无人驾驶定位与贝叶斯滤波
无人驾驶需要精确的定位。本文将简要介绍无人驾驶定位的相关方法,重点介绍贝叶斯滤波框架进行递归的状态估计。同时附上一维马尔科夫定位的实例及代码。
无人驾驶定位
定位是指在空间中确定自己的位置。
传统的定位方法有GPS(Global Positioning System),但是GPS的误差较大且不稳定(m级)。无人驾驶对定位精度要求较高需要达到cm级的误差,因此需要多传感器融合定位。
定位的数学问题之贝叶斯滤波
定位的目标:记汽车的位置为 x ,定位即是求解 P(x) 。
那么,为了确定汽车的位置,我们有哪些数据呢?
- 地图数据 m ,包含地图上标志物的位置信息
- 观测数据 z ,包含汽车感知到的标志物与汽车的相对位置信息
- 控制数据 u ,包含汽车的油门转弯等控制信息
定位本身是一种位置不确定性的度量,我们的目标是尽量减少这种不确定性。那么,上面的数据信息是如何帮助我们减少不确定性的呢?
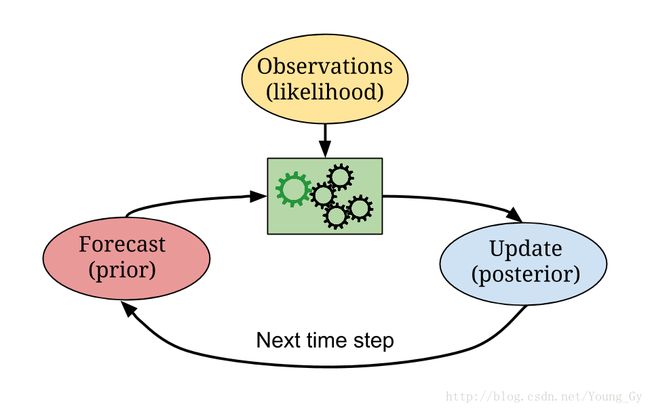
- Sense: P(x|z)∝P(x)P(z|x)
- Move: P(xt+1)=∑P(xt)P(xt+1|xt)
贝叶斯滤波是一种使用递归进行状态估计的框架。其交替利用Move阶段的prediction和Sense阶段的update,便可以对汽车的位置 P(x) 做更精准的描述。
一维马尔科夫定位
一维马尔科夫定位、卡尔曼滤波、粒子滤波都属于贝叶斯滤波的一种,这里将简要介绍一维马尔科夫定位。
数据
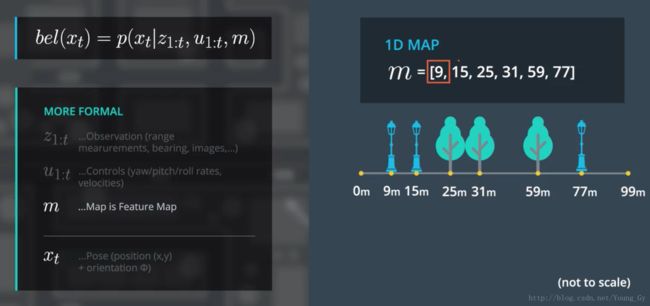
这里使用的数据包含以下三种,目的是要获得汽车在 t 时刻位置的置信为 bel(xt) 。
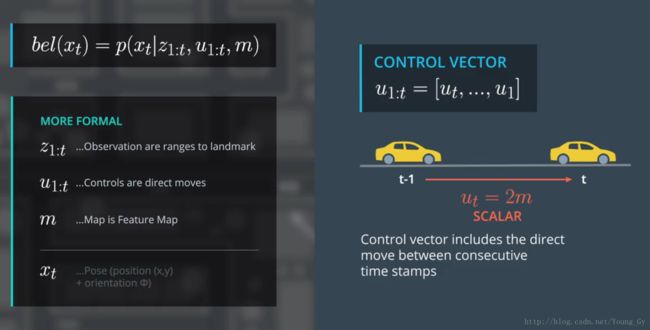
- 地图数据 m ,包含地图上标志物的位置信息
- 观测数据 z ,包含汽车感知到的标志物与汽车的相对位置信息
- 控制数据 u ,包含汽车的油门转弯等控制信息
动机
记汽车在 t 时刻位置的置信为 bel(xt) ,有
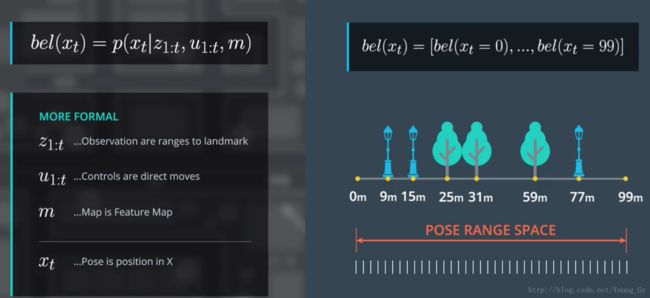
bel(xt)=P(xt|z1:t,u1:t,m)
这里额外提一下,如果求 P(xt,m|z1:t,u1:t) ,那么则从定位问题变成SLAM(simultaneous location and mapping)问题。
容易看到,随着 t 的增大,估计 bel(xt) 需要的数据越来越大。我们的目标是:
- 减少估计所用的数据量
- 需要的数据不随时间增加
也就是:
bel(xt)=f(bel(xt−1),zt,ut,m)
根据贝叶斯公式,可得:
bel(xt)=P(xt|z1:t,u1:t,m)=P(xt|zt,z1:t−1,u1:t,m)=P(xt|z1:t−1,u1:t,m)P(zt|xt,z1:t−1,u1:t,m)P(zt|z1:t−1,u1:t,m)
上面的公式主要包含两部分,下面将对这两部分分别求解:
- motion model(prediction): P(xt|z1:t−1,u1:t,m)
- observation model(likelihood): P(zt|xt,z1:t−1,u1:t,m)
Motion Model
根据马尔科夫假设,可得:
P(xt|z1:t−1,u1:t,m)=∫P(xt−1|z1:t−1,u1:t,m)P(xt|xt−1,z1:t−1,u1:t,m)dxt−1=∫P(xt−1|z1:t−1,u1:t−1,m)P(xt|xt−1,ut,m)dxt−1=∑ibel(xit−1)P(xt|xit−1,ut)
P(xt|xit−1,ut) 被称为transition model,其满足:
P(xt|xit−1,ut)∼N(xt−xit−1:ut,σut)
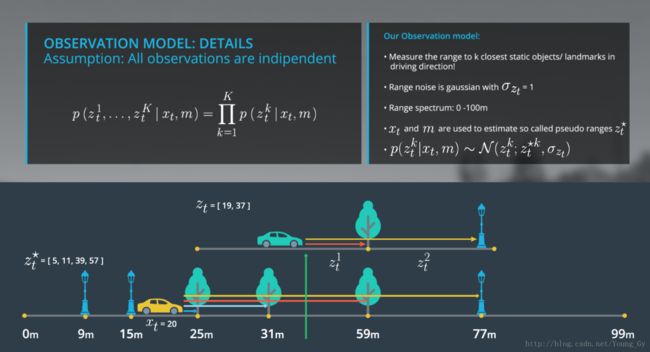
Observation Model
根据马尔科夫假设,可得:
P(zt|xt,z1:t−1,u1:t,m)=P(zt|xt,m)=P(z1t,z2t,...zkt|xt,m)=∏kP(zkt|xt,m)
其中,
P(zkt|xt,m)∼N(zkt:zkt∗,σzk)
代码实例
void bayesianFilter::process_measurement(const MeasurementPackage &measurements,
const map &map_1d,
help_functions &helpers){
/******************************************************************************
* Set init belief of state vector:
******************************************************************************/
if(!is_initialized_){
//run over map:
for (unsigned int l=0; l< map_1d.landmark_list.size(); ++l){
//define landmark:
map::single_landmark_s landmark_temp;
//get landmark from map:
landmark_temp = map_1d.landmark_list[l];
//check, if landmark position is in the range of state vector x:
if(landmark_temp.x_f > 0 && landmark_temp.x_f < bel_x_init.size() ){
//cast float to int:
int position_x = int(landmark_temp.x_f) ;
//set belief to 1:
bel_x_init[position_x] = 1.0f;
bel_x_init[position_x-1] = 1.0f;
bel_x_init[position_x+1] = 1.0f;
} //end if
}//end for
//normalize belief at time 0:
bel_x_init = helpers.normalize_vector(bel_x_init);
//set initial flag to true:
is_initialized_ = true ;
}//end if
/******************************************************************************
