(五)深度学习实战 | MMDetection笔记(2)
1. 简介
上文介绍了 M M D e t e c t i o n {\rm MMDetection} MMDetection的基本内容和简单地测试官方所提供的预训练模型,本文将从四个方面进一步介绍 M M D e t e c t i o n {\rm MMDetection} MMDetection的相关内容:添加新数据集、微调模型、设计数据管道和添加新模块等。
2. 添加新数据集
上文提到,我们在 M M D e t e c t i o n {\rm MMDetection} MMDetection项目中添加了 C O C O {\rm COCO} COCO和 V O C {\rm VOC} VOC两种格式的数据集。所以,在添加新的数据集时,最简便的方法就是将待添加数据集的格式转化成这两种格式之一。 首先,在 C O C O {\rm COCO} COCO数据集中,所有的标注信息集中在一个 J S O N {\rm JSON} JSON文件中,所有数据以字典的形式给出。该文件一共包含五大部分:info介绍数据集的基本信息、licenses介绍许可信息、images图像相关信息(包括文件路径、尺寸、编号等信息)、annotations图像标注信息(包括检测、分割、面积大小、编号等信息)、categories数据集的类别(包括父类、子类、编号等信息),图像、标注和类别通过编号相互关联。
下面是一幅图像的基本信息:
'images':
[{
{
'licenses': xxx, # 许可
'file_name': xxx, # 文件名
'coco_url': xxx, # 地址
'height': xxx, # 高度
'width': xxx, # 宽度
'data_captured': xxx, # 获取
'flickr_url': xxx, # 地址
'id': xxx # 编号
}
...
}]
下面是一幅图像的标注信息:
'annotations':
[{
{
'segmentation': xxx, # 分割
'area': xxx, # 面积
'iscrowed': xxx, # 拥挤
'image_id': xxx, # 编号
'bbox': xxx, # 检测
'category_id': xxx, # 类别
'id': xxx # 编号
}
}]
下面是几个类别的存放形式:
'categories':
[
{
'supercategory': 'person', # 父类
'id': 1, # 编号
'name': 'person' # 类别
}
{
'supercategory': 'vehicle',
'id': 2,
'name': 'bicycle'
}
...
]
其次,在 V O C {\rm VOC} VOC数据集中,图像及其标注信息的存放形式更为明确,每一幅图像都有与之对应的一个 X M L {\rm XML} XML文件。如下:

直观来说, V O C {\rm VOC} VOC数据集格式更加简单,但 C O C O {\rm COCO} COCO数据集的存取所需空间更小。应该将我们的数据集制作成哪一种格式的数据,视具体情况而定。
2. 在MMDetection中添加新数据集
我们以 V O C {\rm VOC} VOC格式的数据集为例添加新数据集。首先在configs/_base_/datasets目录下新建my_custom_config.py文件,其内容类似于voc0712.py,不同之处在于data及路径部分部分:
data = dict(
samples_per_gpu=2,
workers_per_gpu=2,
# 训练集部分
train=dict(
type=dataset_type,
ann_file=[
'path/to/your/train/data',
...
],
image_prefix=[
'path/to/image/prefix',
...
],
pipeline=train_pipeline)
),
# 验证集部分
val=dict(
...
),
# 测试集部分
test=dict(
...
)
)
除此之外,我们也可以不用将数据集格式转化成 C O C O {\rm COCO} COCO格式或 V O C {\rm VOC} VOC格式, M M D e t e c t i o n {\rm MMDetection} MMDetection提供了一种简单的格式。我们仅需将自己制作的数据集格式转化成 M M D e t e c t i o n {\rm MMDetection} MMDetection自定义的格式,然后调用相应的 A P I {\rm API} API也能添加新的数据集。
3. 微调模型
在 M M D e t e c t i o n {\rm MMDetection} MMDetection的Model Zoo中提供了大量的预训练模型,微调模型主要分为以下两个步骤:
- 添加新数据集(见上一部分);
- 修改配置文件(见下面部分)。
3.1 配置文件的继承
在 M M D e t e c t i o n 2.0 {\rm MMDetection2.0} MMDetection2.0中提供了配置文件的继承,在每个训练所用的配置文件中都有如下字段,所有的配置文件都是通过继承或派生得到 :
_base_ = [
# 其他继承
...
