Python数据分析【3】:pandas库详细教程
Python数据分析:pandas库详细教程
- 1. series和读取外部数据
-
- 1.1 前言
- 1.2 数据类型
- 1.3 Series创建
- 1.4 Series索引和切片
- 1.5 Series索引和值
- 1.6 读取外部数据
- 1.7 DataFrame
- 1.8 取行取列
- 1.9 loc
- 1.10 布尔索引
- 1.11 字符串方法
- 1.12 缺失数据的处理
- 2. 统计方法和字符串离散化
-
- 2.1 常用统计方法
- 2.2 电影数据直方图
- 3. 数据的合并和分组聚合
-
- 3.1 数据离散化
- 3.2 数据合并(join和merge)
- 3.3 数组分组聚合(groupby)
- 3.4 数据的索引学习
- 3.5 数据的符合索引
- 4. 时间序列
- 5. pandas案例(PM2.5)
1. series和读取外部数据
1.1 前言
numpy:处理数据
matplotlib:数据分析
pandas:除处理数值之外,还能处理其他类型的数据(字符串,时间序列)。比如:通过爬虫获取到了存储在数据库中的数据;之前YouTube例子中除了数值之外,还有国家信息、视频分类(tag)信息,标题信息等
1.2 数据类型
- Series:一维,带标签数组
- DataFrame:二维,Series容器
1.3 Series创建
Series:本质上由两个数组构成,一个数组构成对象的键(index, 索引),一个数组构成对象的值(values), 键->值
import pandas as pd
t=pd.Series([1,2,31,12,3,4])
>>>0 1
1 2
2 31
3 12
4 3
5 4
dtype: int64
type(t)
>>>pandas.core.series.Series
t1=pd.Series([1,23,2,2,1],index=list('abcde'))
>>>a 1
b 23
c 2
d 2
e 1
dtype: int64
temp_dict={
'name':'xiaohong','age':30,'tel':'10086'}
t2=pd.Series(temp_dict)
>>>name xiaohong
age 30
tel 10086
dtype: object
1.4 Series索引和切片
temp_dict={
'name':'xiaohong','age':30,'tel':'10086'}
t2=pd.Series(temp_dict)
>>>name xiaohong
age 30
tel 10086
dtype: object
# 索引
t2['age']
>>>30
t2[0]
>>>'xiaohong'
t2[['age','tel']]
>>>age 30
tel 10086
dtype: object
# 切片
t2[1:2]
>>>age 30
dtype: object
1.5 Series索引和值
temp_dict={
'name':'xiaohong','age':30,'tel':'10086'}
t2=pd.Series(temp_dict)
>>>name xiaohong
age 30
tel 10086
dtype: object
# 索引
t2.index
>>>Index(['name', 'age', 'tel'], dtype='object')
for i in t2.index:
print(i)
>>>name
age
tel
type(t2.index) # 获取类型
>>>pandas.core.indexes.base.Index
len(t2.index) # 获取长度
>>>3
list(t2.index) # 获取列表
>>>['name', 'age', 'tel']
# 值
t2.values
>>>array(['xiaohong', 30, '10086'], dtype=object)
type(t2.values) # 获取类型
>>>numpy.ndarray
ndarray的很多方法都可以运用于series类型,比如argmax, clip
series具有where方法,但是结果和ndarray不同
百度搜索官网文档:padas Series where
1.6 读取外部数据
CSV数据:pd.read_csv
myql数据:pd.read_sql(sql_sentence,connection)
mongodb:第三方库(from pymongo import MongoClient )
import pandas as pd
# pandas读取csv中的文件
df=pd.read_csv('dogNames2.csv')
# 数据链接:https://www.kaggle.com/new-york-city/nyc-dog-names/data
print(df)
>>> Row_Labels Count_AnimalName
0 1 1
1 2 2
2 40804 1
3 90201 1
4 90203 1
... ... ...
16215 37916 1
16216 38282 1
16217 38583 1
16218 38948 1
16219 39743 1
[16220 rows x 2 columns]
1.7 DataFrame
DataFrame既有行索引,也有列索引
-行索引:表明不同行,横向索引,叫index,0轴,axis=0
-列索引:表明不同列,纵向索引,叫columns,1轴,axis=1
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
pd.DataFrame(np.arange(12).reshape(3,4))
>>>
0 1 2 3
0 0 1 2 3
1 4 5 6 7
2 8 9 10 11
# 竖着是行索引,横着是列索引
pd.DataFrame(np.arange(12).reshape(3,4),index=list('abc'),columns=list('WXYZ'))
>>>
W X Y Z
a 0 1 2 3
b 4 5 6 7
c 8 9 10 11
d1={
'name':['xiaohong','xiaoming'],'age':[20,32],'tel':[10086,10010]}
t1=pd.DataFrame(d1)
>>>
name age tel
0 xiaohong 20 10086
1 xiaoming 32 10010
type(t1)
>>>pandas.core.frame.DataFrame
d2=[{
'name':'xiaohong','age':32,'tel':'10010'},{
'name':'xiaogang','tel':'10000'},{
'name':'xiaowang','age':22}]
t2=pd.DataFrame(d2)
>>>
name age tel
0 xiaohong 32.0 10010
1 xiaogang NaN 10000
2 xiaowang 22.0 NaN
# DataFrame的基础属性
t2.index # 行索引
>>>RangeIndex(start=0, stop=3, step=1)
t2.columns # 列索引
>>>Index(['name', 'age', 'tel'], dtype='object')
t2.values # 对象值,二维ndarray数组
>>>array([['xiaohong', 32.0, '10010'],
['xiaogang', nan, '10000'],
['xiaowang', 22.0, nan]], dtype=object)
t2.shape # 行数 列数
>>>(3, 3)
t2.dtypes # 列数据类型
>>>name object
age float64
tel object
dtype: object
t2.ndim # 数据维度
>>>2
# DataFrame的整体情况查询
t2.head(a) # 显示头部几行
t2.tail(b) # 显示末尾几行
t2.info() # 相关信息概览:行数,列数,列索引,列非空值个数,列类型,内存占用
t2.describe() # 快速综合统计结果:计数,均值,标准差,最大值,最小值,四分位数
from pymongo import MongoClient
client=MongoClient()
collection=client['douban']['tv1']
data=collection.find()
data_list=[]
for i in data:
temp={
}
temp['info']=i['info']
temp['rating_count']=i['rating']['count']
temp['rating_value']=i['rating']['value']
temp['title']=i['title']
temp['country']=i['tv_category']
temp['directors']=i['directors']
temp['actors']=i['actors']
data_list.append(temp)
df=pd.DataFrame(data_list)
print(df)
1.8 取行取列
import pandas as pd
# pandas读取csv中的文件
df=pd.read_csv('dogNames2.csv')
# 数据链接:https://www.kaggle.com/new-york-city/nyc-dog-names/data
print(df.head())
print(df.info())
>>> Row_Labels Count_AnimalName
0 1 1
1 2 2
2 40804 1
3 90201 1
4 90203 1
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 16220 entries, 0 to 16219
Data columns (total 2 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 Row_Labels 16217 non-null object
1 Count_AnimalName 16220 non-null int64
dtypes: int64(1), object(1)
