damping(int dy) {
//计算衰减系数,越大可继续scroll或fling的距离越短
int i = (int) (Math.abs(MAX_HEIGHT - getScrollY()) * 0.01);
return i < 2 ? dy : dy / i;
}
/**
* 调整错位问题(强转精度损失造成的错位)
*/
private void adjust(int condition1, View condition2) {
if (condition1 > 0 && getScrollY() > MAX_HEIGHT && !condition2.canScrollVertically(-1)) {
scrollTo(0, MAX_HEIGHT);
}
if (condition1 < 0 && getScrollY() < MAX_HEIGHT && !condition2.canScrollVertically(1)) {
scrollTo(0, MAX_HEIGHT);
}
}
/**
* 限制滑动 移动y轴不能超出最大范围
*/
@Override
public void scrollTo(int x, int y) {
if (y < 0) {
y = 0;
} else if (y > MAX_HEIGHT * 2) {
y = MAX_HEIGHT * 2;
}
super.scrollTo(x, y);
}
/**
* 回弹动画
*/
private class ReboundAnimator extends ValueAnimator {
private View target;
private ReboundAnimator() {
init();
}
private void init() {
this.setInterpolator(new DecelerateInterpolator());//添加减速插值器
this.setDuration(260);
//添加值更新监听器
this.addUpdateListener(new AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) {
float currValue = (float) getAnimatedValue();
scrollTo(0, (int) currValue);
// 调整错位问题(强转精度损失造成的错位)
if (getScrollY() > MAX_HEIGHT && !target.canScrollVertically(-1)) {
scrollTo(0, MAX_HEIGHT);
}
if (getScrollY() < MAX_HEIGHT && !target.canScrollVertically(1)) {
scrollTo(0, MAX_HEIGHT);
}
}
});
}
private void startOfFloat(View target, float startY) {
this.setFloatValues(startY, MAX_HEIGHT);
this.target = target;
this.start();
}
}
}
先不慌,我们挑重点进行分析
1.onFinishInflate
@Override
protected void onFinishInflate() {//在setContentView之后、onMeasure之前调用的方法
super.onFinishInflate();
childView = getChildAt(0); //这里的childView将是你xml中嵌套进的子view,我这里是RecyclerView
LayoutParams layoutParams = new LayoutParams(LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, MAX_HEIGHT);
addView(headerView, 0, layoutParams);
addView(footerView, getChildCount(), layoutParams);
// 上移,即隐藏header
scrollBy(0, MAX_HEIGHT);
}
在这里要做的先是获取你要嵌套滑动的child,我这里是RecyclerView,然后添加两个view在RecyclerView的头和脚的位置,这样做的目的是为了在过度滚动以后能有一块白色的view来填充(MAX_HEIGHT就是头和脚的高度)。大致的布局效果如下

最后要达到的效果就是当RecyclerView到达顶部或底部,继续滑动显示的就是headerView或footerView,就是这么个思想。初始化布局就是按部就班。
2.onStartNestedScroll与onNestedScrollAccepted
@Override
public boolean onStartNestedScroll(@NonNull View child, @NonNull View target, int nestedScrollAxes, int type) {
return target instanceof RecyclerView;
}
@Override
public void onNestedScrollAccepted(@NonNull View child, @NonNull View target, int axes, int type) {
if (animator == null) {//初始化动画对象
animator = new ReboundAnimator();
}
}
大家都知道,这个onNestedScrollAccepted会在回调了onStartNestedScroll以后,如果onStartNestedScroll返回true的话,会立即回调onNestedScrollAccepted。
在onNestedScrollAccepted中我做了一个初始化回弹动画的操作(动画会在后面讲解)。
在onStartNestedScroll中,一般情况下就直接返回target instanceof RecyclerView,判断该target是你所需要的view类或者子类即可。
3.ReboundAnimator回弹动画
private class ReboundAnimator extends ValueAnimator {
private View target;
private ReboundAnimator() {
init();
}
private void init() {
