SpringBoot2.X 实战笔记
文章目录
- 多环境配置
- 自定义Starter
- war包方式启动与部署
- Jar包方式运行web项目
- 使用 devtools 热部署
-
- 在pom.xml中引入devtools模块
- IntelliJ IDEA 设置
- properties.yml
- 过滤器(Filter)
-
- 概述
- 第一种方法:FilterRegistrationBean注册
- 第二种方法:@WebServlet+ @ServletComponentScan(推荐)
- 拦截器(Intercepter)
-
- 拦截器的处理流程
- 自定义拦截器
- 过滤器和拦截器比较
- 设置支持跨域请求
- @SpringBootTest单元测试
- 测试进阶之MockMvc
- 全局异常配置
-
- 默认异常机制
- 自定义json格式异常响应
- 自定义异常处理页面
- 整合 Freemaker 模板引擎
- 整合 Thymeleaf 模板引擎
- 整合 Mybatis + MySQL
- Prometheus + Grafana 实现可视化的监控
-
- Prometheus 组件
-
- 下载 & 安装 & 启动
- 集成SpringBoot
-
- Grafana 组件
-
- 下载 & 安装 & 启动
- 整合RabbitMQ
-
- 概述
- SpringBoot Test
-
- java.lang.IllegalStateException Unable to find a @SpringBootConfiguration错误解决方案
多环境配置
yaml 语法参考: https://www.jianshu.com/p/97222440cd08
在线properties转yaml工具: http://www.toyaml.com/index.html
server:
port: 8181
spring:
application:
name: multipart-environment
profiles:
active: dev # 指定启动环境
# 开发环境
---
spring:
profiles: dev
test:
env: dev
# 测试环境
---
spring:
profiles: test
test:
env: test
# 生产环境
---
spring:
profiles: prod
test:
env: prod
自定义Starter
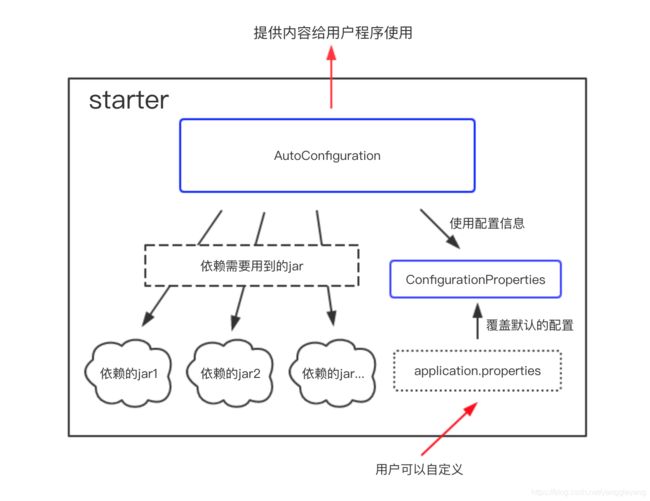
如果你想要自己创建一个starter,那么基本上包含以下几步:
- 创建一个starter项目
- 创建一个ConfigurationProperties用于保存你的配置信息(如果你的项目不使用配置信息则可以跳过这一步,不过这种情况非常少见)
- 创建一个AutoConfiguration,引用定义好的配置信息;在AutoConfiguration中实现所有starter应该完成的操作,并且把这个类加入spring.factories配置文件中进行声明
- 打包项目,之后在一个SpringBoot项目中引入该项目依赖,然后就可以使用该starter了
新建一个Maven项目,设置 pom.xml 文件
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion>
<artifactId>http-starterartifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOTversion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-startersartifactId>
<version>2.2.2.RELEASEversion>
parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starterartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombokartifactId>
<version>1.16.10version>
dependency>
dependencies>
project>
创建proterties类来保存配置信息
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "http")
@Setter
@Getter
public class HttpProperties {
// 如果配置文件中配置了http.url属性,则该默认属性会被覆盖
private String url = "http://www.baidu.com/";
}
创建业务类
@Setter
@Getter
public class HttpClient {
private String url;
// 根据url获取网页数据
public String getHtml() {
try {
URL url = new URL(this.url);
URLConnection urlConnection = url.openConnection();
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(urlConnection.getInputStream(), "utf-8"));
String line = null;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
sb.append(line).append("\n");
}
return sb.toString();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "error";
}
}
创建AutoConfiguration
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties(HttpProperties.class)
public class HttpAutoConfiguration {
@Resource
private HttpProperties properties;
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public HttpClient init() {
HttpClient client = new HttpClient();
String url = properties.getUrl();
client.setUrl(url);
return client;
}
}
在 resources 文件夹下新建目录 META-INF,在目录中新建 spring.factories 文件,并且在 spring.factories 中配置AutoConfiguration:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
com.nosuchfield.httpstarter.HttpAutoConfiguration
测试
@Component
