《Java程序设计习题精析与实验指导》一3.3 实验指导
3.3 实验指导
3.3.1 实验目的与要求
- 熟悉Java结构化程序设计的基本方法和过程。
- 掌握顺序、选择、循环结构的语义及编程规律。
- 理解方法的作用域并掌握方法的定义和调用及参数的传递。
- 掌握数组的定义和应用。
3.3.2 实验样例
一、程序改错
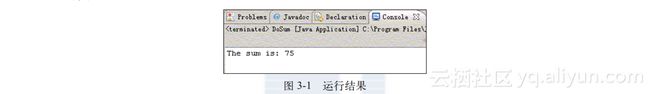
- 下面的应用程序用于计算两个整数之和,正确的应用程序执行后输出的结果应如图3-1所示。
请指出程序中的三处错误,并将其改正。
#1 public class DoSum
#2 public static void pain(String[] args) {
#3 int a = 23;
#4 int b = 52;
#5 int c = sum(a, b);
#6 System.out.println("The sum is: " + c);
#7 }
#8 public int sum(int a, int b) {
#9 return a + b;
#10 }
#11 }答案:
#1 应改为:public class DoSum{
#2 应改为:public static void main(String[] args) {
#8 应改为:public static int sum(int a, int b) {解析:第1行是因为对于类的定义必须做到左右括号匹配;第2行中类中所定义的主方法main()名字不可随意更改;第8行的修改理由是作为可以在类中被调用的方法,此处需要定义为类方法(又称为静态方法)。
求得圆周率。n的取值为10000000。请指出程序中的两处错误,并将其改正。
#1 public class PI{
#2 public void main(String args[]) {
#3 long n=1;
#4 int pi=2;
#5 while (n>10000000){
#6 pi=pi*(2*n)/(2*n-1)*(2*n)/(2*n+1);
#7 n++;
#8 }
#9 System.out.println("n="+n);
#10 }
#11 } 答案:
#4 应改为:double pi=2;
#5 应改为:while (n<10000000){解析:第2行中的pi是用于存放值的变量,显然应该定义为双精度(实数)类型数据;对于while循环语句,只有在其后面的表达式为真的前提下才进行循环,当前的n值取最大值为10000000,故只有当n小于该值时,继续计算有意义,也才能循环下去。
运行程序后正确的输出结果为:
13 24 18
请指出下面程序中的三处错误,并将其改正。
#1 public class Te22 {
#2 private static int[] testaa(int[][] ms) {
#3 int[] result = new int[ms.length];
#4 for (int i = 0; i < result.length; i++) {
#5 for (int j = 0; j < ms.length; j++)
#6 result[i] += ms[j][i];
#7 }
#8 }
#9 public static void main(String[] args){
#10 int[][] arrays = {{9,8,7}, {6,5,5}, {-2,5,1}, {0,6,5}};
#11 int[] answer = testaa(arrays);
#12 for (int i = 1; i < answer.length; i++)
#13 System.out.print(answer[i] + " ");
#14 }
#15 }答案:
#3 应改为:int[] result = new int[ms[0].length];
#7 应改为:} return result;
#12 应改为:for (int i = 0; i < answer.length; i++)解析:对于本程序中的二维数组ms 来说,Java规定:ms.length返回数组的行数,ms[i].length(此处i为0、1、2)返回数组的列数,此处所定义的result数组的长度必须与ms数组的列数相同,故应采用返回数组列数的表示方法;对于有返回值的方法,必须用return语句将其计算的结果返回其主调程序,所以第7行要做修改;由于数组的下标计数都是从0开始的,故若将数组的所有元素逐个输出,循环操作自然也应该从0开始。
- 下面应用程序实现找出1000以内的所有水仙数。水仙数是其各个位数的立方数之和等于该数。例如:153=13+53+33。找出程序中存在的三个错误之处并予以纠正。
#1 public class Shuixianshu{
#2 int a,b,c;
#3 public static boolean sxs(){
#4 a=m%10;