memory usage: 253.6+ KB
None
# 问题:使用次数最高的前几个名字是什么呢?
# DataFrame中排序的方法
df=df.sort_values(by='Count_AnimalName',ascending=False)
df.head(5) # 取前面5行
# 等价于df[:5]
>>> Row_Labels Count_AnimalName
1156 BELLA 1195
9140 MAX 1153
2660 CHARLIE 856
3251 COCO 852
12368 ROCKY 823
# 取前面5行的具体某一列
df[:5]['Row_Labels']
>>>1156 BELLA
9140 MAX
2660 CHARLIE
3251 COCO
12368 ROCKY
Name: Row_Labels, dtype: object
# pandas取行或者取列的注意点
# - [] 写数组,表示取行,对行进行排序
# - [] 写字符串,表示取列索引,对列进行操作
# 问题:如果有10列数据,按照其中第1,3,8列排序(看ipythpn的帮助文档)
1.9 loc
- df.loc: 通过标签索引行数据
- df.iloc:通过位置获取行数据
t3=pd.DataFrame(np.arange(12).reshape(3,4),index=list('abc'),columns=list('WXYZ'))
t3.loc['a','Z']
type(t3.loc['a','Z'])
>>>
W X Y Z
a 0 1 2 3
b 4 5 6 7
c 8 9 10 11
>>>numpy.int32
# loc
# 取行
t3.loc['a']
>>>W 0
X 1
Y 2
Z 3
Name: a, dtype: int32
# 取列
t3.loc[:,'Y']
>>>a 2
b 6
c 10
Name: Y, dtype: int32
# 取多行
t3.loc[['a','c']] # 等价于t3.loc[['a','c'],:]
>>> W X Y Z
a 0 1 2 3
c 8 9 10 11
# 取多列
t3.loc[:,['W','Z']]
>>> W Z
a 0 3
b 4 7
c 8 11
# 取间隔的多行多列
t3.loc[['a','c'],['W','Z']]
>>> W Z
a 0 3
c 8 11
t3.loc['a':,['W','Z']]
>>>
W Z
a 0 3
b 4 7
c 8 11
# iloc
# 取行
t3.iloc[1]
>>>W 4
X 5
Y 6
Z 7
Name: b, dtype: int32
# 取列
t3.iloc[:,2]
>>>a 2
b 6
c 10
Name: Y, dtype: int32
# 取不连续的多行多列
t3.iloc[:,[2,1]]
>>>
Y X
a 2 1
b 6 5
c 10 9
# 取连续的多行多列
t3.iloc[[0,2],[2,1]]
>>>
Y X
a 2 1
c 10 9
t3.iloc[1:,:3]=10
>>> W X Y Z
a 0 1 2 3
b 10 10 10 7
c 10 10 10 11
t3.iloc[1:,:2]=np.nan
>>> W X Y Z
a 0.0 1.0 2 3
b NaN NaN 10 7
c NaN NaN 10 11
1.10 布尔索引
import pandas as pd
# pandas读取csv中的文件
df=pd.read_csv('dogNames2.csv')
# 数据链接:https://www.kaggle.com/new-york-city/nyc-dog-names/data
# 找到使用次数超过800的狗的名字
df[df['Count_AnimalName']>800]
>>>
Row_Labels Count_AnimalName
1156 BELLA 1195
9140 MAX 1153
2660 CHARLIE 856
3251 COCO 852
12368 ROCKY 823
# 找到使用次数800-1000的狗的名字 &或 |且
df[(800<df['Count_AnimalName']) & (df['Count_AnimalName']<1000)]
>>> Row_Labels Count_AnimalName
2660 CHARLIE 856
3251 COCO 852
12368 ROCKY 823
1.11 字符串方法
常用:contains, len, lower/upper, replace, split
contains: 返回表示各字符串是否含有指定模式的布尔型数值
# 找到使用次数超过800的狗的名字并且名字的字符串的长度大于4
df[(700<df['Count_AnimalName']) & (df['Row_Labels'].str.len()>4)]
>>>
Row_Labels Count_AnimalName
1156 BELLA 1195
2660 CHARLIE 856
12368 ROCKY 823
8552 LUCKY 723
1.12 缺失数据的处理
数据缺失有两种情况:
① 空,None等,在pandas是nan(和np.nan一样)
② 没有数据,为0
判断数据是否为nan:pd.isnull(df), pd.notnull(df),
处理方式1:删除nan所在的行列dropna(axis,how=‘any’,inplace=False)
处理方式2:填充数据,t.fillna(t.mean()), t.fillna(t.median()), t.fillna(0),
处理为0的数据:t[t==0]=np.nan
当然并不是每次为0的数据都需要处理
计算平均值等情况,nan是不参与计算的,但是0会
pd.isnull(t3)
>>> W X Y Z
a False False False False
b True True False False
c True True False False
pd.notnull(t3)
>>> W X Y Z
a True True True True
b False False True True
c False False True True
t3[pd.notnull(t3['w'])]
>>> W X Y Z
a 0.0 1.0 2 3
t3.dropna(axis=0,how='all') # 所在行全为nan时,删掉
>>>
W X Y Z
a 0.0 1.0 2 3
b NaN NaN 10 7
c NaN NaN 10 11
t3.dropna(axis=0,how='any',inplace=True) # 所在行有nan时,删掉所在行,并赋值给t3
>>> W X Y Z
a 0.0 1.0 2 3
d2=[{
'name':'xiaohong','age':32,'tel':'10010'},{
'name':'xiaogang','tel':'10000'},{
'name':'xiaowang','age':22}]
t2=pd.DataFrame(d2)
>>>
name age tel
0 xiaohong 32.0 10010
1 xiaogang NaN 10000
2 xiaowang 22.0 NaN
t2.fillna(0) # 将nan的值替换为0
>>> name age tel
0 xiaohong 32.0 10010
1 xiaogang 0.0 10000
2 xiaowang 22.0 0
t2.fillna(t2.mean()) # 将nan的值替换为均值
>>> name age tel
0 xiaohong 32.0 10010
1 xiaogang 27.0 10000
2 xiaowang 22.0 NaN
t2 # t2值不变
>>> name age tel
0 xiaohong 32.0 10010
1 xiaogang NaN 10000
2 xiaowang 22.0 NaN
t2['age'].fillna(t2['age'].mean()) # 将age中nan的值替换为均值
>>>0 32.0
1 27.0
2 22.0
Name: age, dtype: float64
2. 统计方法和字符串离散化
2.1 常用统计方法
问题:假设现在我们有一组从2006-2016年1000部最流行的电影数据,想知道这些电影数据中评分的平均分,导演的人数等信息,我们应该怎么获取?