public class RunIt {
@Resource
private HttpClient httpClient;
public void hello() {
System.out.println(httpClient.getHtml());
}
}
war包方式启动与部署
- 在pom.xml中将打包形式修改为war
<packaging>warpackaging>
- 修改SpringBoot启动类
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application extends SpringBootServletInitializer {
@Override
protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder application) {
return application.sources(Application.class);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
Jar包方式运行web项目
在pom.xml文件中加入如下依赖
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-pluginartifactId>
plugin>
plugins>
build>
- 执行启动环境
java -jar -Xms1024m -Xmx1024m XXX.jar --spring.profiles.active=dev &
使用 devtools 热部署
在pom.xml中引入devtools模块
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtoolsartifactId>
<optional>trueoptional>
dependency>
dependencies>
IntelliJ IDEA 设置
- 首先,File --> Settings --> Complier --> 选中 Build project automatically
- 使用该组合键 Shift+ALT+Ctrl+/ ,选择 Registry勾选 “complier.automake.allow.when.app.running” 选项
properties.yml
- 自定义排除某些文件,可以通过 spring.devtools.restart.exclude
- 通过spring.devtools.restart.trigger-file 配置监听某个特定的文件触发热部署
过滤器(Filter)
概述
配置在web.xml中,依赖于servlet容器。
优点:
在实现上Filter是基于函数回调,可以对几乎所有请求进行过滤
缺点:
一个过滤器实例只能在容器初始化时调用一次 . 当容器第一次加载该过滤器时,init() 方法将被调用
使用场景:
比如设置编码、过滤敏感词汇、禁止浏览器缓存所有动态页面、实现用户自动登陆、实现URL级别的权限认证等等 ,具体案例参考Filter(过滤器)常见应用
传统的JavaEE项目开发filter的主要2个步骤
- 实现Filter接口,并实现其doFilter方法。
- 在 web.xml 文件中使用和元素对编写的filter类进行注册,并设置它所能拦截的资源。
- 可以开发编写多个Filter,组成一个Filter链,根据Filter在web.xml文件中的注册顺序,决定先调用哪个Filter。
它使用户可以改变一个 request和修改一个response,Filter 不是一个servlet,它不能产生一个response,它能够在一个request到达servlet之前预处理request,也可以在离开 servlet时处理response,换种说法,filter其实是一个 “servlet chaining” (servlet 链)。
一个Filter包括:
1)在servlet被调用之前截获
2)在servlet被调用之前检查servlet request
3)根据需要修改request头和request数据
4)根据需要修改response头和response数据
5)在servlet被调用之后截获
第一种方法:FilterRegistrationBean注册
- 实现Filter方法
public class GlobalFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) servletRequest;
String requestURI = request.getRequestURI();
System.out.println(requestURI);
filterChain.doFilter(request, servletResponse);
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
}
}
- 加载Filter配置
@Configuration
public class FilterConfig {
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean filterRegistration(){
// 新建过滤器注册类
FilterRegistrationBean registration = new FilterRegistrationBean();
// 添加自定义过滤器
registration.setFilter(globalFilter());
// 设置过滤器的URL模式
registration.addUrlPatterns("/*");
//设置过滤器顺序
registration.setOrder(1);
return registration;
}
@Bean
public GlobalFilter globalFilter(){
return new GlobalFilter();
}
}
第二种方法:@WebServlet+ @ServletComponentScan(推荐)
- 自定义MyFilter
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebFilter;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.io.IOException;
@WebFilter(filterName = "myFilter", urlPatterns = "/*")
public class MyFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
System.out.println("init...");
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) servletRequest;
String requestURI = request.getRequestURI();
if(requestURI.contains("my")){