this.setInterpolator(new DecelerateInterpolator());//添加减速插值器
this.setDuration(260);
//添加值更新监听器
this.addUpdateListener(new AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) {
float currValue = (float) getAnimatedValue();
scrollTo(0, (int) currValue);
// 调整错位问题(强转精度损失造成的错位)
if (getScrollY() > MAX_HEIGHT && !target.canScrollVertically(-1)) {
scrollTo(0, MAX_HEIGHT);
}
if (getScrollY() < MAX_HEIGHT && !target.canScrollVertically(1)) {
scrollTo(0, MAX_HEIGHT);
}
}
});
}
private void startOfFloat(View target, float startY) {
this.setFloatValues(startY, MAX_HEIGHT);
this.target = target;
this.start();
}
}
这里我重新封装了一下ValueAnimator,对值动画不明白的同学进传送门。在startOfFloat方法中为值动画设置起始-终点值,并开始动画。初始化中,为它添加一个listener监听值的变化(这里要注意强转类型造成的精度损失问题,后面也有需要解决错位的问题)。
4.onStopNestedScroll
@Override
public void onStopNestedScroll(@NonNull View target, int type) {
isFirstRunAnim = false;
if (getScrollY() != MAX_HEIGHT) {//优化代码执行效率
animator.startOfFloat(target, getScrollY());
}
}
没啥大问题,当回调该函数标志着一轮的Scroll或Fling结束。处理一下isFirstRunAnim 标志(在后面会讲解到其作用),开始动画。
5.onNestedPreScroll
@Override
public void onNestedPreScroll(@NonNull View target, int dx, int dy, @NonNull int[] consumed, int type) {
// 如果在自定义ViewGroup之上还有父View交给我来处理
getParent().requestDisallowInterceptTouchEvent(true);
if (type == ViewCompat.TYPE_TOUCH) {//手指触发的滑动
// dy>0向下scroll dy<0向上scroll
boolean hiddenTop = dy > 0 && getScrollY() < MAX_HEIGHT && !target.canScrollVertically(-1);
boolean showTop = dy < 0 && !target.canScrollVertically(-1);
boolean hiddenBottom = dy < 0 && getScrollY() > MAX_HEIGHT && !target.canScrollVertically(1);
boolean showBottom = dy > 0 && !target.canScrollVertically(1);
if (hiddenTop || showTop || hiddenBottom || showBottom) {
if (animator.isStarted()) {
animator.pause();
}
scrollBy(0, damping(dy));
if (animator.isPaused()) {//手动cancel 避免内存泄漏
animator.cancel();
}
consumed[1] = dy;
}
adjust(dy, target);//调整错位
}
}
这是在child开始Scroll或Fling之前回调的函数,通过这个函数parent可以选择先于child进行滑动。一开始判断一下type,表示只处理手指产生的Scroll。当满足条件时,用到scrollBy函数对位移进行消耗,并将消耗的值赋给consumed数组。
这里很重要,在NestedScrollingChildHelper中会对consumed数组进行判断,不为空代表parent进行了消费
5.onNestedScroll
@Override
public void onNestedScroll(@NonNull View target, int dxConsumed, int dyConsumed, int dxUnconsumed, int dyUnconsumed, int type) {
getParent().requestDisallowInterceptTouchEvent(true);
if (type == ViewCompat.TYPE_NON_TOUCH) {//非手指触发的滑动,即Filing
//解决冗余fling问题
if (((Math.floor(getScrollY()) == 0) || ((Math.ceil(getScrollY()) == 2 * MAX_HEIGHT))) && !isFirstRunAnim) {
int startY = 0;
if (dyUnconsumed > 0) {
startY = 2 * MAX_HEIGHT;
}
animator.startOfFloat(target, startY);
isFirstRunAnim = true;
}
if (isFirstRunAnim)
return;
// dy>0向下fling dy<0向上fling
boolean showTop = dyUnconsumed < 0 && !target.canScrollVertically(-1);
boolean showBottom = dyUnconsumed > 0 && !target.canScrollVertically(1);
if (showTop || showBottom) {
if (animator.isStarted()) {
animator.pause();
}
scrollBy(0, damping(dyUnconsumed));