#5 b=(m/10)%10;
#6 c=m%100;
#7 return (a*a*a+b*b*b+c*c*c==m);
#8 }
#9 public static void main(String [] args){
#10 for (int i=100;i<1000;i++){
#11 if (sxs(i))
#12 System.out.println(i+"是水仙数.");
#13 }
#14 }
#15 }答案:
#2 应改为:static int a,b,c;
#3 应改为:public static boolean sxs(int m ){
#6 应改为:c=m/100;解析:一般我们把定义于类之中且处于所有方法之外的变量称为类变量或者静态变量,这类变量在定义时,一般需要加上修饰符static,所以第2行做此修改;在第11行调用sxs()方法的语句中,可以看到调用语句中包含实际参数,并且在sxs()方法中出现了从未定义的变量m,很显然m应该是参数传递过程中的形式参数;变量c中存放的应是整数m百位数上的数值,其获得该数值的运算显然应该是m整除100以后的结果,而不是m除以100以后取余的结果。
- 下面程序用于从键盘上接收用户输入的十个字符,然后将它们倒置输出。例如:若用户输入为a、b、c、d、e、f、g、h、i、j,则程序输出为j、i、h、g、f、e、d、c、b、a。找出程序中存在的三个错误之处并予以纠正。
#1 import java.io.* ;
#2 public class StrTest{
#3 public static void main(String args[ ]) throws IOException{
#4 int i , N =10;
#5 char s1;
#6 char arr[ ] = new char[N];
#7 BufferedReader buf;
#8 buf= new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
#9 s1=buf.readLine( );
#10 for (i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++)
#11 arr[i]=s1;
#12 for (i = N-1 ; i >= 0 ; i ++)
#13 System.out.print(arr[i]+" ");
#14 System.out.println();
#15 }
#16 } 答案:
#5 应改为:String s1;
#11 应改为:arr[i]=s1.charAt(i);
#12 应改为:for ( i = N-1; i >= 0 ; i --)解析:本程序中,s1存放的是直接从键盘输入的内容,而此程序从键盘输入的内容作为字符串处理,所以s1应该声明为String数据类型;一旦s1为String数据类型,它的内容就不能直接赋值给字符型的变量了,在第11行须使用charAt(i)方法将该字符串中的字符逐个地赋值给arr数组;对于for循环来说,如果循环变量的初值大于终值,则循环变量的增值就应该是负数,否则程序将无法停止循环。
二、编程题
- 执行应用程序时带输入参数的练习。
在Java应用程序中,程序的执行是从主方法开始的。在主方法的头部定义
public static void main (String args[])
中,大家是否注意到“args[]”?它意味着什么?args[]是一个字符串数组,用来接收应用程序执行时由用户输入的参数,其中args[0]表示应用程序接收的第一个参数,args[1]表示接收的第二个参数,依次类推。
请建立下面的Java应用程序,然后按步骤操作:
public class MyFriend{
public static void main (String arg[]){
System.out.println(arg[0]+ "and"+ arg[1] +"are my good friends! ");
}
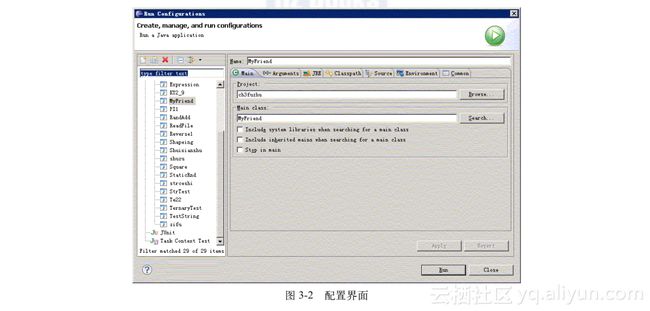
}1)打开“Run”菜单,点击“Run Configurations”按钮,进入运行配置界面。
2)在“Main”选项卡的左侧选择要运行的程序(此处为MyFriend),使配置界面如图3-2所示。
3)点击“(x)=Arguments”标签,在下面的“Program arguments:”文本框中输入程序运行需要的参数(如图3-3所示)。
4)点击下面的“Run”按钮运行程序。本程序运行结果如图3-4所示。
应用程序含有参数的情形,在早期的Java运行环境(比如SDK)中为用户提供了相当大的便利,然而在Eclipse环境中,由于创建用户界面不再是繁琐的事情,因此如果确实需要在应用程序开始运行时提供数据,也可以在创建用户界面后将数据通过用户界面输入(这些内容将在第5章中做详细介绍),而上述方法在目前则较少使用了。