System.out.println("成功啦, 请求URI是:" + requestURI);
}
filterChain.doFilter(request, servletResponse);
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("destroy...");
}
}
- 在Application 启动类添加@ServletComponentScan注解
在 SpringBootApplication 上使用@ServletComponentScan 注解后,Servlet、Filter、Listener 可以直接通过 @WebServlet、@WebFilter、@WebListener 注解自动注册。
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletComponentScan;
@ServletComponentScan
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
拦截器(Intercepter)
Interceptor依赖于web框架,我们经常在Spring MVC中用到该配置,在这个场景下Interceptor 就依赖于SpringMVC框架。Interceptor 基于Java的反射机制,属于AOP的一种运用。
优点:
由于拦截器是基于web框架的调用,因此可以使用Spring的依赖注入进行一些业务操作,同时一个拦截器实例在一个controller生命周期之内可以多次调用。
缺点:
只能对controller请求进行拦截,对其他的一些比如直接访问静态资源的请求则没办法进行拦截处理。
拦截器的处理流程
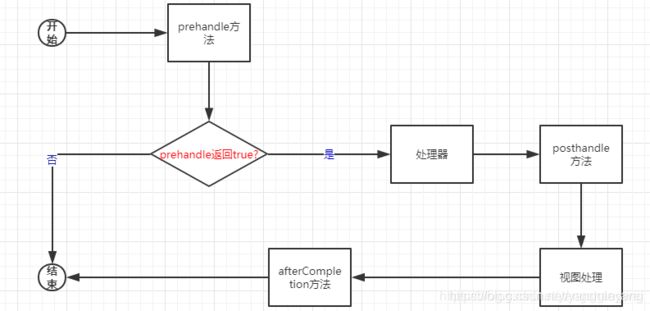
多个拦截器的执行顺序是按照责任链模式的规则,对于处理器前方法采用先注册先执行,而处理器后方法和完成方法则是先注册后执行的规则。
自定义拦截器
- 自定义拦截器
实现接口HandlerInterceptor,或者继承继承HandlerInterceptorAdapter
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
@Component
public class MyInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
/**
* 进入controller层之前拦截请求
*/
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) {
System.out.println("getContextPath:" + request.getContextPath());
System.out.println("getServletPath:" + request.getServletPath());
System.out.println("getRequestURI:" + request.getRequestURI());
System.out.println("getRequestURL:" + request.getRequestURL());
System.out.println("getRealPath:" + request.getSession().getServletContext().getRealPath("image"));
return true;
}
/**
* 处理请求完成后视图渲染之前的处理操作
*/
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) {
}
/**
* 视图渲染之后的操作
*/
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) {
}
}
-
拦截器注册
可以用来注册拦截器的类和接口:
- WebMvcConfigurerAdapter: 2.0以后的版本已失效
- WebMvcConfigurationSupport: 不需要返回逻辑视图,可以选择继承此类
- WebMvcConfigurer:返回逻辑视图,可以选择实现此方法,重写addInterceptor方法
import com.fxbin.demo.interceptor.MyInterceptor;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.InterceptorRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
@Configuration
public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Bean
public MyInterceptor myInterceptor(){
return new MyInterceptor();
}
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
//添加拦截路径和排除拦截路径
registry.addInterceptor(myInterceptor()).addPathPatterns("/**").excludePathPatterns("/test");
}
}
过滤器和拦截器比较
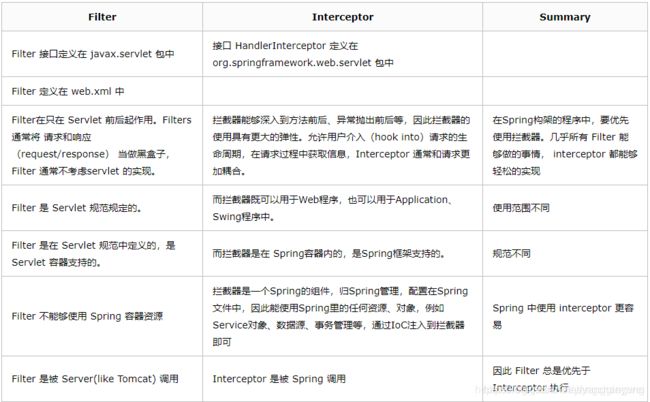
Filter的执行顺序在Interceptor之前 。拦截器(Interceptor)是基于Java的反射机制,而过滤器(Filter)是基于函数回调。从灵活性上说拦截器功能更强大些,Filter能做的事情,Interceptor都能做,而且可以在请求前,请求后执行,比较灵活。
设置支持跨域请求
参考:浏览器同源政策及其规避方法
浏览器安全的基石是"同源政策"(same-origin policy),现代浏览器出于安全的考虑,在http/https请求时必须遵守同源策略,否则跨域的http/https 请求,默认情况下是被禁止的,协议、域名、端口但凡有一个不同都会造成跨域问题。如果发生跨域,则浏览器中每次请求的session都是一个新的,即sessionId肯定不相同。
所谓"同源"指的是"三个相同"
- 协议相同
- 域名相同
- 端口相同
非同源,共有三种行为受到限制
- Cookie、LocalStorage 和 IndexDB 无法读取。
- DOM 无法获得。
- AJAX 请求不能发送。
前端解决方案
- 使用 JSONP 来支持跨域的请求,JSONP 实现跨域请求的原理简单的说,就是动态创建script标签,然后利用script的SRC不受同源策略约束来跨域获取数据。缺点是需要后端配合输出特定的返回信息。
- 利用反向代理的机制来解决跨域的问题,前端请求的时候先将请求发送到同源地址的后端,通过后端请求转发来避免跨域的访问,如通过Nginx反向代理解决跨域问题。