数据来源:https://www.kaggle.com/damianpanek/sunday-eda/data
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
file_path='IMDB-Movie-Data.csv'
df=pd.read_csv(file_path)
print(df.info())
>>><class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 1000 entries, 0 to 999
Data columns (total 12 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 Rank 1000 non-null int64
1 Title 1000 non-null object
2 Genre 1000 non-null object
3 Description 1000 non-null object
4 Director 1000 non-null object
5 Actors 1000 non-null object
6 Year 1000 non-null int64
7 Runtime (Minutes) 1000 non-null int64
8 Rating 1000 non-null float64
9 Votes 1000 non-null int64
10 Revenue (Millions) 872 non-null float64
11 Metascore 936 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(3), int64(4), object(5)
memory usage: 93.9+ KB
None
print(df.head())
>>> Rank Title Genre \
0 1 Guardians of the Galaxy Action,Adventure,Sci-Fi
1 2 Prometheus Adventure,Mystery,Sci-Fi
2 3 Split Horror,Thriller
3 4 Sing Animation,Comedy,Family
4 5 Suicide Squad Action,Adventure,Fantasy
Description Director \
0 A group of intergalactic criminals are forced ... James Gunn
1 Following clues to the origin of mankind, a te... Ridley Scott
2 Three girls are kidnapped by a man with a diag... M. Night Shyamalan
3 In a city of humanoid animals, a hustling thea... Christophe Lourdelet
4 A secret government agency recruits some of th... David Ayer
Actors Year Runtime (Minutes) \
0 Chris Pratt, Vin Diesel, Bradley Cooper, Zoe S... 2014 121
1 Noomi Rapace, Logan Marshall-Green, Michael Fa... 2012 124
2 James McAvoy, Anya Taylor-Joy, Haley Lu Richar... 2016 117
3 Matthew McConaughey,Reese Witherspoon, Seth Ma... 2016 108
4 Will Smith, Jared Leto, Margot Robbie, Viola D... 2016 123
Rating Votes Revenue (Millions) Metascore
0 8.1 757074 333.13 76.0
1 7.0 485820 126.46 65.0
2 7.3 157606 138.12 62.0
3 7.2 60545 270.32 59.0
4 6.2 393727 325.02 40.0
# 获取电影的平均评分
df['Rating'].mean()
>>>6.723200000000003
# 获取导演的人数
len(set(df['Director'].tolist()))
>>>644
# 方法二
len(df['Director'].unique())
>>>644
# 获取演员的人数
temp_actors_list=df['Actors'].str.split(',').tolist()
# 二维数组转变为一维数组
actors_list=[i for j in temp_actors_list for i in j]
actors_num=len(set(actors_list))
print(actors_num)
>>>2394
2.2 电影数据直方图
问题:对于一组电影数据,如果我们想rating,runtime的分布情况,应该如何呈现数据?
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
# 不同数据
file_path='IMDB-Movie-Data.csv'
df=pd.read_csv(file_path)
# runtime分布情况
# 选择图形:直方图
# 准备数据
runtime_data=df['Runtime (Minutes)'].values
max_runtime=runtime_data.max()
min_runtime=runtime_data.min()
# 计算组数
num_bin=(max_runtime-min_runtime)//10
print(type(num_bin))
# 设置图形大小
plt.figure(figsize=(20,8),dpi=80)
plt.hist(runtime_data,num_bin)
plt.show()
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
# 不同数据
file_path='IMDB-Movie-Data.csv'
df=pd.read_csv(file_path)
# rating分布情况
# 选择图形:直方图
# 准备数据
runtime_data=df['Rating'].values
max_runtime=runtime_data.max()
min_runtime=runtime_data.min()
# 计算组数
num_bin=int((max_runtime-min_runtime)//0.5)
# 设置图形大小
plt.figure(figsize=(20,8),dpi=80)
plt.hist(runtime_data,num_bin)
# x轴刻度
_x=[min_runtime]
i=min_runtime
while i<=max_runtime+0.5:
i=i+0.5
_x.append(i)
plt.xticks(_x)
plt.show()
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
# 不同数据
file_path='IMDB-Movie-Data.csv'
df=pd.read_csv(file_path)
# rating,runtime分布情况
# 选择图形:直方图
# 准备数据
runtime_data=df['Rating'].values
max_runtime=runtime_data.max()
min_runtime=runtime_data.min()
# 计算组数
num_bin_list=[1.6,3.5]
i=3.5
while i<=max_runtime:
i+=0.5
num_bin_list.append(i)
# 设置图形大小
plt.figure(figsize=(20,8),dpi=80)
plt.hist(runtime_data,num_bin_list)
plt.xticks(num_bin_list)
plt.show()
3. 数据的合并和分组聚合
3.1 数据离散化
问题:对于这一组电影数据,如果我们我们希望统计电影分类(Genre)的情况,应该如何处理数据?
思路:重新构造一个全为0的数组,列名为分类,如果某一条数据中分类出现过,就让0变为1
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
# 不同数据
file_path='IMDB-Movie-Data.csv'
df=pd.read_csv(file_path)
df['Genre']
>>>0 Action,Adventure,Sci-Fi
1 Adventure,Mystery,Sci-Fi
2 Horror,Thriller
3 Animation,Comedy,Family
4 Action,Adventure,Fantasy
...