# 数据集
'../_base_/datasets/xxx.py',
# 优化器和学习策略
'../_base_/schedules/xxx.py',
# 运行时
'.../_base_default_runtime.py'
]
3.2 修改检测头
由于检测头处一般会包含数据集的类别信息,所以需要将configs/_base_/models内配置文件的num_classes字段改为相应的数值。
3.3 修改数据集
上面提到了,将数据集放到对应目录下。为了方便,我们将整个数据集放到整个工程的data目录下。
3.4 修改训练策略
在configs/_base_/schedules文件夹下,我们可以修改或新建关于优化器和学习策略等信息。其中,配置文件都继承自schedule_1x.py文件。
3.5 使用预训练模型
M M D e t e c t i o n {\rm MMDetection} MMDetection官方提供的预训练模型可以从这里下载。
4. 设计数据管道
M M D e t e c t i o n {\rm MMDetection} MMDetection基于 P y T o r c h {\rm PyTorch} PyTorch实现,所以在加载数据时使用的是Dataset类和DataLoader类。Dataset以字典的形式返回数据,但由于在目标检测中图像或真实框的尺寸不尽相同, M M D e t e c t i o n {\rm MMDetection} MMDetection引入DataContainer类来处理不同尺寸的输入。
数据管道和数据集是相对独立的。通常,数据集定义了如何处理标注信息;数据管道定义产生数据字典的过程,其包含一系列操作,每一步操作以字典作为输入同时以字典作为输出。下图是 M M D e t e c t i o n {\rm MMDetection} MMDetection中的数据管道设计流程。蓝色块是数据管道中的操作;随着管道的进行,每一步操作会添加新的值(绿色)作为输出结果,橙色表示更新的值。
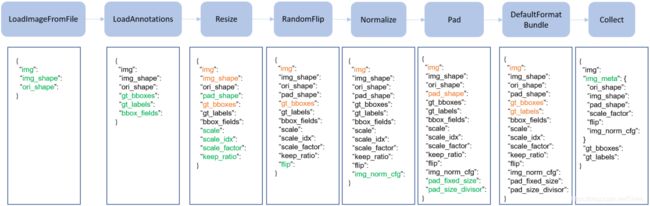
从整体来看,管道的输入是图像以及标注信息;管道的输出也是图像的相关信息,此时该信息可以直接作为DataLoader类的输入对象。下面以 F a s t e r {\rm Faster} Faster- R C N N {\rm RCNN} RCNN来说明管道的设计机制:
img_norm_cfg = dict(
mean=[123.675, 116.28, 103.53], std=[58.395, 57.12, 57.375], to_rgb=True)
train_pipeline = [
dict(type='LoadImageFromFile'),
dict(type='LoadAnnotations', with_bbox=True),
dict(type='Resize', img_scale=(1333, 800), keep_ratio=True),
dict(type='RandomFlip', flip_ratio=0.5),
dict(type='Normalize', **img_norm_cfg),
dict(type='Pad', size_divisor=32),
dict(type='DefaultFormatBundle'),
dict(type='Collect', keys=['img', 'gt_bboxes', 'gt_labels']),
]
test_pipeline = [
dict(type='LoadImageFromFile'),
dict(
type='MultiScaleFlipAug',
img_scale=(1333, 800),
flip=False,
transforms=[
dict(type='Resize', keep_ratio=True),
dict(type='RandomFlip'),
dict(type='Normalize', **img_norm_cfg),
dict(type='Pad', size_divisor=32),
dict(type='ImageToTensor', keys=['img']),
dict(type='Collect', keys=['img']),
])
]
5. 添加新模块
5.1 添加优化器
如果我们想要在 M M D e t e c t i o n {\rm MMDetection} MMDetection中自定义优化器,其步骤如下:首先创建目录mmdet/core/optimizer,自定义文件名,如得到mmdet/core/optimizer/my_optimizer.py。在 M M D e t e c t i o n {\rm MMDetection} MMDetection中定义新的模块前需要注册。文件内容如下:
from .registry import OPTIMIZERS
from torch.optim import Optimizer
@OPTIMIZERS.register_module()
class MyOptimizer(Optimizer):
def __init__(self, a, b, c):
...
