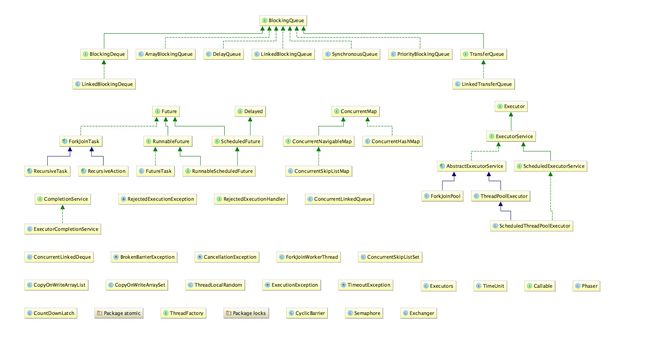
其实从类图我们能发现concurrent包(除去java.util.concurrent.atomic 和 java.util.concurrent.locks)中的内容并没有特别多,大概分为四类:BlockingQueue阻塞队列体系、Executor线程组执行框架、Future线程返回值体系、其他各种单独的并发工具等。
首先学习的是Executor体系,是我们处理多线程最常接触的内容。首先我们单独看下继承体系:
Executor是顶级接口,里面只有一个方法:
public interface Executor {
void execute(Runnable command);---执行一个Runnable对象,Runnable在前面的文章里面已经讲到,是线程的顶级接口,里面有个run方法
}
ExecutorService是我们经常用到的多线程执行框架的声明,源码也很少,我们逐个方法进行解释:
public interface ExecutorService extends Executor {
void shutdown();----关闭线程执行框架中的线程,但效果是不再接受新线程加入,并且等待线程执行结束后关闭Executor
List shutdownNow();---大体同上的,但是该命令会尝试关闭正在运行中的线程,但是也仅仅是调用terminate方法然后让jdk去决定是否结束,同时该方法返回那些awaiting状态的线程组
boolean isShutdown();---是否已经被关闭的状态
boolean isTerminated();---是否已经被中止的状态,在shutdown和shutdownnow被调用后,并且线程全部执行结束,该状态才是true,否则都是false
boolean awaitTermination(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) ---如果线程组terminate了,返回true,超时时间到了返回false。
throws InterruptedException;
Future submit(Callable task);--提交一个Callable的回调,然后执行完成后将结果放入Future对象。
Future submit(Runnable task, T result);--提交一个Runnable接口实现,然后result是Future返回值
Future submit(Runnable task);--提交一个Runnable接口实现,如果执行完成,future.get()可以返回一个null
List> invokeAll(Collection> tasks)--执行提交的Callable集合,然后返回各自的执行结果的Future对象列表,每个元素isDone都是true
throws InterruptedException;
List> invokeAll(Collection> tasks,
long timeout, TimeUnit unit)--执行提交的task集合,执行完成或者timeout之后返回结果,isDone为true
throws InterruptedException;
T invokeAny(Collection> tasks)--执行提交的task集合,有一个执行完成就返回结果
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException;
T invokeAny(Collection> tasks,
long timeout, TimeUnit unit)--同上,有一个执行完成或者有timeout出现
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException;
AbstractExecutorService实现了ExecutorService接口,并且声明为抽象类,然而其中一个抽象方法都没有。。.
public abstract class AbstractExecutorService implements ExecutorService {protectedRunnableFuture newTaskFor(Runnable runnable, T value) {---为子类定义了一个创建RunnableFuture对象的快捷方法
return new FutureTask(runnable, value);
}
---其余方法都是接口的实现方法
}
还有一个继承了ExecutorService的接口的接口:
public interface ScheduledExecutorService extends ExecutorService { ---定义延迟执行的动作 public ScheduledFuture schedule(Runnable command, long delay, TimeUnit unit); ---延迟delay个时间单位后开始执行 publicScheduledFuture schedule(Callable callable, long delay, TimeUnit unit);---延迟delay个时间单位后执行并返回Future对象 public ScheduledFuture scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long period, TimeUnit unit);在initialDelay、initialDelay+N*period分别出发 public ScheduledFuture scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long delay, TimeUnit unit); }--initialDelay开始进行,后面每次执行成功后的dealy时间单位开始
接下来是重磅的内容ThreadPoolExecutor 也就是Executor框架的核心逻辑所在,ThreadPoolExecutor类算上注释有2100多行,但里面有很多一部分是方法的详细说明,还有大量的变量和private/protected的方法,真正开放出来的public方法很少,我们只要逐个分析这些public方法就可以了。
我们首先来看构造函数,构造函数有多个重载方法,目前只看参数最全的情况:
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, ----池子里面的线程数量,即便idle状态的线程也会保留这个数量 int maximumPoolSize,----池子里面能盛放最大线程数量 long keepAliveTime,----当线程数量大于core核心数量的时候,并且里有idle状态的线程,那么最大可以被terminate的的等待时间
(就是在cpu借的线程资源如果闲置多久就必须还回去) TimeUnit unit,--timeUnit BlockingQueueworkQueue,---任务的队列 ThreadFactory threadFactory,---线程工厂 RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {---线程池处理不过来任务队列的时候的默认处理方法 if (corePoolSize < 0 || maximumPoolSize <= 0 || maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize || keepAliveTime < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException(); if (workQueue == null || threadFactory == null || handler == null) throw new NullPointerException(); this.corePoolSize = corePoolSize; this.maximumPoolSize = maximumPoolSize; this.workQueue = workQueue; this.keepAliveTime = unit.toNanos(keepAliveTime); this.threadFactory = threadFactory; this.handler = handler; }
public void execute(Runnable command) {}---执行一个任务
public void shutdown() {---使用可重入锁实现,关闭线程池执行框架,不再接受新的任务,关闭idle状态的线程,等待正在执行的执行完成。
final ReentrantLock mainLock = this.mainLock;
}
public ListshutdownNow() {}--- 同ExecutorService中的接口说明,与shuwdown的区别在于会尝试关闭正在执行的线程
public boolean isShutdown() {}---是否已经关闭(没有running状态的线程了)
-------一堆get和set方法
public int getActiveCount() {}---获得活动的线程数量
public long getCompletedTaskCount() {}---或者完成的任务数量
其实我们只要知道ThreadPoolExecutor的构造参数就可以明白它的工作方式,而且我们需要做的也是把这些内容构造好。
我们最常用的Executors里面的更加方便的Pool的类型其实都是为我们加了一些default参数的ThreadPoolExecutor:
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) { return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue()); }
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue()));
}
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue());
}
public static ScheduledExecutorService newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor(ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
return new DelegatedScheduledExecutorService
(new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(1, threadFactory));
}
也就是其实最后都是会到ThreadPoolExecutor上面去实现,区别就是一个用着方便,一个你可以控制的粒度更小,进而可能效率更高。
我们在类图的继承体系里面还能发现一个叫做ForkJoinPool的类,这个类其实是很多人口中所谓未来java并发方向的类,由于涉及的内容较多,后面单独随笔进行学习和理解吧。