0037-【Linux-Shell】-Linux_Shell脚本攻略-第一章-小试牛刀
Linux_Shell脚本攻略-第一章-小试牛刀
1.1 简介
脚本开头格式编写
vim work.sh
#!/bin/bash
echo "hello world"文件保存后,输出权限,没有执行权限
-rw-rw-r-- 1 toucan toucan 31 Jun 9 16:26 work.sh可以使用sh直接运行
$sh work.sh
hello world但是,不能直接./运行
$./work.sh
-bash: ./work.sh: Permission denied修改权限权限后,可以直接./运行
$chmod a+x work.sh
$ll
-rwxrwxr-x 1 toucan toucan 31 Jun 9 16:26 work.sh*
$./work.sh
hello world本用户的所有执行目录记录,在~/.bash_history文件中。
1.2 终端打印
显示打印信息
echo
- 打印后自动换行
“ 变量”,双引号可以声明变量'变量‘, 单引号不能声明变量- 特殊字符,需要加转义符
\t \n
e.g.
$echo "hello"
hello
$echo "$PATH"
/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/games:/usr/local/games:/snap/bin
$echo "$HOME"
/home/toucan
$echo "$SHELL"
/bin/bash
$echo '$HOME'
$HOME-n忽略结尾的换行符-e声明转义序列
$echo -n "1\t\2"
1\t\2toucan@tssys /home/toucan/Train
$echo "1\t2\t3"
1\t2\t3
$echo -e "1\t2\t3"
1 2 3printf
C风格打印
- %s、%c 、%d、%f 格式化替换字符
-%5s表示左对齐且宽度为5的字符串替换,-为左对齐,不指定,则右对齐。宽度为数字。%f指定有效数字位数和保留小数点位数- 末尾需要加换行符
\n
$printf "hello world"
hello worldtoucan@tssys /home/toucan/Train Sat Jun 09 16:40 forstart
$vim printf.sh
printf "%-5s %-10s %-4s\n" No Name Mark
printf "%-5s %-10s %-4.2f\n" 1 xiaoming 60.1234
printf "%-5s %-10s %-4.2f\n" 1 xiaohong 80.1234
$sh printf.sh
No Name Mark
1 xiaoming 60.12
1 xiaohong 80.121.3 玩转变量和环境变量
- 变量的等号左右一定不能出现有空格,否则语法不对
# number
count=5
echo $count
echo ${count}
5
5
# str or path
name="xiaoming"
echo ${name}
echo ${#name}
xiaoming
8
环境变量
# 环境变量
$echo $PATH
/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/games:/usr/local/games:/snap/bin
# 哪种shell
$echo $SHELL
/bin/bash
# 哪种shell
$echo $0
-bash
# 当前目录
$echo $PWD
/home/toucan/Train
# 判断是否为超级用户
# root为0,普通用户为1000或其他
root@tssys:/home/toucan/Train# echo $UID
0
$echo $UID
10001. 通过shell进行数学计算
let
[ ]
no1=1;
no2=2;
let result=no1+no2
echo $result
result2=$[no1 + no2]
echo $result2
3
3expr 表达式计算
i=10
b=20
echo $i
# 变量与常数相加
i=`expr $i + 10` #10+10
echo $i
# 变量之间相加
c=`expr $i + $b` #10+20
echo $c
10
20
40bc 高精度显示
i=10
echo $i
j=3;
echo $j
m=`expr $i / $j` #3
echo $m
n=`echo "scale=9; $i / $j" | bc` #3.333333333