- switch语句的练习。
建立下面的程序,该程序实现从键盘输入学生成绩(0~100)、分级并输出的功能。
import java.io.*;
class Score {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException{
int c;
BufferedReader buf;
System.out.print("请输入学生成绩: ");
buf= new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
c=Integer.parseInt(buf.readLine());
switch (c<60?1:c<75?2:c<90?3:4) {
case 1:
System.out.println(" "+c+"分.不合格,要多努力.");
case 2:
System.out.println(" "+c+"分.合格,还要加劲.");
case 3:
System.out.println(" "+c+"分.良好,再接再厉.");
default:
System.out.println(" "+c+"分.优秀,恭喜恭喜.");
}
}
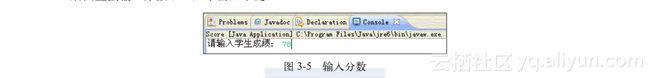
}运行该程序,用鼠标单击如图3-5所示的选项卡视图窗口,在“请输入学生成绩:”文字的后面直接输入分数:78,单击回车键。
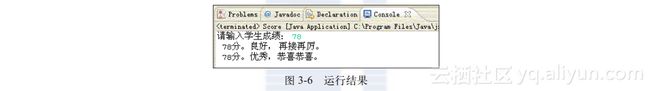
程序将显示如图3-6所示的结果。
作为一项成绩,其结果既是良好又是优秀显然是不符合要求的,关键的问题是switch语句中的所有case语句都没有break语句,78分属于case 3的运行范畴,但程序执行了case 3之后,又会去执行default中的语句,因而就造成了上面的运行结果。
现将源程序修改如下:
import java.io.*;
class Score {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException{
int c;
BufferedReader buf;
System.out.print("请输入学生成绩: ");
buf= new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
c=Integer.parseInt(buf.readLine());
switch (c<60?1:c<75?2:c<90?3:4) {
case 1:
System.out.println(" "+c+"分.不合格,要多努力.");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println(" "+c+"分.合格,还要加劲.");
break;
case 3:
System.out.println(" "+c+"分.良好,再接再厉.");
break;
default:
System.out.println(" "+c+"分.优秀,恭喜恭喜.");
}
}
}再次运行程序,这次你将看到正确的运行结果。
- 循环语句与变量的作用域。
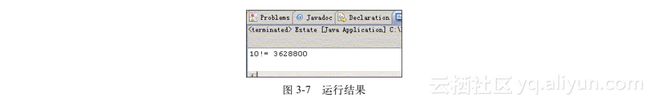
建立程序实现计算并输出10的阶乘(如图3-7所示)。
输入如下的程序代码:
public class Estate {
public static void main(String args[]) {
long n=0;
for (int i=1;i<=10,i++)
n=n*i;
System.out.println(i-1+"!= "+n);
}
}输入完毕后将看到系统提示:程序的最后一个语句“System.out.println(i–1+"!= "+n)”的左边出现了,这里的问题并不是指这个语句本身有什么语法错误,而是指该语句中的变量i没有声明过,变量i虽然在循环语句中进行了声明,但它的作用范围仅在该循环语句之内,一旦出了循环,该变量就被系统自动回收了;也就是说,在循环语句的外面是看不到变量i的,要解决这个问题的方法是将变量i声明到循环语句的外面,使程序改变为:
public class Estate {
public static void main(String args[]) {
long n=0;
int i;
for (i=1;i<=10,i++)
n=n*i;
System.out.println(i-1+"!= "+n);
}
}提示错误的信号就消失了,现在运行程序,可以看到运行结果为0,而不是正确的结果,这个原因想必大多数细心的读者都可猜到:连乘运算,变量的初始值是不能为0的,不管自乘多少次结果都将是0,因此只需将语句“long n=0”改成“long n=1”,再运行程序就可以得到正确的结果了。
- 自定义方法的练习。