995 Crime,Drama,Mystery
996 Horror
997 Drama,Music,Romance
998 Adventure,Comedy
999 Comedy,Family,Fantasy
Name: Genre, Length: 1000, dtype: object
# 统计分类的列表
temp_list=df['Genre'].str.split(',').tolist() # 列表嵌套列表
genre_list=list(set(i for j in temp_list for i in j)) # 去重
# 构造全为0的数组
zeros_df=pd.DataFrame(np.zeros(df.shape[0],len(genre_list)),columns=genre_list)
>>>Animation Romance Adventure Western History Fantasy Sport Biography Drama Sci-Fi Action Crime Horror Musical Thriller Music Family War Comedy Mystery
0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
1 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
2 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
3 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
4 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
995 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
996 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
997 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
998 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
999 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
1000 rows × 20 columns
# 给每个电影出现分类的位置赋值为1
for i in range(df.shape[0]):
# zeros_df.loc[i,['Sci-fi','Mucical]]=1
zeros_df.loc[i,temp_list[i]]=1
print(zeros_df.head(3))
>>> Animation Romance Adventure Western History Fantasy Sport Biography \
0 0.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
1 0.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
2 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
Drama Sci-Fi Action Crime Horror Musical Thriller Music Family \
0 0.0 1.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
1 0.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
2 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 0.0
War Comedy Mystery
0 0.0 0.0 0.0
1 0.0 0.0 1.0
2 0.0 0.0 0.0
# 统计每个分类电影的数量和
genre_count=zeros_df.sum(axis=0)
print(genre_count)
>>>Animation 49.0
Romance 141.0
Adventure 259.0
Western 7.0
History 29.0
Fantasy 101.0
Sport 18.0
Biography 81.0
Drama 513.0
Sci-Fi 120.0
Action 303.0
Crime 150.0
Horror 119.0
Musical 5.0
Thriller 195.0
Music 16.0
Family 51.0
War 13.0
Comedy 279.0
Mystery 106.0
dtype: float64
# 排序
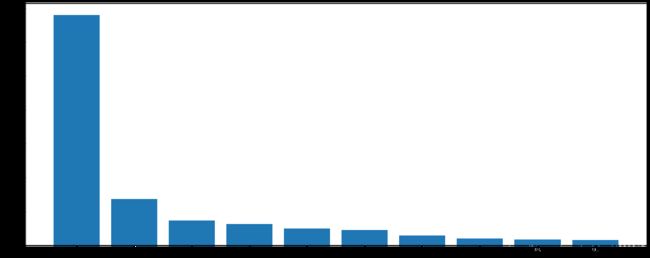
genre_count=genre_count.sort_values()
# 画图
_x=genre_count.index
_y=genre_count.values
plt.figure(figsize=(20,8),dpi=80)
plt.bar(range(len(_x)),_y,width=0.4)
plt.xticiks=(range(len(_x)),_x)
plt.show()
3.2 数据合并(join和merge)
join: 默认情况下把行索引相同的数据合并到一起
merge: 默认情况下把列索引相同的数据合并到一起
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# join
df1=pd.DataFrame(np.ones((2,4)),index=['A','B'],columns=list('abcd'))
>>> a b c d
A 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
B 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
df2=pd.DataFrame(np.zeros((3,3)),index=['A','B','C'],columns=list('xyz'))
>>> x y z
A 0.0 0.0 0.0
B 0.0 0.0 0.0
C 0.0 0.0 0.0
df1.join(df2)
>>>a b c d x y z
A 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
B 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
df2.join(df1)
>>>x y z a b c d
A 0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
B 0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
C 0.0 0.0 0.0 NaN NaN NaN NaN
# merge
df3=pd.DataFrame(np.zeros((3,3)),columns=list('fax'))
>>>
f a x
0 0.0 0.0 0.0
1 0.0 0.0 0.0
2 0.0 0.0 0.0
df1.merge(df,on='a')
>>>Empty DataFrame
df1=pd.DataFrame(np.ones((2,4)),index=['A','B'],columns=list('abcd'))
>>> a b c d
A 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
B 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
df4=pd.DataFrame(np.arange(9).reshape((3,3)),columns=list('fax'))
>>>
f a x
0 0 1 2
1 3 4 5
2 6 7 8
df1.merge(df4,on='a',how='inner') # 交集
>>>a b c d f x
0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 0 2
1 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 0 2
df1.merge(df4,on='a',how='outer') # 并集,nan补全
>>> a b c d f x
0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 0 2
1 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 0 2
2 4.0 NaN NaN NaN 3 5
3 7.0 NaN NaN NaN 6 8
df1.merge(df4,on='a',how='left') # 左连接,nan补全
>>>
a b c d f x
0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 0 2
1 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 0 2
df1.merge(df4,on='a',how='right') # 右连接,nan补全
>>>a b c d f x
0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 0 2
1 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 0 2
2 4.0 NaN NaN NaN 3 5
3 7.0 NaN NaN NaN 6 8
3.3 数组分组聚合(groupby)
问题:现在我们有一组关于全球星巴克店铺的统计数据,如果我想知道美国的星巴克数量和中国的哪个多,或者我想知道中国每个省份星巴克的数量的情况,那么应该怎么办?
数据来源:https://www.kaggle.com/starbucks/store-locations/data
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
# 不同数据
file_path='directory.csv'
df=pd.read_csv(file_path)
print(df.head(1))
print(df.info())
>>>
Brand Store Number Store Name Ownership Type Street Address \
0 Starbucks 47370-257954 Meritxell, 96 Licensed Av. Meritxell, 96
City State/Province Country Postcode Phone Number \
0 Andorra la Vella 7 AD AD500 376818720
Timezone Longitude Latitude
0 GMT+1:00 Europe/Andorra 1.53 42.51
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 25600 entries, 0 to 25599
Data columns (total 13 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 Brand 25600 non-null object
1 Store Number 25600 non-null object
2 Store Name 25600 non-null object
3 Ownership Type 25600 non-null object
4 Street Address 25598 non-null object
5 City 25585 non-null object
6 State/Province 25600 non-null object
7 Country 25600 non-null object
8 Postcode 24078 non-null object
9 Phone Number 18739 non-null object
10 Timezone 25600 non-null object
11 Longitude 25599 non-null float64
12 Latitude 25599 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(2), object(11)
memory usage: 2.5+ MB
None
# 分组和聚合
grouped=df.groupby(by='Country')
# 可以进行遍历
#for i,j in grouped:
# print(i)
# print('-'*100)
# print(j,type(j))
# print('i'*100)
# 等价于
# df[df['Country']]='US'
# 调用聚合方法
country_count=grouped['Brand'].count() # 统计数量
>>>Country
AD 1
AE 144
AR 108
AT 18
AU 22
...
TT 3
TW 394
US 13608
VN 25
ZA 3
Name: Brand, Length: 73, dtype: int64
# 统计美国和中国星巴克的数量比较
print(country_count['US'])
print(country_count['CN'])
>>>13608
2734
# 统计中国每个省份的星巴克数量
china_data=df[df['Country']=='CN']
Province_data=china_data.groupby(by='State/Province').count()['Brand'] # 统计数量,DataFrameGroupBy对象
print(Province_data)
>>>State/Province
11 236
12 58
13 24
14 8
15 8
21 57
22 13
23 16
31 551
32 354
33 315
34 26
35 75
36 13
37 75
41 21
42 76
43 35
44 333
45 21
46 16
50 41
51 104
52 9
53 24
61 42
62 3
63 3
64 2
91 162
92 13
Name: Brand, dtype: int64
# 数据按照多个条件分组:对国家和省份进行分组统计,返回series
grouped_CP=df['Brand'].groupby(by=[df['Country'],df['State/Province']]).count()
>>>Country State/Province
AD 7 1
AE AJ 2
AZ 48
DU 82
FU 2
..
US WV 25
WY 23
VN HN 6
SG 19
ZA GT 3
Name: Brand, Length: 545, dtype: int64
# 前两列是索引,第三列才是数据
type(grouped_CP)
>>>pandas.core.series.Series
# 数据按照多个条件分组,返回DataFrame,三种方法
grouped_CP1=df[['Brand']].groupby(by=[df['Country'],df['State/Province']]).count()
grouped_CP2=df.groupby(by=[df['Country'],df['State/Province']])[['Brand']].count()
grouped_CP3=df.groupby(by=[df['Country'],df['State/Province']]).count()[['Brand']]
# 获取分组之后的某一部分数据
df.groupby(by=[df['Country'],df['State/Province']])['Brand'].count()
# 对某几列数据进行分组
df['Brand'].groupby(by=[df['Country'],df['State/Province']]).count()
3.4 数据的索引学习
t1=pd.DataFrame(np.arange(9).reshape((3,3)),columns=list('fax'))
>>>
f a x
0 0 1 2
1 3 4 5
2 6 7 8
# 索引的方法和属性
t1.index # 获取index
>>>RangeIndex(start=0, stop=3, step=1)
t1.index=['x','y','z'] # 指定index
>>> f a x
x 0 1 2
y 3 4 5
z 6 7 8
t1.reindex(list('xoz')) # 重新设置Index
>>> f a x
x 0.0 1.0 2.0
o NaN NaN NaN
z 6.0 7.0 8.0
t1.set_index('a',drop=False) # 指定某一列作为Index
>>>
f a x
a
1 0 1 2
4 3 4 5
7 6 7 8
t1.set_index('a',drop=False).index.unique() # 返回Index的唯一值
>>>Int64Index([1, 4, 7], dtype='int64', name='a')
3.5 数据的符合索引
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
a=pd.DataFrame({
'a':range(7),'b':range(7,0,-1),'c':['one','one','one','two','two','two','two'],'d':list('hjklmno')})
>>> a b c d
0 0 7 one h
1 1 6 one j
2 2 5 one k
3 3 4 two l
4 4 3 two m
5 5 2 two n
6 6 1 two o
b=a.set_index(['c','d']) # 指定某一列作为Index
>>>
a b
c d
one h 0 7
j 1 6
k 2 5
two l 3 4
m 4 3
n 5 2
o 6 1
c=b['a']
>>>
c d
one h 0
j 1
k 2
two l 3
m 4
n 5
o 6
Name: a, dtype: int64
c['one']
>>>
d
h 0
j 1
k 2
Name: a, dtype: int64
c['one']['j']
>>>1
d=a.set_index(['d','c'])['a']
>>>
d c
h one 0
j one 1
k one 2
l two 3
m two 4
n two 5
o two 6
Name: a, dtype: int64
d.index
>>>MultiIndex([('h', 'one'),
('j', 'one'),
('k', 'one'),
('l', 'two'),
('m', 'two'),
('n', 'two'),
('o', 'two')],
names=['d', 'c'])
d.swaplevel()
>>>
c d
one h 0
j 1
k 2
two l 3
m 4
n 5
o 6
Name: a, dtype: int64
b=a.set_index(['c','d']) # 指定某一列作为Index
>>>
a b
c d
one h 0 7
j 1 6
k 2 5
two l 3 4
m 4 3
n 5 2
o 6 1
b.swaplevel().loc['h']
>>>
a b
c
one 0 7
问题:使用matplotlib呈现出店铺总数排名前10的国家;使用matplotlib呈现出中国每个城市的店铺数量;
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
# 不同数据
file_path='directory.csv'
df=pd.read_csv(file_path)
# 使用matplotlib呈现出店铺总数排名前10的国家
data1=df.groupby(by='Country').count()['Brand'].sort_values(ascending=False)[:10]
_x=data1.index
_y=data1.values
# 画图
plt.figure(figsize=(20,8),dpi=80)
plt.bar(range(len(_x)),_y)
plt.xticks(range(len(_x)),_x)
plt.show()
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
# 不同数据
file_path='directory.csv'
df=pd.read_csv(file_path)
df=df[df['Country']=='CN']
# 使用matplotlib呈现出中国每个城市的店铺数量
data1=df.groupby(by='City').count()['Brand'].sort_values(ascending=False)[:50]
_x=data1.index
_y=data1.values
# 画图
plt.figure(figsize=(20,12),dpi=80)
# plt.bar(range(len(_x)),_y,width=0.3,color='orange')
plt.barn(range(len(_x)),_y,height=0.3,color='orange')
plt.yticks(range(len(_x)),_x,fontproperties='SimHei')
plt.show()

问题:我们有全球排名靠前的10000本书的数据,那么请统计一下下面几个问题
- 不同年份数的数量
- 不同年份的平均评分情况
数据来源:https://www.kaggle.com/zygmunt/goodbooks-10k
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
# 不同数据
file_path='books.csv'
df=pd.read_csv(file_path)
print(df.head(2))
>>>
id book_id best_book_id work_id books_count isbn isbn13 \
0 1 2767052 2767052 2792775 272 439023483 9.780439e+12
1 2 3 3 4640799 491 439554934 9.780440e+12
authors original_publication_year \
0 Suzanne Collins 2008.0
1 J.K. Rowling, Mary GrandPré 1997.0
original_title ... ratings_count \
0 The Hunger Games ... 4780653
1 Harry Potter and the Philosopher's Stone ... 4602479
work_ratings_count work_text_reviews_count ratings_1 ratings_2 \
0 4942365 155254 66715 127936
1 4800065 75867 75504 101676
ratings_3 ratings_4 ratings_5 \
0 560092 1481305 2706317
1 455024 1156318 3011543
image_url \
0 https://images.gr-assets.com/books/1447303603m...
1 https://images.gr-assets.com/books/1474154022m...
small_image_url
0 https://images.gr-assets.com/books/1447303603s...
1 https://images.gr-assets.com/books/1474154022s...
[2 rows x 23 columns]
print(df.info())
>>>
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 10000 entries, 0 to 9999
Data columns (total 23 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 id 10000 non-null int64
1 book_id 10000 non-null int64
2 best_book_id 10000 non-null int64
3 work_id 10000 non-null int64
4 books_count 10000 non-null int64
5 isbn 9300 non-null object
6 isbn13 9415 non-null float64
7 authors 10000 non-null object
8 original_publication_year 9979 non-null float64
9 original_title 9415 non-null object
10 title 10000 non-null object
11 language_code 8916 non-null object
12 average_rating 10000 non-null float64
13 ratings_count 10000 non-null int64
14 work_ratings_count 10000 non-null int64
15 work_text_reviews_count 10000 non-null int64
16 ratings_1 10000 non-null int64
17 ratings_2 10000 non-null int64
18 ratings_3 10000 non-null int64
19 ratings_4 10000 non-null int64
20 ratings_5 10000 non-null int64
21 image_url 10000 non-null object
22 small_image_url 10000 non-null object
dtypes: float64(3), int64(13), object(7)
memory usage: 1.8+ MB
None
# 1. 不同年份数的数量
# 删除original_publication_year列中有缺失的字段
data1=df[pd.notnull(df['original_publication_year'])]
grouped1=data1.groupby(by='original_publication_year').count()['title']
>>>original_publication_year
-1750.0 1
-762.0 1
-750.0 2
-720.0 1
-560.0 1
...