然后在mmdet/core/optimizer/__init__.py中添加模块:
from .my_optimizer import MyOptimizer
然后就可以在配置文件中指定自定义的优化器:
optimizer = dict(type='MyOptimizer', a=a_value, b=b_balue, c=c_value)
此外,在 M M D e t e c t i o n {\rm MMDetection} MMDetection中已经继承了所有 P y T o r c h {\rm PyTorch} PyTorch中的优化器,只需更改type字段的值即可换成切换。
5.2 添加新的优化器构造器
有时候可能需要修改指定参数,如批量归一化层的衰减系数等。配合上一步构造的优化器,程序如下:
from mmcv.utils import build_from_cfg
from mmcv.runner.optimizer import OPTIMIZER_BUILDERS, OPTIMIZERS
from mmdet.utils import get_root_logger
from .my_optimizer import MyOptimizer
@OPTIMIZER_BUILDERS.register_module()
class MyOptimizerConstructor(object):
def __init__(self, optimizer_cfg, paramwise_cfg=None):
def __call__(self, model):
return my_optimizer
5.3 添加新的模型部件
在 M M D e t e c t i o n {\rm MMDetection} MMDetection中添加新的模型部件主要涉及四个方面:
- 骨干网络:如 R e s N e t {\rm ResNet} ResNet、 M o b i l e N e t {\rm MobileNet} MobileNet;
- 网络颈:如 F P N {\rm FPN} FPN、 P A F P N {\rm PAFPN} PAFPN;
- 网络头:如边界框预测头、掩膜预测头;
- 感兴趣区域提取:如 R o I A l i g n {\rm RoI\ Align} RoI Align等。
5.3.1 骨干网络
以添加新的骨干网络 M o b i l e N e t {\rm MobileNet} MobileNet为例。首先创建文件mmdet/models/backbones/mobilenet.py:
import torch.nn as nn
from ..registry import BACKBONES
@BACKBONES.registry_module()
class MobileNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, arg1, arg2):
pass
def __forward(self, x): # 以元组的形式返回,如:tuple(x)
pass
def init_weights(self, pretrained=None):
pass
然后在mmdet/models/backbones/__init__.py中添加模块:
from .mobilenet import MobileNet
最后就可以在配置文件中指定自定义的骨干网络:
model = dict(
...
backbone=dict(
type='MobileNet',
arg1=xxx,
arg2=xxx
),
...
)
5.3.2 网络颈
网络颈用以连接骨干网络和网络头,以添加新的网络颈 P A F P N {\rm PAFPN} PAFPN为例。首先创建文件mmdet/models/necks/pafpn.py:
from ..registry import NECKS
@NECKS.register
class PAFPN(nn.module):
def __init__(self,
in_channels,
out_channels,
num_outs,
start_level=0,
end_level=1,
add_extra_convs=False):
pass
def forward(self, inputs):
pass
然后在mmdet/models/necks/__init__.py中添加模块:
from .pafpn import PAFPN
最后就可以在配置文件中指定自定义的网络颈:
model = dict(
...
neck=dict(
type='PAFPN',
in_channels=[256, 512, 1024, 2048],
out_channels=256,
num_outs=5
),
...
)
5.3.3 网络头
以 C V P R 2020 {\rm CVPR\ 2020} CVPR 2020中提出的双检测头为例来说明在 M M D e t e c t i o n {\rm MMDetection} MMDetection中添加检测头的流程。首先创建文件mmdet/models/bbox_heads/double_bbox_head.py:
@HEADS.register_module()
class DoubleConvFCBBoxHead(BBoxHead):
def __init__(self,
num_convs=0,
conv_out_channels=1024,
fc_out_channels=1024,
conv_cfg=None,
norm_cfg=dict(type='BN'),
**kwargs):
kwargs.setdefault('with_avg_pool', True)
super(DoubleConvFCBBoxHead, self).__init__(**kwargs)
def init_weights(self):
pass
def forward(self, x_cls, x_reg):
pass
其次,在添加新的检测头时需要实现 R o I {\rm RoI} RoI头。定义DoubleHeadRoIHead继承自StandardRoIHead,其中基类StandardRoIHead中已经实现了如下函数:
import torch
from mmdet.core import bbox2result, bbox2roi, build_assigner, build_sampler
from ..builder import HEADS, build_head, build_roi_extractor
from .base_roi_head import BaseRoIHead
from .test_mixins import BBoxTestMixin, MaskTestMixin
@HEADS.register_module()
class StandardRoIHead(BaseRoIHead, BBoxTestMixin, MaskTestMixin):
def init_assigner_sampler(self):
def init_bbox_head(self, bbox_roi_extractor, bbox_head):
def init_mask_head(self, mask_roi_extractor, mask_head):
def init_weights(self, pretrained):
def forward_dummy(self, x, proposals):
def forward_train(self, x, img_metas, proposals_list, gt_bboxes, gt_labels, gt_bboxes_ignore=None, gt_masks=None):
def _bbox_forward(self, x, rois):