已知圆球体积公式为,编写程序,设计一个求圆球体积的方法,并在主程序中调用
它,求出当r =3时,圆球的体积值。
根据题意:首先可以定义当前类的类名为VCircle,该类中除了主方法之外还应该有一个专门用于计算球体积的方法,我们把该方法的方法名定义为setCircle。这个方法在被调用时,其半径值应由调用它的程序将其传入,故方法在定义的时候必须有一个形式参数;主方法在调用setCircle()方法的同时还肩负有输出运算结果的任务。因此程序参考答案如下:
public class VCircle{
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println("volumn="+setCircle(3.0));
}
static double setCircle(double r){
double pi=3.1415926;
return 4/3*pi*Math.pow(r, 3);
}
} - 下面程序的功能是完成由用户从键盘输入一个5~100之间的整数n,编写方法cha()计算并输出用n元人民币换成1元、2元、5元的所有兑换方案。
例如:若用户输入10,则输出为:
1:10 2: 0 5:0
1:8 2: 1 5:0
1:6 2: 2 5:0
1:4 2: 3 5:0
1:2 2: 4 5:0
1:0 2: 5 5:0
1:5 2: 0 5:1
1:3 2: 1 5:1
1:1 2: 2 5:1
1:0 2: 0 5:2
import java.io.*;
public class Change{
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
int money;
String str;
Change cc1=new Change();
BufferedReader buf;
buf=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.print("Input an integer:");
str=buf.readLine();
money=Integer.parseInt(str);
if (money>5 && money<=100) cc1.cha(money);
}
public void cha(int num) {
…
}
}程序分析:
本方法声明了3个局部变量r1、r2、r5,分别用于存放1元、2元及5元的个数,在程序中使用两重循环遍历3个变量的取值,将符合条件的数逐项输出;由于本方法无返回值,故在方法中应完成所需结果的输出。
参考程序:
int r1,r2,r5;
for (r5=0;r5<=num/5;r5++)
for (r2=0;r2<=num/2;r2++){
r1=num-r5*5-r2*2;
if (r1>=0)
System.out.println("1:"+r1+" "+"2: "+r2+" "+"5:"+r5);
}3.3.3 实验内容
一、程序改错
- 本程序要求正确的运行结果如图3-8所示。程序有错,请改正。
#1 public class Te21 {
#2 public void main(String[] args) {
#3 int size = 5;
#4 for (int i=0; i<=size; i++) {
#5 for (int j=i; j>=0; j--)
#6 System.out.print(i);
#7 System.out.print ();
#8 }
#9 }
#10 }- 本程序实现对一个16位的长整数统计0~9这十个数字每一个出现的次数。程序有错,请改正。
#1 public class StatNum{
#2 public static void main(String args[]){
#3 int m;
#4 int a[]=new int[10];
#5 long aa=1586488654895649;
#6 for (int i=0;i<=15;i++){
#7 m=aa %10;
#8 a[m]=a[m]+1;
#9 aa=aa/10;
#10 }
#11 for (m=0;m<10;m++)
#12 System.out.println(m+": "+a[m]);
#13 }
#14 }- 本程序的功能为实现字符串的连接。在主程序中建立两个字符串数组:{"pen", "pencil", "paper"}、{"computer", "eraser"}。程序运行后正确的输出结果为pen pencil paper computer eraser。程序有错,请改正。
#1 public class Te23{
#2 public static void main(String[] args){
#3 String[] strs = {"pen", "pencil", "paper"};
#4 String[] morestrs = {"computer", "eraser"};
#5 String[] result = joinstrs(strs, morestrs);
#6 for (int i = 0; i < result.length; i++)
#7 System.out.print(result);
#8 }
#9 private static String[] joinstrs(String[] a, String[] b) {
#10 String[] result = new String[a.length + b.length];
#11 for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++)
#12 result = a[i];
#13 for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i++)
#14 result = b[i];
#15 return result;
#16 }
#17}- 本程序实现将两个各有6个整数的数组合并成一个由小至大排列的数组(该数组的长度为12)。程序有错,请改正。
#1 import java.io.*;
#2 public class SortArray{
#3 public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException{
#4 int m,n,k;
#5 int aa[]=new int[6];
#6 int bb[]=new int[6];
#7 int cc[]=new int[12];
#8 for (int i=0;i<=6;i++){ //利用产生随机数的方式为数组赋值
#9 m=100*Math.random();
#10 aa[i]=m;
#11 n=100*Math.random();
#12 bb[i]=n;
#13 System.out.println(aa[i]+" "+bb[i]);
#14 }
#15 for (int i=0;i<6;i++) //先将两个数组进行排序
#16 for (int j=i;j<6;j++){
#17 if (aa[i]>aa[j])
#18 {int t=aa[i];aa[i]=aa[j];aa[j]=t;}
#19 if (bb[i]>bb[j])
#20 {int t=bb[i];bb[i]=bb[j];bb[j]=t;}
#21 }
#22 m=0; //用合并法将两个有序数组排序并合并
#23 n=0;
#24 k=0;
#25 while (m==6 && n==6) {
#26 if (aa[m]<=bb[n])
#27 cc[k]=aa[m];m++;
#28 else
#29 cc[k]=bb[n];n++;
#30 k++;
#31 }
#32 while (m==6)
#33 { cc[k]=aa[m];m++;k++;}
#34 while (n==6)
#35 { cc[k]=bb[n];n++;k++;}
#36 for (int i=0;i<12;i++)
#37 System.out.print(cc[i]+" ");
#38 }
#39 }- 本程序以递归的方式实现1+2+3+…+n(n = 200)的计算。程序有错,请改正。
#1 class RecuSum{
#2 long Sum1(int n){
#3 if (n==1)
#4 Sum1= 1;
#5 else
#6 Sum1= n+Sum1(n-1);
#7 }
#8 public static void main(String args[]) {
#9 int n=200;
#10 System.out.println("Sum="+Sum1(n));
#11 }
#12 }二、编程题
- 由键盘输入两个字符串“12”与“24”,将它们转换成整数,然后计算并输出这两个数的和。
- 由键盘输入一个百分制成绩,要求按等级A、B、C和D形式输出成绩,90分以上为A,75~89分为B,60~74分为C,60分以下为D。
- 求一个由10项组成的等差数列,其奇数项之和为135,偶数项之和为150。
- 用for语句输出下列数字金字塔:
1
1 3 1
1 3 5 3 1
1 3 5 7 5 3 1
1 3 5 7 9 7 5 3 1
- 由键盘输入一正整数,求出小于等于这个数的所有质数。
- 由键盘输入一整数,求出该数所有的因子,如输入6,则输出的6的所有因子为1、2、3、6。
- 假设有一条钢材长2000米,每天截取其中的一半,编一程序求出多少天后,钢材的长度开始短于5米?
- 利用数列来取得的近似值。并计算在得到3.14159之前,这
个数列要取到第几项? - 声明一数组来存放12个月的英文名称,由用户从键盘输入月份,如输入8,则程序输出相应的月份名称August。同时请大家考虑若是用户输入了1~12以外的内容,你的程序将如何应对?