后来 HTML5 支持了 CORS 协议。CORS 是一个 W3C 标准,全称是”跨域资源共享”(Cross-origin resource sharing),允许浏览器向跨源服务器,发出 XMLHttpRequest 请求,从而克服了 AJAX 只能同源使用的限制。它通过服务器增加一个特殊的 Header[Access-Control-Allow-Origin]来告诉客户端跨域的限制,如果浏览器支持 CORS、并且判断 Origin 通过的话,就会允许 XMLHttpRequest 发起跨域请求。
前端使用了 CORS 协议,就需要后端设置支持非同源的请求,对于SpringBoot 对于CORS 同样有着良好的支持。
浏览器和session
- 用户向服务器发送请求,比如登录操作发送用户名和密码
- 服务器验证通过后,通过HttpServletRequest#getSession()#setAttribute等方法保存相关数据
- 服务器向用户返回一个 session_id,浏览器set-cookie Cookie 即Cookie = session_id
- 用户随后的每一次请求,都会通过 Cookie,将 session_id 传回服务器。
- 服务器收到 session_id,找到前期保存的数据,由此得知用户的身份。
集群环境下Session管理思路
- session复制,比如Tomcat支持的Session复制. 优点:tomcat内置支持 缺点:如果集群过大,session 复制为all to all占用带宽,效率不高。
- session 数据持久化,写入redis或者数据库等。优点架构清晰,缺点是工程量大。而且也需要考虑session数据的持久层的高可用,否则单点登录就会失败。
- 服务端不保存 session ,所有数据都保存在客户端,比如 JWT (JSON WEB TOKEN)
小结
- 通过Nginx去解决跨域问题本质上是间接跨域,因为使用反向代理欺骗浏览器,所以浏览器任务客户端和服务端在相同的域名中,可以认为是同源访问,所以session不会丢失。
- 如果使用CORS实现了直接跨域,主要是在服务端通过给response设置header属性,帮助服务器资源进行跨域授权。 因为发生跨域访问,服务器会每次都创建新的Session,会导致session丢失,安全性和灵活性更高,但需要开发人员去解决跨域session丢失的问题。
三种配置方式:
- 过滤器(全局的配置方式)
@Configuration
public class GlobalCorsConfig {
@Bean
public CorsFilter corsFilter() {
CorsConfiguration config = new CorsConfiguration();
config.addAllowedOrigin("*");
config.setAllowCredentials(true);
config.addAllowedMethod("*");
config.addAllowedHeader("*");
config.addExposedHeader("*");
UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource configSource = new UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource();
configSource.registerCorsConfiguration("/**", config);
return new CorsFilter(configSource);
}
}
- 拦截器(全局的配置方式)
@Configuration
public class MyConfiguration extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
public void addCorsMappings(CorsRegistry registry) {
registry.addMapping("/**")
.allowCredentials(true)
.allowedHeaders("*")
.allowedOrigins("*")
.allowedMethods("*");
}
}
- @CrossOrigin 注解
单个请求的跨域通过 @CrossOrigin 注解来实现
@RequestMapping("/hello")
@CrossOrigin("http://localhost:8080")
public String hello( ){
return "Hello World";
}
@SpringBootTest单元测试
在pom.xml文件中加入如下依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes={
Application.class})// 指定启动类
public class ApplicationTests {
@Test
public void testOne(){
System.out.println("test hello one");
}
@Before
public void testBefore(){
System.out.println("before");
}
@After
public void testAfter(){
System.out.println("after");
}
}
测试进阶之MockMvc
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = Application.class)
public class MockMvcTest {
//注入一个web应用环境(容器)
@Resource
private WebApplicationContext webApplicationContext;
//mvc环境对象
private MockMvc mockMvc;
@Before
public void init(){
mockMvc = MockMvcBuilders.webAppContextSetup(webApplicationContext).build();
}
}
@Test
public void findObject() throws Exception {
String str = mockMvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/1/2")
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8)).andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk())
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.jsonPath("$.length()").value(2))
.andReturn().getResponse().getContentAsString();
System.out.println(str);
}
perform:执行一个RequestBuilder请求,会自动执行SpringMVC的流程并映射到相应的控制器执行处理;
andExpect:添加ResultMatcher验证规则,验证控制器执行完成后结果是否正确;