def _bbox_forward_train(self, x, sampling_results, gt_bboxes, gt_labels, img_metas):
def _mask_forward_train(self, x, sampling_results, bbox_feats, gt_masks, img_metas):
def _maks_forward(self, x, rois=None, pos_inds=None, bbox_feats=None):
def simple_test(self, x, proposals_list, img_metas, proposals=None, rescale=False):
然后新建文件mmdet/models/roi_heads/double_roi_head.py:
from .standard_roi_head import StandardRoIHead
@HEADS.register_module()
class DoubleHeadRoIHead(StandardRoIHead):
def __init__(self, reg_roi_scale_factor, **kwargs):
super(DoubleHeadRoIHead, slef).__init___(**kwargs)
self.reg_roi_scale_factor = reg_roi_scale_factor
def _bbox_forward(self, x, rois): # 重写基类函数
bbox_cls_feats = self.bbox_roi_extractor(
x[:self.bbox_roi_extractor.num_inputs], rois)
bbox_reg_feats = self.bbox_roi_extractor(
x[:self.bbox_roi_extractor.num_inputs],
rois,
roi_scale_factor=self.reg_roi_scale_factor)
if self.with_shared_head:
bbox_cls_feats = self.shared_head(bbox_cls_feats)
bbox_reg_feats = self.shared_head(bbox_reg_feats)
cls_score, bbox_pred = self.bbox_head(bbox_cls_feats, bbox_reg_feats)
bbox_results = dict(
cls_score=cls_score,
bbox_pred=bbox_pred,
bbox_feats=bbox_cls_feats)
return bbox_results
接着在mmdet/models/bbox_heads/__init__.py和mmdet/models/roi_heads/__init__.py中分别添加相应的模块:
from .double_bbox_head import DoubleConvFCBBoxHead
from .double_roi_head import DoubleHeadRoIHead
最后就可以在配置文件中指定自定义的网络头:
_base_ = '../faster_rcnn/faster_rcnn_r50_fpn_1x_coco.py'
model = dict(
roi_head=dict(
type='DoubleHeadRoIHead',
reg_roi_scale_factor=1.3,
bbox_head=dict(
_delete_=True,
type='DoubleConvFCBBoxHead',
num_convs=4,
num_fcs=2,
in_channels=256,
conv_out_channels=1024,
fc_out_channels=1024,
roi_feat_size=7,
num_classes=80,
bbox_coder=dict(
type='DeltaXYWHBBoxCoder',
target_means=[0., 0., 0., 0.],
target_stds=[0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.2]),
reg_class_agnostic=False,
loss_cls=dict(
type='CrossEntropyLoss', use_sigmoid=False, loss_weight=2.0),
loss_bbox=dict(type='SmoothL1Loss', beta=1.0, loss_weight=2.0))))
5.3.4 损失函数
需要在 M M D e t e c t i o n {\rm MMDetection} MMDetection中自定义损失函数时,首先新建文件mmdet/models/losses/my_loss.py:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from ..builder import LOSSES
from .utils import weighted_loss
@weighted_loss
def my_loss(pred, target):
assert pred.size() == target.size() and target.numel() > 0
loss = torch.abs(pred - target)
return loss
@LOSSES.register_module()
class MyLoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, reduction='mean', loss_weight=1.0):
super(MyLoss, self).__init__()
self.reduction = reduction
self.loss_weight = loss_weight
def forward(self,
pred,
target,
weight=None,
avg_factor=None,
reduction_override=None):
assert reduction_override in (None, 'none', 'mean', 'sum')
reduction = (
reduction_override if reduction_override else self.reduction)
loss_bbox = self.loss_weight * my_loss(
pred, target, weight, reduction=reduction, avg_factor=avg_factor)
return loss_bbox
然后在mmdet/models/losses/__init__.py中添加新模块:
from .my_loss import MyLoss
最后就可以在配置文件中指定自定义的损失函数:
loss_bbox=dict(type='MyLoss', loss_weight=1.0))
6. 总结
本文简单地介绍了如何在 M M D e t e c t i o n {\rm MMDetection} MMDetection中添加自定义模块,如骨干网络、网络颈、网络头和损失函数等。在 M M D e t e c t i o n {\rm MMDetection} MMDetection中的配置文件的定义是核心,下文将详细介绍 M M D e t e c t i o n {\rm MMDetection} MMDetection中配置文件。
参考
- https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmdetection.