在使用Hive的时候,有时候只是想取表中某个分区的前几条的记录看下数据格式,比如一个很常用的查询:
select * from foo where partition_column=bar limit 10;这种对数据基本没什么要求,随便来点就行,既然如此为什么不直接读取本地存储的数据作为结果集呢。
Hive命令都要转换为MapReduce任务去执行,但是因为启动MapReduce需要消耗资源,然后速度还很慢(相比较于直接从本地文件中读取而言),所以Hive对于查询做了优化,对于某些查询可以不启动MapReduce任务的就尽量不去启动MapReduce任务,而是直接从本地文件读取。
个人理解: fetch task = 不启动MapReduce,直接读取本地文件输出结果。
在hive-site.xml中有三个fetch task相关的值:
hive.fetch.task.conversion
hive.fetch.task.conversion.threshold
hive.fetch.task.aggr
hive.fetch.task.conversion
这个属性有三个可选的值:
none:关闭fetch task优化
minimal:只在select *、使用分区列过滤、带有limit的语句上进行优化
more:在minimal的基础上更加强大了,select不仅仅可以是*,还可以单独选择几列,并且filter也不再局限于分区字段,同时支持虚拟列(别名)
hive.fetch.task.conversion
more
Expects one of [none, minimal, more].
Some select queries can be converted to single FETCH task minimizing latency.
Currently the query should be single sourced not having any subquery and should not have
any aggregations or distincts (which incurs RS), lateral views and joins.
0. none : disable hive.fetch.task.conversion
1. minimal : SELECT STAR, FILTER on partition columns, LIMIT only
2. more : SELECT, FILTER, LIMIT only (support TABLESAMPLE and virtual columns)
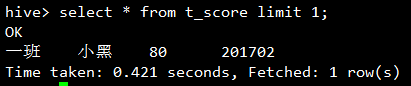
对于查询所有列的情况,会使用fetch task:
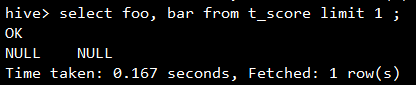
如果是查询部分列呢?
为什么查询部分列也使用了Fetch Task?查看一下当前的set hive.fetch.task.conversion的值:
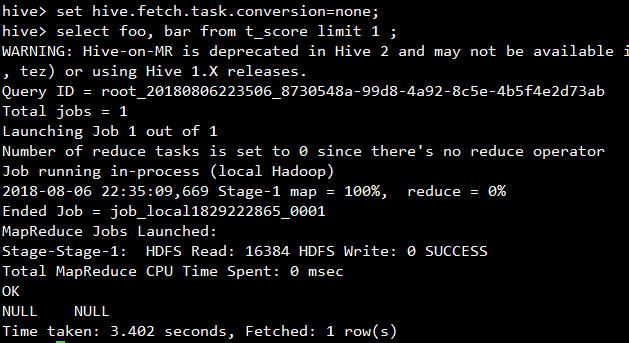
尝试将hive.fetch.task.conversion设置为none,再查询:
启动了MapReduce任务。
hive.fetch.task.conversion.threshold
在输入大小为多少以内的时候fetch task生效,默认1073741824 byte = 1G。
hive.fetch.task.conversion.threshold
1073741824
Input threshold for applying hive.fetch.task.conversion. If target table is native, input length
is calculated by summation of file lengths. If it's not native, storage handler for the table
can optionally implement org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.metadata.InputEstimator interface.
hive.fetch.task.aggr
对于没有group by的聚合查询,比如select count(*) from src,这种最终都会在一个reduce中执行,像这种查询,可以把这个置为true将将其转换为fetch task,这可能会节约一些时间。
hive.fetch.task.aggr
false
Aggregation queries with no group-by clause (for example, select count(*) from src) execute
final aggregations in single reduce task. If this is set true, Hive delegates final aggregation
stage to fetch task, possibly decreasing the query time.
.