andDo:添加ResultHandler结果处理器,比如调试时打印结果到控制台;
andReturn:最后返回相应的MvcResult;然后进行自定义验证/进行下一步的异步处理;
测试过程如下:
1、准备测试环境
2、通过MockMvc执行请求
3.1、添加验证断言
3.2、添加结果处理器
3.3、得到MvcResult进行自定义断言/进行下一步的异步请求
4、卸载测试环境
全局异常配置
默认异常机制
SpringBoot 默认提供了两种机制:
- 一种是针对于web浏览器访问的错误页面响应
- 另一种则是针对于 接口测试工具等 的参数响应处理
自定义json格式异常响应
通过 @ControllerAdvice、@RestControllerAdvice、@ExceptionHandler 注解全局异常自定义响应类。
- 定义响应状态码枚举类
public enum ResultCode {
SUCCESS(200),//成功
FAIL(400),//失败
UNAUTHORIZED(401),//未认证(签名错误)
NOT_FOUND(404),//接口不存在
INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR(500);//服务器内部错误
private final int code;
ResultCode(int code) {
this.code = code;
}
public int code() {
return code;
}
}
定义响应类
public class Result {
/**
* 状态响应码
*/
private int code;
/**
* 响应结果 成功/失败
*/
private boolean success;
/**
* 响应信息
*/
private String message;
/**
* 响应数据
*/
@JsonInclude(JsonInclude.Include.NON_NULL)
private Object data;
public Result setCode(ResultCode resultCode) {
this.code = resultCode.code();
return this;
}
public int getCode() {
return code;
}
public boolean isSuccess() {
return success;
}
public Result setSuccess(boolean success) {
this.success = success;
return this;
}
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
public Result setMessage(String message) {
this.message = message;
return this;
}
public Object getData() {
return data;
}
public Result setData(Object data) {
this.data = data;
return this;
}
}
- 对响应结果封装,做预处理
public class ResultGenerator {
private static final String DEFAULT_SUCCESS_MESSAGE = "SUCCESS";
public static Result genSuccessResult() {
return new Result()
.setCode(ResultCode.SUCCESS)
.setSuccess(true)
.setMessage(DEFAULT_SUCCESS_MESSAGE);
}
public static Result genSuccessResult(Object data) {
return new Result()
.setCode(ResultCode.SUCCESS)
.setSuccess(true)
.setMessage(DEFAULT_SUCCESS_MESSAGE)
.setData(data);
}
public static Result genFailResult(String message) {
return new Result()
.setCode(ResultCode.FAIL)
.setSuccess(false)
.setMessage(message);
}
}
- 异常处理类
import com.fxbin123.dto.Result;
import com.fxbin123.dto.ResultGenerator;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestControllerAdvice;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
@RestControllerAdvice
public class ExceptionControllerAdvice {
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public Result jsonErrorHandler(HttpServletRequest req, Exception e){
return ResultGenerator.genFailResult(e.getMessage());
}
}
自定义异常处理页面
- 添加
thymeleaf依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleafartifactId>
dependency>
- resource目录下新建templates,并新建error.html
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org" xmlns:layout="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" layout:decorator="layout">
<head>
<title>Spring Boot 自定义异常页面title>
<script type="text/javascript">
script>
head>
<body>
<div layout:fragment="content" th:remove="tag">
<div id="navbar">
<h1>系统异常统一处理h1>
<h3 th:text="'错误信息:'+${msg}">h3>
<h3 th:text="'请求地址:'+${url}">h3>
<h2>Debugh2>
<a th:href="@{
'https://www.google.com/webhp?hl=zh-CN#safe=strict&hl=zh-CN&q='+${msg}}"
class="btn btn-primary btn-lg" target="_blank" id="Google">Googlea>
<a th:href="@{
'https://www.baidu.com/s?wd='+${msg}}" class="btn btn-info btn-lg" target="_blank" id="Baidu">Baidua>
<a th:href="@{
'http://stackoverflow.com/search?q='+${msg}}"
class="btn btn-default btn-lg" target="_blank" id="StackOverFlow">StackOverFlowa>
<h2>异常堆栈跟踪日志StackTraceh2>
<div th:each="line:${stackTrace}">
<div th:text="${line}">div>
div>
div>
div>
<div layout:fragment="js" th:remove="tag">
div>
body>
html>
做错误页面异常处理 返回 ModelAndView
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public Object handleException(Exception e){
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.addObject("msg", e.getMessage());
modelAndView.addObject("url", req.getRequestURL());
modelAndView.addObject("stackTrace", e.getStackTrace());
modelAndView.setViewName("error");
return modelAndView;
}
整合 Freemaker 模板引擎
官网:https://freemarker.apache.org/
在线手册:http://freemarker.foofun.cn/
- pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-freemarkerartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
- yaml配置
spring:
application:
name: freemarker
freemarker:
# 禁用模板缓存
cache: false
# 编码格式
charset: UTF-8
# freemarker模板后缀 默认是 .ftl
suffix: .html
# 是否为此技术启用MVC视图分辨率。
enabled: true
# Content-Type值
content-type: text/html
# #模板加载路径 按需配置 ,默认路径是 classpath:/templates/
template-loader-path: classpath:/templates/
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>indextitle>
head>
<body>
Hello ${content}
body>
html>
@Controller
public class FreemarkerController {
@RequestMapping("/index")
public String index(Model model){
model.addAttribute("content", "Freemarker");
return "index";
}
}
整合 Thymeleaf 模板引擎
官网:https://www.thymeleaf.org/
- pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleafartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
- yaml配置
server:
port: 8081
spring:
application:
name: thymeleaf
thymeleaf:
# 是否启用模板缓存。
cache: true
# 是否检查模板位置是否存在。
check-template: true
# 是否为Web框架启用Thymeleaf视图分辨率。
enabled: true
# 编码格式, 默认UTF-8
encoding: UTF-8
# 应用于模板的模板模式。另请参阅Thymeleaf的TemplateMode枚举。
mode: HTML
# 后缀 默认 .html
suffix: .html
# 模板文件存放位置 , 默认 classpath:/templates/
prefix: classpath:/templates/
<html lang="en" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"
xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
<h1 th:text="${content}">h1>
body>
html>
@Controller
public class ThymeleafController {
@RequestMapping("/test")
public String test(Model model){
model.addAttribute("content", "Hello Thymeleaf");
return "index";
}
}
整合 Mybatis + MySQL
- pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>1.3.2version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.pagehelpergroupId>
<artifactId>pagehelper-spring-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>1.2.9version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibabagroupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>1.1.9version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
<scope>runtimescope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombokartifactId>
dependency>
- application.yml
spring:
application:
name: mybatis-curd
datasource:
username: root
password: root
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?zeroDateTimeBehavior=convertToNull&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=UTC&autoReconnect=true
continue-on-error: true
sql-script-encoding: UTF-8
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
druid:
initial-size: 5
min-idle: 5
max-active: 20
max-wait: 60000
# 间隔多久进行一次检测,检测需要关闭的空闲连接
time-between-eviction-runs-millis: 60000
# 一个连接在池中最小生存的时间
min-evictable-idle-time-millis: 300000
validation-query: SELECT 1 FROM DUAL
test-while-idle: true
test-on-borrow: false
test-on-return: false
pool-prepared-statements: true
max-pool-prepared-statement-per-connection-size: 20
connect-properties: druid.stat.mergeSql=true;druid.stat.slowSqlMillis=5000
use-global-data-source-stat: true
filters: stat,wall,log4j2
mybatis:
type-aliases-package: com.yanggle.mybaits.*
configuration:
map-underscore-to-camel-case: true
# 打印sql, 方便调试
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
use-generated-keys: true
default-statement-timeout: 60
default-fetch-size: 100
import lombok.Data;
import java.util.Date;
@Data
public class User {
// 主键ID
private Integer id;
// 用户名
private String username;
// 密码
private String password;
// 创建时间
private Date gmtCreate;
// 修改时间
private Date gmtModified;
}
import com.github.pagehelper.PageHelper;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import java.util.Properties;
@Configuration
public class MyBatisConfig {
@Bean
public PageHelper pageHelper(){
PageHelper pageHelper = new PageHelper();
Properties p = new Properties();
// 设置为true时,会将RowBounds第一个参数offset当成pageNum页码使用
p.setProperty("offsetAsPageNum","true");
//设置为true时,使用RowBounds分页会进行count查询
p.setProperty("rowBoundsWithCount","true");
p.setProperty("reasonable","true");
pageHelper.setProperties(p);
return pageHelper;
}
}
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.fxbin.mybatis.bean.User;
import com.fxbin.mybatis.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@RestController
public class UserController {
@Resource
private UserService userService;
@RequestMapping("/listAll")
public Object listAll(@RequestParam(value = "page",defaultValue = "1")int page,
@RequestParam(value = "size",defaultValue = "10")int size){
return userService.listAll(page, size);
}
@RequestMapping("/insert")
public int insert (User user){
return userService.insert(user);
}
@RequestMapping("/remove")
public int remove(Integer userId){
return userService.remove(userId);
}
@RequestMapping("/update")
public int update(User user){
return userService.update(user);
}
}
import com.fxbin.mybatis.bean.User;
import java.util.List;
public interface UserService {
Object listAll(int page, int size);
int insert(User user);
int remove(Integer userId);
int update(User user);
}
import com.fxbin.mybatis.bean.User;
import com.fxbin.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper;
import com.fxbin.mybatis.service.UserService;
import com.github.pagehelper.PageHelper;
import com.github.pagehelper.PageInfo;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.util.List;
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Resource
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Override
public Object listAll(int page, int size) {