if (animator.isPaused()) {//手动cancel 避免内存泄漏
animator.cancel();
}
}
adjust(dyUnconsumed, target);//调整错位
}
}
这里就是child滑动以后回调的函数,同样,这里我们只处理Fling。满足一定条件调用scrollBy进行消费。
这里的冗余Fling是个什么?我们先试着不解决这个问题,注释掉关于冗余Fling的代码看是什么样的

发现了吗,Fling后有一个停顿期,为什么会出现这样的情况,这段期间在干嘛?通过调试在该函数里打印Log发现,在Fling时,该函数被回调了很多次。一直回调该函数代表Fling没有被消费完,也就是一直不会回调onStopNestedScroll方法,也就不会开始动画,所以造成了那样的停顿期。我们单独拎出这段解决代码
if (((Math.floor(getScrollY()) == 0) || ((Math.ceil(getScrollY()) == 2 * MAX_HEIGHT))) && !isFirstRunAnim) {
int startY = 0;
if (dyUnconsumed > 0) {
startY = 2 * MAX_HEIGHT;
}
animator.startOfFloat(target, startY);
isFirstRunAnim = true;
}
if (isFirstRunAnim)
return;
getScrollY() == 0 代表顶部滑动到最大值
getScrollY() == 2 * MAX_HEIGHT 代表底部滑动到最大值
也就是说当第一次到达顶部或底部最大,我们立刻开始动画,达到消除停顿期的作用,并为isFirstRunAnim标志赋值为true,代表以及到达过了最大值了,所以后面还有冗余的Fling传递到该函数,我们通过判断isFirstRunAnim决定是否要放弃后面传递过来的Fling的消费,直到冗余Fling也结束了,开始回调onStopNestedScroll来正式结束该次Fling。
NestedScrollingParent2结束
接下来我将分析RecyclerView的源码,分析RecyclerView是如何利用NestedScrollingChild2传递事件消费的,不想了解的可以止步了。
原理
RecyclerView是默认实现的NestedScrollingChild2接口的,我们主要分析一下RecyclerView是如何传递Fling事件给parent进行消费的。先从onTouchEvent函数开始吧。
上源码!
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent e) {
if (!this.mLayoutFrozen && !this.mIgnoreMotionEventTillDown) {
......
......
switch(action) {
case ACTION_DOWN:
......
......
this.startNestedScroll(nestedScrollAxis, TYPE_TOUCH);
break;
case ACTION_UP: //!!!!!!!看这里
this.mVelocityTracker.addMovement(vtev);
eventAddedToVelocityTracker = true;
this.mVelocityTracker.computeCurrentVelocity(1000, (float)this.mMaxFlingVelocity);
float xvel = canScrollHorizontally ? -this.mVelocityTracker.getXVelocity(this.mScrollPointerId) : 0.0F;
float yvel = canScrollVertically ? -this.mVelocityTracker.getYVelocity(this.mScrollPointerId) : 0.0F;
if (xvel == 0.0F && yvel == 0.0F || !this.fling((int)xvel, (int)yvel)) {//!!!!!!!看这里
this.setScrollState(0);
}
this.resetTouch();
break;
case ACTION_MOVE:
......
......
if (this.dispatchNestedPreScroll(dx, dy, this.mScrollConsumed, this.mScrollOffset, TYPE_TOUCH)) {
......
}
......
......
break;
}
} else {
return false;
}
}
这里是简化后的源码,只需要看两处地方,在接收到up事件,使用VelocityTracker类计算当前手指滑动的速度以后,在if判断里会调用fling方法,将当前的速度传递过去,嗯,然后是fling的源码
public boolean fling(int velocityX, int velocityY) {
if (this.mLayout == null) {
......
......
if (!canScrollHorizontal || Math.abs(velocityX) < this.mMinFlingVelocity) {
velocityX = 0;
}
if (!canScrollVertical || Math.abs(velocityY) < this.mMinFlingVelocity) {
velocityY = 0;
}
if (velocityX == 0 && velocityY == 0) {
return false;
} else {
if (!this.dispatchNestedPreFling((float)velocityX, (float)velocityY)) {
boolean canScroll = canScrollHorizontal || canScrollVertical;
this.dispatchNestedFling((float)velocityX, (float)velocityY, canScroll);
//如果是使用一代接口,会调用dispatchNestedPreFling和dispatchNestedFling传递fling给parent
//dispatchNestedPreFling()方法默认return的是false
......
if (canScroll) {
......