2013.0 518
2014.0 437
2015.0 306
2016.0 198
2017.0 11
Name: title, Length: 293, dtype: int64
# 负数是公元前
# 2. 不同年份的平均评分情况
# 删除original_publication_year列中有缺失的字段
data2=df[pd.notnull(df['original_publication_year'])]
grouped2=data2['average_rating'].groupby(by=data2['original_publication_year']).mean()
>>>original_publication_year
-1750.0 3.630000
-762.0 4.030000
-750.0 4.005000
-720.0 3.730000
-560.0 4.050000
...
2013.0 4.012297
2014.0 3.985378
2015.0 3.954641
2016.0 4.027576
2017.0 4.100909
Name: average_rating, Length: 293, dtype: float64
_x=grouped2.index
_y=grouped2.values
# 画图
plt.figure(figsize=(20,8),dpi=80)
plt.plot(range(len(_x)),_y)
plt.xticks(list(range(len(_x)))[::10],_x[::10].astype(int),rotation=90)
plt.show()
4. 时间序列
问题:现在我们有2015-2017年25万条911的紧急电话的数据,请统计出这些数据中不同类型的紧急情况的次数,如果我们还想统计出不同月份不同类型紧急电话的次数的变化情况,应该怎么做呢?
数据来源:https://www.kaggle.com/mchirico/montcoalert/data
import pandas as pd
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
df=pd.read_csv('911.csv')
df.head() # 前五条信息
>>> lat lng desc zip title timeStamp twp addr e
0 40.297876 -75.581294 REINDEER CT & DEAD END; NEW HANOVER; Station ... 19525.0 EMS: BACK PAINS/INJURY 2015-12-10 17:10:52 NEW HANOVER REINDEER CT & DEAD END 1
1 40.258061 -75.264680 BRIAR PATH & WHITEMARSH LN; HATFIELD TOWNSHIP... 19446.0 EMS: DIABETIC EMERGENCY 2015-12-10 17:29:21 HATFIELD TOWNSHIP BRIAR PATH & WHITEMARSH LN 1
2 40.121182 -75.351975 HAWS AVE; NORRISTOWN; 2015-12-10 @ 14:39:21-St... 19401.0 Fire: GAS-ODOR/LEAK 2015-12-10 14:39:21 NORRISTOWN HAWS AVE 1
3 40.116153 -75.343513 AIRY ST & SWEDE ST; NORRISTOWN; Station 308A;... 19401.0 EMS: CARDIAC EMERGENCY 2015-12-10 16:47:36 NORRISTOWN AIRY ST & SWEDE ST 1
4 40.251492 -75.603350 CHERRYWOOD CT & DEAD END; LOWER POTTSGROVE; S... NaN EMS: DIZZINESS 2015-12-10 16:56:52 LOWER POTTSGROVE CHERRYWOOD CT & DEAD END 1
df.info() # 基本信息
>>><class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 634774 entries, 0 to 634773
Data columns (total 9 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 lat 634774 non-null float64
1 lng 634774 non-null float64
2 desc 634774 non-null object
3 zip 557625 non-null float64
4 title 634774 non-null object
5 timeStamp 634774 non-null object
6 twp 634502 non-null object
7 addr 634774 non-null object
8 e 634774 non-null int64
dtypes: float64(3), int64(1), object(5)
memory usage: 43.6+ MB
# 1. 获取不同类型的紧急情况的次数('title')
# 获取分类情况
temp_list=df['title'].str.split(':').tolist() # series是tolist,DataFrame是to_list
cate_list=list(set([i[0] for i in temp_list])) # 取第1列
print('cate_list')
>>>['EMS', 'Fire', 'Traffic']
# 构造全为0的数组
zeros_df=pd.DataFrame(np.zeros((df.shape[0],len(cate_list))),columns=cate_list)
# 赋值
for cate in cate_list:
zeros_df[cate][df['title'].str.contains(cate)]=1
print(zeros_df)
>>>
Traffic Fire EMS
0 0.0 0.0 1.0
1 0.0 0.0 1.0
2 0.0 1.0 0.0
3 0.0 0.0 1.0
4 0.0 0.0 1.0
... ... ... ...
634769 0.0 0.0 1.0
634770 0.0 1.0 0.0
634771 0.0 0.0 1.0
634772 0.0 0.0 1.0
634773 0.0 0.0 1.0
[634774 rows x 3 columns]
# 第二种方法,速度很慢
#for i in range(df.shape[0]):
# zeros_df.loc[i,temp_list[i][0]]=1
#print(zeros_df)
# 求和
sum_ret=zeros_df.sum(axis=0)
>>>Traffic 222192.0
Fire 95236.0
EMS 317353.0
dtype: float64
# 第二种求和方法,更简单
cate_list=[i[0] for i in temp_list] # 取第1列
df['cate']=pd.DataFrame(np.array(cate_list).reshape((df.shape[0],1)))
print(df['cate'])
>>>
lat lng desc \
0 40.297876 -75.581294 REINDEER CT & DEAD END; NEW HANOVER; Station ...
1 40.258061 -75.264680 BRIAR PATH & WHITEMARSH LN; HATFIELD TOWNSHIP...
2 40.121182 -75.351975 HAWS AVE; NORRISTOWN; 2015-12-10 @ 14:39:21-St...
3 40.116153 -75.343513 AIRY ST & SWEDE ST; NORRISTOWN; Station 308A;...