PageHelper.startPage(page, size);
List<User> userList = userMapper.listAll();
PageInfo<User> pageInfo = new PageInfo<>(userList);
return pageInfo;
}
@Override
public int insert(User user) {
return userMapper.insert(user);
}
@Override
public int remove(Integer userId) {
return userMapper.remove(userId);
}
@Override
public int update(User user) {
return userMapper.update(user);
}
}
import com.fxbin.mybatis.bean.User;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.*;
import java.util.List;
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper {
@Select({
"select * from user"
})
List<User> listAll();
@Insert({
"insert into user(`username`, `password`) values(#{username}, #{password})"
})
int insert(User user);
@Delete({
"delete from user where id = #{userId}"
})
int remove(Integer userId);
@Update({
"update user set username = #{username}, password = #{password} where id = #{id}"
})
int update(User user);
}
Prometheus + Grafana 实现可视化的监控
Prometheus 组件
官网: https://prometheus.io/
下载地址: https://prometheus.io/download/
官方文档: https://prometheus.io/docs/prometheus/latest/getting_started/
Prometheus是一套开源的监控&报警&时间序列数据库的组合,基于应用的metrics来进行监控的开源工具 。
更多信息请参考官网介绍: https://prometheus.io/docs/introduction/overview/
下载 & 安装 & 启动
#下载
[root@artisan ~]# wget http://cactifans.hi-www.com/prometheus/prometheus-2.1.0.linux-amd64.tar.gz
#解压
[root@artisan ~]# tar -xvzf prometheus-2.1.0.linux-amd64.tar.gz
#创建软连接
[root@artisan ~]# ln -s prometheus-2.1.0.linux-amd64 prometheus
#后台运行 &
[root@artisan prometheus]# ./prometheus --config.file=prometheus.yml &
集成SpringBoot
#SpringBoot应用配置
job_name: 'app-prometheus-grafana'
scrape_interval: 5s
metrics_path: '/actuator/prometheus'
static_configs:
targets: ['192.168.0.1:8080']
Grafana 组件
官网:https://grafana.com/
下载地址: https://grafana.com/grafana/download
入门:http://docs.grafana.org/guides/getting_started/
Grafana是一个跨平台的开源的度量分析和可视化工具,可以通过将采集的数据查询然后可视化的展示,并及时通知。它主要有以下六大特点:
- 展示方式:快速灵活的客户端图表,面板插件有许多不同方式的可视化指标和日志,官方库中具有丰富的仪表盘插件,比如热图、折线图、图表等多种展示方式。
- 数据源:Graphite,InfluxDB,OpenTSDB,Prometheus,Elasticsearch,CloudWatch和KairosDB等。
- 通知提醒:以可视方式定义最重要指标的警报规则,Grafana将不断计算并发送通知,在数据达到阈值时通过Slack、PagerDuty等获得通知。
- 混合展示:在同一图表中混合使用不同的数据源,可以基于每个查询指定数据源,甚至自定义数据源。
- 注释:使用来自不同数据源的丰富事件注释图表,将鼠标悬停在事件上会显示完整的事件元数据和标记。
- 过滤器:Ad-hoc过滤器允许动态创建新的键/值过滤器,这些过滤器会自动应用于使用该数据源的所有查询。
下载 & 安装 & 启动
# 下载
[root@artisan ~]# wget http://cactifans.hi-www.com/grafana/grafana-5.4.2-1.x86_64.rpm
# yum本地安装
[root@artisan ~]# yum localinstall grafana-5.4.2-1.x86_64.rpm
# 启动
[root@artisan ~]# systemctl start grafana-server
# 设置为开机启动
[root@artisan ~]# systemctl enable grafana-server
# 查看进程
[root@artisan ~]# ps -ef|grep grafana-server |grep -v grep
整合RabbitMQ
概述
RabbitMQ名词
- Broker:简单来说就是消息队列服务器实体,可以理解为一个节点。
- Exchange:消息交换机,它指定消息按什么规则,路由到哪个队列。
- Queue:消息队列载体,每个消息都会被投入到一个或多个队列。
- Binding:绑定,它的作用就是把exchange和queue按照路由规则绑定起来。
- Routing Key:路由关键字,exchange根据这个关键字进行消息投递。
- vhost:虚拟主机,一个broker里可以开设多个vhost,用作不同用户的权限分离。
- Producer:消息生产者,投递消息的程序。
- Consumer:消息消费者,接受消息的程序。
- Channel:消息通道,在客户端的每个连接里,可建立多个channel,每个channel代表一个会话任务。
SpringBoot Test
java.lang.IllegalStateException Unable to find a @SpringBootConfiguration错误解决方案
将包名改为与其被测试代码分支一样的路径