算法-力扣-N叉树遍历
N叉树节点的定义
public class Node {
public int val;
public List<Node> children;
public Node() {}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, List<Node> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
}
力扣[590] N叉树的后序遍历
题目
给定一个 N 叉树,返回其节点值的后序遍历。
例如,给定一个 3叉树 :
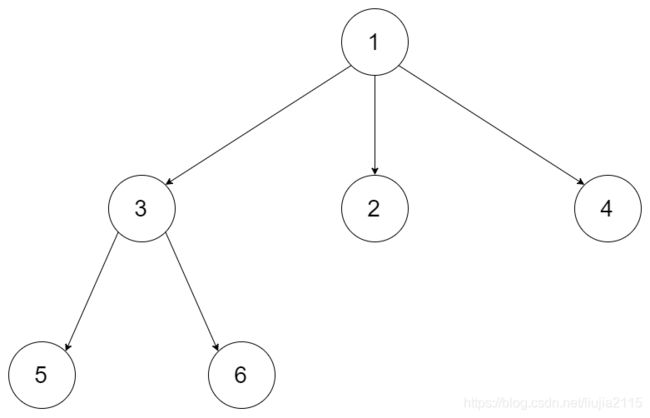
返回其后序遍历: [5,6,3,2,4,1].
解法一:递归
先访问其所有孩子节点,最后再访问本节点。
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorder(Node root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
help(root, list);
return list;
}
public void help(Node root, List<Integer> list) {
if (root != null) {
if (root.children != null) {
for (Node node : root.children) {
help(node, list);
}
}
list.add(root.val);
}
}
}
解法二:迭代用栈
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorder(Node root) {
//用LinkedList,这样的话就可以把每次出栈节点的值加到列表的头部
LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
if (root != null) {
stack.push(root);
}
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
Node current = stack.pop();
list.addFirst(current.val);
if (current.children != null) {
for (Node node : current.children) {
stack.push(node);
}
}
}
return list;
}
}
力扣[589] N叉树的前序遍历
题目
给定一个 N 叉树,返回其节点值的前序遍历。
例如,给定一个 3叉树 :
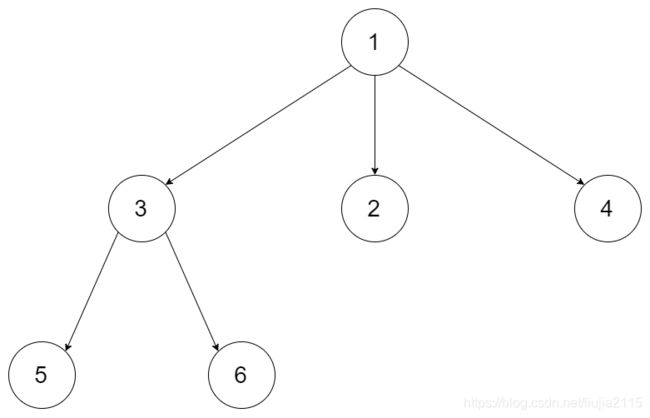
返回其前序遍历: [1,3,5,6,2,4]。
解法一:递归
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorder(Node root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
help(root, list);
return list;
}
public void help(Node root, List<Integer> list) {
if (root != null) {
list.add(root.val);
if (root.children != null) {
for (Node node : root.children) {
help(node, list);
}
}
}
}
}
解法二:迭代用栈
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorder(Node root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
if (root != null) {
stack.push(root);
}
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
Node current = stack.pop();
list.add(current.val);
if (current.children != null) {
Collections.reverse(current.children);
for (Node node : current.children) {
stack.push(node);
}
}
}
return list;
}
}
总结
N叉树的前序遍历和后续遍历都属于深度优先遍历,所以在迭代方法时,选取的数据结构为栈,也就是栈应用于深度优先搜索。下面再看一道应用队列的广度优先遍历问题。
力扣[429] N叉树的层次遍历
给定一个 N 叉树,返回其节点值的层序遍历。 (即从左到右,逐层遍历)。
[
[1],
[3,2,4],
[5,6]
]
解法一:迭代用队列
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(Node root) {
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
if (root != null) {
queue.add(root);
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
List<Integer> level = new ArrayList<>();
int size = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Node current = queue.poll();
level.add(current.val);
queue.addAll(current.children);
}
list.add(level);
}
return list;
}
}
所以涉及到广度优先遍历的题目,应该考虑队列的使用。通常我们不能使用递归进行广度优先搜索。这是因为广度优先搜索基于队列,而递归运行时使用堆栈,适合深度优先搜索。当然此题也是可以用递归解决,但是意义不大且不具有通用性,故不予以讨论
