手写springmvc框架,实现三个基础注解(controller、requestMapping、requestParam)
参考文章https://my.oschina.net/liughDevelop/blog/1622646。本文实现了springmvc的url映射,但没实现requestParam功能和多个参数,在原基础上优化一下。
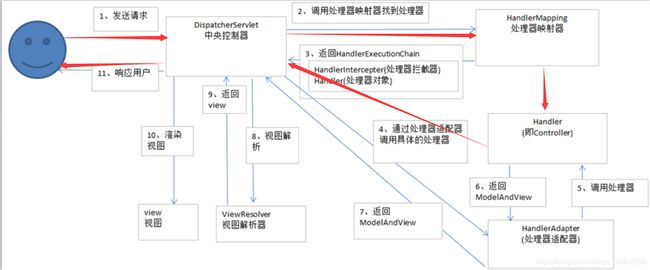
一、springmvc的基本流程
⑴ 用户发送请求至前端控制器DispatcherServlet
⑵ DispatcherServlet收到请求调用HandlerMapping处理器映射器。
⑶ 处理器映射器根据请求url找到具体的处理器,生成处理器对象及处理器拦截器(如果有则生成)一并返回给DispatcherServlet。
⑷ DispatcherServlet通过HandlerAdapter处理器适配器调用处理器
⑸ 执行处理器(Controller,也叫后端控制器)。
⑹ Controller执行完成返回ModelAndView
⑺ HandlerAdapter将controller执行结果ModelAndView返回给DispatcherServlet
⑻ DispatcherServlet将ModelAndView传给ViewReslover视图解析器
⑼ ViewReslover解析后返回具体View
⑽ DispatcherServlet对View进行渲染视图(即将模型数据填充至视图中)。
⑾ DispatcherServlet响应用户。
二、手写springmvc,简化流程
git:https://gitee.com/chuanxin1123/ymvc
红色箭头为简化版的执行流程。
本文实现@Controller、@RequestMapping、@RequestParam三个注解。
项目结构:
依赖:
javax.servlet
javax.servlet-api
3.0.1
三、代码实现
1.MyDispatcherServlet初始化
首先编写web.xml文件
内容为MyDispatcherServlet拦截所有请求。
MySpringMVC
com.chuan.servlet.MyDispatcherServlet
config
main.properties
1
MySpringMVC
/*
在MyDispatcherServlet初始化过程中要做如下内容:
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException{
//将main.properties文件加载进来
loadProperties(config.getInitParameter("config"));
//扫描properties文件里指定的路径
doScanner(properties.getProperty("scanPackage"));
//将包含controller注解的类的对象放到ioc容器中
doPutIoc();
//映射url
getMapping();
System.out.println("init完毕!");
}让springmvc扫描相关的包,那么我们要指定路径。
main.properties文件:
scanPackage=com.chuan.test然后加载配置文件并扫描:
private void loadProperties(String location){
InputStream resourceAsStream = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(location);
try {
properties.load(resourceAsStream);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void doScanner(String packageName){
URL url = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource("/" + packageName.replaceAll("\\.", "/"));
File file =new File(url.getFile());
for (File curFile:file.listFiles()){
if (curFile.isDirectory()){
doScanner(packageName+"."+curFile.getName());
}else {
String fileNmae=packageName+"."+curFile.getName().replace(".class","");
classNames.add(fileNmae);
}
}
}这时我们去创建三个注解 @MyController、@MyRequestMapping、@MyRequestParam。
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)中的ElementType是一个枚举类型,里面代表了该注解适用于什么内容上。type则代表在类上。method则代表在方法上。parameter则代表在参数上。
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface MyController {
String value() default ""; //别名,不做解释
}@Target({ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface MyRequestMapping {
String value() default "";
}@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface MyRequestParam {
String value() default "";
}接下来就是将扫描到的bean对象实例注入到ioc容器中,顺便提一句在spring中的ioc容器里的对象叫bean对象,普通new出来是对象。
private void doPutIoc(){
if (classNames.isEmpty()){
return;
}
for (String className:classNames){
try {
Class clazz= Class.forName(className);
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(MyController.class)){
IOCObject.put(toLowerFirstWord(clazz.getSimpleName()),clazz.newInstance());
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("类未找到!");
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("不能实例化!");
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("无权限操作!");
}
}
}
private String toLowerFirstWord(String name){
char[] charArray = name.toCharArray();
charArray[0] += 32;
return String.valueOf(charArray);
}接下来将url映射到handleMapping里。
if (IOCObject.isEmpty()||IOCObject.size()==0){
return;
}
for (Entry entry:IOCObject.entrySet()){
Class clazz=entry.getValue().getClass();
if (!clazz.isAnnotationPresent(MyController.class)){
continue;
}