4 40.251492 -75.603350 CHERRYWOOD CT & DEAD END; LOWER POTTSGROVE; S...
zip title timeStamp twp \
0 19525.0 EMS: BACK PAINS/INJURY 2015-12-10 17:10:52 NEW HANOVER
1 19446.0 EMS: DIABETIC EMERGENCY 2015-12-10 17:29:21 HATFIELD TOWNSHIP
2 19401.0 Fire: GAS-ODOR/LEAK 2015-12-10 14:39:21 NORRISTOWN
3 19401.0 EMS: CARDIAC EMERGENCY 2015-12-10 16:47:36 NORRISTOWN
4 NaN EMS: DIZZINESS 2015-12-10 16:56:52 LOWER POTTSGROVE
addr e cate
0 REINDEER CT & DEAD END 1 EMS
1 BRIAR PATH & WHITEMARSH LN 1 EMS
2 HAWS AVE 1 Fire
3 AIRY ST & SWEDE ST 1 EMS
4 CHERRYWOOD CT & DEAD END 1 EMS
df.groupby(by='cate').count()['title'] # 求和
>>>
cate
EMS 317346
Fire 95236
Traffic 222192
Name: title, dtype: int64
# 总结:构造数组→赋值→求和
生成一段时间范围:pd.date_range(start=None,end=None,periods=None,freq=‘D’)
-start:起始时间
-end:结束时间
-periods: 生成个数
-freq:时间间隔
频率缩写:
| 字母 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| D | Day: 每日历日 |
| B | BusinessDay: 每工作日 |
| H | Hour: 每小时 |
| T | Minute: 每分 |
| S | Second: 每秒 |
| L | Milli: 每毫秒 |
| U | Micro: 每微秒 |
| M | MonthEnd: 每月最后一个日历日 |
| BM | BusinessMonthEnd: 每月最后一个工作日 |
| MS | MonthBegin: 每日第一个日历日 |
| BMS | BusinessMonthBegin: 每日第一个工作日 |
时间字符串转化为时间序列:
df[‘timeStamp’]=pd.to_datetime(df[‘timeStamp’],format=’’)
pandas重采样:resample, 指的是将时间序列从一个频率转化为另一个频率进行处理的过程,将高频率数据转化为低频率数据为降采样,低频率数据转化为高频率为升采样。
pd.date_range(start='20171230',end='20180131',freq='D')
>>>
DatetimeIndex(['2017-12-30', '2017-12-31', '2018-01-01', '2018-01-02',
'2018-01-03', '2018-01-04', '2018-01-05', '2018-01-06',
'2018-01-07', '2018-01-08', '2018-01-09', '2018-01-10',
'2018-01-11', '2018-01-12', '2018-01-13', '2018-01-14',
'2018-01-15', '2018-01-16', '2018-01-17', '2018-01-18',
'2018-01-19', '2018-01-20', '2018-01-21', '2018-01-22',
'2018-01-23', '2018-01-24', '2018-01-25', '2018-01-26',
'2018-01-27', '2018-01-28', '2018-01-29', '2018-01-30',
'2018-01-31'],
dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq='D')
pd.date_range(start='20171230',end='20180131',freq='10D')
>>>DatetimeIndex(['2017-12-30', '2018-01-09', '2018-01-19', '2018-01-29'], dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq='10D')
pd.date_range(start='20171230',periods=10,freq='D')
>>>DatetimeIndex(['2017-12-30', '2017-12-31', '2018-01-01', '2018-01-02',
'2018-01-03', '2018-01-04', '2018-01-05', '2018-01-06',
'2018-01-07', '2018-01-08'],
dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq='D')
index=pd.date_range('20200510',periods=10)
df=pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(10),index=index)
>>>
0
2020-05-10 0.602105
2020-05-11 0.539859
2020-05-12 0.038534
2020-05-13 0.001627
2020-05-14 0.110605
2020-05-15 0.602238
2020-05-16 0.579460
2020-05-17 0.081276
2020-05-18 0.125397
2020-05-19 0.762709
import pandas as pd
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
df=pd.read_csv('911.csv')
df['timeStamp']=pd.to_datetime(df['timeStamp']) # 时间字符转化成时间序列
df.set_index('timeStamp',inplace=True)
print(df.head(5))
>>>
lat lng \
timeStamp
2015-12-10 17:10:52 40.297876 -75.581294
2015-12-10 17:29:21 40.258061 -75.264680
2015-12-10 14:39:21 40.121182 -75.351975
2015-12-10 16:47:36 40.116153 -75.343513
2015-12-10 16:56:52 40.251492 -75.603350
desc \
timeStamp
2015-12-10 17:10:52 REINDEER CT & DEAD END; NEW HANOVER; Station ...
2015-12-10 17:29:21 BRIAR PATH & WHITEMARSH LN; HATFIELD TOWNSHIP...
2015-12-10 14:39:21 HAWS AVE; NORRISTOWN; 2015-12-10 @ 14:39:21-St...
2015-12-10 16:47:36 AIRY ST & SWEDE ST; NORRISTOWN; Station 308A;...
2015-12-10 16:56:52 CHERRYWOOD CT & DEAD END; LOWER POTTSGROVE; S...
zip title twp \
timeStamp
2015-12-10 17:10:52 19525.0 EMS: BACK PAINS/INJURY NEW HANOVER
2015-12-10 17:29:21 19446.0 EMS: DIABETIC EMERGENCY HATFIELD TOWNSHIP
2015-12-10 14:39:21 19401.0 Fire: GAS-ODOR/LEAK NORRISTOWN
2015-12-10 16:47:36 19401.0 EMS: CARDIAC EMERGENCY NORRISTOWN
2015-12-10 16:56:52 NaN EMS: DIZZINESS LOWER POTTSGROVE
addr e
timeStamp
2015-12-10 17:10:52 REINDEER CT & DEAD END 1
2015-12-10 17:29:21 BRIAR PATH & WHITEMARSH LN 1
2015-12-10 14:39:21 HAWS AVE 1
2015-12-10 16:47:36 AIRY ST & SWEDE ST 1
2015-12-10 16:56:52 CHERRYWOOD CT & DEAD END 1
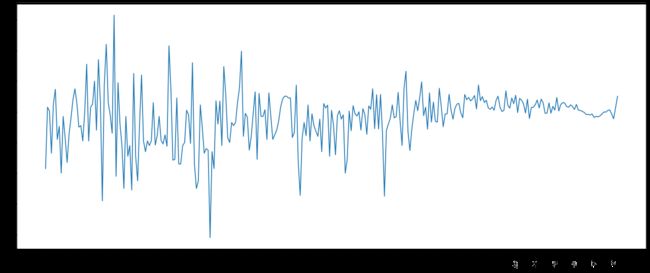
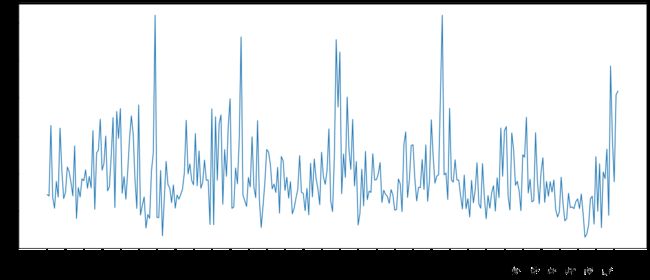