}
//!!!!!!!看这里
this.startNestedScroll(nestedScrollAxis, TYPE_NON_TOUCH);
velocityX = Math.max(-this.mMaxFlingVelocity, Math.min(velocityX, this.mMaxFlingVelocity));
velocityY = Math.max(-this.mMaxFlingVelocity, Math.min(velocityY, this.mMaxFlingVelocity));
this.mViewFlinger.fling(velocityX, velocityY);//!!!!!!!看这里
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
}
调用了startNestedScroll并传递一个非手指的Fling标志过去,也就是说,理想状态下只要抬起手指,接收到up,有速度,就会开启TYPE_NON_TOUCH的Fling。所以我们还可以对parent的onStartNestedScroll进行优化一下。
@Override
public boolean onStartNestedScroll(@NonNull View child, @NonNull View target, int nestedScrollAxes, int type) {
if (type == ViewCompat.TYPE_NON_TOUCH
&& (!target.canScrollVertically(-1) || !target.canScrollVertically(1))) {//非手指的fling状态
return false;
} else {
return target instanceof RecyclerView;
}
}
在主内容本身位于顶部或底部时,我们可以直接通过这样的逻辑,对于该种情况下产生的Fling直接不予处理,也就不用等到在onNestedScroll中处理冗余Fling(哈哈,选择不看原理的同学get不到这一点!)
回到主题,开启了TYPE_NON_TOUCH的Fling后,通过this.mViewFlinger.fling(velocityX, velocityY) 会将这个消息继续往下传递,陆续调用dispatchNestedPreScroll和dispatchNestedScroll。
接着看this.mViewFlinger.fling的源码
public void fling(int velocityX, int velocityY) {
RecyclerView.this.setScrollState(2);
this.mLastFlingX = this.mLastFlingY = 0;
this.mScroller.fling(0, 0, velocityX, velocityY, -2147483648, 2147483647, -2147483648, 2147483647);
this.postOnAnimation(); //看这里
}
注意!这里的fling是RecyclerView的一个内部类ViewFlinger里的方法,它继承自Runnable,专门用于处理Fling
通过postOnAnimation函数最终会开启这个ViewFlinger线程,所以我们来了解一下它的run()方法里都干了些什么。
public void run() {
if (RecyclerView.this.mLayout == null) {
this.stop();
} else {
......
......
if (scroller.computeScrollOffset()) {
int[] scrollConsumed = RecyclerView.this.mScrollConsumed;
int x = scroller.getCurrX();
int y = scroller.getCurrY();
int dx = x - this.mLastFlingX;
int dy = y - this.mLastFlingY;
int hresult = 0;
int vresult = 0;
this.mLastFlingX = x;
this.mLastFlingY = y;
int overscrollX = 0;
int overscrollY = 0;
//!!!!!!!!!!!看这里
if (RecyclerView.this.dispatchNestedPreScroll(dx, dy, scrollConsumed, (int[])null, TYPE_NON_TOUCH)) {
dx -= scrollConsumed[0];
dy -= scrollConsumed[1];
}
......
......
//!!!!!!!!!!!看这里
if (!RecyclerView.this.dispatchNestedScroll(hresult, vresult, overscrollX, overscrollY, (int[])null, TYPE_NON_TOUCH) && (overscrollX != 0 || overscrollY != 0)) {
......
......
if (RecyclerView.this.getOverScrollMode() != 2) {
//这里其实就是这种列表view滑动到顶部或底部出现的阴影的开启位置
RecyclerView.this.absorbGlows(velX, velY);
}
......
......
if (scroller.isFinished() || !fullyConsumedAny && !RecyclerView.this.hasNestedScrollingParent(TYPE_NON_TOUCH)) {
RecyclerView.this.setScrollState(0);
if (RecyclerView.ALLOW_THREAD_GAP_WORK) {
RecyclerView.this.mPrefetchRegistry.clearPrefetchPositions();
}
//!!!!!!!!!!!看这里
RecyclerView.this.stopNestedScroll(TYPE_NON_TOUCH);
} else {
this.postOnAnimation();
if (RecyclerView.this.mGapWorker != null) {
RecyclerView.this.mGapWorker.postFromTraversal(RecyclerView.this, dx, dy);
}
}
}
......
......
}
}
很明显,这里面就是一般的处理套路,先计算出当前Fling的距离,通过dispatchNestedPreScroll传递给parent,并标记type为TYPE_NON_TOUCH,如果parent消费了就减去已消费的。之后通过dispatchNestedScroll将child已经消费的和没消费的Fling传递给parent,并标记type为TYPE_NON_TOUCH。Fling完成以后调用stopNestedScroll传递给parent一个TYPE_NON_TOUCH类型的停止信息,结束Fling。
至此,源码分析结束。
文章参考
有什么讲的不对的地方,欢迎各位纠错,谢谢!