if (!clazz.isAnnotationPresent(MyRequestMapping.class)){
continue;
}
//获取类上的路径
String baseUrl = clazz.getAnnotation(MyRequestMapping.class).value();
for (Method method:clazz.getMethods()){
if (!method.isAnnotationPresent(MyRequestMapping.class)){
continue;
}
String url = baseUrl+ method.getAnnotation(MyRequestMapping.class).value();
url=url.replaceAll("/+","/");
try {
handlerMapping.put(url,method);
// 优化了重复创建handlercontroller实例
Object obj=null;
String objName=toLowerFirstWord(clazz.getSimpleName());
//如果已经存在,则复用同一个对象
if (IOCObject.containsKey(objName)){
obj =IOCObject.get(objName);
}else {
obj=clazz.newInstance();
}
handlerController.put(url,obj);
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} 那么到这里,初始化就完成了,试着放在tomcat里运行一下,成功则继续。
2.写service方法(get或post)
我们重点不在http上,就简单处理:
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
try {
//处理请求
doDispatch(req,resp);
} catch (Exception e) {
resp.getWriter().write("500!! Server Exception");
}
}
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(req,resp);
}重点在请求处理上
private void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws Exception{
if (handlerMapping.isEmpty()||handlerMapping.size()==0){
resp.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
resp.setHeader("Content-Type", "text/html;charset=UTF-8");
resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");
resp.getWriter().write("404 页面未找到");
return;
}
String uri = req.getRequestURI();
String contextPath = req.getContextPath();
String url = uri.replace(contextPath,"");
if (!handlerMapping.containsKey(url)){
resp.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
resp.setHeader("Content-Type", "text/html;charset=UTF-8");
resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");
resp.getWriter().write("404 页面未找到");
return;
}
Method method = handlerMapping.get(url);
Class[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
Annotation[][] parameterAnnotations = method.getParameterAnnotations();
List requestParamList=new ArrayList();
int j=0;
for (Annotation[] annotations : parameterAnnotations) {
for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {
Class aClass = annotation.annotationType();
if (aClass.getName().equals("com.chuan.annotation.MyRequestParam")){
//获取注解的value
String paramName = ((MyRequestParam)annotation).value();
requestParamList.add(paramName);
}
}
}
Object[] paramValues = new Object[parameterTypes.length];
//获取请求参数
Map parameterMap = req.getParameterMap();
for (int i=0;i entry:parameterMap.entrySet()){
if (requestParamList.get(j).equals(entry.getKey())) {
//相同的参数只取第一个的值
paramValues[i]=entry.getValue()[0];
continue;
}
}
j++;
}
}
method.invoke(handlerController.get(url),paramValues);
} 写一个测试的controller测试一下。
无参的,1个参数,2个参数。
@MyController
@MyRequestMapping("/chuan")
public class ChuanController {
@MyRequestMapping("/doChuan")
public void test2(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @MyRequestParam("pam") String pam){
try {
response.getWriter().println(" success!pam:"+pam);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
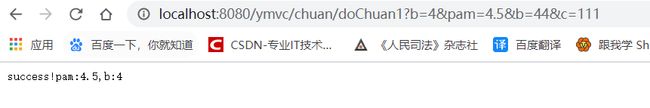
@MyRequestMapping("/doChuan1")
public void doChuan1(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @MyRequestParam("pam") String pam,@MyRequestParam("b") String b){
try {
response.getWriter().println(" success!pam:"+pam+",b:"+b);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@MyRequestMapping("/doChuan2")
public void test2(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response){
try {
response.getWriter().println("success!");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}大功告成!第一阶段完成!