echo $n
10
3
3
3.3333333331.5 玩转文件描述符合重定向
- 0 ——stdin 标准输入
- 1 —— stdout 标准输出
2 —— stderr 标准错误
<写入>写出>>追加
# 标准输入
cat < input.txt
# 标准输出
echo "hello" 1> hello.txt
echo "hello" 1> hello.txt
# 标准错误
ls 2>error.txt
# 合并标准输出和标准错误
ls > log.txt 2>&1
# 或者
ls &> log.txt1.6 数组和关联数组
索引从0开始
# 数组赋值
$array_var=(1 2 3 4 5 6);echo ${array_var[0]}
1
# inde-value pari 方式赋值
$array[0]="test1";array[1]="test2";echo ${array[0]}
test1
# 显示所有参数
$array[0]="test1";array[1]="test2";echo ${array[*]}
test1 test2
# 显示所有参数
$array[0]="test1";array[1]="test2";echo ${array[@]}
test1 test2
# 显示参数个数
$array[0]="test1";array[1]="test2";echo ${#array[*]}
21.7 使用别名
alias
alias le='less -SN'
source ~/.bashrc1.8 获取终端信息
获取、设置日期和延时
date
$date
Sat Jun 9 18:14:43 CST 2018
$date +%A
Saturdaysleep 睡眠
# 空命令运行10s
sleep 101.10 调试命令
set
set -x在执时显示参数和命令set +x禁止调试set -v当命令读取是显示输入set +v禁止打印输入
for i in {1..6}
do
set -x
echo $i
set +x
done显示结果:
$sh test1.sh
+ echo 1
1
+ set +x
+ echo 2
2
+ set +x
+ echo 3
3
+ set +x
+ echo 4
4
+ set +x
+ echo 5
5
+ set +x
+ echo 6
6
+ set +x1.11 函数和参数
$cat test1.sh
function fname()
{
echo $1,$2; # $1为第一个参数
echo $@; # 被扩展为"$1","$2",将输出为单独一个字符,常用
echo $*; # 被扩展为“$1c$2" ,将输出为单个字符,不常用
return 0;
}
fname $1 $2
显示结果
$sh test1.sh aaa bbb
aaa,bbb
aaa bbb
aaa bbb1.12 读取命令序列输出
|管道
cmd1|cmd2|cmd31.13 以不按回车键的方式读取字符串”n”
read
1.14 字段分隔符和迭代器
IFS 用于分隔
不懂例子
迭代
$echo {1..10}
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
$echo {a..z}
a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y zfor 循环
$for i in {a..z};do echo $i;done
a
b
c
d
e
f
...C风格的循环
$cat test1.sh
for((i=0;i<10;i++))
{
echo $i
}
$sh test1.sh
0
1
2
3
4
...while 循环
while condition
do
conmands;
doneuntil循环
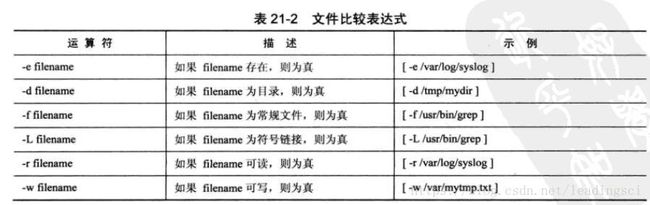
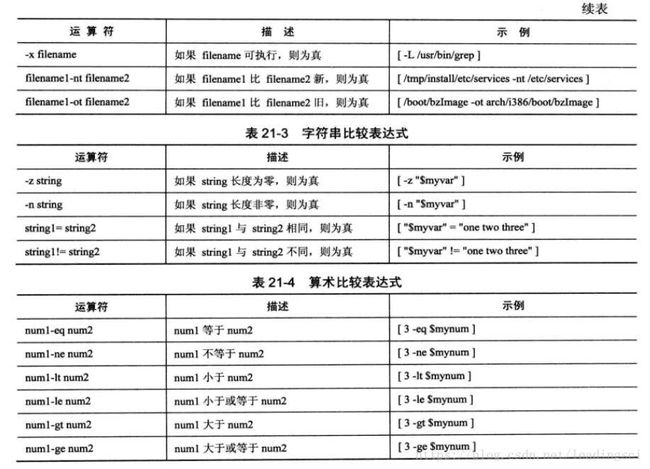
1.15 比较与测试
if
if conditon;
then
commands;
fiif else
if condition;
then
commands
elif conditon;
then
commands
elif
conmands
fi使用&&与运算,使用||或运算,为真实执行,节省行数
[condtion] && action # 如果条件为真,则运行
[condtion] || action # 如果条件为真,则运行算数比较
[ $var -eq 0] # 等于0时,为真
[ $var -ne 0] # 为非0,为真