# 1. 统计出911数据中不同月份电话次数的变化情况
count_by_month=df.resample('M').count()['title']
print(count_by_month)
# 画图
_x=count_by_month.index
_y=count_by_month.values
_x=[i.strftime('%Y%m%d') for i in _x]
plt.figure(figsize=(20,8),dpi=80)
plt.plot(range(len(_x)),_y)
plt.xticks(range(len(_x)),_x,rotation=45)
plt.show()
# 2. 统计出911数据中不同月份不同类型电话次数的变化情况
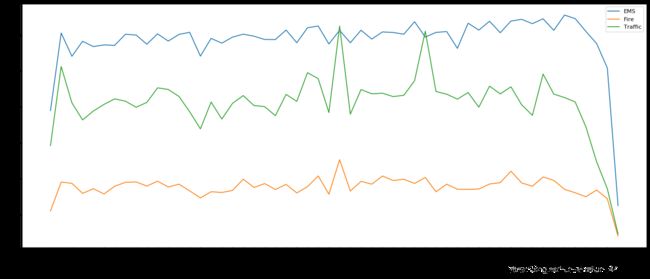
import pandas as pd
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# 时间字符转化成时间序列 设置为索引
df=pd.read_csv('911.csv')
df['timeStamp']=pd.to_datetime(df['timeStamp'])
# 添加列,表示分类
temp_list=df['title'].str.split(':').tolist()
cate_list=[i[0] for i in temp_list]
df['cate']=pd.DataFrame(np.array(cate_list).reshape((df.shape[0],1)))
df.set_index('timeStamp',inplace=True)
plt.figure(figsize=(20,8),dpi=80)
# 不同类型分组
for group_name,group_data in df.groupby(by='cate'):
# 对不同的分类都进行绘图
count_by_month=group_data.resample('M').count()['title']
# 画图
_x=count_by_month.index
_y=count_by_month.values
_x=[i.strftime('%Y%m%d') for i in _x]
plt.plot(range(len(_x)),_y,label=group_name)
plt.xticks(range(len(_x)),_x,rotation=45)
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.show()
5. pandas案例(PM2.5)
问题:现在我们有北上广、深圳、和沈阳5个城市空气质量数据,请绘制出5个城市的PM2.5随时间的变化情况
观察这组数据中的时间结构,并不是字符串,这个时候我们应该怎么办?
数据来源:https://www.kaggle.com/uciml/pm25-data-for-five-chinese-cities
import pandas as pd
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# 读取数据
df=pd.read_csv('BeijingPM20100101_20151231.csv')
print(df.head(5))
>>> No year month day hour season PM_Dongsi PM_Dongsihuan \
0 1 2010 1 1 0 4 NaN NaN
1 2 2010 1 1 1 4 NaN NaN
2 3 2010 1 1 2 4 NaN NaN
3 4 2010 1 1 3 4 NaN NaN
4 5 2010 1 1 4 4 NaN NaN
PM_Nongzhanguan PM_US Post DEWP HUMI PRES TEMP cbwd Iws \
0 NaN NaN -21.0 43.0 1021.0 -11.0 NW 1.79
1 NaN NaN -21.0 47.0 1020.0 -12.0 NW 4.92
2 NaN NaN -21.0 43.0 1019.0 -11.0 NW 6.71
3 NaN NaN -21.0 55.0 1019.0 -14.0 NW 9.84
4 NaN NaN -20.0 51.0 1018.0 -12.0 NW 12.97
precipitation Iprec
0 0.0 0.0
1 0.0 0.0
2 0.0 0.0
3 0.0 0.0
4 0.0 0.0
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
print(df.info())
>>>RangeIndex: 52584 entries, 0 to 52583
Data columns (total 18 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 No 52584 non-null int64
1 year 52584 non-null int64
2 month 52584 non-null int64
3 day 52584 non-null int64
4 hour 52584 non-null int64
5 season 52584 non-null int64
6 PM_Dongsi 25052 non-null float64
7 PM_Dongsihuan 20508 non-null float64
8 PM_Nongzhanguan 24931 non-null float64
9 PM_US Post 50387 non-null float64
10 DEWP 52579 non-null float64
11 HUMI 52245 non-null float64
12 PRES 52245 non-null float64
13 TEMP 52579 non-null float64
14 cbwd 52579 non-null object
15 Iws 52579 non-null float64
16 precipitation 52100 non-null float64
17 Iprec 52100 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(11), int64(6), object(1)
memory usage: 7.2+ MB
None
PeriodIndex: 时间段
DatetimeIndex: 时间戳
periods=PeriodIndex(year=data[‘year’],month=data[‘month’],day=data[‘day’],hour=data[‘hour’],freq=‘H’)
# 读取数据
df=pd.read_csv('BeijingPM20100101_20151231.csv')
# 把分开的时间字符串通过periodindex的方法转化为pandas的时间类型
df['datetime']=period
period=pd.PeriodIndex(year=df['year'],month=df['month'],day=df['day'],hour=df['hour'],freq='H')
df['datetime']=period # 添加一列
print(period)
print(type(period))
>>>PeriodIndex(['2010-01-01 00:00', '2010-01-01 01:00', '2010-01-01 02:00',
'2010-01-01 03:00', '2010-01-01 04:00', '2010-01-01 05:00',
'2010-01-01 06:00', '2010-01-01 07:00', '2010-01-01 08:00',
'2010-01-01 09:00',
...
'2015-12-31 14:00', '2015-12-31 15:00', '2015-12-31 16:00',
'2015-12-31 17:00', '2015-12-31 18:00', '2015-12-31 19:00',
'2015-12-31 20:00', '2015-12-31 21:00', '2015-12-31 22:00',
'2015-12-31 23:00'],
dtype='period[H]', length=52584, freq='H')
<class 'pandas.core.indexes.period.PeriodIndex'>
# 把datetime设置为索引
df.set_index('datetime',inplace=True)
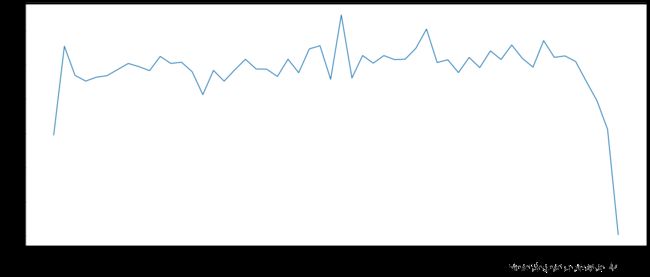
# 进行降采样
df=df.resample('7D').mean()
# 绘制北京的变化情况
# 处理缺失数据(PM_US Post),删除缺失数据
data=df['PM_US Post'].dropna()
# 画图
_x=data.index
_x=[i.strftime('%Y%m%d') for i in _x]
_y=data.values
plt.figure(figsize=(20,8),dpi=80)
plt.plot(range(len(_x)),_y)
plt.xticks(range(0,len(_x),10),list(_x)[::10],rotation=45)
plt.show()