* motion model and observation update
******************************************************************************/
std::cout <<"-->motion model for state x ! \n" << std::endl;
//get current observations and control information:
MeasurementPackage::control_s controls = measurements.control_s_;
MeasurementPackage::observation_s observations = measurements.observation_s_;
//run over the whole state (index represents the pose in x!):
for (unsigned int i=0; i< bel_x.size(); ++i){
float pose_i = float(i) ;
/**************************************************************************
* posterior for motion model
**************************************************************************/
// motion posterior:
float posterior_motion = 0.0f;
//loop over state space x_t-1 (convolution):
for (unsigned int j=0; j< bel_x.size(); ++j){
float pose_j = float(j) ;
float distance_ij = pose_i-pose_j;
//transition probabilities:
float transition_prob = helpers.normpdf(distance_ij,
controls.delta_x_f,
control_std) ;
//motion model:
posterior_motion += transition_prob*bel_x_init[j];
}
/**************************************************************************
* observation update:
**************************************************************************/
//define pseudo observation vector:
std::vector<float> pseudo_ranges ;
//define maximum distance:
float distance_max = 100;
//loop over number of landmarks and estimate pseudo ranges:
for (unsigned int l=0; l< map_1d.landmark_list.size(); ++l){
//estimate pseudo range for each single landmark
//and the current state position pose_i:
float range_l = map_1d.landmark_list[l].x_f - pose_i;
//check, if distances are positive:
if(range_l > 0.0f)
pseudo_ranges.push_back(range_l) ;
}
//sort pseudo range vector:
sort(pseudo_ranges.begin(), pseudo_ranges.end());
//define observation posterior:
float posterior_obs = 1.0f ;
//run over current observation vector:
for (unsigned int z=0; z< observations.distance_f.size(); ++z){
//define min distance:
float pseudo_range_min;
//check, if distance vector exists:
if(pseudo_ranges.size() > 0){
//set min distance:
pseudo_range_min = pseudo_ranges[0];
//remove this entry from pseudo_ranges-vector:
pseudo_ranges.erase(pseudo_ranges.begin());
}
//no or negative distances: set min distance to maximum distance:
else{
pseudo_range_min = distance_max ;
}
//estimate the posterior for observation model:
posterior_obs*= helpers.normpdf(observations.distance_f[z],
pseudo_range_min,
observation_std);
}
/**************************************************************************
* finalize bayesian localization filter:
*************************************************************************/
//update = observation_update* motion_model
bel_x[i] = posterior_obs*posterior_motion ;
};
//normalize:
bel_x = helpers.normalize_vector(bel_x);
//set bel_x to belief_init:
bel_x_init = bel_x;
};